Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access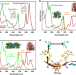 Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
The spectra of light used by photosynthetic organisms are determined by their pigmentation colour palettes. Here Liu et al. show that a genetically-encoded chimera of light-harvesting proteins from plants and reaction centres from purple bacteria allows for polychromatic solar energy harvesting.
- Juntai Liu
- , Vincent M. Friebe
- & Michael R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating vesicle bilayer permeability and selectivity via stimuli-triggered polymersome-to-PICsome transition
Regulating vesicle bilayer permeability and selectivity via stimuli-triggered polymersome-to-PICsome transition
Polyion complex vesicles have advantageous applications but have poorly tuneable permeability and nanostructure stability. Here, the authors develop polyion complex vesicles created using a stimuli-triggered transition from polymersomes and show high stability and switchable bilayer permaselectivity.
- Xiaorui Wang
- , Chenzhi Yao
- & Shiyong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation of hard pollen into soft matter
Transformation of hard pollen into soft matter
Pollen is an abundant material; but, currently has limited applications. Here, the authors turn pollen grains into soft microgel by de-esterification of pectin molecules and explore the mechanical and structural changes of the pollen grains using physical and modelling approaches.
- Teng-Fei Fan
- , Soohyun Park
- & Nam-Joon Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting the role of nanoparticle shape in enhancing hydrogel adhesive and mechanical properties
Exploiting the role of nanoparticle shape in enhancing hydrogel adhesive and mechanical properties
The ability to control nanostructure shape and dimensions presents opportunities to design materials in which their macroscopic properties are dependent upon the nature of the nanoparticle. Here the authors show nanoparticle shape is a critical consideration in the determination of nanocomposite hydrogel properties.
- Maria C. Arno
- , Maria Inam
- & Rachel K. O’Reilly
-
Article
| Open Access Bisphosphonate nanoclay edge-site interactions facilitate hydrogel self-assembly and sustained growth factor localization
Bisphosphonate nanoclay edge-site interactions facilitate hydrogel self-assembly and sustained growth factor localization
Nanoclays have been used in composites and for drug delivery but have suffered from a trade-off in properties when used for both. Here the authors report on the use of bisphosphonate interactions with nanoclay edges to made drug loaded composites without compromising materials properties or drug loading.
- Yang-Hee Kim
- , Xia Yang
- & Jonathan I. Dawson
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting gene expression using morphological cell responses to nanotopography
Predicting gene expression using morphological cell responses to nanotopography
The surface nanotopography of biomaterials direct cell behavior, but screening for desired effects is inefficient. Here, the authors introduce a platform that enables prediction of nanotopography-induced gene expression changes from changes in cell morphology, including in co-culture environments.
- Marie F. A. Cutiongco
- , Bjørn Sand Jensen
- & Nikolaj Gadegaard
-
Article
| Open Access A supertough electro-tendon based on spider silk composites
A supertough electro-tendon based on spider silk composites
Tendon driven systems offer a simple way to transmit actuation force in robotic hands but current tendon fibres have low toughness, limiting the further development of tendon-driven actuators. Here the authors report a super tough electro-tendon based on spider silk, mechanically toughened by SWCNT and electrically enhanced by PEDOT:PSS.
- Liang Pan
- , Fan Wang
- & Xiaodong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Complex microparticle architectures from stimuli-responsive intrinsically disordered proteins
Complex microparticle architectures from stimuli-responsive intrinsically disordered proteins
The production of microparticles with complex geometries for biotechnological use historically requires sophisticated fabrication techniques. Here, the authors create complex particle geometries by exploiting the metastable region of the phase diagram of thermally responsive intrinsically disordered proteins within microdroplets.
- Stefan Roberts
- , Vincent Miao
- & Ashutosh Chilkoti
-
Article
| Open Access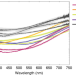 Diverse nanostructures underlie thin ultra-black scales in butterflies
Diverse nanostructures underlie thin ultra-black scales in butterflies
Nature has developed the ability to produce a wide range of optical effects most notably in the butterfly wing. Here, the authors report on the analysis of the structures responsible for ultra-black coloration across different butterflies and combine this with modelling to identify the key characteristics
- Alexander L. Davis
- , H. Frederik Nijhout
- & Sönke Johnsen
-
Article
| Open Access Complexation-induced resolution enhancement of 3D-printed hydrogel constructs
Complexation-induced resolution enhancement of 3D-printed hydrogel constructs
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel printing enables production of volumetric architectures but achieving good resolutions for miniaturized features remains challenging. Here the authors demonstrate shrinking of a printed structure by immersing a 3D-printed patterned hydrogel consisting of a hydrophilic polyionic polymer network in a solution of polyions of the opposite net charge.
- Jiaxing Gong
- , Carl C. L. Schuurmans
- & Yu Shrike Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Design of AIEgens for near-infrared IIb imaging through structural modulation at molecular and morphological levels
Design of AIEgens for near-infrared IIb imaging through structural modulation at molecular and morphological levels
Light has limited penetration depth in vivo which has led to increasing interest in NIR-II fluorophores. Here, the authors report on the design and testing of an organic aggregation induced emission fluorophore with high quantum yield and demonstrate imaging of vasculature and intestines in live mice.
- Yuanyuan Li
- , Zhaochong Cai
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access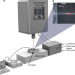 Single particles as resonators for thermomechanical analysis
Single particles as resonators for thermomechanical analysis
Eliminating the need for cleanroom fabrication for thermomechanical characterization of organic samples in a biomedical setting remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose the use of a single drug and collagen particles as resonators, enabling direct measurements on a material during thermal cycling.
- Peter Ouma Okeyo
- , Peter Emil Larsen
- & Anja Boisen
-
Article
| Open Access Photobactericidal activity activated by thiolated gold nanoclusters at low flux levels of white light
Photobactericidal activity activated by thiolated gold nanoclusters at low flux levels of white light
Antibiotic resistant bacteria have increased the interest in the development of antibacterial surfaces to reduce the risk of infection. Here, the authors report on a thiolated gold nanocluster enhanced crystal violet polymer with bactericidal properties under low level white light illumination.
- Gi Byoung Hwang
- , He Huang
- & Ivan P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Self-organising systems have huge potential in device design and fabrication; however, demonstrations of this are limited. Here, the authors report on a combination of disordered proteins and graphene oxide which allows spatio-temporal patterning and demonstrate the fabrication of microfluidic devices.
- Yuanhao Wu
- , Babatunde O. Okesola
- & Alvaro Mata
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum scale organic semiconductors for SERS detection of DNA methylation and gene expression
Quantum scale organic semiconductors for SERS detection of DNA methylation and gene expression
The low detection sensitivity of organic semiconductors has limited their use in biomedical surface-enhanced Raman scattering applications. Here, the authors use quantum scale organic semiconductors and show detection of genomic DNA methylation as well as gene expression.
- Swarna Ganesh
- , Krishnan Venkatakrishnan
- & Bo Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically and biologically skin-like elastomers for bio-integrated electronics
Mechanically and biologically skin-like elastomers for bio-integrated electronics
Designing biodegradable and biocompatible polymers to mimic both mechanical and biological properties of skins for emerging electronic devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose PSeD-U skin-like elastomers with both mechanical and biological properties for bio-integrated electronics.
- Shuo Chen
- , Lijie Sun
- & Zhengwei You
-
Article
| Open Access Fatigue-resistant adhesion of hydrogels
Fatigue-resistant adhesion of hydrogels
Fatigue-resistant adhesion is of interest for a range of applications, but has been limited in synthetic hydrogels. Here, the authors report on a synthetic hydrogel with ordered nanocrystalline domains resulting in high fatigue-resistant adhesion and demonstrate the coating of different surfaces.
- Ji Liu
- , Shaoting Lin
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA
Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA
Endosomal sequestration of lipid-based nanoparticles is a barrier to delivery of nucleic acids. Here the authors test an array of cholesterol variants and perform in-depth investigation of nanoparticle shape, internal structure and intracellular trafficking.
- Siddharth Patel
- , N. Ashwanikumar
- & Gaurav Sahay
-
Article
| Open Access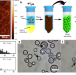 Primary cell wall inspired micro containers as a step towards a synthetic plant cell
Primary cell wall inspired micro containers as a step towards a synthetic plant cell
Assembling synthetic plant cell is difficult due to the presence of primary cell wall. Here, the authors describe the assembly of lipid-containing bodies that can be coated with cellulose and pectin, and show how these so-called plantosomes can be manipulated by changing surrounding milieu.
- T. Paulraj
- , S. Wennmalm
- & A. J. Svagan
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchically-structured metalloprotein composite coatings biofabricated from co-existing condensed liquid phases
Hierarchically-structured metalloprotein composite coatings biofabricated from co-existing condensed liquid phases
The mussel byssus cuticle is a wear-resistant and extensible metalloprotein composite. Here, the authors probed the cuticle nanostructure and composition before, during and after fabrication revealing a crucial role of metal-binding proteins that self-organize via liquid-liquid phase separation.
- Franziska Jehle
- , Elena Macías-Sánchez
- & Matthew J. Harrington
-
Article
| Open Access Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Bio-hybrid LEDs (HLED) are an environmental friendly alternative to LEDs based on inorganic phosphors but achieving long term is challenging. Here, the authors present a long-living Bio-HLED based on a zero-thermal-quenching biophosphor design and investigate the photo-induced heat generation and dissipation processes.
- Anna Espasa
- , Martina Lang
- & Rubén D. Costa
-
Article
| Open Access Microchannel network hydrogel induced ischemic blood perfusion connection
Microchannel network hydrogel induced ischemic blood perfusion connection
Restoration of blood flow to damaged sites has commonly involved treatment with pro-angiogenic molecules but these have undesired side effects. Here the authors present a microchannel-patterned gelatin hydrogel that is able to rescue mouse and porcine models of hindlimb ischemia.
- Jung Bok Lee
- , Dae-Hyun Kim
- & Hak-Joon Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Dual functionalized brain-targeting nanoinhibitors restrain temozolomide-resistant glioma via attenuating EGFR and MET signaling pathways
Dual functionalized brain-targeting nanoinhibitors restrain temozolomide-resistant glioma via attenuating EGFR and MET signaling pathways
Receptor tyrosine kinases are often activated in malignant gliomas. Here, the authors develop a dual functionalized brain targeting nano-inhibitor to simultaneously target EGFR and MET pathways, and show this can overcome temozolomide resistance in glioma.
- Xiangqi Meng
- , Yu Zhao
- & Jinquan Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Photosynthesis-inspired H2 generation using a chlorophyll-loaded liposomal nanoplatform to detect and scavenge excess ROS
Hydrogen can be used to reduce the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS), but its delivery to diseased tissues is challenging due to its low solubility. Here the authors develop a photosynthesis-inspired FRET nanocomplex to detect and scavenge local excess of ROS in the tissue using photocatalytic hydrogen production.
- Wei-Lin Wan
- , Bo Tian
- & Hsing-Wen Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications
Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications
Biodegradable implants are of great interest in orthopaedic applications but have been limited by low mechanical strength. Here, the authors examine systematically in detail the strengthening of biodegradable zinc by alloying with beneficial elements using mechanical, biodegradability and biocompatibility testing.
- Hongtao Yang
- , Bo Jia
- & Yufeng Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Design of a unidirectional water valve in Tillandsia
Design of a unidirectional water valve in Tillandsia
The valve-like trichomes of the desert plant Tillandsia landbeckii allow water acquisition from fog while minimising transpiration. Here, Raux et al. show that a hygroscopic cell-wall adjacent to a semi-permeable plasma membrane at the base of the trichome confers this asymmetry in water conductance.
- Pascal S. Raux
- , Simon Gravelle
- & Jacques Dumais
-
Article
| Open Access Polypeptide templating for designer hierarchical materials
Polypeptide templating for designer hierarchical materials
Despite recent progress in directed assembly of protein molecules into well-defined nanostructures, bridging materials fabrication from nano- to macroscale remains a challenge. Here, using silk fibroin as an example, the authors demonstrate templated crystallization to drive hierarchical materials growth from disordered molecules all the way up to centimeter scale.
- Hui Sun
- & Benedetto Marelli
-
Article
| Open Access Lamellar architectures in stiff biomaterials may not always be templates for enhancing toughness in composites
Lamellar architectures in stiff biomaterials may not always be templates for enhancing toughness in composites
Nacre is a biological composite whose architecture greatly enhances its toughness. Here, the authors report on the toughness enhancement in the spicules of a marine sponge. The spicules display similar architecture to nacre; however, their architecture does not lead to similar toughness enhancement.
- Michael A. Monn
- , Kaushik Vijaykumar
- & Haneesh Kesari
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled single-atom nanozyme for enhanced photodynamic therapy treatment of tumor
Self-assembled single-atom nanozyme for enhanced photodynamic therapy treatment of tumor
The hypoxic microenvironment in solid tumors limits the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) since oxygen is necessary to produce high cytotoxic singlet oxygen species. Here, the authors develop an improved self-assembled single-atom nanozyme which allows oxygen generation to enhance PDT efficacy.
- Dongdong Wang
- , Huihui Wu
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Nested helicoids in biological microstructures
Nested helicoids in biological microstructures
Helicoids are common structures found in many structural biological materials. Here, the authors report on a study of helicoids in the claws of scorpions and report different microstructures to what have previously been reported which have implications in materials stiffness, strength and toughness.
- Israel Greenfeld
- , Israel Kellersztein
- & H. Daniel Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed magnetic manipulation of vesicles into spatially coded prototissue architectures arrays
Programmed magnetic manipulation of vesicles into spatially coded prototissue architectures arrays
To execute higher-order functions, cells self-assemble into spatially coded tissue configurations. Here the authors magnetically assembly giant unilamellar vesicles into three dimensional tissue-mimic structures with collective osmotic stability.
- Qingchuan Li
- , Shubin Li
- & Xiaojun Han
-
Article
| Open Access Integrin-specific hydrogels modulate transplanted human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell survival, engraftment, and reparative activities
Integrin-specific hydrogels modulate transplanted human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell survival, engraftment, and reparative activities
Mesenchymal stromal cells enhance bone and cartilage repair, but are limited by poor survival and retention after transplantation. Here, the authors show that synthetic hydrogels presenting integrin-specific peptides enhance the survival and persistence of human mesenchymal stromal cells after transplant, as well as bone repair.
- Amy Y. Clark
- , Karen E. Martin
- & Andrés J. García
-
Article
| Open Access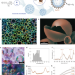 Catalytic processing in ruthenium-based polyoxometalate coacervate protocells
Catalytic processing in ruthenium-based polyoxometalate coacervate protocells
The development of microscale materials with cell-like functions and collective behaviors is an important milestone in bottom-up synthetic biology. Here the authors employ a bio-inspired inorganic synzyme to construct a micro-compartment with multi-functional activity providing a step towards the development of protocell reaction networks.
- Pierangelo Gobbo
- , Liangfei Tian
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment
Biointerfacial self-assembly generates lipid membrane coated bacteria for enhanced oral delivery and treatment
Oral microbiota delivery is an approach to treat and prevent disease but suffers from low retention and bioavailability. Here the authors report on a lipid coating to protect against environmental assault maintaining viability and bioactivity of the bacteria and demonstrate effective application in a colitis model.
- Zhenping Cao
- , Xinyue Wang
- & Jinyao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access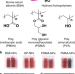 Hydroxyl-rich macromolecules enable the bio-inspired synthesis of single crystal nanocomposites
Hydroxyl-rich macromolecules enable the bio-inspired synthesis of single crystal nanocomposites
Calcium carbonate biomineralisation has long been linked to acidic macromolecules. Here, the authors challenge this view and show that a huge number of gold nanoparticles coated with hydroxyl-rich proteins can be incorporated into a calcium carbonate crystal while maintaining single crystal character.
- Yi-Yeoun Kim
- , Robert Darkins
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from decellularized tissues enables endodermal organoid culture
Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from decellularized tissues enables endodermal organoid culture
Organoid cultures have been developed from multiple tissues, opening new possibilities for regenerative medicine. Here the authors demonstrate the derivation of GMP-compliant hydrogels from decellularized porcine small intestine which support formation and growth of human gastric, liver, pancreatic and small intestinal organoids.
- Giovanni Giuseppe Giobbe
- , Claire Crowley
- & Paolo De Coppi
-
Article
| Open Access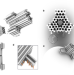 A large size-selective DNA nanopore with sensing applications
A large size-selective DNA nanopore with sensing applications
Artificial nanopores can perform selective gating of molecules analogous to transmembrane proteins. Here, the authors design a DNA origami pore with a controllable lid for size-selective gating and translocation of macromolecules and evaluate its biosensing properties by single particle assay.
- Rasmus P. Thomsen
- , Mette Galsgaard Malle
- & Jørgen Kjems
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired design of flexible armor based on chiton scales
Bioinspired design of flexible armor based on chiton scales
Biology has often served as the inspiration for the design of body armor; one common limitation is the flexibility of the resultant armor. Here, the authors examine the armour of chiton and use the observed design principles to 3D print flexible armor.
- Matthew Connors
- , Ting Yang
- & Ling Li
-
Article
| Open Access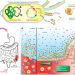 Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Anti-inflammatory treatments for gastrointestinal diseases can often have detrimental side effects. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle 1917 to create a fibrous matrix that has a protective effect in DSS-induced colitis mice.
- Pichet Praveschotinunt
- , Anna M. Duraj-Thatte
- & Neel S. Joshi
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse protein assembly driven by metal and chelating amino acids with selectivity and tunability
Diverse protein assembly driven by metal and chelating amino acids with selectivity and tunability
Precise manipulation of protein self-assembly in vitro is challenging. Here, the authors developed an approach for driving metal-mediated reversible protein assembly by genetically installing a bipyridine residue into an oligomeric (D3) protein.
- Minwoo Yang
- & Woon Ju Song
-
Article
| Open Access Superhydrophobic hemostatic nanofiber composites for fast clotting and minimal adhesion
Superhydrophobic hemostatic nanofiber composites for fast clotting and minimal adhesion
Nanotechnology can bring significant advancements to hemostatic patches. Here, the authors design a superhydrophobic hemostatic surface with immobilized carbon nanofibers that can stop bleeding instantaneously upon application, seal the wound subsequently by promoting quick fibrin formation, and facilitate unforced and facile patch removal without tearing the wound.
- Zhe Li
- , Athanasios Milionis
- & Choon Hwai Yap
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon-nanotube reinforcement of DNA-silica nanocomposites yields programmable and cell-instructive biocoatings
Carbon-nanotube reinforcement of DNA-silica nanocomposites yields programmable and cell-instructive biocoatings
DNA composite materials have potential for biomedical sciences; however, control over the materials can be an issue. Here, the authors report on a carbon-nanotube reinforced DNA-silica gel with controllable mechanical properties to steer the attachment, proliferation, migration and release of cells.
- Yong Hu
- , Carmen M. Domínguez
- & Christof M. Niemeyer
-
Article
| Open Access Self-regenerating giant hyaluronan polymer brushes
Self-regenerating giant hyaluronan polymer brushes
Polymer brushes are often used to functionalise surfaces. Here, the authors report on the creation of high-density, regenerating hyaluronan brushes using hyaluronan synthase enzymes which can be patterned by photo-deactivation and demonstrate biocompatibility and resistance to biofilm formation.
- Wenbin Wei
- , Jessica L. Faubel
- & Jennifer E. Curtis
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable polycarbonate adhesives for dry and aqueous conditions with thermoresponsive properties
Sustainable polycarbonate adhesives for dry and aqueous conditions with thermoresponsive properties
Adhesives are ubiquitous in commodity products, however it it essential that their synthesis and degradation be sustainable without compromising their performance. Here, the authors report a library of adhesives based on environmentally benign building blocks that perform in both dry and wet environments.
- Anjeza Beharaj
- , Ethan Z. McCaslin
- & Mark W. Grinstaff
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen bond guidance and aromatic stacking drive liquid-liquid phase separation of intrinsically disordered histidine-rich peptides
Hydrogen bond guidance and aromatic stacking drive liquid-liquid phase separation of intrinsically disordered histidine-rich peptides
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of intrinsically disordered proteins plays an important part in the formation of extracellular biological materials. Here, the authors show that repeats of the peptide motif GHGLY are necessary for the LLPS of pH-responsive histidine-rich squid beak proteins.
- Bartosz Gabryelczyk
- , Hao Cai
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical unfolding of protein domains induces shape change in programmed protein hydrogels
Chemical unfolding of protein domains induces shape change in programmed protein hydrogels
Tailoring and programing the behavior of protein biomaterials is complex. Here, the authors report on the use of polyelectrolytes for controlling the stiffness to allow programing of protein hydrogels and generate reversible shape changes via folding and unfolding reactions.
- Luai R. Khoury
- & Ionel Popa
-
Article
| Open Access Extravascular gelation shrinkage-derived internal stress enables tumor starvation therapy with suppressed metastasis and recurrence
Extravascular gelation shrinkage-derived internal stress enables tumor starvation therapy with suppressed metastasis and recurrence
The efficacy of tumour starvation therapy is limited by lack of persistent tumour suppression, tumour metastasis and recurrence. Here, the authors report biocompatible gold nanorods and thermal-sensitive hydrogel to promote narrowing of blood vessels and show this to reduce tumour growth and metastasis.
- Kun Zhang
- , Yan Fang
- & Huixiong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Zwitterionically modified alginates mitigate cellular overgrowth for cell encapsulation
Zwitterionically modified alginates mitigate cellular overgrowth for cell encapsulation
Cellular overgrowth and fibrosis in the foreign body response can compromise the function of transplanted cells. Here, the authors report on the zwitterionically modified alginates for the encapsulation of cells to reduce cellular overgrowth and demonstrate application in mice, dogs and pigs.
- Qingsheng Liu
- , Alan Chiu
- & Minglin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible, sticky, and biodegradable wireless device for drug delivery to brain tumors
Flexible, sticky, and biodegradable wireless device for drug delivery to brain tumors
There is a need to further improve the efficacy of biodegradable wafers used in surgically treated brain tumors. Here, the authors report a flexible, biodegradable wireless device capable of adhesion to surgical site for optimal drug delivery upon mild-thermic actuation and report therapeutic efficacy in mouse and canine tumor models.
- Jongha Lee
- , Hye Rim Cho
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim

 Introducing the crystalline phase of dicalcium phosphate monohydrate
Introducing the crystalline phase of dicalcium phosphate monohydrate