Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand efficacy modulates conformational dynamics of the µ-opioid receptor
Ligand efficacy modulates conformational dynamics of the µ-opioid receptor
Studies on the µ-opioid receptor using fluorescent labelling of intracellular residues and energy transfer experiments in the presence of different ligands with or without G-protein binding reveals conformational changes that correlate to ligand efficacy.
- Jiawei Zhao
- , Matthias Elgeti
- & Chunlai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular insights into capsular polysaccharide secretion
Molecular insights into capsular polysaccharide secretion
An ensemble of cryo-electron microscopy structures of the KpsMT ABC transporter in complex with the KpsE co-polymerase and a glycolipid substrate reveal how capsular polysaccharides are recognized and translocated across bacterial cell membranes.
- Jeremi Kuklewicz
- & Jochen Zimmer
-
Article |
 The structure and physical properties of a packaged bacteriophage particle
The structure and physical properties of a packaged bacteriophage particle
Multiresolution computational simulations generate all-atom models of a complete packaged virus particle.
- Kush Coshic
- , Christopher Maffeo
- & Aleksei Aksimentiev
-
Review Article |
 Ion and lipid orchestration of secondary active transport
Ion and lipid orchestration of secondary active transport
This Review describes the various mechanisms of ion-coupled transport across membranes and how the activities of transporter proteins are modulated by the composition of the lipid bilayer.
- David Drew
- & Olga Boudker
-
Technology Feature |
 How phase separation is revolutionizing biology
How phase separation is revolutionizing biology
Imaging and molecular manipulation reveal how biomolecular condensates form and offer clues to the role of phase separation in health and disease.
- Elie Dolgin
-
News & Views Forum |
 Energetic laser pulses alter outcomes of X-ray studies of proteins
Energetic laser pulses alter outcomes of X-ray studies of proteins
Cutting-edge X-ray sources have enabled the structural dynamics of proteins to be tracked during biochemical processes, but the findings have been questioned. Two experts discuss the implications of a study that digs into this issue.
- Richard Neutze
- & R. J. Dwayne Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of pump laser fluence on ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics
Influence of pump laser fluence on ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics
Ultrafast time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography is used to investigate a photodissociation reaction in a protein, revealing the strong impact of the pump laser fluence on the structural changes and the reaction mechanism.
- Thomas R. M. Barends
- , Alexander Gorel
- & Ilme Schlichting
-
Research Briefing |
 Several transient binding events create a strong, adaptable interface between organelles
Several transient binding events create a strong, adaptable interface between organelles
Rapid communication between intracellular structures such as the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondria is crucial for the coordinated functioning of cells. Such interactions occur mainly at sites where the compartments are in direct contact, and are mediated by specific tethering machinery. High-speed single-molecule tracking reveals a well-regulated interface at which many rapid binding and unbinding events provide highly adaptable interactions.
-
Article
| Open Access Matrix viscoelasticity promotes liver cancer progression in the pre-cirrhotic liver
Matrix viscoelasticity promotes liver cancer progression in the pre-cirrhotic liver
Structural changes mediated by advanced glycation end-products enhance extracellular matrix viscoelasticity, and that viscoelasticity can promote cancer progression in vivo, independent of stiffness.
- Weiguo Fan
- , Kolade Adebowale
- & Natalie J. Török
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen-evolving photosystem II structures during S1–S2–S3 transitions
Oxygen-evolving photosystem II structures during S1–S2–S3 transitions
Serial femtosecond crystallography reveals the structural dynamics of photosystem II during the S-state transitions that produce dioxygen, providing insight into electron transfer, water insertion, proton release and O–O bond formation on sub-microsecond timescales.
- Hongjie Li
- , Yoshiki Nakajima
- & Jian-Ren Shen
-
Article |
 Conformational ensembles of the human intrinsically disordered proteome
Conformational ensembles of the human intrinsically disordered proteome
A computational model generates conformational ensembles of 28,058 intrinsically disordered proteins and regions (IDRs) in the human proteome and sheds light on the relationship between sequence, conformational properties and functions of IDRs.
- Giulio Tesei
- , Anna Ida Trolle
- & Kresten Lindorff-Larsen
-
Article
| Open Access Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
Motion of VAPB molecules reveals ER–mitochondria contact site subdomains
High-speed molecular tracking is integrated with three-dimensional electron microscopy to map the diffusion distribution and ultrastructure of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contact sites, revealing the ability of high-speed single-molecule imaging to map contact site interface structures and corresponding diffusion landscapes.
- Christopher J. Obara
- , Jonathon Nixon-Abell
- & Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
-
Nature Video |
 Super-propulsion: how sharpshooting insects flick their pee
Super-propulsion: how sharpshooting insects flick their pee
High-speed cameras reveal tiny insects employing a physical phenomenon, never-before seen in a natural system to avoid drowning in their own urine
- Noah Baker
-
Article
| Open Access The energetic and allosteric landscape for KRAS inhibition
The energetic and allosteric landscape for KRAS inhibition
Analysis of the effects of more than 26,000 KRAS mutations on abundance and interactions with six other proteins is used to construct an energy landscape of KRAS and identify allosteric drug target sites.
- Chenchun Weng
- , Andre J. Faure
- & Ben Lehner
-
Article |
 SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB, a lipoprotein in the PhoPQ stress regulon in Gram-negative bacteria, forms stable stress-induced complexes with the outer membrane proteome.
- Arne Janssens
- , Van Son Nguyen
- & Han Remaut
-
Article |
 Transport and inhibition mechanisms of human VMAT2
Transport and inhibition mechanisms of human VMAT2
Structures of human vesicular monoamine transporter 2 in complexes with serotonin and three clinical drugs provide insights into the structural basis for serotonin transport and inhibition of transporter activity by the drugs.
- Di Wu
- , Qihao Chen
- & Daohua Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Stress granules plug and stabilize damaged endolysosomal membranes
Stress granules plug and stabilize damaged endolysosomal membranes
Stress granules function at sites of intracellular membrane damage by forming on and stabilizing the ruptured membrane and promoting membrane repair.
- Claudio Bussi
- , Agustín Mangiarotti
- & Maximiliano G. Gutierrez
-
Article |
 Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
As well as being the substrate for the lipopolysaccharide transport protein complex comprising LptA–G, lipopolysaccharide binding to Lpt proteins promotes their assembly into a bridge linking the inner and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria.
- Lisa Törk
- , Caitlin B. Moffatt
- & Daniel Kahne
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the human cardiac myosin filament
Cryo-EM structure of the human cardiac myosin filament
The intricate molecular architecture and interactions of the human cardiac myosin filament offer insights into cardiac physiology, disease and drug therapy.
- Debabrata Dutta
- , Vu Nguyen
- & Roger Craig
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and electromechanical coupling of a voltage-gated Na+/H+ exchanger
Structure and electromechanical coupling of a voltage-gated Na+/H+ exchanger
Upon hyperpolarization, the S4 voltage-sensing segment of sea urchin SLC9C1 moves down, removing inhibition caused by an intracellular helix and enabling Na+/H+ exchange, leading to pH-dependent activation of sAC and sperm chemotaxis.
- Hyunku Yeo
- , Ved Mehta
- & David Drew
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of a sperm-specific solute carrier gated by voltage and cAMP
Structures of a sperm-specific solute carrier gated by voltage and cAMP
This study proposes a molecular mechanism of voltage activation in SLC9C1, a transporter essential for male fertility.
- Valeria Kalienkova
- , Martin F. Peter
- & Cristina Paulino
-
News & Views |
 Protein condensation regulates water availability in cells
Protein condensation regulates water availability in cells
Proteins can condense to form membraneless organelles, which act as vessels for biochemical reactions in cells. An investigation shows that protein condensation is also a cellular mechanism for controlling water availability.
- J. Pedro de Souza
- & Howard A. Stone
-
Article
| Open Access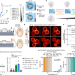 Macromolecular condensation buffers intracellular water potential
Macromolecular condensation buffers intracellular water potential
Water thermodynamics drive changes in macromolecular assembly that rapidly restore intracellular water availability in response to physiological fluctuations in temperature, pressure and osmotic strength.
- Joseph L. Watson
- , Estere Seinkmane
- & Emmanuel Derivery
-
Article |
 A bioelectrical phase transition patterns the first vertebrate heartbeats
A bioelectrical phase transition patterns the first vertebrate heartbeats
The first heartbeat of a zebrafish was captured, and development of cardiac excitability and conduction around this singular event were analysed, showing how development of single-cell properties produces a transition from quiescence to coordinated beating.
- Bill Z. Jia
- , Yitong Qi
- & Adam E. Cohen
-
Article |
 A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
A pentameric TRPV3 channel with a dilated pore
High-speed atomic force microscopy single-molecule imaging and cryo-EM analysis discover and reveal the structure of a TRPV3 pentamer, providing evidence for a non-canonical pentameric TRP-channel assembly, laying the foundation for new directions in TRP channel research.
- Shifra Lansky
- , John Michael Betancourt
- & Simon Scheuring
-
News & Views |
 Dynamic ion channel defies dogma
Dynamic ion channel defies dogma
It is well established that proteins in the TRP family of ion channels assemble from four subunits. But do they always do this? A five-subunit structure has now been observed, and might be involved in channel regulation.
- Ute A. Hellmich
-
Article
| Open Access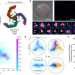 Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1
The plasma membrane can expand the blades of the PIEZO1 ion channel, impacting channel activation.
- Eric M. Mulhall
- , Anant Gharpure
- & Ardem Patapoutian
-
Article |
 Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Proteins of the Mycobacterium smegmatis Mce1 system assemble to form an elongated ABC transporter complex that is long enough to span the impermeable mycobacterial cell envelope.
- James Chen
- , Alice Fruhauf
- & Damian C. Ekiert
-
News & Views |
 Dynamics of protein droplets revealed by bridging multiple scales
Dynamics of protein droplets revealed by bridging multiple scales
Many biological processes rely on proteins that aggregate into droplets governed by dynamics that span myriad scales. A clever combination of spectroscopy and simulation offers a way to probe these diverse dynamics.
- Marina G. Guenza
-
Research Briefing |
 Protein folding stability measured at scale
Protein folding stability measured at scale
Protein sequences vary widely in their folding stabilities (the energetic favourability of folded compared with unfolded conformations), and protein alterations that affect stability have profound effects on evolution, health and disease, and biotechnological applications. An innovative method has made it possible to measure these stabilities on a massive scale, revealing evolutionary trends and opening up possibilities for machine learning.
-
Article |
 Extreme dynamics in a biomolecular condensate
Extreme dynamics in a biomolecular condensate
Two highly charged disordered human proteins phase-separate into viscous complex coacervates while retaining their rapid conformational dynamics through pico- to nanosecond exchange of short-lived side-chain interactions.
- Nicola Galvanetto
- , Miloš T. Ivanović
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
Article
| Open Access Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Large-scale assays using cDNA display proteolysis are used to measure the folding stabilities of protein domains, providing a method to quantify the effects of mutations on protein folding, with applications in protein design.
- Kotaro Tsuboyama
- , Justas Dauparas
- & Gabriel J. Rocklin
-
Article |
 Structural insights into BCDX2 complex function in homologous recombination
Structural insights into BCDX2 complex function in homologous recombination
Analyses of the structure and biochemical properties of the tetrameric complex of RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D and XRCC2 reveal details of its role in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks.
- Yashpal Rawal
- , Lijia Jia
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access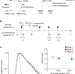 Single-photon absorption and emission from a natural photosynthetic complex
Single-photon absorption and emission from a natural photosynthetic complex
Using a heralded single-photon source along with coincidence counting, we establish time correlation functions for B800 excitation and B850 fluorescence emission and demonstrate that both events involve single photons.
- Quanwei Li
- , Kaydren Orcutt
- & K. Birgitta Whaley
-
Technology Feature |
 Powerful microscope captures motor proteins in unprecedented detail
Powerful microscope captures motor proteins in unprecedented detail
Called MINFLUX, the super-resolution method allows researchers to track molecules under cellular conditions.
- Amanda Heidt
-
Article |
 Outer membrane utilisomes mediate glycan uptake in gut Bacteroidetes
Outer membrane utilisomes mediate glycan uptake in gut Bacteroidetes
A structural and functional analysis of the systems involved in oligosaccharide uptake in gut Bacteroidetes describes multicomponent complexes termed utilisomes that include pre-processing and transport subunits.
- Joshua B. R. White
- , Augustinas Silale
- & Neil A. Ranson
-
News |
 The human brain’s characteristic wrinkles help to drive how it works
The human brain’s characteristic wrinkles help to drive how it works
A model of the brain’s geometry better explains neuronal activity than a model based on the ‘connectome’.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Article
| Open Access Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Ångström-resolution fluorescence microscopy
The authors introduce a single-molecule DNA-barcoding method, resolution enhancement by sequential imaging, that improves the resolution of fluorescence microscopy down to the Ångström scale using off-the-shelf fluorescence microscopy hardware and reagents.
- Susanne C. M. Reinhardt
- , Luciano A. Masullo
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of NINJ1-mediated plasma membrane rupture in cell death
Structural basis of NINJ1-mediated plasma membrane rupture in cell death
Structural, biochemical and mutagenesis studies indicate that, in dying cells, the membrane protein NINJ1 assembles into filaments, disrupting the cell membrane.
- Morris Degen
- , José Carlos Santos
- & Sebastian Hiller
-
Article |
 RNA conformational propensities determine cellular activity
RNA conformational propensities determine cellular activity
Systematic alteration of HIV-1 TAR RNA and quantitative determination of its propensity to bind to the Tat protein establish a key role role for a rare and short-lived RNA state in Tat-dependent transactivation in cells.
- Megan L. Ken
- , Rohit Roy
- & Hashim M. Al-Hashimi
-
Article |
 EMC chaperone–CaV structure reveals an ion channel assembly intermediate
EMC chaperone–CaV structure reveals an ion channel assembly intermediate
Interactions between the endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) and the high-voltage-activated calcium channel CaVα2δ are mutually exclusive, and EMC-to-CaVα2δ hand-off involves a divalent ion-dependent step and CaV1.2 element ordering.
- Zhou Chen
- , Abhisek Mondal
- & Daniel L. Minor Jr
-
Article |
 Peroxisome biogenesis initiated by protein phase separation
Peroxisome biogenesis initiated by protein phase separation
A study presents evidence to support a model in which liquid–liquid phase separation of components of the transport machinery mediates formation of transient protein transport channels on peroxisomes.
- Rini Ravindran
- , Isabel O. L. Bacellar
- & Stephen W. Michnick
-
Article |
 De novo evolution of macroscopic multicellularity
De novo evolution of macroscopic multicellularity
After 600 rounds of selection, anaerobic snowflake yeast evolved to be macroscopic, becoming around 20,000 times larger (approximately mm scale) and about 10,000-fold more biophysically tough, while retaining a clonal multicellular life cycle.
- G. Ozan Bozdag
- , Seyed Alireza Zamani-Dahaj
- & William C. Ratcliff
-
Article
| Open Access Structural evidence for intermediates during O2 formation in photosystem II
Structural evidence for intermediates during O2 formation in photosystem II
Using serial femtosecond X-ray cystallography, we provide structural insights into the final reaction step of Kok’s photosynthetic water oxidation cycle, specifically the S3→[S4]→S0 transition where O2 is formed.
- Asmit Bhowmick
- , Rana Hussein
- & Vittal K. Yachandra
-
Article
| Open Access The electron–proton bottleneck of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
The electron–proton bottleneck of photosynthetic oxygen evolution
Microsecond infrared spectroscopy together with quantum chemistry reveal the rate-determining proton and electron movements and identify an oxygen-radical state of the manganese cluster as the S4 state.
- Paul Greife
- , Matthias Schönborn
- & Holger Dau
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing the disordered nuclear transport machinery in situ
Visualizing the disordered nuclear transport machinery in situ
Previously shown as a 60-nm hole in the nuclear pore complex, the transport machinery by FG-nucleoporins is mapped.
- Miao Yu
- , Maziar Heidari
- & Edward A. Lemke
-
Article
| Open Access The Smc5/6 complex is a DNA loop-extruding motor
The Smc5/6 complex is a DNA loop-extruding motor
Using single-molecule imaging, the authors show that Smc5/6 forms DNA loops by extrusion, which establishes DNA loop extrusion as a conserved mechanism among eukaryotic SMC complexes.
- Biswajit Pradhan
- , Takaharu Kanno
- & Eugene Kim
-
Article
| Open Access CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is a DNA-tension-dependent barrier to cohesin-mediated loop extrusion
CTCF is sufficient to block loop extruding cohesin in a DNA tension dependent manner, and induces loop extrusion direction switching and loop shrinkage.
- Iain F. Davidson
- , Roman Barth
- & Jan-Michael Peters
-
Article |
 Structural basis of sensory receptor evolution in octopus
Structural basis of sensory receptor evolution in octopus
Cryo-electron microscopy analyses reveal adaptations that facilitate the octopus chemotactile receptor’s evolutionary transition from an ancestral role in neurotransmission to detecting greasy environmental agonists for ‘taste by touch’ sensory behaviour.
- Corey A. H. Allard
- , Guipeun Kang
- & Nicholas W. Bellono

 Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor
Stepwise activation of a metabotropic glutamate receptor