Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Anti-TIGIT antibody improves PD-L1 blockade through myeloid and Treg cells
Anti-TIGIT antibody improves PD-L1 blockade through myeloid and Treg cells
A high baseline of intratumoural macrophages and regulatory T cells is associated with better outcomes in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab plus tiragolumab, but not with atezolizumab alone.
- Xiangnan Guan
- , Ruozhen Hu
- & Namrata S. Patil
-
Article
| Open Access Organ aging signatures in the plasma proteome track health and disease
Organ aging signatures in the plasma proteome track health and disease
Blood plasma protein data was combined with machine learning models for a simple method to determine differences in organ-specific aging; the study provides a basis for the prediction of diseases and aging effects using plasma proteomics.
- Hamilton Se-Hwee Oh
- , Jarod Rutledge
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Sturgeon is a pretrained neural network that uses incremental results from nanopore sequencing to rapidly classify central nervous system tumours and can be used to aid critical decision-making during surgery.
- C. Vermeulen
- , M. Pagès-Gallego
- & J. de Ridder
-
Article
| Open Access Cingulate dynamics track depression recovery with deep brain stimulation
Cingulate dynamics track depression recovery with deep brain stimulation
This study demonstrates how activity in the cingulate cortex tracks depression recovery, providing symptom relief using deep brain stimulation.
- Sankaraleengam Alagapan
- , Ki Sueng Choi
- & Christopher J. Rozell
-
Perspective |
 Practical recommendations for using ctDNA in clinical decision making
Practical recommendations for using ctDNA in clinical decision making
This Perspective reviews the utility and interpretation of circulating tumour DNA for the detection of residual and recurrent cancers and provides recommendations regarding its clinical application for a variety of solid tumours.
- Stacey A. Cohen
- , Minetta C. Liu
- & Alexey Aleshin
-
Article |
 Y chromosome loss in cancer drives growth by evasion of adaptive immunity
Y chromosome loss in cancer drives growth by evasion of adaptive immunity
Loss of the Y chromosome in tumour cells is associated with a poor prognosis for patients with bladder cancer by causing local T cell exhaustion, which also increases the response to immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
- Hany A. Abdel-Hafiz
- , Johanna M. Schafer
- & Dan Theodorescu
-
Article
| Open Access Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer
Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer
Indole-3-acetic acid (3-IAA), a tryptophan metabolite derived from the gut microbiota, is associated with a better response to chemotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and dietary interventions could have a role in the treatment of PDAC.
- Joseph Tintelnot
- , Yang Xu
- & Nicola Gagliani
-
Article
| Open Access A DNA methylation atlas of normal human cell types
A DNA methylation atlas of normal human cell types
We describe a human DNA methylome atlas based on deep whole-genome bisulfite sequencing, allowing fragment-level analysis of cell-type-specific markers and providing an essential resource for studies of gene regulation and for deconvolution of cell mixtures and liquid biopsies.
- Netanel Loyfer
- , Judith Magenheim
- & Tommy Kaplan
-
Article
| Open Access Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries
Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries
A cross-ancestry meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies association signals for stroke and its subtypes at 89 (61 new) independent loci, reveals putative causal genes, highlighting F11, KLKB1, PROC, GP1BA, LAMC2 and VCAM1 as potential drug targets, and provides cross-ancestry integrative risk prediction.
- Aniket Mishra
- , Rainer Malik
- & Stephanie Debette
-
Article |
 Genomics to select treatment for patients with metastatic breast cancer
Genomics to select treatment for patients with metastatic breast cancer
Targeted therapies matched to genomics improved progression-free survival when genomic alterations were classified as level I/II (according to ESCAT), and genomics should thus be driven by target actionability in patients with metastatic breast cancer.
- Fabrice Andre
- , Thomas Filleron
- & Ivan Bieche
-
Article
| Open Access Early prediction of preeclampsia in pregnancy with cell-free RNA
Early prediction of preeclampsia in pregnancy with cell-free RNA
Analyses of circulating cell-free RNA (cfRNA) in blood samples from pregnant mothers identify changes in gene expression that could be used in liquid biopsy tests to identify and monitor individuals who are at risk of preeclampsia.
- Mira N. Moufarrej
- , Sevahn K. Vorperian
- & Stephen R. Quake
-
Perspective |
 An open science study of ageing in companion dogs
An open science study of ageing in companion dogs
The Dog Aging Project is an open-data, community science study to identify genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors associated with canine healthy lifespan, generating knowledge that could readily translate to human ageing.
- Kate E. Creevy
- , Joshua M. Akey
- & Benjamin S. Wilfond
-
Article
| Open Access RNA profiles reveal signatures of future health and disease in pregnancy
RNA profiles reveal signatures of future health and disease in pregnancy
Expression signatures from cell-free RNA of pregnant women can be used to reveal normal biology of pregnancy and predict development of pre-eclampsia.
- Morten Rasmussen
- , Mitsu Reddy
- & Thomas F. McElrath
-
Article |
 Combinatorial, additive and dose-dependent drug–microbiome associations
Combinatorial, additive and dose-dependent drug–microbiome associations
An analysis of 2,173 individuals from the MetaCardis cohort quantifies the individual and combinatorial effects of a range of drugs on host health, metabolome and gut microbiome in cardiometabolic disease.
- Sofia K. Forslund
- , Rima Chakaroun
- & Peer Bork
-
Article |
 Using DNA sequencing data to quantify T cell fraction and therapy response
Using DNA sequencing data to quantify T cell fraction and therapy response
A robust, cost-effective technique based on whole-exome sequencing data can be used to characterize immune infiltrates, relate the extent of these infiltrates to somatic changes in tumours, and enables prediction of tumour responses to immune checkpoint inhibition therapy.
- Robert Bentham
- , Kevin Litchfield
- & Nicholas McGranahan
-
Article |
 A lymphocyte–microglia–astrocyte axis in chronic active multiple sclerosis
A lymphocyte–microglia–astrocyte axis in chronic active multiple sclerosis
Single-nucleus transcriptomics defines a diverse set of immune and glial cells at the chronically inflamed leading edge of demyelinated white matter lesions in patients with multiple sclerosis.
- Martina Absinta
- , Dragan Maric
- & Daniel S. Reich
-
Article |
 ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma
ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma
The authors report on prospective exploratory analyses of circulating tumour DNA in an urothelial carcinoma immunotherapy clinical trial.
- Thomas Powles
- , Zoe June Assaf
- & Sanjeev Mariathasan
-
Article
| Open Access Swarm Learning for decentralized and confidential clinical machine learning
Swarm Learning for decentralized and confidential clinical machine learning
Swarm Learning is a decentralized machine learning approach that outperforms classifiers developed at individual sites for COVID-19 and other diseases while preserving confidentiality and privacy.
- Stefanie Warnat-Herresthal
- , Hartmut Schultze
- & Joachim L. Schultze
-
Article |
 ALDH4A1 is an atherosclerosis auto-antigen targeted by protective antibodies
ALDH4A1 is an atherosclerosis auto-antigen targeted by protective antibodies
An autoantibody found in a mouse model of atherosclerosis recognizses ALDH4A1, and infusion of the antibody delays plaque formation in mice.
- Cristina Lorenzo
- , Pilar Delgado
- & Almudena R. Ramiro
-
Article |
 Metallaphotoredox aryl and alkyl radiomethylation for PET ligand discovery
Metallaphotoredox aryl and alkyl radiomethylation for PET ligand discovery
A versatile and rapid metallaphotoredox catalytic method of making 3H- and 11C-labelled tracer compounds for use in positron emission tomography (PET) is reported.
- Robert W. Pipal
- , Kenneth T. Stout
- & David W. C. MacMillan
-
Matters Arising |
Transparency and reproducibility in artificial intelligence
- Benjamin Haibe-Kains
- , George Alexandru Adam
- & Hugo J. W. L. Aerts
-
Article |
 COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T cell responses
COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and TH1 T cell responses
In a phase I/II dose-escalation clinical trial, the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits specific T cell and antibody responses that suggest it has protective potential.
- Ugur Sahin
- , Alexander Muik
- & Özlem Türeci
-
Perspective |
 LifeTime and improving European healthcare through cell-based interceptive medicine
LifeTime and improving European healthcare through cell-based interceptive medicine
The LifeTime initiative is an ambitious, multidisciplinary programme that aims to improve healthcare by tracking individual human cells during disease processes and responses to treatment in order to develop and implement cell-based interceptive medicine in Europe.
- Nikolaus Rajewsky
- , Geneviève Almouzni
- & Frauke Zipp
-
Article |
 Hepatic NADH reductive stress underlies common variation in metabolic traits
Hepatic NADH reductive stress underlies common variation in metabolic traits
The authors identify an increased hepatic NADH/NAD+ ratio as an underlying metabolic parameter that is shaped by human genetic variation and contributes causally to key metabolic traits and diseases.
- Russell P. Goodman
- , Andrew L. Markhard
- & Vamsi K. Mootha
-
Article |
 Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer
diagnostic approach
Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer
diagnostic approach
Microbial nucleic acids are detected in samples of tissues and blood from more than 10,000 patients with cancer, and machine learning is used to show that these can be used to discriminate between and among different types of cancer, suggesting a new microbiome-based diagnostic approach.
- Gregory D. Poore
- , Evguenia Kopylova
- & Rob Knight
-
Article |
 Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy
Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy
Protein misfolding cyclic amplification (PMCA) technology can discriminate between patients with Parkinson’s disease and patients with multiple system atrophy on the basis of the characteristics of the α-synuclein aggregates in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Mohammad Shahnawaz
- , Abhisek Mukherjee
- & Claudio Soto
-
Article |
 B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response
B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response
Multiomic profiling of several cohorts of patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade highlights the presence and potential role of B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures in promoting therapy response.
- Beth A. Helmink
- , Sangeetha M. Reddy
- & Jennifer A. Wargo
-
Article |
 B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma
B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma
Immune profiling of the tumour microenvironment of soft-tissue sarcoma identifies a group of patients with high levels of B-cell infiltration and tertiary lymphoid structures that have improved survival and a high response rate to immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
- Florent Petitprez
- , Aurélien de Reyniès
- & Wolf H. Fridman
-
Review Article |
 Why and where an HIV cure is needed and how it might be achieved
Why and where an HIV cure is needed and how it might be achieved
Current barriers and limitations to HIV treatments are reviewed, and suggestions for future steps to achieve an effective curative intervention are discussed.
- Thumbi Ndung’u
- , Joseph M. McCune
- & Steven G. Deeks
-
Letter |
 A clinically applicable approach to continuous prediction of future acute kidney injury
A clinically applicable approach to continuous prediction of future acute kidney injury
A deep learning approach that predicts the risk of acute kidney injury may help to identify patients at risk of health deterioration within a time window that enables early treatment.
- Nenad Tomašev
- , Xavier Glorot
- & Shakir Mohamed
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal multi-omics of host–microbe dynamics in prediabetes
Longitudinal multi-omics of host–microbe dynamics in prediabetes
Deep profiling of transcriptomes, metabolomes, cytokines, and proteomes, alongside changes in the microbiome, in samples from individuals with and without prediabetes reveal insights into inter-individual variability and associations between changes in the microbiome and other factors.
- Wenyu Zhou
- , M. Reza Sailani
- & Michael Snyder
-
Letter |
 Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
Actively personalized vaccination trial for newly diagnosed glioblastoma
In a phase I trial, highly individualized peptide vaccines against unmutated tumour antigens and neoepitopes elicited sustained responses in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, respectively, in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma.
- Norbert Hilf
- , Sabrina Kuttruff-Coqui
- & Wolfgang Wick
-
Article |
 Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia
Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia
Analyses of samples from patients with acute myeloid leukaemia reveal that drug response is associated with mutational status and gene expression; the generated dataset provides a basis for future clinical and functional studies of this disease.
- Jeffrey W. Tyner
- , Cristina E. Tognon
- & Brian J. Druker
-
Letter |
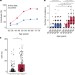 Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals
Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals
Individuals who are at high risk of developing acute myeloid leukaemia can be identified years before diagnosis using genetic information from blood samples.
- Sagi Abelson
- , Grace Collord
- & Liran I. Shlush
-
Letter |
 Induction of innate immune memory via microRNA targeting of chromatin remodelling factors
Induction of innate immune memory via microRNA targeting of chromatin remodelling factors
The microRNAs miR-221 and miR-222 regulate the reprogramming of macrophages during the development of lipopolysaccharide tolerance, and increased expression of these microRNAs is associated with immunosuppression and poor prognosis in patients with sepsis.
- John J. Seeley
- , Rebecca G. Baker
- & Sankar Ghosh
-
Article
| Open Access The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers
The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers
Analyses of genomes from 914 children, adolescents, and young adults provide a comprehensive resource of genomic alterations across a spectrum of common childhood cancers.
- Susanne N. Gröbner
- , Barbara C. Worst
- & Stefan M. Pfister
-
Letter |
 TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells
TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells
In humans, TGFβ signalling is associated with lack of response to immunotherapy in immune-excluded tumours; in mouse models of this immune phenotype, robust tumour infiltration by T cells and tumour regression are observed only when checkpoint inhibition is combined with inhibition of TGFβ signalling.
- Sanjeev Mariathasan
- , Shannon J. Turley
- & Thomas Powles
-
Letter |
 High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease
High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease
Measurement of human plasma amyloid-β biomarkers using immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry reliably predicts individual brain amyloid-β status and has potential clinical utility.
- Akinori Nakamura
- , Naoki Kaneko
- & Katsuhiko Yanagisawa
-
Article |
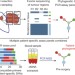 Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution
Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution
Circulating tumour DNA profiling in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer can be used to track single-nucleotide variants in plasma to predict lung cancer relapse and identify tumour subclones involved in the metastatic process.
- Christopher Abbosh
- , Nicolai J. Birkbak
- & Charles Swanton
-
Letter |
 Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder
Early brain development in infants at high risk for autism spectrum disorder
Surface area expansion from 6–12 months precedes brain overgrowth in high risk infants diagnosed with autism at 24 months and cortical features in the first year predict individual diagnostic outcomes.
- Heather Cody Hazlett
- , Hongbin Gu
- & Core H. Gu
-
Article |
 Genomic hallmarks of localized, non-indolent prostate cancer
Genomic hallmarks of localized, non-indolent prostate cancer
Genomic analyses of localized, non-indolent prostate cancer identify recurrent aberrations that can predict relapse, and also highlight differences between early prostate cancer and metastatic, castration-resistant disease.
- Michael Fraser
- , Veronica Y. Sabelnykova
- & Paul C. Boutros
-
Letter |
 A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia
A 17-gene stemness score for rapid determination of risk in acute leukaemia
A rapid gene signature test (LSC17) that captures stem cell expression programs in acute myeloid leukaemia patients at diagnosis is associated with therapy response and survival, facilitating initial treatment stratification.
- Stanley W. K. Ng
- , Amanda Mitchell
- & Jean C. Y. Wang
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Safikhani et al. reply
- Zhaleh Safikhani
- , Nehme El-Hachem
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Consistency in large pharmacogenomic studies
Consistency in large pharmacogenomic studies
- Paul Geeleher
- , Eric R. Gamazon
- & R. Stephanie Huang
-
Letter |
 Transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons after stroke
Transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons after stroke
In a mouse model of ischaemia, mitochondrial particles released from astroctyes are taken up by adjacent neurons, leading to enhanced cell survival signalling; disruption of this release mechanism resulted in worsened neurological outcomes.
- Kazuhide Hayakawa
- , Elga Esposito
- & Eng H. Lo
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Decompensated cirrhosis and microbiome interpretation
Decompensated cirrhosis and microbiome interpretation
- Jasmohan S. Bajaj
- , Naga S. Betrapally
- & Patrick M. Gillevet
-
-
Article |
 Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer
Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer
Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and serves as a biomarker for detection of early pancreatic cancer in patients and mouse models of the disease; the findings may enable early and non-invasive identification, and prevention of malignant cancer.
- Sonia A. Melo
- , Linda B. Luecke
- & Raghu Kalluri
-
Letter |
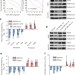 EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors
EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors
A subset of lung cancer cells with EGFR or BRG1 mutations shows selective sensitivity to a combination of EZH2 inhibitors with topoisomerase II inhibitors such as the commonly used chemotherapeutic drug etoposide.
- Christine M. Fillmore
- , Chunxiao Xu
- & Carla F. Kim

 Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers
Genome-wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers