Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytically potent and selective clusterzymes for modulation of neuroinflammation through single-atom substitutions
Catalytically potent and selective clusterzymes for modulation of neuroinflammation through single-atom substitutions
Artificial enzymes with reprogrammed and augmented catalytic activity and substrate selectivity have emerged to tackle limitations of noble metals or transition metal oxides. Here, the authors report Au25 clusterzymes which are endowed with high catalytic activity and selectivity in a range of enzyme-mimicking reactions.
- Haile Liu
- , Yonghui Li
- & Xiao-Dong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access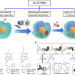 Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Subcellular Zn2+ compartmentalisation is essential for cell biology. Here the authors make a turn-on fluorescent Zn2+ probe that localises to multiple organelles, and correlate its location using organelle morphology derived from structured illumination microscopy.
- Hongbao Fang
- , Shanshan Geng
- & Jiajie Diao
-
Article
| Open Access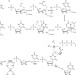 Reverse C-glycosidase reaction provides C-nucleotide building blocks of xenobiotic nucleic acids
Reverse C-glycosidase reaction provides C-nucleotide building blocks of xenobiotic nucleic acids
C-nucleosides are analogues of the canonical N-nucleosides and, despite their synthetic value, biocatalysis has not targeted them yet. Here, the authors report a pseudouridine monophosphate C-glycosidase enzyme for selective 5-β-C-glycosylation of uracil and its derivatives from pentose 5- phosphate substrates.
- Martin Pfeiffer
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of regio- and stereo-specificity in biosynthesis of bacterial heterodimeric diketopiperazines
Molecular basis of regio- and stereo-specificity in biosynthesis of bacterial heterodimeric diketopiperazines
Bacterial heterodimeric tryptophan-containing diketopiperazines (HTDKPs) are bioactive natural products that are difficult to access chemically. Here, the authors identify a family of three related HTDKP-forming cytochrome P450s and engineer key amino acid residues to produce distinct diketopiperazines frameworks.
- Chenghai Sun
- , Zhenyao Luo
- & Xudong Qu
-
Article
| Open Access UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
The success of protein evolution is dependent on the sequence context mutations are introduced into. Here the authors present UMIC-seq that allows consensus generation for closely related genes by using unique molecular identifiers linked to gene variants.
- Paul Jannis Zurek
- , Philipp Knyphausen
- & Florian Hollfelder
-
Article
| Open Access Awakening a latent carbon fixation cycle in Escherichia coli
Awakening a latent carbon fixation cycle in Escherichia coli
Current efforts to establish synthetic carbon fixation in model heterotrophs rely on expression of heterologous enzymes. Here, the authors explore the presence and activity of a latent CO2-assimilation pathway in E. coli based only on endogenous enzymes and a reversible decarboxylase.
- Ari Satanowski
- , Beau Dronsella
- & Arren Bar-Even
-
Article
| Open Access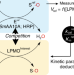 Kinetic insights into the peroxygenase activity of cellulose-active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs)
Kinetic insights into the peroxygenase activity of cellulose-active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs)
Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) catalyze the hydroxylation of glycosidic bonds in polysaccharides, but the catalytic properties of these monocopper enzymes remain poorly characterized. Here authors employ competition between reference enzymes and LPMOs for the H2O2 co-substrate to kinetically characterize LPMO-catalyzed cellulose oxidation.
- Riin Kont
- , Bastien Bissaro
- & Priit Väljamäe
-
Article
| Open Access Allomorphy as a mechanism of post-translational control of enzyme activity
Allomorphy as a mechanism of post-translational control of enzyme activity
β-phosphoglucomutase (βPGM) from Lactococcus lactis is a phosphoryl transfer enzyme required for catabolism of trehalose and maltose. Coupled analyses of multiple βPGM structures and enzymatic activity lead to the proposal of allomorphy — a post-translational mechanism controlling enzyme activity.
- Henry P. Wood
- , F. Aaron Cruz-Navarrete
- & Jonathan P. Waltho
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming bacterial protein organelles as a nanoreactor for hydrogen production
Reprogramming bacterial protein organelles as a nanoreactor for hydrogen production
The extreme oxygen sensitive character of hydrogenases is a longstanding issue for hydrogen production in bacteria. Here, the authors build carboxysome shells in E. coli and incorporate catalytically active hydrogenases and functional partners within the empty shell for the production of hydrogen.
- Tianpei Li
- , Qiuyao Jiang
- & Lu-Ning Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring and applying the substrate promiscuity of a C-glycosyltransferase in the chemo-enzymatic synthesis of bioactive C-glycosides
Exploring and applying the substrate promiscuity of a C-glycosyltransferase in the chemo-enzymatic synthesis of bioactive C-glycosides
C-glycosides are of pharmaceutical interest due to their stability against in vivo hydrolysis, however their enzymatic synthesis faces challenges. Here, the authors report a C-glycosyltransferase from Aloe barbadensis catalysing the C-glycosylation of drug-like acceptors to generate bioactive C-glycosides.
- Kebo Xie
- , Xiaolin Zhang
- & Jungui Dai
-
Article
| Open Access One-pot biocatalytic route from cycloalkanes to α,ω‐dicarboxylic acids by designed Escherichia coli consortia
One-pot biocatalytic route from cycloalkanes to α,ω‐dicarboxylic acids by designed Escherichia coli consortia
Aliphatic α,ω-dicarboxylic acids (DCAs) are widely used chemicals that are synthesised by multistage chemical oxidations. Here, the authors report an artificially designed biocatalytic cascade for the oxidation of cycloalkanes or cycloalkanols to DCAs in the form of microbial consortia, composed of three Escherichia coli cell modules.
- Fei Wang
- , Jing Zhao
- & Aitao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Thioglycoligase derived from fungal GH3 β-xylosidase is a multi-glycoligase with broad acceptor tolerance
Thioglycoligase derived from fungal GH3 β-xylosidase is a multi-glycoligase with broad acceptor tolerance
Thioglycoligases have proved useful for bonding carbohydrates to non-sugar acceptors, however, the scope of these biocatalysts is usually limited. Here, the authors engineer a xylosidase into a thioglycoligase with the ability to form O-, N-, S- and Se- glycosides together with sugar esters and phosphoesters.
- Manuel Nieto-Domínguez
- , Beatriz Fernández de Toro
- & María Jesús Martínez
-
Article
| Open Access Ensemble-based enzyme design can recapitulate the effects of laboratory directed evolution in silico
Ensemble-based enzyme design can recapitulate the effects of laboratory directed evolution in silico
Kemp eliminases are artificial enzymes that catalyze the concerted deprotonation and ring-opening of benzisoxazoles. Here, the authors use room-temperature X-ray crystallography to investigate changes to the conformational ensemble of the Kemp eliminase HG3 along a directed evolutionary trajectory, and develop an experimentally guided, ensemble-based computational enzyme design procedure.
- Aron Broom
- , Rojo V. Rakotoharisoa
- & Roberto A. Chica
-
Article
| Open Access ATP-dependent hydroxylation of an unactivated primary carbon with water
ATP-dependent hydroxylation of an unactivated primary carbon with water
Monooxygenases catalyse the hydroxylation of C-H bonds using oxygen as a co-substrate, which, in turn, is unavailable for anaerobic bacteria. Here, the authors report a three-step reaction cascade involving two hydroxylases and one dehydratase which hydroxylate the C26 methyl group of cholesterol with water as a co-substrate.
- Christian Jacoby
- , Sascha Ferlaino
- & Matthias Boll
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the DOCK2−ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state
Structure of the DOCK2−ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state
DOCK2 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that activates RHO GTPases and interacts with ELMO1, which stimulates its GEF activity. Here, the authors provide mechanistic insights into how ELMO1 regulates DOCK2 activity by determining the structure of the DOCK2–ELMO1 binary complex representing the closed, auto-inhibited state and the DOCK2−ELMO1−RAC1 ternary complex structure, where DOCK2−ELMO1 adopts an open, active conformation.
- Leifu Chang
- , Jing Yang
- & David Barford
-
Article
| Open Access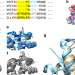 Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Glutaredoxins are a family of essential enzymes divided into two major classes with either a CGFS or a CxxC active site, of which only the latter exhibits oxidoreductase activity. Here the authors address the structural basis for the functional difference between the two classes of glutaredoxins.
- Daniel Trnka
- , Anna D. Engelke
- & Christopher Horst Lillig
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and catalytic regulation of Plasmodium falciparum IMP specific nucleotidase
Structure and catalytic regulation of Plasmodium falciparum IMP specific nucleotidase
Plasmodium falciparum IMP-specific 5′-nucleotidase 1 (PfISN1) is of interest as a potential malaria drug target. Here, the authors report that IMP is a substrate, and ATP an allosteric activator, of PfISN1 and present PfISN1 crystal structures in the ligand-free state and bound to either IMP or ATP.
- Loïc Carrique
- , Lionel Ballut
- & Nushin Aghajari
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrolase–like catalysis and structural resolution of natural products by a metal–organic framework
Hydrolase–like catalysis and structural resolution of natural products by a metal–organic framework
Elucidation of the chemical structure of natural products constitutes one of the main challenges in Natural Sciences. Here, the authors show that an amino acid-based metal–organic framework exhibits hydrolase-like catalytic activity and crystallographic determination of the resulting products.
- Marta Mon
- , Rosaria Bruno
- & Emilio Pardo
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for divergent C–H hydroxylation selectivity in two Rieske oxygenases
Structural basis for divergent C–H hydroxylation selectivity in two Rieske oxygenases
Rieske oxygenases are iron-dependent enzymes that catalyse C–H mono- and dihydroxylation reactions. Here, the authors characterise two cyanobacterial Rieske oxygenases, SxtT and GxtA that are involved in the biosynthesis of paralytic shellfish toxins and determine their substrate free and saxitoxin analog-bound crystal structures and by using mutagenesis experiments identify residues, which are important for substrate positioning and reaction selectivity.
- April L. Lukowski
- , Jianxin Liu
- & Alison R. H. Narayan
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insight into the electron transfer pathway of a self-sufficient P450 monooxygenase
Structural insight into the electron transfer pathway of a self-sufficient P450 monooxygenase
Self-sufficient cytochrome P450 monooxygenases, which contain all redox partners in a single polypeptide chain, are of interest for biotechnological applications. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of full-length Thermobispora bispora CYP116B46 and discuss the potential electron transfer pathway.
- Lilan Zhang
- , Zhenzhen Xie
- & Chun-Chi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Photoinduced monooxygenation involving NAD(P)H-FAD sequential single-electron transfer
Photoinduced monooxygenation involving NAD(P)H-FAD sequential single-electron transfer
The number of usable light-responsive enzymes is limited, despite the potential biotechnological applications. Here, the authors report a flavoprotein monooxygenase which is controllable by blue light illumination, and propose a mechanism involving protein-mediated radical photoreduction of FAD via a semiquinone intermediate.
- Simon Ernst
- , Stefano Rovida
- & Steffen L. Drees
-
Article
| Open Access Photobiocatalytic synthesis of chiral secondary fatty alcohols from renewable unsaturated fatty acids
Photobiocatalytic synthesis of chiral secondary fatty alcohols from renewable unsaturated fatty acids
Natural fatty acids are important starting materials in bio-based chemical production. Here, the authors developed a two-enzyme cascade to produce enantiomerically pure secondary fatty alcohols from natural unsaturated fatty acids in one pot.
- Wuyuan Zhang
- , Jeong-Hoo Lee
- & Frank Hollmann
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures reveal intricate Fe-S cluster arrangement and charging in Rhodobacter capsulatus formate dehydrogenase
Cryo-EM structures reveal intricate Fe-S cluster arrangement and charging in Rhodobacter capsulatus formate dehydrogenase
Rhodobacter capsulatus NAD+ dependent formate dehydrogenase (RcFDH) is a molybdoenzyme that catalyses the reversible oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, and is of interest for biotechnological applications. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structures of RcFDH as isolated from R. capsulatus and in the reduced state with bound NADH, and discuss the enzyme mechanism.
- Christin Radon
- , Gerd Mittelstädt
- & Petra Wendler
-
Article
| Open Access The chloroalkaloid (−)-acutumine is biosynthesized via a Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent halogenase in Menispermaceae plants
The chloroalkaloid (−)-acutumine is biosynthesized via a Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent halogenase in Menispermaceae plants
Halogenated plant natural products are rare and plant halogenation enzymes are thus far unknown. Here Kim et al. identify a dechloroacutumine halogenase from Common Moonseed that catalyzes the final chlorination step in the biosynthesis of acutumine, a chloroalkaloid with selective cytotoxicity to cultured T cells.
- Colin Y. Kim
- , Andrew J. Mitchell
- & Jing-Ke Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative assessment of the determinant structural differences between redox-active and inactive glutaredoxins
Quantitative assessment of the determinant structural differences between redox-active and inactive glutaredoxins
Glutaredoxins play a central role in numerous biological processes including cellular redox homeostasis and Fe-S cluster biogenesis. Here the authors establish the molecular basis for glutaredoxin redox catalysis through comprehensive biochemical and structural analyses.
- Linda Liedgens
- , Jannik Zimmermann
- & Marcel Deponte
-
Article
| Open Access Bringing biocatalytic deuteration into the toolbox of asymmetric isotopic labelling techniques
Bringing biocatalytic deuteration into the toolbox of asymmetric isotopic labelling techniques
Deuterated chemicals are widely exploited in analytical chemistry and increasingly in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds. Here, the authors developed a mild biocatalytic method for the selective asymmetric reductive deuteration of organic compounds, by using H2 and 2H2O to generate 2H-NADH.
- J. S. Rowbotham
- , M. A. Ramirez
- & K. A. Vincent
-
Article
| Open Access BrtB is an O-alkylating enzyme that generates fatty acid-bartoloside esters
BrtB is an O-alkylating enzyme that generates fatty acid-bartoloside esters
O-alkylation of carboxylates by alkyl halides has only been observed transiently in enzymatic processes. Here, the authors show a carboxylate alkylating enzyme, BrtB, that catalyzes C-O bond formation between free fatty acids and secondary alkyl chlorides.
- João P. A. Reis
- , Sandra A. C. Figueiredo
- & Pedro N. Leão
-
Article
| Open Access A combined experimental and modelling approach for the Weimberg pathway optimisation
A combined experimental and modelling approach for the Weimberg pathway optimisation
Metabolic engineering is often hampered by non-linear kinetics and allosteric regulatory mechanisms. Here, the authors construct a quantitative model for the pentose degradation Weimberg pathway in Caulobacter crescentus and demonstrate its biotechnological applications in cell-free system and standard metabolic engineering.
- Lu Shen
- , Martha Kohlhaas
- & Bettina Siebers
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis of fungal glucuronoyl esterase activity on natural substrates
The structural basis of fungal glucuronoyl esterase activity on natural substrates
Glucuronoyl esterases have the potential to be used in the biocatalytic conversion of lignin-carbohydrate complexes to obtain pure lignin for downstream biofuel conversion. Here the authors present a detailed structural analysis of the glucuronoyl esterase from Cerrena unicolor, providing the basis for its activity on natural substrate and for how lignin can be selectively separated from lignocellulosic materials.
- Heidi A. Ernst
- , Caroline Mosbech
- & Sine Larsen
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled depolymerization of cellulose by light-driven lytic polysaccharide oxygenases
Controlled depolymerization of cellulose by light-driven lytic polysaccharide oxygenases
Lytic polysaccharide (mono)oxygenases (LPMOs) perform oxidative cleavage of polysaccharides. Here, the authors showed that the light-driven activity of LPMOs is dependent on hydrogen peroxide availability and can be controlled via the light intensity provided.
- Bastien Bissaro
- , Eirik Kommedal
- & Vincent G. H. Eijsink
-
Article
| Open Access Compartmentalized microbes and co-cultures in hydrogels for on-demand bioproduction and preservation
Compartmentalized microbes and co-cultures in hydrogels for on-demand bioproduction and preservation
Large scale suspension fermentation technology is not easily portable or reusable. Here the authors describe a hydrogel system suitable for long-term and reusable production with both single and multi-organism consortia.
- Trevor G. Johnston
- , Shuo-Fu Yuan
- & Hal S. Alper
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic processing in ruthenium-based polyoxometalate coacervate protocells
Catalytic processing in ruthenium-based polyoxometalate coacervate protocells
The development of microscale materials with cell-like functions and collective behaviors is an important milestone in bottom-up synthetic biology. Here the authors employ a bio-inspired inorganic synzyme to construct a micro-compartment with multi-functional activity providing a step towards the development of protocell reaction networks.
- Pierangelo Gobbo
- , Liangfei Tian
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access An in vitro platform for engineering and harnessing modular polyketide synthases
An in vitro platform for engineering and harnessing modular polyketide synthases
A robust platform to study modular polyketide synthases (PKSs) in vitro is still unavailable. Here, the authors report the reconstitution of the venemycin PKS, engineer hybrid venemycin/pikromycin PKSs, and obtain much improved yields through employing the updated module boundaries.
- Takeshi Miyazawa
- , Melissa Hirsch
- & Adrian T. Keatinge-Clay
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial metalloenzyme biosensor can detect ethylene gas in fruits and Arabidopsis leaves
An artificial metalloenzyme biosensor can detect ethylene gas in fruits and Arabidopsis leaves
Existing methods to detect ethylene in plant tissue typically require gas chromatography or use ethylene-dependent gene expression as a proxy. Here Vong et al. show that an artificial metalloenzyme-based ethylene probe can be used to detect ethylene in plants with improved spatiotemporal resolution.
- Kenward Vong
- , Shohei Eda
- & Katsunori Tanaka
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Conformational fitting of a flexible oligomeric substrate does not explain the enzymatic PET degradation
Conformational fitting of a flexible oligomeric substrate does not explain the enzymatic PET degradation
- Ren Wei
- , Chen Song
- & Wolfgang Zimmermann
-
Article
| Open Access Two-tiered enforcement of high-fidelity DNA ligation
Two-tiered enforcement of high-fidelity DNA ligation
DNA ligases catalyze the joining of DNA strands to complete DNA replication, recombination and repair transactions. Here the authors present X-ray structures and kinetic analyses of LIG1 complexes with undamaged and oxidatively damaged DNA that unveil determinants of LIG1 substrate recognition and enzymatic fidelity.
- Percy P. Tumbale
- , Thomas J. Jurkiw
- & R. Scott Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Unassisted solar lignin valorisation using a compartmented photo-electro-biochemical cell
Unassisted solar lignin valorisation using a compartmented photo-electro-biochemical cell
The effective valorisation of lignin is crucial for realizing a sustainable biorefinery. Here, the authors report that a compartmented photo-electro-biochemical design enables unassisted, selective, and stable solar lignin valorisation without the need for any additional bias or chemicals.
- Myohwa Ko
- , Le Thanh Mai Pham
- & Ji-Wook Jang
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-enzymatic cascades to produce cycloalkenes from bio-based resources
Chemo-enzymatic cascades to produce cycloalkenes from bio-based resources
Cycloalkenes are bulk petrochemicals that are currently obtained from fossil fuels. Here, the authors developed multi enzyme pathways in combination with a Ru-catalyzed metathesis reaction for the one-pot production of cyclopentene, cyclohexene, and cycloheptene from olive oil-derived intermediates.
- Shuke Wu
- , Yi Zhou
- & Thomas R. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid mechanochemical encapsulation of biocatalysts into robust metal–organic frameworks
Rapid mechanochemical encapsulation of biocatalysts into robust metal–organic frameworks
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are attractive for encapsulating enzymes for industrial purposes because they can increase selectivity, stability, and/or activity of the enzymes. Here, the authors developed an economical solid-state mechanochemical method to encapsulate enzymes during MOF synthesis.
- Tz-Han Wei
- , Shi-Hong Wu
- & Fa-Kuen Shieh
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming protein-polymer conjugate purification by tuning protein solubility
Transforming protein-polymer conjugate purification by tuning protein solubility
Therapeutic proteins are often conjugated with polymers, but separating the conjugate from unconjugated protein and free polymer is a major challenge. Here, the authors discover that proteins conjugated to charged or zwitterionic polymers maintain solubility in 100% ammonium sulfate, greatly simplifying purification.
- Stefanie L. Baker
- , Aravinda Munasinghe
- & Alan J. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of azoxy bond formation for azoxymycins biosynthesis
Molecular mechanism of azoxy bond formation for azoxymycins biosynthesis
Azoxy bonds are frequently found in liquid crystals, chemical intermediates, dyes, agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. Here, the authors investigated azoxy bond formation by the non-heme diiron N-oxygenase AzoC in azoxymycin biosynthesis and show that the nitroso group plays a key part in it.
- Yuan-Yang Guo
- , Zhen-Hua Li
- & Yong-Quan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Galactose to tagatose isomerization at moderate temperatures with high conversion and productivity
Galactose to tagatose isomerization at moderate temperatures with high conversion and productivity
Production of tagatose, a sugar substitute, by isomerization of galactose suffers from unfavorable enzymatic kinetics, low enzyme stability, and low equilibrium constant. Here, the authors simultaneously overcome these limitations by encapsulating l-arabinose isomerase in permeabilized Lactobacillus plantarum.
- Josef R. Bober
- & Nikhil U. Nair
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of amine dehydrogenases with increased catalytic performance and substrate scope from ε-deaminating L-Lysine dehydrogenase
Generation of amine dehydrogenases with increased catalytic performance and substrate scope from ε-deaminating L-Lysine dehydrogenase
Amine dehydrogenases (AmDHs) catalyse the conversion of ketones into amines. Here, the authors created AmDH variants, the best of which showing a substrate-dependent stereo-switchable selectivity, affording either S- or R-configured amine products with up to >99.9% enantiomeric excess.
- Vasilis Tseliou
- , Tanja Knaus
- & Francesco G. Mutti
-
Article
| Open Access A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids
A biocatalytic hydroxylation-enabled unified approach to C19-hydroxylated steroids
C19 hydroxylation is a unique feature of some bioactive steroids. Here, the authors developed a direct C19 hydroxylation approach to scalably access 19-OH-cortexolone in the host T. cucumeris and then converted the product into various pharmaceutically useful products via chemical synthesis.
- Junlin Wang
- , Yanan Zhang
- & Qianghui Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial cysteine-lipases with high activity and altered catalytic mechanism created by laboratory evolution
Artificial cysteine-lipases with high activity and altered catalytic mechanism created by laboratory evolution
Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) is a serine lipase. Here, the authors use directed evolution to exchange serine with cysteine in the catalytic triad of the enzyme, thereby obtaining a highly active CALB variant that — unlike the wild type — accommodates bulky substrates.
- Yixin Cen
- , Warispreet Singh
- & Manfred T. Reetz
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrophobic recognition allows the glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 to catalyze its substrate in two orientations
Hydrophobic recognition allows the glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 to catalyze its substrate in two orientations
UGT76G1 is an UDP-glucose dependent glycosyltransferase and a component of the biosynthesis pathway for the natural sugar substitute steviol glycoside. Here, the authors present substrate bound crystal structures of UGT76G1 and provide insights into substrate recognition and catalysis by the enzyme.
- Ting Yang
- , Jinzhu Zhang
- & Xiaofeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Repeated evolution of cytochrome P450-mediated spiroketal steroid biosynthesis in plants
Repeated evolution of cytochrome P450-mediated spiroketal steroid biosynthesis in plants
Diosgenin is a spiroketal natural product that is used as a precursor in the industrial synthesis of steroids. Here, the authors identified key cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for the conversion of cholesterol to diosgenin from two phylogenetical distinct diosgenin-producing plant species.
- Bastien Christ
- , Chengchao Xu
- & Jing-Ke Weng
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic enzymatic properties modulate the self-propulsion of micromotors
Intrinsic enzymatic properties modulate the self-propulsion of micromotors
Self-propulsion of biocatalytic micro- and nanomotors is facilitated by enzymes converting substrates into products. Here, the authors show that intrinsic enzymatic properties such as conformational changes are crucial for the self-propulsion of silica microcapsules modified with urease.
- Xavier Arqué
- , Adrian Romero-Rivera
- & Samuel Sánchez
-
Article
| Open Access A mechanism to prevent production of reactive oxygen species by Escherichia coli respiratory complex I
A mechanism to prevent production of reactive oxygen species by Escherichia coli respiratory complex I
Respiratory complex I plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism coupling NADH oxidation to proton translocation. Here, the authors report the structure of the electron input part of Aquifex aeolicus complex I at up to 1.8 Å resolution with bound substrates in the reduced and oxidized states.
- Marius Schulte
- , Klaudia Frick
- & Thorsten Friedrich

 The power of electrified nanoconfinement for energising, controlling and observing long enzyme cascades
The power of electrified nanoconfinement for energising, controlling and observing long enzyme cascades