Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access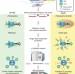 An AP-MS- and BioID-compatible MAC-tag enables comprehensive mapping of protein interactions and subcellular localizations
An AP-MS- and BioID-compatible MAC-tag enables comprehensive mapping of protein interactions and subcellular localizations
AP-MS and BioID provide complementary insights into cellular protein interaction networks. To facilitate their combined use, the authors here present an AP-MS- and BioID-compatible affinity tag, enabling efficient determination of cellular protein locations and interaction distances.
- Xiaonan Liu
- , Kari Salokas
- & Markku Varjosalo
-
Article
| Open Access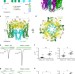 Cryo-EM structure of the polycystic kidney disease-like channel PKD2L1
Cryo-EM structure of the polycystic kidney disease-like channel PKD2L1
Polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1 protein (PKD2L1) is a voltage-dependent calcium-dependent nonselective ion channel involved in sour taste perception and regulation of pH-dependent action potential of spinal cord neurons. Here the authors present the 3.4 Å cryo-EM structure of PKD2L1 in the open state and propose a model for the gating mechanism.
- Qiang Su
- , Feizhuo Hu
- & Tingliang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of binding between the global post-transcriptional regulator CsrA and the T3SS chaperone CesT
Molecular basis of binding between the global post-transcriptional regulator CsrA and the T3SS chaperone CesT
CesT is a type III secretion system chaperone that interacts with the post-transcriptional regulator CsrA, which is important for the modulation of post-attachment signaling in enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Here the authors present the structure of the CsrA/CesT complex and propose a mechanism for CsrA-modulation by CesT.
- Fei Ye
- , Fanli Yang
- & Guangwen Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Schlafen13 reveals a new class of tRNA/rRNA- targeting RNase engaged in translational control
Structure of Schlafen13 reveals a new class of tRNA/rRNA- targeting RNase engaged in translational control
Translation inhibition is a strategy for organisms to overcome various environmental stresses including viral infections. Here the authors show that a tRNA/rRNA-targeting RNase Schlafen13 inhibits protein synthesis by directly digesting cytoplasmic tRNA and rRNA with the ability to restrict viral propagation.
- Jin-Yu Yang
- , Xiang-Yu Deng
- & Song Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical origins of heat capacity changes in enzyme-catalysed reactions
Dynamical origins of heat capacity changes in enzyme-catalysed reactions
Heat capacity changes affect the temperature dependence of enzyme catalysis, with implications for thermoadaptation, however their physical basis is unknown. Here the authors show that heat capacity changes are calculable by simulation, revealing distinct dynamical contributions from regions remote from the active site.
- Marc W. van der Kamp
- , Erica J. Prentice
- & Vickery L. Arcus
-
Article
| Open Access Reactive-site-centric chemoproteomics identifies a distinct class of deubiquitinase enzymes
Reactive-site-centric chemoproteomics identifies a distinct class of deubiquitinase enzymes
Deubiquitinases are proteases that cleave after the C-terminus of ubiquitin to hydrolyze ubiquitin chains and cleave ubiquitin from substrates. Here the authors describe a reactive-site-centric chemoproteomics approach to studying deubiquitinase activity, and expand the repertoire of known deubiquitinases.
- David S. Hewings
- , Johanna Heideker
- & Ingrid E. Wertz
-
Article
| Open Access JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
JMJD5 is a human arginyl C-3 hydroxylase
Jumonji-C domain containing protein 5 (JMJD5) is essential for animal development but its catalytic activity has remained elusive so far. Here the authors show that human JMJD5 is an arginyl-hydroxylase and present the cofactor, substrate and product bound JMJD5 crystal structures.
- Sarah E. Wilkins
- , Md. Saiful Islam
- & Rasheduzzaman Chowdhury
-
Article
| Open Access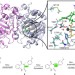 Catalytic mechanism and molecular engineering of quinolone biosynthesis in dioxygenase AsqJ
Catalytic mechanism and molecular engineering of quinolone biosynthesis in dioxygenase AsqJ
The catalytic activity of dioxygenase AsqJ is strictly relying on the methylation of quinolone substrates. Here, the authors apply molecular simulations, X-ray crystallography and in vitro biochemical studies to the engineering of dioxygenase AsqJ with improved catalytic activity for modified non-methylated surrogates.
- Sophie L. Mader
- , Alois Bräuer
- & Ville R. I. Kaila
-
Article
| Open Access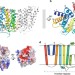 Crystal structure of an intramembranal phosphatase central to bacterial cell-wall peptidoglycan biosynthesis and lipid recycling
Crystal structure of an intramembranal phosphatase central to bacterial cell-wall peptidoglycan biosynthesis and lipid recycling
Undecaprenyl pyrophosphate phosphatase (UppP) recycles the lipid carrier essential for bacterial cell wall synthesis. Here authors present the crystal structure of UppP from E. coli at 2.0 Å resolution, which sheds light on its phosphatase mechanism and indicates a potential flippase role for UppP.
- Sean D. Workman
- , Liam J. Worrall
- & Natalie C. J. Strynadka
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the activated Edc1-Dcp1-Dcp2-Edc3 mRNA decapping complex with substrate analog poised for catalysis
Structure of the activated Edc1-Dcp1-Dcp2-Edc3 mRNA decapping complex with substrate analog poised for catalysis
The decapping enzyme Dcp2 removes the 5′ eukaryotic cap from mRNA transcripts and acts in concert with its essential activator Dcp1 and various coactivators. Here the authors present the structure of the fully-activated mRNA decapping complex, which reveals how Dcp2 recognizes the cap substrate and coactivators Edc1 and Edc3 activate catalysis.
- Jeffrey S. Mugridge
- , Ryan W. Tibble
- & John D. Gross
-
Article
| Open Access The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development
The MerR-like protein BldC binds DNA direct repeats as cooperative multimers to regulate Streptomyces development
BldC regulates the onset of differentiation in Streptomycetes by a yet unknown molecular mechanism. Using a combination of structural, biochemical and in vivo approaches, the authors show that BldC controls the transcription of several developmental regulators and unravel its DNA binding mode.
- Maria A. Schumacher
- , Chris D. den Hengst
- & Mark J. Buttner
-
Article
| Open Access An evolutionary hotspot defines functional differences between CRYPTOCHROMES
An evolutionary hotspot defines functional differences between CRYPTOCHROMES
The molecular mechanisms that define the periodicity or rate of the circadian clock are not well understood. Here the authors use a multidisciplinary approach and identify a mechanism for period regulation that depends on the affinity of the core clock proteins for one another.
- Clark Rosensweig
- , Kimberly A. Reynolds
- & Carla B. Green
-
Article
| Open Access A common mechanism of proteasome impairment by neurodegenerative disease-associated oligomers
A common mechanism of proteasome impairment by neurodegenerative disease-associated oligomers
Disruption of the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) is often associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Here the authors demonstrate the existence of a general mechanism of proteasomal impairment triggered by a specific protein oligomer structure, irrespective of its protein constituent.
- Tiffany A. Thibaudeau
- , Raymond T. Anderson
- & David M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access How RNA transcripts coordinate DNA recombination and repair
How RNA transcripts coordinate DNA recombination and repair
Homologous recombination (HR) typically uses DNA as a donor template to accurately repair DNA breaks. Here, the authors elucidate two mechanisms by which RAD52 uses RNA as a template for HR: one involving RNA-mediated synapsis of a homologous DNA break, and the other involving reverse transcriptase dependent RNA-to-DNA sequence transfer at DNA breaks.
- Shane McDevitt
- , Timur Rusanov
- & Richard T. Pomerantz
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of undecaprenyl-pyrophosphate phosphatase and its role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis
Crystal structure of undecaprenyl-pyrophosphate phosphatase and its role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis
Bacterial cell wall components are assembled in a transmembrane cycle that involves the membrane integral pyrophosphorylase, BacA. Here the authors solve the crystal structure of BacA which shows an interdigitated inverted topology repeat that hints towards a flippase function for BacA.
- Meriem El Ghachi
- , Nicole Howe
- & Martin Caffrey
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of Teneurin adhesion receptors reveal an ancient fold for cell-cell interaction
Structures of Teneurin adhesion receptors reveal an ancient fold for cell-cell interaction
Teneurins are cell-cell adhesion receptors that evolved through horizontal gene transfer in which a bacterial YD-repeat protein fused to a eukaryotic receptor. Here the authors present crystallographic and cryo-EM structures of two Teneurins, revealing an ancient YD-repeat protein super-fold.
- Verity A. Jackson
- , Dimphna H. Meijer
- & Elena Seiradake
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of an agarose metabolic pathway acquired by a human intestinal symbiont
Molecular basis of an agarose metabolic pathway acquired by a human intestinal symbiont
Polysaccharides are the primary structural cell wall and energy storage molecules of seaweed. Here, the authors show how the geographically restricted dietary polysaccharide agarose is selectively utilized by the human intestinal bacterium Bacteroides uniformis, providing insight into how carbohydrate metabolism evolves within the human microbiome.
- Benjamin Pluvinage
- , Julie M. Grondin
- & D. Wade Abbott
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally distinct and selectively phosphorylated GPCR subpopulations co-exist in a single cell
Functionally distinct and selectively phosphorylated GPCR subpopulations co-exist in a single cell
β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR) can be phosphorylated by G protein receptor kinases and second messenger-dependent kinases. Here, the authors demonstrate that these phosphorylation events are specific to functionally distinct and spatially segregated subpopulations of β2AR that co-exist in a single cell.
- Ao Shen
- , Madeline Nieves-Cintron
- & Yang K. Xiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the recognition of LDL-receptor family members by VSV glycoprotein
Structural basis for the recognition of LDL-receptor family members by VSV glycoprotein
Glycoprotein G of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) enables viral entry by binding to the major VSV receptor LDL-R. Here the authors present crystal structures of G in complex with two distinct CR domains of LDL-R, identifying structural determinants for VSV infectivity in mammalian and insect cells.
- Jovan Nikolic
- , Laura Belot
- & Aurélie A. Albertini
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform
Efficient molecular evolution to generate enantioselective enzymes using a dual-channel microfluidic droplet screening platform
Optimizing an enzyme usually requires testing thousands of variants, thus consuming large amounts of material and time. Here, the authors present a method that allows for measuring two different activities of the same enzyme simultaneously instead of doing two consecutive rounds of screening.
- Fuqiang Ma
- , Meng Ting Chung
- & Guang-Yu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access TRiC controls transcription resumption after UV damage by regulating Cockayne syndrome protein A
TRiC controls transcription resumption after UV damage by regulating Cockayne syndrome protein A
An integrated network of chaperones and protein degradation machineries called the proteostasis network (PN) is required to maintain protein homeostasis. Here the authors show that one of the components of the PN, the chaperonin TRiC, interacts with the core transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair protein CSA to ensure its assembly into the CRLCSA complex.
- Alex Pines
- , Madelon Dijk
- & Haico van Attikum
-
Article
| Open Access Insc:LGN tetramers promote asymmetric divisions of mammary stem cells
Insc:LGN tetramers promote asymmetric divisions of mammary stem cells
During asymmetric divisions fate determinants and niche contacts segregate unequally between daughter cells, but the mechanism is unclear. Here the authors show that Insc:LGN tetramers promote assembly of Par3-Insc-LGN-GαiGDP complexes and asymmetric fate specification independently of microtubule motors.
- Simone Culurgioni
- , Sara Mari
- & Marina Mapelli
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of single amino acid differences in uniformly charged homopolymeric peptides with aerolysin nanopore
Identification of single amino acid differences in uniformly charged homopolymeric peptides with aerolysin nanopore
Existing methods used for peptide analysis suffer from low sensitivity and specificity. Here the authors demonstrate the nanopore-based size-discrimination and purity analysis of short homopolymeric peptides with a single amino acid resolution.
- Fabien Piguet
- , Hadjer Ouldali
- & Abdelghani Oukhaled
-
Article
| Open Access Life times of metastable states guide regulatory signaling in transcriptional riboswitches
Life times of metastable states guide regulatory signaling in transcriptional riboswitches
Riboswitches are RNA-based regulatory elements, which regulate downstream gene expression by binding of small molecular weight ligands. Here the authors demonstrate the molecular mechanism of a transcriptional riboswitch that integrates changes in transcription rates, metabolite concentration, and kinetic on- and off-rates of ligand binding.
- Christina Helmling
- , Dean-Paulos Klötzner
- & Harald Schwalbe
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient nitrate switches the ammonium consumption pathway in the euphotic ocean
Ambient nitrate switches the ammonium consumption pathway in the euphotic ocean
The underlying regulatory mechanisms of phytoplankton assimilation and microbial oxidation of ammonium in the surface ocean are unclear. Here, using isotope labeling experiments, the authors show that ambient nitrate is a key variable bifurcating ammonium flow through assimilation or oxidation.
- Xianhui Sean Wan
- , Hua-Xia Sheng
- & Shuh-Ji Kao
-
Article
| Open Access CryoEM structure of the human SLC4A4 sodium-coupled acid-base transporter NBCe1
CryoEM structure of the human SLC4A4 sodium-coupled acid-base transporter NBCe1
Na+-coupled acid-base membrane transport proteins regulate blood pressure, ion homeostasis and acid-base chemistry. Here the authors present the 3.9 Å resolution cryoEM structure of the sodium-bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 and characterize its ion coordination site and ion accessibility pathway with mutagenesis experiments.
- Kevin W. Huynh
- , Jiansen Jiang
- & Ira Kurtz
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanism for CO regulation of ion channels
A mechanism for CO regulation of ion channels
Despite being highly toxic, carbon monoxide (CO) is also essential as an intracellular signalling molecule, but CO-dependent signalling is poorly understood. Here, authors employ spectroscopic and electrophysiology methods and find that CO activates KATP channels via SUR2A, a heme-regulated receptor.
- Sofia M. Kapetanaki
- , Mark J. Burton
- & Emma Raven
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved roles of C. elegans and human MANFs in sulfatide binding and cytoprotection
Conserved roles of C. elegans and human MANFs in sulfatide binding and cytoprotection
MANF is a secreted ER stress-inducible protein that protects neurons, pancreatic β cells and cardiomyocytes from cell death under oxidative stress, hypoxic or ischemic conditions. Here the authors show that MANF confers cytoprotection through direct binding to sulfatide followed by cellular uptake in both C. elegans and mammalian cells.
- Meirong Bai
- , Roman Vozdek
- & Dengke K. Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid measurement of inhibitor binding kinetics by isothermal titration calorimetry
Rapid measurement of inhibitor binding kinetics by isothermal titration calorimetry
There is growing evidence that the kinetics of interactions between inhibitors and their targets can strongly impact therapeutic efficacy. Here the authors describe an isothermal titration calorimetry-based method that can rapidly quantify inhibition kinetics and measure sub-nM binding affinities.
- Justin M. Di Trani
- , Stephane De Cesco
- & Anthony K. Mittermaier
-
Article
| Open Access Two distinct domains contribute to the substrate acyl chain length selectivity of plant acyl-ACP thioesterase
Two distinct domains contribute to the substrate acyl chain length selectivity of plant acyl-ACP thioesterase
The substrate specificity of acyl-ACP thioesterase (TE) plays a crucial role in determining the product profile of type II fatty acid synthase. Utilizing two FatB-type acyl-ACP TEs, the authors here define determinants of substrate specificity and create synthetic enzymes with distinct catalytic traits.
- Fuyuan Jing
- , Le Zhao
- & Basil J. Nikolau
-
Article
| Open Access Aggregating sequences that occur in many proteins constitute weak spots of bacterial proteostasis
Aggregating sequences that occur in many proteins constitute weak spots of bacterial proteostasis
Aggregation is sequence-specific and nucleated by short aggregating protein segments (APR). Here authors use a multidisciplinary approach to show that in E.coli some frequently occurring APRs lead to protein aggregation and ultimately bacterial cell death, which could serve as antibacterial strategy.
- Ladan Khodaparast
- , Laleh Khodaparast
- & Joost Schymkowitz
-
Article
| Open Access NAD+ analog reveals PARP-1 substrate-blocking mechanism and allosteric communication from catalytic center to DNA-binding domains
NAD+ analog reveals PARP-1 substrate-blocking mechanism and allosteric communication from catalytic center to DNA-binding domains
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) catalyse ADP-ribose posttranslational modifications using NAD+ as a substrate. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of PARP-1 bound to the non-hydrolyzable NAD+ analog BAD and provide insights into the mechanism of PARP-1 allosteric regulation.
- Marie-France Langelier
- , Levani Zandarashvili
- & John M. Pascal
-
Article
| Open Access How ligand binds to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor
How ligand binds to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor
The human type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) is important for normal human growth and development. Here, the authors present the crystal structures of the IGF-1R ectodomain both in its apo form and in complex with its ligand insulin-like growth factor I and discuss the receptor activation mechanism.
- Yibin Xu
- , Geoffrey K.-W. Kong
- & Michael C. Lawrence
-
Article
| Open Access A family of unconventional deubiquitinases with modular chain specificity determinants
A family of unconventional deubiquitinases with modular chain specificity determinants
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are essential to modulate ubiquitin signaling. While known DUBs can be grouped into six families, the authors here present biochemical and structural evidence for a seventh DUB family, defining determinants of substrate specificity for two representative enzymes.
- Thomas Hermanns
- , Christian Pichlo
- & Kay Hofmann
-
Article
| Open Access An ancient family of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases with roles in arthropod development and biomass digestion
An ancient family of lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases with roles in arthropod development and biomass digestion
LPMOs catalyze the oxidative breakdown of polysaccharides, thereby facilitating biomass degradation. By analyzing the digestive proteome of firebrats, the authors here identify a yet uncharacterized LPMO family and provide phylogenetic, structural and biochemical insights into its origin and functions.
- Federico Sabbadin
- , Glyn R. Hemsworth
- & Simon J. McQueen-Mason
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of iPLA2β reveals dimeric active sites and suggests mechanisms of regulation and localization
The structure of iPLA2β reveals dimeric active sites and suggests mechanisms of regulation and localization
Calcium-independent phospholipase A2β (iPLA2β) is involved in many physiological and pathological processes but the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, the authors present the structure of dimeric iPLA2β, providing insights into the regulation of its activity and cellular localization.
- Konstantin R. Malley
- , Olga Koroleva
- & Sergey Korolev
-
Article
| Open Access Basal condensation of Numb and Pon complex via phase transition during Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric division
Basal condensation of Numb and Pon complex via phase transition during Drosophila neuroblast asymmetric division
Polarized localization of Numb and Pon in Drosophila neuroblasts (NBs) enables their unequal segregation during asymmetric cell divisions. Here, the authors demonstrate liquid-liquid phase separation of Pon and Numb in NBs mediated by multivalent intermolecular interactions is required for their basal condensation.
- Zelin Shan
- , Yuting Tu
- & Wenyu Wen
-
Article
| Open Access A single NaK channel conformation is not enough for non-selective ion conduction
A single NaK channel conformation is not enough for non-selective ion conduction
NaK is a non-selective cation channel that conducts sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) equally well. Here authors use ssNMR and MD simulations to show that the selectivity filter of NaK adopts two conformations in the absence of ions, one of which is preferred by Na+ and the other by K+.
- Chaowei Shi
- , Yao He
- & Han Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Physical basis of amyloid fibril polymorphism
Physical basis of amyloid fibril polymorphism
Amyloid fibril structures can display polymorphism. Here the authors reveal the cryo-EM structures of several different fibril morphologies of a peptide derived from an amyloidogenic immunoglobulin light chain and present a mathematical analysis of physical factors that influence fibril polymorphism.
- William Close
- , Matthias Neumann
- & Marcus Fändrich
-
Article
| Open Access Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Microrchidia CW-type zinc finger protein 2 (MORC2) is an effector of epigenetic silencing by the human silencing hub (HUSH). Here the authors present the crystal structures of MORC2 and disease-causing MORC2 mutants and give mechanistic insights into how MORC2 mediates HUSH-dependent silencing.
- Christopher H. Douse
- , Stuart Bloor
- & Yorgo Modis
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorogenic RNA Mango aptamers for imaging small non-coding RNAs in mammalian cells
Fluorogenic RNA Mango aptamers for imaging small non-coding RNAs in mammalian cells
Many aptamer-fluorophore complexes suffer from low quantum yield and low extinction coefficients limiting their usability. Here the authors isolate new Mango aptamers with improved fluorescent properties for both fixed and live-cell imaging by using competitive ligand binding microfluidic selection.
- Alexis Autour
- , Sunny C. Y. Jeng
- & Peter J. Unrau
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial hydrogels with biochemical gradients for screening 3D cellular microenvironments
Combinatorial hydrogels with biochemical gradients for screening 3D cellular microenvironments
Tools to investigate a wide range of 3D microenvironmental parameters are important for understanding and controlling cell fate. Here, the authors develop hydrogels with orthogonal biochemical gradients and use this screening system to identify microenvironments that induce mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis.
- Sebastián L. Vega
- , Mi Y. Kwon
- & Jason A. Burdick
-
Article
| Open Access LARP7-like protein Pof8 regulates telomerase assembly and poly(A)+TERRA expression in fission yeast
LARP7-like protein Pof8 regulates telomerase assembly and poly(A)+TERRA expression in fission yeast
A functional telomerase complex requires that the catalytic TERT subunit be assembled with the template RNA TER1. Here the authors show that Pof8, a possible LARP7 family protein, is required for assembly of the telomerase complex, and repression of lncRNA transcripts at telomeres in S. pombe.
- Amanda K. Mennie
- , Bettina A. Moser
- & Toru M. Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access Pof8 is a La-related protein and a constitutive component of telomerase in fission yeast
Pof8 is a La-related protein and a constitutive component of telomerase in fission yeast
The core of the telomerase holoenzyme is composed of the reverse transcriptase and the non-coding RNA template. Here the authors identify Pof8 as a new constitutive component of fission yeast telomerase, loss of which causes telomerase assembly defects and critically short telomeres.
- Diego J. Páez-Moscoso
- , Lili Pan
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article
| Open Access LARP7 family proteins have conserved function in telomerase assembly
LARP7 family proteins have conserved function in telomerase assembly
The telomerase holoenzyme is minimally composed of the reverse transcriptase and the RNA template. Here the authors identify Lar7 as a member of the full complex that helps to stabilise it and protect telomerase RNA from degradation.
- Laura C. Collopy
- , Tracy L. Ware
- & Kazunori Tomita
-
Article
| Open Access Design of ultra-swollen lipidic mesophases for the crystallization of membrane proteins with large extracellular domains
Design of ultra-swollen lipidic mesophases for the crystallization of membrane proteins with large extracellular domains
In meso crystallization of membrane proteins is limited to proteins with small extracellular domains (ECDs). Here, authors combine monoacylglycerols and phospholipids to design stable ultra-swollen bicontinuous cubic phases that allow in meso crystallization of proteins with large ECDs.
- Alexandru Zabara
- , Josephine Tse Yin Chong
- & Raffaele Mezzenga
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for amino acid transport by the CAT family of SLC7 transporters
Structural basis for amino acid transport by the CAT family of SLC7 transporters
Cationic amino acid transporters (CATs) belong to the physiologically important solute carrier (SLC) 7 family. Here, the authors present the structure of the mammalian CAT transporter homologue Geobacillus kaustophilus GkApcT, which reveals how arginine is recognized, and propose a model for proton-coupled amino acid transport.
- Katharina E. J. Jungnickel
- , Joanne L. Parker
- & Simon Newstead
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of overactive TGF-β attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice
Inhibition of overactive TGF-β attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is a painful disease of unknown etiology characterized by extraskeletal bone formation after injury. Here the authors show that TGF-β is increased in HO lesions, where it promotes the early stages of HO pathology, and demonstrate that TGF-β inhibition ameliorates HO in mice.
- Xiao Wang
- , Fengfeng Li
- & Xu Cao
-
Article
| Open Access A chiral selectivity relaxed paralog of DTD for proofreading tRNA mischarging in Animalia
A chiral selectivity relaxed paralog of DTD for proofreading tRNA mischarging in Animalia
The number of tRNA isodecoders has expanded significantly during evolution, which has resulted in ambiguity in tRNA selection by synthetases. Here the authors identify and characterize a dedicated proofreading factor that eliminates errors caused by ambiguity in tRNA selection by eukaryotic tRNA synthetases.
- Santosh Kumar Kuncha
- , Mohd Mazeed
- & Rajan Sankaranarayanan
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biogeochemistry
- Bioinorganic chemistry
- Biophysical chemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical modification
- Cytokines
- DNA
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Histocytochemistry
- Hormones
- Immunochemistry
- Ion channels
- Isoenzymes
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Neurochemistry
- Peptides
- Prions
- Proteases
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Structural biology

 Engineering enhanced cellobiohydrolase activity
Engineering enhanced cellobiohydrolase activity