Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Aegilops sharonensis genome-assisted identification of stem rust resistance gene Sr62
Aegilops sharonensis genome-assisted identification of stem rust resistance gene Sr62
Aegilops sharonensis is a wild diploid relative of wheat. Here, the authors assemble the genome of Ae. sharonensis and use the assembly as an aid to clone the Ae. sharonensis-derived stem rust resistance gene Sr62 in the allohexaploid genome of wheat.
- Guotai Yu
- , Oadi Matny
- & Brande B. H. Wulff
-
Comment
| Open Access Breeding future crops to feed the world through de novo domestication
Breeding future crops to feed the world through de novo domestication
By the end of this century, a 50% increase in agricultural productivity is required to feed the world. Recent studies have demonstrated de novo domestication of wild plants as a new crop breeding strategy to meet future food challenges.
- Hong Yu
- & Jiayang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Natural variation in Glume Coverage 1 causes naked grains in sorghum
Natural variation in Glume Coverage 1 causes naked grains in sorghum
Low glume coverage is the preferred for easy threshing in grain production, but the genetic basis remains unclear. Here, the authors report the gene GC1, which encodes an atypical G protein γ subunit, negatively regulates sorghum glume coverage and the naturally truncated alleles can be useful in the naked grain breeding.
- Peng Xie
- , Sanyuan Tang
- & Qi Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic variants affecting homoeologous gene expression dosage contribute to agronomic trait variation in allopolyploid wheat
Genomic variants affecting homoeologous gene expression dosage contribute to agronomic trait variation in allopolyploid wheat
The connection between expression variation and phenotypic diversity in the populations of polyploid crops remains elusive. Here, the authors reveal the impact of genetic variants leading to biased expression of homoeologous genes in hexaploid wheat on agronomic traits.
- Fei He
- , Wei Wang
- & Eduard Akhunov
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic insights into the evolution of Echinochloa species as weed and orphan crop
Genomic insights into the evolution of Echinochloa species as weed and orphan crop
Echinochloa is an important genus in the grass family as many of them are either problematic weeds or domesticated millets. Here, the authors assemble three polyploidy genomes in this genus using the diploid-assisted scaffolding method DipHic and provide genomic insights into the dual roles of some species as weeds and orphan crops.
- Dongya Wu
- , Enhui Shen
- & Chu-Yu Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Graph-based pan-genome reveals structural and sequence variations related to agronomic traits and domestication in cucumber
Graph-based pan-genome reveals structural and sequence variations related to agronomic traits and domestication in cucumber
Increasing studies have suggested that single reference genome is insufficient to capture all variations in the genome. Here, the authors report a graph-based cucumber pan-genome by analyzing 12 chromosome-scale assemblies and reveal variations associated with agronomic traits and domestication.
- Hongbo Li
- , Shenhao Wang
- & Zhonghua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of selection in recently domesticated macadamia
Signatures of selection in recently domesticated macadamia
Macadamia is a recently domesticated nut crop. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of Hawaiian cultivar ‘Kau’ and conduct population genomic analyses to reveal the origin of Hawaiian cultivars and the genomic basis for one-step operation for the clonal crop domestication.
- Jishan Lin
- , Wenping Zhang
- & Ray Ming
-
Article
| Open Access The genomes of 204 Vitis vinifera accessions reveal the origin of European wine grapes
The genomes of 204 Vitis vinifera accessions reveal the origin of European wine grapes
Reports on the origin of European wine grapes are controversial. Here, the authors perform population genetics analyses on a large set of representative wine-making varieties and reveal a single domestication event at the origin of the entire germplasm followed by repeated introgression from wild populations.
- Gabriele Magris
- , Irena Jurman
- & Michele Morgante
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analyses provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits
Genomic analyses provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits
Spinach is a nutritious leafy vegetable growing worldwide. Here, the authors report a high-quality chromosome-scale reference genome assembly of spinach and genome resequencing of 305 accessions, and provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits.
- Xiaofeng Cai
- , Xuepeng Sun
- & Quanhua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access VviPLATZ1 is a major factor that controls female flower morphology determination in grapevine
VviPLATZ1 is a major factor that controls female flower morphology determination in grapevine
Unlike wild Vitis species, which produce either female or male flowers, modern grapevine cultivars form hermaphrodite flowers for self-pollination. Here, the authors report that the VviPLATZ1 (plant AT-rich sequence-and zinc-binding protein1) transcription factor functions in controlling female flower morphology determination.
- Pat Iocco-Corena
- , Jamila Chaïb
- & Harley M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access The barley immune receptor Mla recognizes multiple pathogens and contributes to host range dynamics
The barley immune receptor Mla recognizes multiple pathogens and contributes to host range dynamics
The genes underlying stripe rust host specificity between wheat and barley remain unknown. Here, the authors report that Rps6, Rps7 and Rps8 determine host species specificity in barley at different stages of the pathogen lifecycle and the barley powdery mildew immune receptor Mla8 and Rps7 are the same gene.
- Jan Bettgenhaeuser
- , Inmaculada Hernández-Pinzón
- & Matthew J. Moscou
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction of two MADS-box genes leads to growth phenotype divergence of all-flesh type of tomatoes
Interaction of two MADS-box genes leads to growth phenotype divergence of all-flesh type of tomatoes
The all-flesh type of tomato fruits is caused by mutation of the MBP3 gene, however, knocking down MBP3 in certain genotypes also affect plant and fruit development. Here, the authors show that a natural mutation of AGL11, a close homolog of MBP3, is responsible for the phenotypic divergence.
- Baowen Huang
- , Guojian Hu
- & Mondher Bouzayen
-
Comment
| Open Access Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Developing more productive and sustainable crops will be essential to achieving food security in coming decades. A core process in plant evolution has been the transfer of chloroplast-encoded genes to the nuclear genome. We propose reverting this process as a new approach to improve plant disease resistance and photosynthesis in future crops.
- Briardo Llorente
- , María Eugenia Segretin
- & Nicolás E. Blanco
-
Article
| Open Access A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean
A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean
While multiple resistance-to-Phytophthora sojae loci/alleles have been mapped in soybean, many of them have become ineffective to newly evolved isolates. Here, the authors show that a 27.7-kb nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to P. sojae in soybean.
- Weidong Wang
- , Liyang Chen
- & Jianxin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Three chromosome-level duck genome assemblies provide insights into genomic variation during domestication
Three chromosome-level duck genome assemblies provide insights into genomic variation during domestication
Domestic ducks are descended from the Mallard and have been bred for several purposes. Here the authors present three high-quality duck genome assemblies which recover previously missing genes and provide a rich resource of variants potentially related to domestication.
- Feng Zhu
- , Zhong-Tao Yin
- & Zhuo-Cheng Hou
-
Article
| Open Access The identification of grain size genes by RapMap reveals directional selection during rice domestication
The identification of grain size genes by RapMap reveals directional selection during rice domestication
Cloning quantitative trait loci (QTL) in crops is often slow and laborious. Here, the authors describe RapMap, a method to rapidly clone multiple QTL based on F2 gradient populations coupled with a co-segregation standard, and show how it can be used to identify genes controlling grain size in rice.
- Juncheng Zhang
- , Dejian Zhang
- & Yibo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic basis and adaptation trajectory of soybean from its temperate origin to tropics
Genetic basis and adaptation trajectory of soybean from its temperate origin to tropics
How soybean, a temperate origin crop, adapted to a tropical environment remains unclear. Here, the authors report Tof16, an ortholog of LHY, and the previously identified J locus, control soybean yield under short-day condition and loss of function of these two genes contributes to the adaptation to tropics.
- Lidong Dong
- , Chao Fang
- & Baohui Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Natural variation in a type-A response regulator confers maize chilling tolerance
Natural variation in a type-A response regulator confers maize chilling tolerance
The genetic basis of low-temperature tolerance in maize is unclear. Here, the authors show that the type-A Response Regulator 1 (ZmRR1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MPK8) are positive and negative regulators of maize chilling tolerance, and ZmRR1 is phosphorylated by ZmMPK8 during cold treatment.
- Rong Zeng
- , Zhuoyang Li
- & Shuhua Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Diversification of mandarin citrus by hybrid speciation and apomixis
Diversification of mandarin citrus by hybrid speciation and apomixis
To explore the nature of wild and cultivated mandarins, the authors carry out genomic analysis of diverse east Asian citrus. The discovery of a wild species Citrus ryukyuensis native to the Ryukyu islands and a new population of wild mainland Asian mandarin explains the origin and diversity of mandarins and their ability to reproduce apomictically.
- Guohong Albert Wu
- , Chikatoshi Sugimoto
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article
| Open Access Four chromosome scale genomes and a pan-genome annotation to accelerate pecan tree breeding
Four chromosome scale genomes and a pan-genome annotation to accelerate pecan tree breeding
Pecan is an important specialty crop that has experienced extensive interspecific hybridization and nearly-obligate outcrossing. Here, the authors assemble diploid genomes of four outbred genotypes, identify interspecific introgressions through comparative genomics analyses, and map QTLs associated with pest resistance.
- John T. Lovell
- , Nolan B. Bentley
- & Jennifer J. Randall
-
Article
| Open Access Population genomics of apricots unravels domestication history and adaptive events
Population genomics of apricots unravels domestication history and adaptive events
The evolutionary and domestication history of apricots is poorly understood. Here, the authors provide four apricot high-quality genome assemblies, the genomes of 578 accessions from natural and cultivated populations, and show that Chinese and European apricots constitute two different gene pools, resulting from independent domestication events.
- Alexis Groppi
- , Shuo Liu
- & Véronique Decroocq
-
Article
| Open Access Population-scale peach genome analyses unravel selection patterns and biochemical basis underlying fruit flavor
Population-scale peach genome analyses unravel selection patterns and biochemical basis underlying fruit flavor
Longhua Shui Mi (LHSM) is a representative of the Chinese Cling peaches that have been central in global peach genetic improvement. Here, the authors assemble the genome of LHSM and show convergent selection for sweetness yet divergent selection for acidity in eastern vs. western cultivars through population genomics analyses.
- Yang Yu
- , Jiantao Guan
- & Hua Xie
-
Article
| Open Access A recombined Sr26 and Sr61 disease resistance gene stack in wheat encodes unrelated NLR genes
A recombined Sr26 and Sr61 disease resistance gene stack in wheat encodes unrelated NLR genes
The tall wheat grass-derived stem rust resistance genes Sr26 and Sr61 are among a few ones that are effective to all current dominant races of stem rust, including Ug99. Here, the authors show that the two genes are present in a small non-recombinogenic segment but encode two unrelated NLR proteins.
- Jianping Zhang
- , Timothy C. Hewitt
- & Evans S. Lagudah
-
Article
| Open Access The tepary bean genome provides insight into evolution and domestication under heat stress
The tepary bean genome provides insight into evolution and domestication under heat stress
In contrast to common bean, tepary bean is highly adapted to heat and drought. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of tepary bean landrace and wild accession, discuss the possible mechanism for resilience to heat stress, and reveal a reduced disease resistance gene repertoire.
- Samira Mafi Moghaddam
- , Atena Oladzad
- & Phillip E. McClean
-
Article
| Open Access Subtelomeric assembly of a multi-gene pathway for antimicrobial defense compounds in cereals
Subtelomeric assembly of a multi-gene pathway for antimicrobial defense compounds in cereals
The genomic organization and origin of the avenacin biosynthetic gene cluster remain unknown. Here, the authors assemble the genome of diploid oat Avena strigosa, reveal the structure and organization of the consecutive genes, characterize the last two missing pathway steps, and investigate the origin of the pathway in cereals.
- Yan Li
- , Aymeric Leveau
- & Anne Osbourn
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome-scale assembly and analysis of biomass crop Miscanthus lutarioriparius genome
Chromosome-scale assembly and analysis of biomass crop Miscanthus lutarioriparius genome
The genus Miscanthus has great potential for bio-energy production due to its high biomass yield and strong stress resistance. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of the diploid M. lutarioriparius, showing it has an allotetraploid origin and an expanded number of genes in families related to stress resistance.
- Jiashun Miao
- , Qi Feng
- & Bin Han
-
Article
| Open Access O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase is involved in fine regulation of flowering time in winter wheat
O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase is involved in fine regulation of flowering time in winter wheat
Little is known about genes that regulate flowering time difference among winter wheat cultivars. Here, via map-based cloning, the authors show the role of an O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase TaOGT1 in regulating flowering time difference among winter wheat cultivars.
- Min Fan
- , Fang Miao
- & Liuling Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vital resources for comparative and agricultural research
Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vital resources for comparative and agricultural research
In order to interpret non-coding variants, information about regulatory elements in the genome is essential. Here, the authors annotate regulatory elements in chicken, pig and cattle, and characterize conservation of these elements between species.
- Colin Kern
- , Ying Wang
- & Huaijun Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Genome assembly and population genomic analysis provide insights into the evolution of modern sweet corn
Genome assembly and population genomic analysis provide insights into the evolution of modern sweet corn
Sweet corn is one of the most important vegetables in North America and has undergone different selection pressures than non-sweet cultivars. Here, the authors report its genome assembly and reveal the evolutionary history of modern sweet corn through population genomic analyses.
- Ying Hu
- , Vincent Colantonio
- & Marcio F. R. Resende Jr.
-
Article
| Open Access EARLY BUD-BREAK 1 and EARLY BUD-BREAK 3 control resumption of poplar growth after winter dormancy
EARLY BUD-BREAK 1 and EARLY BUD-BREAK 3 control resumption of poplar growth after winter dormancy
An AP2/ERF family gene EBB1 and a MADS-box gene SVL encode two regulators of poplar bud break. Here, the authors report another AP2/ERF transcription factor EBB3, which functions together with EBB1, SVL, and cell cycle progression promoter CYCD3.1 to regulate poplar bud break.
- Abdul Azeez
- , Yiru Chen Zhao
- & Victor B. Busov
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic determination of fruit traits of pear
Genome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic determination of fruit traits of pear
Studies of fruit quality traits in pears are lagging behind the other major fruit trees. Here, the authors conduct GWAS of fruit quality and phenological traits in a panel of 312 sand pear accessions using SNPs called from resequencing data, and reveal the involvement of a lignin formation-related protein in regulating stone cell development.
- Ming-Yue Zhang
- , Cheng Xue
- & Jun Wu
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in wheat
The genetic basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in wheat
The development of hybrid wheat cultivars is hampered by the lack of an effective way to control male fertility in breeding lines. Here, the authors report the identification of two restorer-of-fertility genes Rf1 and Rf3 that can restore fertility of wheat plants carrying Triticum timopheevii-type cytoplasmic male sterility.
- Joanna Melonek
- , Jorge Duarte
- & Ian Small
-
Article
| Open Access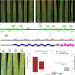 A membrane-bound ankyrin repeat protein confers race-specific leaf rust disease resistance in wheat
A membrane-bound ankyrin repeat protein confers race-specific leaf rust disease resistance in wheat
Winter wheat cultivar Forno harbors a race-specific leaf rust resistance locus Lr14a, but the causative gene is unknown. Here, the authors show that Lr14a encodes a membrane-localized protein containing ankyrin repeats and Lr14a-containing segments have been introgressed into the bread wheat gene pool multiple times.
- Markus C. Kolodziej
- , Jyoti Singla
- & Beat Keller
-
Article
| Open Access Genetics of nodulation in Aeschynomene evenia uncovers mechanisms of the rhizobium–legume symbiosis
Genetics of nodulation in Aeschynomene evenia uncovers mechanisms of the rhizobium–legume symbiosis
The establishment of symbiotic interaction between Aeschynomene evenia and photosynthetic bradyrhizobia doesn’t involve the canonical Nod factors and infection threads. Here, the authors assemble the draft genome of A. evenia and identify a receptor-like kinase in mediating the symbiotic interaction.
- Johan Quilbé
- , Léo Lamy
- & Jean-François Arrighi
-
Article
| Open Access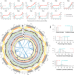 Comprehensive genomic resources related to domestication and crop improvement traits in Lima bean
Comprehensive genomic resources related to domestication and crop improvement traits in Lima bean
Lima bean is an important crop for improving food security in Latin America and elsewhere. Here, the authors assemble its genome, conduct population genomics analysis using genotyping-by-sequencing data, and identify differentially expressed genes between two pod developmental stages.
- Tatiana Garcia
- , Jorge Duitama
- & Maria Isabel Chacón-Sánchez
-
Article
| Open Access White pupae phenotype of tephritids is caused by parallel mutations of a MFS transporter
White pupae phenotype of tephritids is caused by parallel mutations of a MFS transporter
The white pupae (wp) phenotype has been used for decades to selectively remove females of tephritid species in genetic sexing, but the determining gene is unknown. Here, the authors show that wp phenotype is produced by parallel mutations in a Major Facilitator Superfamily domain containing gene across multiple species.
- Christopher M. Ward
- , Roswitha A. Aumann
- & Marc F. Schetelig
-
Article
| Open Access The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean
The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean
The accumulation of recombination events in selfing species may lead to a rapid fixation of both beneficial and deleterious mutations. Here, the authors resequence 781 soybean accessions, show purging of deleterious mutation during domestication, and report genome-wide associations for seed protein and oil traits.
- Myung-Shin Kim
- , Roberto Lozano
- & Soon-Chun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Cloning of wheat keto-acyl thiolase 2B reveals a role of jasmonic acid in grain weight determination
Cloning of wheat keto-acyl thiolase 2B reveals a role of jasmonic acid in grain weight determination
It has been reported that several phytohormones are involved in the regulation of grain weight, but the role of jasmonic acids (JA) remains elusive. Here, via bulked segregant analysis (BSA)-based cloning, the authors show keto-acyl thiolase 2B involved in β-oxidation during JA synthesis is a positive regulator of wheat grain weight.
- Yun Chen
- , Yan Yan
- & Jin-Ying Gou
-
Article
| Open Access Two nuclear effectors of the rice blast fungus modulate host immunity via transcriptional reprogramming
Two nuclear effectors of the rice blast fungus modulate host immunity via transcriptional reprogramming
Plant pathogens secrete various effectors to manipulate host immunity. Here, Kim et al. describe two Magnaporthe oryzae effectors that translocate into the nuclei of infected rice cells and reprogram expression of immunity-associated genes, increasing susceptibility to hemibiotrophic pathogens.
- Seongbeom Kim
- , Chi-Yeol Kim
- & Yong-Hwan Lee
-
Article
| Open Access FIS1 encodes a GA2-oxidase that regulates fruit firmness in tomato
FIS1 encodes a GA2-oxidase that regulates fruit firmness in tomato
Fruit firmness is an important target for breeders and a key determinant of shelf life for many fruits. Here the authors show that mutating tomato FIS1, a GA2-oxidase, increases the concentration of bioactive gibberellins, enhances cutin and wax biosynthesis and increases fruit firmness.
- Ren Li
- , Shuai Sun
- & Xia Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Plant hairy roots enable high throughput identification of antimicrobials against Candidatus Liberibacter spp.
Plant hairy roots enable high throughput identification of antimicrobials against Candidatus Liberibacter spp.
The putative causal agent of citrus greening Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) cannot be cultured, which hampers finding new therapies to control this devastating disease. Here, the authors show that hairy roots support CLas propagation and enable high throughput antimicrobial screening.
- Sonia Irigoyen
- , Manikandan Ramasamy
- & Kranthi K. Mandadi
-
Article
| Open Access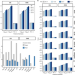 Evolutionary and functional genomics of DNA methylation in maize domestication and improvement
Evolutionary and functional genomics of DNA methylation in maize domestication and improvement
Variation and evolution of DNA methylation during maize domestication remain largely unknown. Here, the authors generate genome and methylome sequencing data as well as HiChIP-based interactome data to investigate the adaptive and phenotypic consequences of methylation variations in maize.
- Gen Xu
- , Jing Lyu
- & Jinliang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access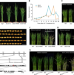 Natural variations of SLG1 confer high-temperature tolerance in indica rice
Natural variations of SLG1 confer high-temperature tolerance in indica rice
Understanding the mechanism of high-temperature tolerance will help to breed crops adaptive to warming climate. Here, the authors show SLG1, a cytosolic tRNA 2-thiolation protein 2 encoding gene, is differentiated between the two Asian cultivated rice subspecies and confers high temperature tolerance of indica rice.
- Yufang Xu
- , Li Zhang
- & Shanguo Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Genome biology of the paleotetraploid perennial biomass crop Miscanthus
Genome biology of the paleotetraploid perennial biomass crop Miscanthus
The perennial grass Miscanthus is a promising biomass crop. Here, via genomics and transcriptomics, the authors reveal its allotetraploid origin, characterize gene expression associated with rhizome development and nutrient recycling, and describe the hybrid origin of the triploid M. x giganteus.
- Therese Mitros
- , Adam M. Session
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article
| Open Access Carotenoids modulate kernel texture in maize by influencing amyloplast envelope integrity
Carotenoids modulate kernel texture in maize by influencing amyloplast envelope integrity
Very little is known about how vitreous endosperm in the mature maize kernel is created. Here, via map-based cloning, the authors find that mutation of a β-carotene hydroxylase 3 encoding gene Ven1 affects carotenoids and lipids composition, which consequently influences amyloplast envelope integrity.
- Haihai Wang
- , Yongcai Huang
- & Yongrui Wu
-
Article
| Open Access MSH1-induced heritable enhanced growth vigor through grafting is associated with the RdDM pathway in plants
MSH1-induced heritable enhanced growth vigor through grafting is associated with the RdDM pathway in plants
The meiotic transmissibility and progeny phenotypic influence of graft-mediated epigenetic changes remain unclear. Here, the authors use the msh1 mutant in the rootstock to trigger heritable enhanced growth vigor in Arabidopsis and tomato, and show it is associated with the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway.
- Hardik Kundariya
- , Xiaodong Yang
- & Sally A. Mackenzie
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome-level genome assembly of a parent species of widely cultivated azaleas
Chromosome-level genome assembly of a parent species of widely cultivated azaleas
Azaleas are one of the most diverse ornamental plants and have cultural and economic importance. Here, the authors report a chromosome-scale genome assembly for the primary ancestor of the azalea cultivar Rhododendro simsi and identify transcription factors that may function in flower coloration at different stages.
- Fu-Sheng Yang
- , Shuai Nie
- & Jian-Feng Mao
-
Perspective
| Open Access Multiplying the efficiency and impact of biofortification through metabolic engineering
Multiplying the efficiency and impact of biofortification through metabolic engineering
Biofortification is an effective means to reduce micronutrient malnutrition. Here, the authors review recent advances in biofortification and propose stacking multiple micronutrient traits into high-yielding varieties through the combination of conventional breeding and genetic engineering approaches.
- Dominique Van Der Straeten
- , Navreet K. Bhullar
- & Howarth Bouis
-
Article
| Open Access MYB61 is regulated by GRF4 and promotes nitrogen utilization and biomass production in rice
MYB61 is regulated by GRF4 and promotes nitrogen utilization and biomass production in rice
The molecular connection between nitrogen utilization efficiency (NUE) and biomass production is unclear. Here, the authors show that differences in NUE and cellulose biogenesis between rice indica and japonica subspecies can be explained by variation at the MYB61 locus, which is regulated by the NUE regulator GRF4.
- Yihong Gao
- , Zuopeng Xu
- & Yihua Zhou

 Chromosome evolution and the genetic basis of agronomically important traits in greater yam
Chromosome evolution and the genetic basis of agronomically important traits in greater yam