Correspondence
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Closing the gender gap in competitiveness through priming
Closing the gender gap in competitiveness through priming
Men are often more willing to compete compared to women, which may contribute to gender differences in wages and career advancement. Here, the authors show that ‘power priming’ - encouraging people to imagine themselves in a situation of power - can close the gender gap in competitiveness.
- Loukas Balafoutas
- , Helena Fornwagner
- & Matthias Sutter
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale genome-wide enrichment analyses identify new trait-associated genes and pathways across 31 human phenotypes
Large-scale genome-wide enrichment analyses identify new trait-associated genes and pathways across 31 human phenotypes
In genome-wide association studies, variant-level associations are hard to identify and can be difficult to interpret biologically. Here, the authors develop a new model-based enrichment analysis method, and apply it to identify new associated genes, pathways and tissues across 31 human phenotypes.
- Xiang Zhu
- & Matthew Stephens
-
Article
| Open Access Common mechanism of transcription termination at coding and noncoding RNA genes in fission yeast
Common mechanism of transcription termination at coding and noncoding RNA genes in fission yeast
Termination of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription is an essential step of gene expression. Here the authors provide evidence that in fission yeast termination of ncRNA genes occurs by a cleavage-dependent mechanism involving recruitment of mRNA 3′ end processing factors and requires the conserved Ysh1/CPSF-73 and Dhp1/XRN2 nucleases.
- Marc Larochelle
- , Marc-Antoine Robert
- & François Bachand
-
Article
| Open Access Incompatibility of the circadian protein BMAL1 and HNF4α in hepatocellular carcinoma
Incompatibility of the circadian protein BMAL1 and HNF4α in hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) is regulated by different promoters to generate two isoforms, one of which functions as a tumor suppressor. Here, the authors reveal that induction of the alternative isoform in hepatocellular carcinoma inhibits the circadian clock by repressing BMAL1, and the reintroduction of BMAL1 prevents HCC tumor growth.
- Baharan Fekry
- , Aleix Ribas-Latre
- & Kristin Eckel-Mahan
-
Article
| Open Access Mycobacterial DnaB helicase intein as oxidative stress sensor
Mycobacterial DnaB helicase intein as oxidative stress sensor
Inteins can act as post-translational environmental sensors in vivo. Here the authors characterize two inteins present in the Mycobacterium smegmatis replicative helicase DnaB that display distinct splicing behaviors and are differentially sensitive to inhibition by biological stressors and propose that splicing inhibition could modulate DnaB levels to protect the cell against replication stress.
- Danielle S. Kelley
- , Christopher W. Lennon
- & Marlene Belfort
-
Article
| Open Access Src regulates amino acid-mediated mTORC1 activation by disrupting GATOR1-Rag GTPase interaction
Src regulates amino acid-mediated mTORC1 activation by disrupting GATOR1-Rag GTPase interaction
The growth-promoting activity of mTORC1 is regulated by amino acid availability via the Rag GTPases. Here, the authors demonstrate Src-dependent control of cell size and autophagy through disruption of the Rag GTPase–GATOR1 complex and mTORC1 activation at the lysosomal surface.
- Rituraj Pal
- , Michela Palmieri
- & Marco Sardiello
-
Article
| Open Access TRIP13 and APC15 drive mitotic exit by turnover of interphase- and unattached kinetochore-produced MCC
TRIP13 and APC15 drive mitotic exit by turnover of interphase- and unattached kinetochore-produced MCC
The mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) is assembled during both mitosis and interphase. Here, the authors use auxin-inducible degron tags to rapidly degrade TRIP13 and find that mitotic exit requires MCC disassembly by TRIP13-catalyzed removal of Mad2 or APC1-driven ubiquitination of Cdc20.
- Dong Hyun Kim
- , Joo Seok Han
- & Don W. Cleveland
-
Article
| Open Access DHX9 helicase promotes R-loop formation in cells with impaired RNA splicing
DHX9 helicase promotes R-loop formation in cells with impaired RNA splicing
Unresolved R-loops can represent a threat to genome stability. Here the authors reveal that DHX9 helicase can promote R-loop formation in the absence of splicing factors SFPQ and SF3B3.
- Prasun Chakraborty
- , Jeffrey T. J. Huang
- & Kevin Hiom
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based redesign of docking domain interactions modulates the product spectrum of a rhabdopeptide-synthesizing NRPS
Structure-based redesign of docking domain interactions modulates the product spectrum of a rhabdopeptide-synthesizing NRPS
Rhabdopeptides are synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) and the multiple NRPS subunits interact through docking domains (DD). Here the authors provide insights into DD interaction patterns and present the structures of three N-terminal docking domains (NDD) and a NDD-CDD complex and derive a set of recognition rules for DD interactions.
- Carolin Hacker
- , Xiaofeng Cai
- & Jens Wöhnert
-
Article
| Open Access HSP90-incorporating chaperome networks as biosensor for disease-related pathways in patient-specific midbrain dopamine neurons
HSP90-incorporating chaperome networks as biosensor for disease-related pathways in patient-specific midbrain dopamine neurons
The early molecular events that ultimately lead to neuronal cell death in pathologies such as Parkinson’s disease are poorly understood. Here the authors use pluripotent stem-cell-derived human midbrain neurons and chemical biology tools to gain molecular level insight into the events induced by toxic and genetic stresses that mimic those occurring during neurodegeneration.
- Sarah Kishinevsky
- , Tai Wang
- & Lorenz Studer
-
Article
| Open Access Ventral pallidum encodes relative reward value earlier and more robustly than nucleus accumbens
Ventral pallidum encodes relative reward value earlier and more robustly than nucleus accumbens
In the ventral basal ganglia circuit, the ventral pallidum (VP) receives major inputs from the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and is involved in reward processing. Here, the authors report that, contrary to the accepted model, signals related to the relative value of reward in VP emerge before NAc and are more robust.
- David Ottenheimer
- , Jocelyn M. Richard
- & Patricia H. Janak
-
Article
| Open Access Patterns and drivers of recent disturbances across the temperate forest biome
Patterns and drivers of recent disturbances across the temperate forest biome
Climate change may impact forest disturbances, though local variability is high. Here, Sommerfeld et al. show that disturbance patterns across the temperate biome vary with agents and tree traits, yet large disturbances are consistently linked to warmer and drier than average conditions.
- Andreas Sommerfeld
- , Cornelius Senf
- & Rupert Seidl
-
Article
| Open Access Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Nanodiamond autophagy inhibitor allosterically improves the arsenical-based therapy of solid tumors
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) based therapy in solid cancers is limited. Here they repurpose nanodiamonds (NDs) as a safe and potent autophagic inhibitor to improve the efficacy of ATO-based treatment in solid tumors and show the combination therapy to work better in orthotopic liver cancer model.
- Zhifen Cui
- , Yu Zhang
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Mutational interactions define novel cancer subgroups
Mutational interactions define novel cancer subgroups
Tumour heterogeneity hinders translation of large-scale genomic data into the clinic. Here the authors develop a method for the stratification of cancer patients based on the molecular gene status, including genetic interactions, rather than clinico-histological data, and apply it to TCGA data for over 8000 cases across 22 cancer types.
- Jack Kuipers
- , Thomas Thurnherr
- & Niko Beerenwinkel
-
Article
| Open Access Dimethyl fumarate is an allosteric covalent inhibitor of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinases
Dimethyl fumarate is an allosteric covalent inhibitor of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinases
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) is a major drug in the treatment of psoriasis and multiple sclerosis. Here the authors reveal a mechanism of RSK/MSK inhibition through covalent inhibition that can explain the observed clinical effects and the dose–response characteristics of DMF treatment.
- Jacob Lauwring Andersen
- , Borbala Gesser
- & Poul Nissen
-
Article
| Open Access Neurokinin-3 receptor activation selectively prolongs atrial refractoriness by inhibition of a background K+ channel
Neurokinin-3 receptor activation selectively prolongs atrial refractoriness by inhibition of a background K+ channel
The cardiac autonomic nervous system produces various neuropeptides, such as neurokinin substance-P (Sub-P), whose function remains largely unclear. Here, authors show that Sub-P causes a receptor-mediated prolongation of the atrial action potential through a reduced background potassium current, and prevents atrial fibrillation.
- Marieke W. Veldkamp
- , Guillaume S. C. Geuzebroek
- & Ruben Coronel
-
Review Article
| Open Access The dark side of centromeres: types, causes and consequences of structural abnormalities implicating centromeric DNA
The dark side of centromeres: types, causes and consequences of structural abnormalities implicating centromeric DNA
Centromeres are the chromosomal domains that regulate assembly of the components required for chromosome separation. Here the authors review how centromeres are a potential source of genome instability and link centromere aberrations and rearrangements to human diseases such as cancer.
- V. Barra
- & D. Fachinetti
-
Article
| Open Access SMYD2 glutathionylation contributes to degradation of sarcomeric proteins
SMYD2 glutathionylation contributes to degradation of sarcomeric proteins
Ischemic reperfusion or nutrient deprivation that produces reactive oxygen species can lead to a loss of muscle contractile function. Here the authors show that glutathionylation of the lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 contributes to degradation or disassembly of sarcomeres.
- Dhanushka N. P. Munkanatta Godage
- , Garrett C. VanHecke
- & Young-Hoon Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of a social polymorphism in halictid bees
The genetic basis of a social polymorphism in halictid bees
The halictid bee Lasioglossum albipes has both solitary and eusocial individuals, making it a model for social evolution. Here, Kocher et al. identify a genetic variation associated with this social polymorphism, including a variant that can regulate the expression of an autism-associated gene, syntaxin 1a.
- Sarah D. Kocher
- , Ricardo Mallarino
- & Naomi E. Pierce
-
Article
| Open Access mRNAs and lncRNAs intrinsically form secondary structures with short end-to-end distances
mRNAs and lncRNAs intrinsically form secondary structures with short end-to-end distances
It was previously suggested that formation of RNA secondary structure tends to bring the 5′ and 3′ ends of RNA into close proximity. Here the authors use experimental and computational approaches to show that mRNAs and lncRNAs have an intrinsic propensity to fold into structures in which the 5′ end and 3′ end are ≤7 nm apart irrespective of length.
- Wan-Jung C. Lai
- , Mohammad Kayedkhordeh
- & Dmitri N. Ermolenko
-
Article
| Open Access DNA-PK inhibition synergizes with oncolytic virus M1 by inhibiting antiviral response and potentiating DNA damage
DNA-PK inhibition synergizes with oncolytic virus M1 by inhibiting antiviral response and potentiating DNA damage
Oncolytic virotherapy is a promising strategy for cancer treatment. In this study, the authors demonstrate that DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to M1 virus and improves therapeutic effects in refractory cancer models in vivo and in patient tumour samples.
- Xiao Xiao
- , Jiankai Liang
- & Guangmei Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Astrocytes integrate and drive action potential firing in inhibitory subnetworks
Astrocytes integrate and drive action potential firing in inhibitory subnetworks
Specific types of inhibitory neurons exhibit prolonged, high-frequency barrages of action potentials. Here, the authors show that astrocytes might mediate such barrage firing.
- Tara Deemyad
- , Joel Lüthi
- & Nelson Spruston
-
Article
| Open Access Cell shape-independent FtsZ dynamics in synthetically remodeled bacterial cells
Cell shape-independent FtsZ dynamics in synthetically remodeled bacterial cells
The FtsZ protein assembles into a structure known as ‘Z-ring’ at midcell for bacterial cell division. Here, Söderström et al. show that Z-ring assembly and dynamics in E. coli cells with unnatural shapes, such as squares and hearts, are generally similar to those observed in cells with normal shape.
- Bill Söderström
- , Alexander Badrutdinov
- & Ulf Skoglund
-
Article
| Open Access A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
Interfering RNA have a range of therapeutic and research based applications, issues with delivery have made systems that make siRNA in situ of interest. Here, the author report on the creation of a DNA hydrogel with improved stability and transcription efficiency over plasmid DNA.
- Jaejung Song
- , Minhyuk Lee
- & Nokyoung Park
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction
Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction
Enzymes of the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP) family reduce Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions to facilitate metal-ion uptake by mammalian cells. Here, authors employ single-particle cryo-EM to gain insights into the molecular principles of iron reduction by human STEAP4 .
- Wout Oosterheert
- , Laura S. van Bezouwen
- & Piet Gros
-
Article
| Open Access The architecture of EGFR’s basal complexes reveals autoinhibition mechanisms in dimers and oligomers
The architecture of EGFR’s basal complexes reveals autoinhibition mechanisms in dimers and oligomers
To prevent ligand-independent dimerisation the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is autoinhibited by an extracellular dimer interaction. Here, the authors use several imaging technologies and simulations to provide structural insights on the inactive species and on how intracellular mutations circumvent the autoinhibition of the basal state.
- Laura C. Zanetti-Domingues
- , Dimitrios Korovesis
- & Marisa L. Martin-Fernandez
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of MHC class I-like MILL2 reveals heparan-sulfate binding and interdomain flexibility
Structure of MHC class I-like MILL2 reveals heparan-sulfate binding and interdomain flexibility
The MILL (MHC-I-like located near the leukocyte receptor complex) family is a group of related nonclassical MHC-I molecules. Here the authors present the crystal structure of MILL2, which reveals an unusual interdomain flexibility, and show that MILL2 binds heparan sulfate on the surface of fibroblasts through a basic patch.
- Mizuho Kajikawa
- , Toyoyuki Ose
- & Katsumi Maenaka
-
Article
| Open Access Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
The decision when to stop an intervention is a critical component of parasite elimination programmes, but reliance on surveillance data alone can be inaccurate. Here, Michael et al. combine parasite transmission model predictions with disease survey data to more reliably determine when interventions can be stopped.
- Edwin Michael
- , Morgan E. Smith
- & Frank O. Richards
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian cancer screening
Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian cancer screening
Screening methods for early detection of ovarian cancer is technically difficult. Here, the authors investigated circulating microRNA in human blood serum and developed a model using 10 microRNAs to discern between ovarian cancer and being ovarian tumors, solid tumors, and non-cancer patients.
- Akira Yokoi
- , Juntaro Matsuzaki
- & Takahiro Ochiya
-
Article
| Open Access Caenorhabditis elegans sperm carry a histone-based epigenetic memory of both spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Caenorhabditis elegans sperm carry a histone-based epigenetic memory of both spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Paternal contributions to epigenetic inheritance via nucleosomes are poorly understood, as sperm in many organisms replace the majority of nucleosomes with protamines. Here the authors provide evidence that Caenorhabditis elegans sperm retain histone packaging of the genome and provide a histone-based epigenetic memory that is important for germ cell development in offspring.
- Tomoko M. Tabuchi
- , Andreas Rechtsteiner
- & Susan Strome
-
Article
| Open Access DRUG-seq for miniaturized high-throughput transcriptome profiling in drug discovery
DRUG-seq for miniaturized high-throughput transcriptome profiling in drug discovery
RNA-seq is a powerful tool to investigate how drugs affect the transcriptome but library construction can be costly. Here the authors introduce DRUG-seq, an automated platform for high-throughput transcriptome profiling.
- Chaoyang Ye
- , Daniel J. Ho
- & Ajamete Kaykas
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning and structural analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pan-genome identifies genetic signatures of antibiotic resistance
Machine learning and structural analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pan-genome identifies genetic signatures of antibiotic resistance
Mycobacterium tuberculosis exhibits complex evolution of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Here, the authors perform machine learning and structural analysis to identify signatures of AMR evolution to 13 antibiotics.
- Erol S. Kavvas
- , Edward Catoiu
- & Bernhard O. Palsson
-
Article
| Open Access Lin−CCR2+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells overcome resistance to PD-1 blockade
Lin−CCR2+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells overcome resistance to PD-1 blockade
Brain tumors are difficult to treat using existing immunotherapeutic strategies. Here, the authors show that in brain tumors resistant to PD-1 blockade, HSCs expressing CCR2+ can reverse treatment resistance and sensitizes mice to immunotherapy.
- Catherine T. Flores
- , Tyler J. Wildes
- & Duane A. Mitchell
-
Article
| Open Access Recruitment of the mitotic exit network to yeast centrosomes couples septin displacement to actomyosin constriction
Recruitment of the mitotic exit network to yeast centrosomes couples septin displacement to actomyosin constriction
The Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) promotes mitotic exit and cytokinesis but if and how MEN independently controls these two processes is unclear. Here, the authors report that MEN displaces septins from the cell division site to promote actomyosin ring constriction, independently of MEN control of mitotic exit.
- Davide Tamborrini
- , Maria Angeles Juanes
- & Simonetta Piatti
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding the intensity of sensory input by two glutamate receptors in one C. elegans interneuron
Decoding the intensity of sensory input by two glutamate receptors in one C. elegans interneuron
Little is known about how stimuli of different intensities result in different behavioral outcomes in C. elegans. In this study, the authors demonstrate how distinct signal patterns, involving different glutamate receptors, in a single interneuron AIB can encode differential behavioral outputs depending on the stimulus intensity
- Wenjuan Zou
- , Jiajun Fu
- & Tao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for mitochondria-targeted radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy
Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for mitochondria-targeted radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy
Photosensitizers delivered to mitochondria of cancer cells can enhance photodynamic therapy. Here, the authors report mitochondria-targeted radiation therapy and radiodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer models with a cationic nanoscale metal-organic framework to overcome shallow light penetration of Ru-based photosensitizers.
- Kaiyuan Ni
- , Guangxu Lan
- & Wenbin Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Rare truncating variants in the sarcomeric protein titin associate with familial and early-onset atrial fibrillation
Rare truncating variants in the sarcomeric protein titin associate with familial and early-onset atrial fibrillation
Common genetic variants in structural proteins contribute to risk of atrial fibrillation (AF). Here, using whole-exome sequencing, the authors identify rare truncating variants in TTN that associate with familial and early-onset AF and show defects in cardiac sarcomere assembly in ttn.2-mutant zebrafish.
- Gustav Ahlberg
- , Lena Refsgaard
- & Morten S. Olesen
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing the transitions from pluripotency to germ cell fate with CRISPR screening
Tracing the transitions from pluripotency to germ cell fate with CRISPR screening
Primordial Germ Cell-Like Cells (PGCLCs) are an in vitro model for primordial germ cell development. Here, the authors couple a novel compound reporter with CRISPR screening to identify key genes for exit from pluripotency and acquisition of PGCLC fate; specifically identifying Nr5a2 and Zfp296.
- Jamie A. Hackett
- , Yun Huang
- & M. Azim Surani
-
Article
| Open Access Dopamine-dependent prefrontal reactivations explain long-term benefit of fear extinction
Dopamine-dependent prefrontal reactivations explain long-term benefit of fear extinction
The success of extinction learning is not predictive of long-term retrieval of an extinction memory. Using fMRI to study consolidation of fear extinction in human subjects, the authors show that reactivation in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex during memory retrieval predicts extinction memory retrieval, and that increasing dopaminergic signaling increases the number of these activations.
- A. M. V. Gerlicher
- , O. Tüscher
- & R. Kalisch
-
Article
| Open Access Haploinsufficiency of autism spectrum disorder candidate gene NUAK1 impairs cortical development and behavior in mice
Haploinsufficiency of autism spectrum disorder candidate gene NUAK1 impairs cortical development and behavior in mice
Nuak1 is an autism spectrum disorder candidate gene. Here the authors report behavioral and cortical development in mice heterozygous for Nuak1, suggesting loss of function mutations in one copy of Nuak1 may contribute to neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Virginie Courchet
- , Amanda J. Roberts
- & Julien Courchet
-
Article
| Open Access PWWP2A binds distinct chromatin moieties and interacts with an MTA1-specific core NuRD complex
PWWP2A binds distinct chromatin moieties and interacts with an MTA1-specific core NuRD complex
PWWP2A is a chromatin-binding transcriptional regulator that mediates mitosis-progression. Here, the authors provide evidence that PWWP2A directly interacts with H2A.Z nucleosomes, DNA and H3K36me3, binds to an MTA1-specific subcomplex of the NuRD complex (M1HR) and promotes changes to histone acetylation.
- Stephanie Link
- , Ramona M. M. Spitzer
- & Sandra B. Hake
-
Article
| Open Access Action sharpens sensory representations of expected outcomes
Action sharpens sensory representations of expected outcomes
Our brains predict the likely sensory consequences of actions we take; one theory is that these sensory responses are suppressed, but another theory is that they are sharpened. Here, the authors show using fMRI evidence consistent with the sharpening account for sensory consequences of hand movements.
- Daniel Yon
- , Sam J. Gilbert
- & Clare Press
-
Article
| Open Access An intrinsic association between olfactory identification and spatial memory in humans
An intrinsic association between olfactory identification and spatial memory in humans
Olfaction, the sense of smell, may have originally evolved to aid navigation in space, but there is no direct evidence of a link between olfaction and navigation in humans. Here the authors show that olfaction and spatial memory abilities are correlated and rely on similar brain regions in humans.
- Louisa Dahmani
- , Raihaan M. Patel
- & Véronique D. Bohbot
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-stage bioengineering of a layered oesophagus with in vitro expanded muscle and epithelial adult progenitors
Multi-stage bioengineering of a layered oesophagus with in vitro expanded muscle and epithelial adult progenitors
Combining decellularised scaffolds with patient-derived cells holds promise for bioengineering of functional tissues. Here the authors develop a two-stage approach to engineer an oesophageal graft that retains the structural organisation of native oesophagus.
- Luca Urbani
- , Carlotta Camilli
- & Paolo De Coppi
-
Article
| Open Access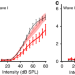 Hidden hearing loss selectively impairs neural adaptation to loud sound environments
Hidden hearing loss selectively impairs neural adaptation to loud sound environments
Hidden hearing loss (HHL) arises through subtle damage to the synapses of hair cells in the inner ear before audiograms reveal hearing threshold shifts. Here, the authors report that HHL in a mouse model disrupts the neural encoding of loud sound environments in the central auditory system.
- Warren Michael Henry Bakay
- , Lucy Anne Anderson
- & Roland Schaette
-
Article
| Open Access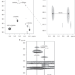 Structural basis for arginine glycosylation of host substrates by bacterial effector proteins
Structural basis for arginine glycosylation of host substrates by bacterial effector proteins
The type III secretion system effectors NleB and SseK are glycosyltransferases (GT) that specifically glycosylate arginine residues. Here the authors provide insights into their mechanism by combining X-ray crystallography, NMR, enzyme kinetics measurements, molecular dynamics simulations and in vivo experiments and show that SseK/NleB enzymes are retaining GTs.
- Jun Bae Park
- , Young Hun Kim
- & Hyun-Soo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access MicroRNA-27a controls the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating calcium-associated autophagy
MicroRNA-27a controls the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating calcium-associated autophagy
How Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) escapes autophagy-mediated clearance is poorly understood. Here, Liu et al. show that Mtb-induced MicroRNA-27a targets the ER-associated calcium transporter CACNA2D3, leading to suppression of antimicrobial autophagy and to enhanced intracellular survival of Mtb.
- Feng Liu
- , Jianxia Chen
- & Baoxue Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Phenome-wide association studies across large population cohorts support drug target validation
Phenome-wide association studies across large population cohorts support drug target validation
Testing the association between genetic variants and a range of phenotypes can assist drug development. Here, in a phenome-wide association study in up to 697,815 individuals, Diogo et al. identify genotype–phenotype associations predicting efficacy, alternative indications or adverse drug effects.
- Dorothée Diogo
- , Chao Tian
- & Heiko Runz
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of Nigerian breast cancer reveals prevalent homologous recombination deficiency and aggressive molecular features
Characterization of Nigerian breast cancer reveals prevalent homologous recombination deficiency and aggressive molecular features
Research on racial and ethnic influence on breast cancer mortality is stymied by a lack of genomic studies in diverse populations. Here, the authors genomically interrogate 194 Nigerian breast cancers, unveiling molecular features that could explain the high mortality rate from breast cancer in an indigenous African population.
- Jason J. Pitt
- , Markus Riester
- & Jordi Barretina
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 The role of MHC supertypes in promoting trans-species polymorphism remains an open question
The role of MHC supertypes in promoting trans-species polymorphism remains an open question