Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A distinct Fusobacterium nucleatum clade dominates the colorectal cancer niche
A distinct Fusobacterium nucleatum clade dominates the colorectal cancer niche
A study reveals that Fusobacterium nucleatum subspecies animalis is bifurcated into two distinct clades, and shows that only one of these dominates the colorectal cancer niche, probably through increased colonization of the human gastrointestinal tract.
- Martha Zepeda-Rivera
- , Samuel S. Minot
- & Christopher D. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access Compensatory evolution in NusG improves fitness of drug-resistant M. tuberculosis
Compensatory evolution in NusG improves fitness of drug-resistant M. tuberculosis
In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the fitness cost of rifampicin resistance is partially due to excessive RNA polymerase pausing and is rescued by mutations in the pro-pausing transcription factor NusG.
- Kathryn A. Eckartt
- , Madeleine Delbeau
- & Jeremy M. Rock
-
Article
| Open Access Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Cultivation of a new anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from Boreal Shield lake water—representing a transition form in the evolution of photosynthesis—offers insights into how the major modes of phototrophy diversified.
- J. M. Tsuji
- , N. A. Shaw
- & J. D. Neufeld
-
Article |
 Structures and activation mechanism of the Gabija anti-phage system
Structures and activation mechanism of the Gabija anti-phage system
Structures of complexes containing GajA and GajB proteins of the prokaryotic Gabija anti-phage defence system reveal the mechanism of its activation after DNA cleavage upon ATP depletion.
- Jing Li
- , Rui Cheng
- & Longfei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Incomplete transcripts dominate the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcriptome
Incomplete transcripts dominate the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcriptome
A study reveals that most transcripts in Mycobacterium tuberculosis are incomplete, likely because of the tendency of the transcription machinery in this species to pause on genomic DNA.
- Xiangwu Ju
- , Shuqi Li
- & Shixin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Translation selectively destroys non-functional transcription complexes
Translation selectively destroys non-functional transcription complexes
Translation actively dislodges stalled transcription elongation complexes (ECs) from damaged DNA, which enables lesion repair and restoration of transcription activity, and coupled ribosomes discriminate between active ECs and stalled ECs, ensuring destruction of only the latter.
- Jason Woodgate
- , Hamed Mosaei
- & Nikolay Zenkin
-
Article |
 Transcription–replication interactions reveal bacterial genome regulation
Transcription–replication interactions reveal bacterial genome regulation
Single-cell expression data from bacteria are used to classify gene regulatory architectures in relation to gene expression dynamics and the cell cycle, revealing distinct categories of gene regulatory mechanisms.
- Andrew W. Pountain
- , Peien Jiang
- & Itai Yanai
-
Article
| Open Access The CRISPR effector Cam1 mediates membrane depolarization for phage defence
The CRISPR effector Cam1 mediates membrane depolarization for phage defence
The prokaryotic non-enzymatic effector protein Cam1 mediates CRISPR immunity by binding tetra-adenylate second messengers and forming a pore in the membrane that induces membrane depolarization and growth arrest.
- Christian F. Baca
- , You Yu
- & Luciano A. Marraffini
-
Article |
 Discovery of a structural class of antibiotics with explainable deep learning
Discovery of a structural class of antibiotics with explainable deep learning
An explainable deep learning model using a chemical substructure-based approach for the exploration of chemical compound libraries identified structural classes of compounds with antibiotic activity and low toxicity.
- Felix Wong
- , Erica J. Zheng
- & James J. Collins
-
Article |
 SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB encapsulates outer membrane proteins in stress-induced lipid nanodomains
SlyB, a lipoprotein in the PhoPQ stress regulon in Gram-negative bacteria, forms stable stress-induced complexes with the outer membrane proteome.
- Arne Janssens
- , Van Son Nguyen
- & Han Remaut
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial cGAS senses a viral RNA to initiate immunity
Bacterial cGAS senses a viral RNA to initiate immunity
Staphylococcus CdnE03 cyclase recognizes structured RNA molecules produced by staphylococcal phages, triggering cyclic oligonucleotide production and, thereby, bacterial cell death—a mechanism of antiviral defence conserved across domains of life.
- Dalton V. Banh
- , Cameron G. Roberts
- & Luciano A. Marraffini
-
Article |
 Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
Single-molecule dynamics show a transient lipopolysaccharide transport bridge
As well as being the substrate for the lipopolysaccharide transport protein complex comprising LptA–G, lipopolysaccharide binding to Lpt proteins promotes their assembly into a bridge linking the inner and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria.
- Lisa Törk
- , Caitlin B. Moffatt
- & Daniel Kahne
-
Article
| Open Access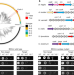 Antiviral type III CRISPR signalling via conjugation of ATP and SAM
Antiviral type III CRISPR signalling via conjugation of ATP and SAM
The Bacteroides fragilis type III CRISPR protein Cmr conjugates ATP to S-adenosyl methionine, generating S-adenosyl methionine (SAM)-AMP, a novel second messenger with a role in antiviral signalling.
- Haotian Chi
- , Ville Hoikkala
- & Malcolm F. White
-
Article |
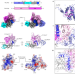 Nucleic-acid-triggered NADase activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Nucleic-acid-triggered NADase activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of a short prokaryotic Argonaute (pAgo) and the associated TIR-APAZ proteins bound by guide RNA and target DNA shed light on the mechanisms of assembly and activation of pAgo systems.
- Xiaopan Gao
- , Kun Shang
- & Sheng Cui
-
Article |
 Transposon-encoded nucleases use guide RNAs to promote their selfish spread
Transposon-encoded nucleases use guide RNAs to promote their selfish spread
TnpB and IscB nucleases use transposon-encoded guide RNAs to target genomic sequences for cleavage, thereby favouring copying and spreading of transposable elements.
- Chance Meers
- , Hoang C. Le
- & Samuel H. Sternberg
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial pathogens deliver water- and solute-permeable channels to plant cells
Bacterial pathogens deliver water- and solute-permeable channels to plant cells
The bacterial effector proteins of the AvrE family function as membrane channels in plant cells, enabling the passage of water and solutes from host cells to support pathogen growth, and disrupting the viability of the host cell.
- Kinya Nomura
- , Felipe Andreazza
- & Sheng Yang He
-
Article |
 Oligomerization-mediated activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Oligomerization-mediated activation of a short prokaryotic Argonaute
Cryo-electron microscopy structures and biochemical analyses provide insight into how short prokaryotic Argonaute proteins are assembled and activated, and reveal that oligomerization has a key role in driving catalytic activity.
- Zhangfei Shen
- , Xiao-Yuan Yang
- & Tian-Min Fu
-
Article |
 Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter
Proteins of the Mycobacterium smegmatis Mce1 system assemble to form an elongated ABC transporter complex that is long enough to span the impermeable mycobacterial cell envelope.
- James Chen
- , Alice Fruhauf
- & Damian C. Ekiert
-
Article
| Open Access Genome expansion by a CRISPR trimmer-integrase
Genome expansion by a CRISPR trimmer-integrase
CRISPR systems lacking Cas4 can use fused or recruited exonucleases for faithful acquisition of new CRISPR immune sequences.
- Joy Y. Wang
- , Owen T. Tuck
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Article
| Open Access A Pseudomonas aeruginosa small RNA regulates chronic and acute infection
A Pseudomonas aeruginosa small RNA regulates chronic and acute infection
A study examining bacterial gene expression in human-derived samples identifies a gene encoding a small RNA and describes how it orchestrates the transition between chronic and acute infection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Pengbo Cao
- , Derek Fleming
- & Marvin Whiteley
-
Article |
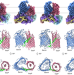 Structural basis of BAM-mediated outer membrane β-barrel protein assembly
Structural basis of BAM-mediated outer membrane β-barrel protein assembly
The structural basis of the late-stage intermediate assembly of outer membrane β-barrel proteins mediated by the bacterial β-barrel assembly machinery is determined.
- Chongrong Shen
- , Shenghai Chang
- & Haohao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Coordination of bacterial cell wall and outer membrane biosynthesis
Coordination of bacterial cell wall and outer membrane biosynthesis
A study demonstrates that specific interactions between the two committed enzymes for the synthesis of lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan enable coordinated assembly of the outer membrane and cell wall in the Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Katherine R. Hummels
- , Samuel P. Berry
- & Thomas G. Bernhardt
-
Article |
 An E1–E2 fusion protein primes antiviral immune signalling in bacteria
An E1–E2 fusion protein primes antiviral immune signalling in bacteria
This study demonstrates that bacteria use a ubiquitin transferase-like enzyme to prime cGAS/DncV-like nucleotidyltransferase activation and use a deubiquitinase-like enzyme to decrease activity.
- Hannah E. Ledvina
- , Qiaozhen Ye
- & Aaron T. Whiteley
-
Article
| Open Access Cas12a2 elicits abortive infection through RNA-triggered destruction of dsDNA
Cas12a2 elicits abortive infection through RNA-triggered destruction of dsDNA
RNA targeting by the Sulfuricurvum type V single-effector nuclease SuCas12a2 drives abortive infection through non-specific cleavage of double-stranded DNA—after recognition of an RNA target through an activating protospacer-flanking sequence, SuCas12a2 efficiently degrades ssRNA, ssDNA and dsDNA.
- Oleg Dmytrenko
- , Gina C. Neumann
- & Chase L. Beisel
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupling of respiration rates and abundance in marine prokaryoplankton
Decoupling of respiration rates and abundance in marine prokaryoplankton
Cell-specific respiration rates differ by more than 1,000× among prokaryoplankton genera, and the majority of respiration was found to be performed by minority members of prokaryoplankton, whereas cells of the most prevalent lineages had extremely low respiration rates.
- Jacob H. Munson-McGee
- , Melody R. Lindsay
- & Ramunas Stepanauskas
-
Article
| Open Access Undecaprenyl phosphate translocases confer conditional microbial fitness
Undecaprenyl phosphate translocases confer conditional microbial fitness
Members of the DUF368-containing and DedA transmembrane protein families have conditional roles in undecaprenyl phosphate translocation in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and may have a widely conserved function in the biogenesis of microbial cell surface glycopolymers.
- Brandon Sit
- , Veerasak Srisuknimit
- & Matthew K. Waldor
-
Article |
 Antiviral signalling by a cyclic nucleotide activated CRISPR protease
Antiviral signalling by a cyclic nucleotide activated CRISPR protease
A CalpL–CalpT–CalpS cascade mediated by cyclic oligoadenylates is identified as a mechanism to detect viral RNA and activate subsequent antivirus responses in microorganisms.
- Christophe Rouillon
- , Niels Schneberger
- & Gregor Hagelueken
-
Article |
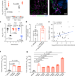 Enterococci enhance Clostridioides difficile pathogenesis
Enterococci enhance Clostridioides difficile pathogenesis
Enterococci enhance the fitness and pathogenesis of Clostridioides difficile in the gut by altering the amino acid composition and providing signals that increase its virulence towards the host.
- Alexander B. Smith
- , Matthew L. Jenior
- & Joseph P. Zackular
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell
Cryo-electron tomography is used to reveal the structural dynamics and functional diversity of translating ribosomes in Mycoplasma pneumoniae, providing insight into the translation elongation cycle inside cells and how it is reshaped by antibiotics.
- Liang Xue
- , Swantje Lenz
- & Julia Mahamid
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation of muramyl peptides by NAGK is required for NOD2 activation
Phosphorylation of muramyl peptides by NAGK is required for NOD2 activation
N-acetylglucosamine kinase catalyses the phosphorylation of muramyl dipeptide and is thus essential for its recognition and immunostimulatory activity in human and mouse cells.
- Che A. Stafford
- , Alicia-Marie Gassauer
- & Veit Hornung
-
Article |
 A monocyte–leptin–angiogenesis pathway critical for repair post-infection
A monocyte–leptin–angiogenesis pathway critical for repair post-infection
Monocytes recruited to skin infection are not involved in bacterial clearance but instead regulate local angiogenesis and healing.
- Rachel M. Kratofil
- , Hanjoo B. Shim
- & Paul Kubes
-
Article |
 Cyclic nucleotide-induced helical structure activates a TIR immune effector
Cyclic nucleotide-induced helical structure activates a TIR immune effector
A bacterial antiviral defence system generates a cyclic tri-adenylate that binds to a TIR–SAVED effector, inducing formation of a superhelical structure with adjacent TIR domains organizing into an active site, allowing NAD+ degradation.
- Gaëlle Hogrel
- , Abbie Guild
- & Malcolm F. White
-
Article
| Open Access Akkermansia muciniphila phospholipid induces homeostatic immune responses
Akkermansia muciniphila phospholipid induces homeostatic immune responses
Overall, this study describes the molecular mechanism of a druggable pathway that recapitulates in cellular assays the immunomodulatory effects associated with Akkermansia muciniphila, a prominent member of the gut microbiota.
- Munhyung Bae
- , Chelsi D. Cassilly
- & Jon Clardy
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of an active bacterial TIR–STING filament complex
Cryo-EM structure of an active bacterial TIR–STING filament complex
Through structural analysis of the activation of bacterial STING, the molecular basis of STING filament formation and TIR effector domain activation in antiphage signalling is defined.
- Benjamin R. Morehouse
- , Matthew C. J. Yip
- & Philip J. Kranzusch
-
Article |
 Membrane-anchored HDCR nanowires drive hydrogen-powered CO2 fixation
Membrane-anchored HDCR nanowires drive hydrogen-powered CO2 fixation
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the filamentous hydrogen-dependent CO2 reductase (HDCR) enzyme from Thermoanaerobacter kivui, together with enzymatic analysis and in situ cryo-electron tomography, provides insight into the high catalytic activity of HDCR.
- Helge M. Dietrich
- , Ricardo D. Righetto
- & Jan M. Schuller
-
Article
| Open Access Archaic chaperone–usher pili self-secrete into superelastic zigzag springs
Archaic chaperone–usher pili self-secrete into superelastic zigzag springs
The Csu pili of the multidrug-resistant nosocomial pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii assemble into an ultrathin zigzag architecture secured by a clinch mechanism that provides the pilus with high mechanical stability and superelasticity.
- Natalia Pakharukova
- , Henri Malmi
- & Anton V. Zavialov
-
Article |
 Bacterial retrons encode phage-defending tripartite toxin–antitoxin systems
Bacterial retrons encode phage-defending tripartite toxin–antitoxin systems
Retron-Sen2 of Salmonella Typhimurium encodes a toxin and a reverse transcriptase, which, together with the Sen2 multi-copy single-stranded DNA synthesized by the reverse transcriptase make up a tripartite toxin–antitoxin system that functions in anti-phage defence.
- Jacob Bobonis
- , Karin Mitosch
- & Athanasios Typas
-
Article |
 Within-host evolution of a gut pathobiont facilitates liver translocation
Within-host evolution of a gut pathobiont facilitates liver translocation
Within-host evolution is a critical regulator of commensal pathogenicity that provides a unique source of stochasticity in the development and progression of microbiota-driven disease.
- Yi Yang
- , Mytien Nguyen
- & Noah W. Palm
-
Article |
 Distinct gene clusters drive formation of ferrosome organelles in bacteria
Distinct gene clusters drive formation of ferrosome organelles in bacteria
A fez gene cluster drives formation of ferrosomes, a distinct lipid-bounded organelle for iron storage, in diverse bacterial species.
- Carly R. Grant
- , Matthieu Amor
- & Arash Komeili
-
Article |
 Structural basis of lipopolysaccharide maturation by the O-antigen ligase
Structural basis of lipopolysaccharide maturation by the O-antigen ligase
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the bacterial O-antigen ligase WaaL, combined with genetics, biochemistry and molecular dynamics simulations, provide insight into the mechanism by which WaaL catalyses the biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide.
- Khuram U. Ashraf
- , Rie Nygaard
- & Filippo Mancia
-
Article |
 Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
A bacterial enzyme is characterized and demonstrated to have Ni2+-dependent activity and high specificity for free guanidine enabling the bacteria to use guanidine as the sole nitrogen source for growth.
- D. Funck
- , M. Sinn
- & J. S. Hartig
-
Article |
 A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice
A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice
The gut-derived molecule 4-ethylphenol influences complex behaviours in mice through effects on oligodendrocyte function and myelin patterning in the brain.
- Brittany D. Needham
- , Masanori Funabashi
- & Sarkis K. Mazmanian
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics
Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics
Methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus appeared in European hedgehogs in the pre-antibiotic era as a co-evolutionary adaptation to antibiotic-producing dermatophytes and have spread within the local hedgehog populations and between hedgehogs and secondary hosts.
- Jesper Larsen
- , Claire L. Raisen
- & Anders R. Larsen
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and dynamics of a mycobacterial type VII secretion system
Structure and dynamics of a mycobacterial type VII secretion system
A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the inner membrane complex of the ESX-5 type VII secretion system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals an important role of interactions with MycP5 protease for complex integrity.
- Catalin M. Bunduc
- , Dirk Fahrenkamp
- & Thomas C. Marlovits
-
Article |
 C. difficile exploits a host metabolite produced during toxin-mediated disease
C. difficile exploits a host metabolite produced during toxin-mediated disease
RNA-sequencing experiments determine that sorbitol, a metabolite produced by the host enzyme aldose reductase, is exploited by Clostridium difficile in its adaptation to inflammatory conditions in the gut.
- Kali M. Pruss
- & Justin L. Sonnenburg
-
Article |
 High CO2 levels drive the TCA cycle backwards towards autotrophy
High CO2 levels drive the TCA cycle backwards towards autotrophy
In the deltaproteobacterium Hippea maritima, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle can be reversed by high partial pressures of CO2 for the autotrophic fixation of carbon.
- Lydia Steffens
- , Eugenio Pettinato
- & Ivan A. Berg
-
Article |
 Type III-A CRISPR immunity promotes mutagenesis of staphylococci
Type III-A CRISPR immunity promotes mutagenesis of staphylococci
In Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus, non-specific DNase activity of the type III-A CRISPR–Cas system increases the rate of mutations in the host and accelerates the evolution of resistance to antibiotics and to phage.
- Charlie Y. Mo
- , Jacob Mathai
- & Luciano A. Marraffini
-
Article
| Open Access Anaerobic endosymbiont generates energy for ciliate host by denitrification
Anaerobic endosymbiont generates energy for ciliate host by denitrification
‘Candidatus Azoamicus ciliaticola’ transfers energy to its ciliate host in the form of ATP and enables this host to breathe nitrate, demonstrating that eukaryotes with remnant mitochondria can secondarily acquire energy-providing endosymbionts.
- Jon S. Graf
- , Sina Schorn
- & Jana Milucka
-
Article |
 Molecular basis for control of antibiotic production by a bacterial hormone
Molecular basis for control of antibiotic production by a bacterial hormone
X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy structures of the transcriptional repressor of the methylomycin gene cluster, MmfR, reveal the molecular basis for regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis by AHFCA hormones in Actinobacteria.
- Shanshan Zhou
- , Hussain Bhukya
- & Christophe Corre
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bacterial development
- Bacterial evolution
- Bacterial genetics
- Bacterial genomics
- Bacterial host response
- Bacterial immune evasion
- Bacterial pathogenesis
- Bacterial physiology
- Bacterial secretion
- Bacterial structural biology
- Bacterial synthetic biology
- Bacterial systems biology
- Bacterial techniques and applications
- Bacterial toxins
- Bacterial transcription
- Cellular microbiology
- Infectious-disease epidemiology
- Marine microbiology
- Metagenomics
- Symbiosis

 Distal colonocytes targeted by C. rodentium recruit T-cell help for barrier defence
Distal colonocytes targeted by C. rodentium recruit T-cell help for barrier defence