Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread extracellular electron transfer pathways for charging microbial cytochrome OmcS nanowires via periplasmic cytochromes PpcABCDE
Widespread extracellular electron transfer pathways for charging microbial cytochrome OmcS nanowires via periplasmic cytochromes PpcABCDE
How do cells put electrons to rest? Using a minimal pathway to get rid of excess metabolic electrons, diverse environmentally important microbes overcome large spatial, kinetic, and thermodynamic barriers in order to survive in extreme anoxic conditions.
- Pilar C. Portela
- , Catharine C. Shipps
- & Nikhil S. Malvankar
-
Article
| Open Access A natural biogenic nanozyme for scavenging superoxide radicals
A natural biogenic nanozyme for scavenging superoxide radicals
The inorganic minerals are believed to exert a critical catalytic role in the prebiotic time, but biominerals (e.g., bones) in modern living organisms are known mainly for their physical property-related functions. Here the authors identify natural ferritin iron core as a superoxide dismutase-like nanozyme exhibiting species-related activity and elucidate its specific catalytic mechanism.
- Long Ma
- , Jia-Jia Zheng
- & Kelong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking the mysterious polytypic features within vaterite CaCO3
Unlocking the mysterious polytypic features within vaterite CaCO3
The structure of vaterite has been debated for a century. Combining systematic TEM characterisations, crystallographic analysis, and machine learning aided molecular dynamics simulations, the authors unlock the structural mystery in vaterite.
- Xingyuan San
- , Junwei Hu
- & Xiaobing Hu
-
Article
| Open Access TerC proteins function during protein secretion to metalate exoenzymes
TerC proteins function during protein secretion to metalate exoenzymes
TerC family membrane proteins associate with the general protein secretion complex to facilitate the co-translocational loading of Mn(II) into nascent metalloenzymes. Here, the authors show that Bacillus subtilis mutants lacking TerC proteins are defective in production of the membrane-embedded lipoteichoic acid synthase and secreted proteases.
- Bixi He
- , Ankita J. Sachla
- & John D. Helmann
-
Article
| Open Access Custom tuning of Rieske oxygenase reactivity
Custom tuning of Rieske oxygenase reactivity
Rieske oxygenase chemistry is important for biochemical pathways, but it remains elusive how a common protein scaffold can be predictively tuned to catalyze divergent reactions. Here, the authors report a strategy that can rationally tune TsaM, a Rieske monooxygenase to catalyze dioxygenation and sequential monooxygenation reactions, and customize the reactivity of other Rieske oxygenases.
- Jiayi Tian
- , Jianxin Liu
- & Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
-
Article
| Open Access Class III hybrid cluster protein homodimeric architecture shows evolutionary relationship with Ni, Fe-carbon monoxide dehydrogenases
Class III hybrid cluster protein homodimeric architecture shows evolutionary relationship with Ni, Fe-carbon monoxide dehydrogenases
Here, the authors present an X-ray crystal structure of a class III hybrid cluster protein (HCP), structurally similar to Ni, Fe-carbon monoxide dehydrogenases (CODHs), enabling conclusions to be drawn regarding the structural evolution of HCP/CODH superfamily.
- Takashi Fujishiro
- & Kyosei Takaoka
-
Article
| Open Access Metallo-sideromycin as a dual functional complex for combating antimicrobial resistance
Metallo-sideromycin as a dual functional complex for combating antimicrobial resistance
Here, the authors utilise cefiderocol, a sideromycin, in complex with colloidal bismuth citrate, to demonstrate antimicrobial efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vivo.
- Chenyuan Wang
- , Yushan Xia
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture of the Heme-translocating CcmABCD/E complex required for Cytochrome c maturation
Architecture of the Heme-translocating CcmABCD/E complex required for Cytochrome c maturation
The covalent linkage of hemes to cytochromes c requires a maturation machinery. Here, the authors provide mechanistic insights into how the heme translocase complex CcmABCD flops a heme group, driven by ATP hydrolysis, and delivers it to the chaperone CcmE.
- Lorena Ilcu
- , Lukas Denkhaus
- & Oliver Einsle
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-mediated DNA strand displacement and molecular device operations based on base-pair switching of 5-hydroxyuracil nucleobases
Metal-mediated DNA strand displacement and molecular device operations based on base-pair switching of 5-hydroxyuracil nucleobases
The development of dynamic DNA nanodevices, whose configuration and function are regulated by specific chemical inputs, represents a rapidly growing area in molecular science. Herein, the authors report the concept of metal-mediated base-pair switching to induce inter- and intramolecular DNA strand displacement in a metal-responsive manner.
- Yusuke Takezawa
- , Keita Mori
- & Mitsuhiko Shionoya
-
Article
| Open Access Designed Rubredoxin miniature in a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light
Designed Rubredoxin miniature in a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light
Living organisms regulate their energy demand by managing electron trafficking in complex transport chains. Here, the authors pioneer a fully artificial electron chain triggered by visible light using designed proteins, unlocking possibilities in bioengineering.
- Marco Chino
- , Luigi Franklin Di Costanzo
- & Vincenzo Pavone
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial ATP synthase as a direct molecular target of chromium(III) to ameliorate hyperglycaemia stress
Mitochondrial ATP synthase as a direct molecular target of chromium(III) to ameliorate hyperglycaemia stress
Despite common use as a diabetes mellitus supplement, chromium(III)’s pharmacological effects remain unknown. We identified the Cr(III)-proteome in cells with a metalloproteomic approach and uncovered ATP synthase as a vital target to relieve hyperglycaemia stress.
- Haibo Wang
- , Ligang Hu
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structural consequences of turnover-induced homocitrate loss in nitrogenase
Structural consequences of turnover-induced homocitrate loss in nitrogenase
Biological nitrogen fixation is achieved by nitrogenase, but the mechanism remains enigmatic. Here, the authors report high resolution single particle cryoEM structures of homocitrate-compromised MoFe-proteins and unveil a new binding partner.
- Rebeccah A. Warmack
- , Ailiena O. Maggiolo
- & Douglas C. Rees
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of paramagnetic states in an organometallic nickel hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst
Characterization of paramagnetic states in an organometallic nickel hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst
The characterization of nickel (Ni)‐centred paramagnetic states relevant to [NiFe] hydrogenases is rare in mononuclear Ni hydrogen evolution catalysts. Here, the authors report the spectroscopic and synthetic characterization of NiI and NiIII states in an organometallic Ni hydrogen evolution catalyst.
- Sagnik Chakrabarti
- , Soumalya Sinha
- & Liviu M. Mirica
-
Article
| Open Access Regioselective protein oxidative cleavage enabled by enzyme-like recognition of an inorganic metal oxo cluster ligand
Regioselective protein oxidative cleavage enabled by enzyme-like recognition of an inorganic metal oxo cluster ligand
Metal-catalysed oxidation of proteins varies in selectivity and depends on the surface residues to direct the reaction. Here, the authors use polyoxometalate clusters as inorganic ligands for Cu ions, enabling the regioselective oxidative cleavage of a protein via reactive oxygen species in the vicinity of its binding sites.
- Shorok A. M. Abdelhameed
- , Francisco de Azambuja
- & Tatjana N. Parac-Vogt
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-sulfur clusters are involved in post-translational arginylation
Iron-sulfur clusters are involved in post-translational arginylation
The enzyme ATE1 catalyzes eukaryotic post-translation arginylation, a key protein modification necessary for cellular homeostasis. Here, the authors show that ATE1s are previously unrealized iron-sulfur proteins that use this oxygen-sensitive inorganic cofactor to control cellular arginylation
- Verna Van
- , Janae B. Brown
- & Aaron T. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the elevator-type transport mechanism of a bacterial ZIP metal transporter
Structural insights into the elevator-type transport mechanism of a bacterial ZIP metal transporter
The ZIP family (SLC39A) is involved in transition metal homeostasis. Here, authors use integrated approaches to conclude that the ZIP from Bordetella bronchiseptica (BbZIP) utilizes the elevator-type transport mechanism to achieve alternating access.
- Yao Zhang
- , Yuhan Jiang
- & Jian Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation disrupts long-distance electron transport in cytochrome c
Phosphorylation disrupts long-distance electron transport in cytochrome c
Electron transfer between mitochondrial cytochrome c and subunit of cytochrome bc1 can proceed at long distance. Here the authors investigate further the mechanism and show phosphorylation regulation of the interactions between the protein partners in the electron transport chain.
- Alexandre M. J. Gomila
- , Gonzalo Pérez-Mejías
- & Anna Lagunas
-
Article
| Open Access Design and directed evolution of noncanonical β-stereoselective metalloglycosidases
Design and directed evolution of noncanonical β-stereoselective metalloglycosidases
Metallohydrolases are ubiquitous enzymes. Here the authors show the design and biochemical characterisation of metalloglycosidase by constructing a hydrolytically active Zn-binding site within a barrel-shaped outer membrane protein OmpF.
- Woo Jae Jeong
- & Woon Ju Song
-
Article
| Open Access Ru(II) photocages enable precise control over enzyme activity with red light
Ru(II) photocages enable precise control over enzyme activity with red light
The cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1B1 is overexpressed in a variety of tumors, and is correlated with poor treatment outcomes; thus, it is desirable to develop CYP1B1 inhibitors to restore chemotherapy efficacy. Here the authors describe the creation of light-triggered CYP1B1 inhibitors as “prodrugs”, and achieve >6000-fold improvement in potency upon activation with low-energy (660 nm) light.
- Dmytro Havrylyuk
- , Austin C. Hachey
- & Edith C. Glazer
-
Article
| Open Access Defect engineering of layered double hydroxide nanosheets as inorganic photosensitizers for NIR-III photodynamic cancer therapy
Defect engineering of layered double hydroxide nanosheets as inorganic photosensitizers for NIR-III photodynamic cancer therapy
Defect engineering of 2 dimensional layered double hydroxide sheets improves their photocatalytic activity. Here, the authors etch sheets in acid and show that the etched sheets generate substantially more reactive oxygen species that untreated sheets and the treated sheets can be used to kill cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Weicheng Shen
- , Tingting Hu
- & Chaoliang Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Molecules offer enormous capacity for information storage. Here, the authors show that information can be encoded into molecules with sequences of paramagnetic lanthanide ions, and decoded using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Jan Kretschmer
- , Tomáš David
- & Miloslav Polasek
-
Article
| Open Access An osmium-peroxo complex for photoactive therapy of hypoxic tumors
An osmium-peroxo complex for photoactive therapy of hypoxic tumors
Photodynamic therapy has been a promising technique for the treatment of tumours. In this manuscript, the authors report on the photoactivation of the osmium peroxo complex and its potential use for chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy under blue light irradiation against tumours in their hypoxic environment.
- Nong Lu
- , Zhihong Deng
- & Pingyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Modifying electron injection kinetics for selective photoreduction of nitroarenes into cyclic and asymmetric azo compounds
Modifying electron injection kinetics for selective photoreduction of nitroarenes into cyclic and asymmetric azo compounds
Modifying the reactivity of substrates by encapsulation is essential for microenvironment catalysts. Herein, the authors report an alternative strategy that modifies the entry behaviour of reactants and substrates to control the electron injection kinetics, thus affecting the selectivity of nitroarene photoreductions.
- Yang Yang
- , Xu Jing
- & Chunying Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-responsive regulation of enzyme catalysis using genetically encoded chemical switches
Metal-responsive regulation of enzyme catalysis using genetically encoded chemical switches
Dynamic control over protein function is a central challenge in synthetic biology. Here the authors present an integrated computational and experimental workflow for engineering reversible protein switches; metal-chelating unnatural amino acids genetically encoded into two conformationally dynamic enzymes to yield robust switches.
- Yasmine S. Zubi
- , Kosuke Seki
- & Jared C. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of a μ-1,2-hydroperoxo FeIIIFeIII and a μ-1,2-peroxo FeIVFeIII Complex
Generation of a μ-1,2-hydroperoxo FeIIIFeIII and a μ-1,2-peroxo FeIVFeIII Complex
Iron coordination complexes can be used to gain insight on biologically relevant iron-oxygen compounds generated in iron metalloenzymes. Here, the authors characterise a μ-1,2-hydroperoxo FeIIIFeIII and a μ-1,2-peroxo FeIVFeIII, and study their reactivity in C-H activation.
- Stephan Walleck
- , Thomas Philipp Zimmermann
- & Thorsten Glaser
-
Article
| Open Access The chemistry of branched condensed phosphates
The chemistry of branched condensed phosphates
The “anti-branching rule”, introduced in 1950, excludes branched polyphosphates from biological relevance due to their supposedly rapid hydrolysis. Here, the authors synthesize monodisperse branched polyphosphates and demonstrate their unexpected stability in water, as well as provide evidence for their competence in phosphorylation.
- Tobias Dürr-Mayer
- , Danye Qiu
- & Henning J. Jessen
-
Article
| Open Access A highly potent ruthenium(II)-sonosensitizer and sonocatalyst for in vivo sonotherapy
A highly potent ruthenium(II)-sonosensitizer and sonocatalyst for in vivo sonotherapy
Sonodynamic therapy has therapeutic promise due to its safety and good tissue penetration, but is currently bottlenecked due to a lack of efficient and safe sonosensitizers. Here the authors show that [Ru(bpy)3]2+ can produce singlet oxygen and sonooxidize NADH in deep tissue, and destroy mouse tumors effectively.
- Chao Liang
- , Jiaen Xie
- & Pingyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biogenesis but the molecular connection between these pathways is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that the heme biosynthesis enzyme ALAD contains an Fe-S cluster, disruption of which reduces ALAD activity and heme production in human cells.
- Gang Liu
- , Debangsu Sil
- & Tracey Ann Rouault
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells
A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells
Dynamic labeling and tracking of organelle–organelle contacts is essential to understand the formation and function of these interactions. Here the authors present a small molecule probe, Coupa, that labels mitochondria and lysosomes with blue and red fluorescence, respectively.
- Qixin Chen
- , Hongbao Fang
- & Jiajie Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the respiratory MBS complex reveals iron-sulfur cluster catalyzed sulfane sulfur reduction in ancient life
Structure of the respiratory MBS complex reveals iron-sulfur cluster catalyzed sulfane sulfur reduction in ancient life
The sulfur-reducing enzyme MBS and the hydrogen-gas evolving MBH are the evolutionary link between the ancestor Mrp antiporter and the mitochondrial respiratory complex I. Here, the authors characterise MBS from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus, solve its cryo-EM structure and discuss the structural evolution from Mrp to MBH and MBS and to the modern-day complex I.
- Hongjun Yu
- , Dominik K. Haja
- & Michael W. W. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed ruthenium complexes for 1- and 2-photon photodynamic therapy
Rationally designed ruthenium complexes for 1- and 2-photon photodynamic therapy
Photosensitizers that are stable in biological conditions with absorption in the biological spectral window are needed for photodynamic therapy. Here, the authors report on the development of a Ruthenium complex for 1 and 2-photon therapy to address these issues and demonstrate application in vivo.
- Johannes Karges
- , Shi Kuang
- & Gilles Gasser
-
Article
| Open Access An evolutionary path to altered cofactor specificity in a metalloenzyme
An evolutionary path to altered cofactor specificity in a metalloenzyme
Many metalloenzymes are highly specific for their cognate metal ion but the molecular principles underlying this specificity often remain unclear. Here, the authors characterize the structural and biochemical basis for the different metal specificity of two evolutionarily related superoxide dismutases.
- Anna Barwinska-Sendra
- , Yuritzi M. Garcia
- & Kevin J. Waldron
-
Article
| Open Access Identity and function of an essential nitrogen ligand of the nitrogenase cofactor biosynthesis protein NifB
Identity and function of an essential nitrogen ligand of the nitrogenase cofactor biosynthesis protein NifB
NifB is a radical SAM enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the Mo-nitrogenase cofactor, which is responsible for the ambient conversion of N2 to NH3. Here, the authors identify and uncover the function of a His43 residue as an essential nitrogen ligand of NifB in cofactor biosynthesis.
- Lee A. Rettberg
- , Jarett Wilcoxen
- & Markus W. Ribbe
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing electron transfer reactions and catalysis in multicopper oxidases with operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Assessing electron transfer reactions and catalysis in multicopper oxidases with operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Understanding enzyme active sites can elucidate fundamental enzymatic reaction pathways and inform designs for synthetic catalysts. Here, authors employ operando X-ray absorption spectroelectrochemistry to assess copper ions in bilirubin oxidase during oxygen reduction electrocatalysis.
- Lucyano J. A. Macedo
- , Ayaz Hassan
- & Frank N. Crespilho
-
Article
| Open Access Metal ions and sugar puckering balance single-molecule kinetic heterogeneity in RNA and DNA tertiary contacts
Metal ions and sugar puckering balance single-molecule kinetic heterogeneity in RNA and DNA tertiary contacts
Mobile group II introns function as ribozymes to splice and reinsert themselves into DNA, thereby colonizing new genomic regions. Here the authors use single-molecule FRET and molecular dynamics simulations to reveal a structural link between metal ion induced kinetic heterogeneity and the sugar puckers at the exon-intron binding interface.
- Fabio D. Steffen
- , Mokrane Khier
- & Roland K. O. Sigel
-
Article
| Open Access Heme and hemoglobin utilization by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Heme and hemoglobin utilization by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Iron is essential for growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, but most of the iron in the human body is stored in heme within hemoglobin. Here, Mitra et al. identify two heme uptake mechanisms in M. tuberculosis, one dependent on the inner-membrane Dpp importer and the other dependent on host albumin.
- Avishek Mitra
- , Ying-Hui Ko
- & Michael Niederweis
-
Article
| Open Access Protein determinants of dissemination and host specificity of metallo-β-lactamases
Protein determinants of dissemination and host specificity of metallo-β-lactamases
Metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) confer resistance to carbapenem antibiotics. Here, López et al. show that the host range of MBLs depends on the efficiency of MBL signal peptide processing and secretion into outer membrane vesicles, which affects bacterial fitness.
- Carolina López
- , Juan A. Ayala
- & Alejandro J. Vila
-
Article
| Open Access Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
The mechanism of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors develop a physiologically relevant in vitro model of Fe-S cluster assembly, allowing them to elucidate the sequence of Fe-S cluster synthesis along with the respective roles of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin.
- Sylvain Gervason
- , Djabir Larkem
- & Benoit D’Autréaux
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization
Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization
Bone regeneration is of interest for treating a wide range of medical conditions. Here, the authors report on bioinspired matrix vesicles loaded with black phosphorus nanosheets and cell-specific aptamers for bone regeneration and demonstrate bone defect repair in vivo.
- Yingqian Wang
- , Xiaoxia Hu
- & Quan Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access A 3,2-Hydroxypyridinone-based Decorporation Agent that Removes Uranium from Bones In Vivo
A 3,2-Hydroxypyridinone-based Decorporation Agent that Removes Uranium from Bones In Vivo
In vivo decorporation of U(VI) from bones is an unsolved challenge because of the formation of stable uranium phosphate complexes. Here, the authors develop a hydroxypyridonone-based ligand with strong uranium complexation and low cytotoxicity. They find this ligand effectively removes uranium from kidney and bones in mice, and is suitable for oral administration.
- Xiaomei Wang
- , Xing Dai
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Native top-down mass spectrometry provides insights into the copper centers of membrane-bound methane monooxygenase
Native top-down mass spectrometry provides insights into the copper centers of membrane-bound methane monooxygenase
The activity of the membrane-bound enzyme pMMO depends on copper but the location of the copper centers is still under debate. Here, the authors reconstitute pMMO in nanodiscs and use native top-down MS to localize its copper centers, providing insights into which sites are essential for activity.
- Soo Y. Ro
- , Luis F. Schachner
- & Amy C. Rosenzweig
-
Article
| Open Access Proton mediated spin state transition of cobalt heme analogs
Proton mediated spin state transition of cobalt heme analogs
Studying the electronic structures and spin transitions of synthetic heme analogs is crucial to advancing our understanding of heme enzyme mechanisms. Here the authors show that a Co(II) porphyrin complex undergoes an unexpected spin state transition upon deprotonation of its axial imidazole ligand.
- Jianping Zhao
- , Qian Peng
- & Jianfeng Li
-
Review Article
| Open Access Ligand design strategies to increase stability of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents
Ligand design strategies to increase stability of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents
Gadolinium(III) complexes are strong enhancers of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) signals, thus are widely used as contrast agents despite their potential toxicity. Here, the authors review ligand design approaches aimed at improving the stability of Gd(III)-based MRI contrast agents.
- Thomas J. Clough
- , Lijun Jiang
- & Nicholas J. Long
-
Article
| Open Access A widely distributed diheme enzyme from Burkholderia that displays an atypically stable bis-Fe(IV) state
A widely distributed diheme enzyme from Burkholderia that displays an atypically stable bis-Fe(IV) state
The diheme enzyme MauG forms a bis-Fe(IV) state. Here the authors identify and determine the structure of BthA, a diheme peroxidase conserved in all Burkholderia and show that BthA also forms a bis-Fe(IV) species but mechanistically differs from MauG by combining magnetic resonance, near-IR and Mössbauer spectroscopies and electrochemical methods.
- Kimberly Rizzolo
- , Steven E. Cohen
- & Sean J. Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Characterized cis-FeV(O)(OH) intermediate mimics enzymatic oxidations in the gas phase
Characterized cis-FeV(O)(OH) intermediate mimics enzymatic oxidations in the gas phase
FeV(O)(OH) species have long been thought to play a role in a range of enzymatic oxidations, but their characterization has remained elusive. Here, using gas-phase ion spectroscopy, the authors characterize an FeV(O)(OH) species and find that its reactivity mimics that of Rieske oxygenases.
- Margarida Borrell
- , Erik Andris
- & Miquel Costas
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrathiomolybdate induces dimerization of the metal-binding domain of ATPase and inhibits platination of the protein
Tetrathiomolybdate induces dimerization of the metal-binding domain of ATPase and inhibits platination of the protein
Tetrathiomolybdate (TM) and Cu-ATPases, e.g. Wilson (WLN) protein, affect the efficacy of common anticancer drug cisplatin. Here, the authors show that TM generates a protein dimer with a WLN domain by expelling copper and provide insight into the synergy of TM and cisplatin in cancer chemotherapy.
- Tiantian Fang
- , Wanbiao Chen
- & Yangzhong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Light-controlled switching of the spin state of iron(III)
Light-controlled switching of the spin state of iron(III)
Controlled switching of the spin state of transition metal ions is key in many enzymatic reactions, but difficult to replicate in synthetic systems. Here the authors report on an iron(III) porphyrin with a photochromic axial ligand that, in solution, reversibly switches between low-spin and high-spin upon irradiation with two different wavelengths.
- Sreejith Shankar
- , Morten Peters
- & Rainer Herges
-
Article
| Open Access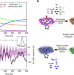 Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Ultrafast carbon monoxide photolysis and heme spin-crossover in myoglobin via nonadiabatic quantum dynamics
Myoglobin bound to carbon monoxide undergoes an ultrafast light-induced reaction, which ends up in a photolyzed carbon monoxide and a spin transition of the iron center. Here, the authors employ quantum wavepacket dynamics to show that photolysis precedes the spin transition, a mechanism dominated by strong electron-nuclear couplings.
- Konstantin Falahati
- , Hiroyuki Tamura
- & Miquel Huix-Rotllant
-
Article
| Open Access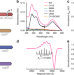 Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
Methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria use the integral membrane, copper-dependent enzymes particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO) and ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) to oxidize methane and ammonia. Here the authors structurally characterize the copper-binding protein PmoD, which contains an unusual CuA site and their genetic analyses strongly support a pMMO and AMO related function of PmoD.
- Oriana S. Fisher
- , Grace E. Kenney
- & Amy C. Rosenzweig

 A hemoprotein with a zinc-mirror heme site ties heme availability to carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria
A hemoprotein with a zinc-mirror heme site ties heme availability to carbon metabolism in cyanobacteria