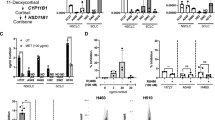
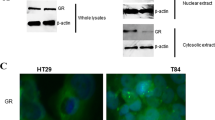
Abstract
Glucocorticoids (GC) have important anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic activities. Initially thought to be exclusively produced by the adrenal glands, there is now increasing evidence for extra-adrenal sources of GCs. We have previously shown that the intestinal epithelium produces immunoregulatory GCs and that intestinal steroidogenesis is regulated by the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1). As LRH-1 has been implicated in the development of colon cancer, we here investigated whether LRH-1 regulates GC synthesis in colorectal tumors and whether tumor-produced GCs suppress T-cell activation. Colorectal cancer cell lines and primary tumors were found to express steroidogenic enzymes and regulatory factors required for the de novo synthesis of cortisol. Both cell lines and primary tumors constitutively produced readily detectable levels of cortisol, as measured by radioimmunoassay, thin-layer chromatography and bioassay. Whereas overexpression of LRH-1 significantly increased the expression of steroidogenic enzymes and the synthesis of cortisol, downregulation or inhibition of LRH-1 effectively suppressed these processes, indicating an important role of LRH-1 in colorectal tumor GC synthesis. An immunoregulatory role of tumor-derived GCs could be further confirmed by demonstrating a suppression of T-cell activation. This study describes for the first time cortisol synthesis in a non-endocrine tumor in humans, and suggests that the synthesis of bioactive GCs in colon cancer cells may account as a novel mechanism of tumor immune escape.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
colorectal carcinoma
- CYP:
-
cytochrome P450
- GC:
-
glucocorticoids
- LRH-1:
-
liver receptor homolog-1/NR5A2
- SF-1:
-
steroidogenic factor-1/NR5A1
- StAR:
-
steroid acute regulatory protein
References
Atanasov AG, Leiser D, Roesselet C, Noti M, Corazza N, Schoonjans K et al. (2008). Cell cycle-dependent regulation of extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial cells. FASEB J 22: 4117–4125.
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby C, Brennan T, Wendling O et al. (2004). Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1 cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell 15: 499–509.
Brunner T, Arnold D, Wasem C, Herren S, Frutschi C . (2001). Regulation of cell death and survival in intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ 8: 706–714.
Camus M, Tosolini M, Mlecnik B, Pages F, Kirilovsky A, Berger A et al. (2009). Coordination of intratumoral immune reaction and human colorectal cancer recurrence. Cancer Res 69: 2685–2693.
Chen JJ, Sun Y, Nabel GJ . (1998). Regulation of the proinflammatory effects of Fas ligand (CD95L). Science 282: 1714–1717.
Cima I, Corazza N, Dick B, Fuhrer A, Herren S, Jakob S et al. (2004). Intestinal epithelial cells synthesize glucocorticoids and regulate T cell activation. J Exp Med 200: 1635–1646.
Cima I, Fuhrer A, Brunner T . (2006). Antagonistic and synergistic effects of glucocorticoids and IL-7 on CD4+ T cell activation. Immunol Lett 106: 99–102.
Coste A, Dubuquoy L, Barnouin R, Annicotte JS, Magnier B, Notti M et al. (2007). LRH-1-mediated glucocorticoid synthesis in enterocytes protects against inflammatory bowel disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 13098–13103.
Dardis A, Miller WL . (2003). Dexamethasone does not exert direct intracellular feedback on steroidogenesis in human adrenal NCI-H295A cells. J Endocrinol 179: 131–142.
Davies E, MacKenzie SM . (2003). Extra-adrenal production of corticosteroids. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30: 437–445.
Davies RJ, Miller R, Coleman N . (2005). Colorectal cancer screening: prospects for molecular stool analysis. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 199–209.
Finn OJ . (2008). Cancer immunology. N Engl J Med 358: 2704–2715.
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pages C et al. (2006). Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 313: 1960–1964.
Griffith TS, Ferguson TA . (1997). The role of FasL-induced apoptosis in immune privilege. Immunol Today 18: 240–244.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70.
He N, Park K, Zhang Y, Huang J, Lu S, Wang L . (2008). Epigenetic inhibition of nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner is associated with and regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Gastroenterology 134: 793–802.
Igney FH, Krammer PH . (2002). Immune escape of tumors: apoptosis resistance and tumor counterattack. J Leukoc Biol 71: 907–920.
Kempna P, Hofer G, Mullis PE, Fluck CE . (2007). Pioglitazone inhibits androgen production in NCI-H295R cells by regulating gene expression of CYP17 and HSD3B2. Mol Pharmacol 71: 787–798.
Lee YK, Choi YH, Chua S, Park YJ, Moore DD . (2006). Phosphorylation of the hinge domain of the nuclear hormone receptor LRH-1 stimulates transactivation. J Biol Chem 281: 7850–7855.
MacKenzie SM, Clark CJ, Fraser R, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Connell JM, Davies E . (2000). Expression of 11beta-hydroxylase and aldosterone synthase genes in the rat brain. J Mol Endocrinol 24: 321–328.
Miller WL . (2008). Steroidogenic enzymes. Endocr Dev 13: 1–18.
Mueller M, Atanasov A, Cima I, Corazza N, Schoonjans K, Brunner T . (2007). Differential regulation of glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial versus adrenocortical cell lines. Endocrinology 148: 1445–1453.
Mueller M, Cima I, Noti M, Fuhrer A, Jakob S, Dubuquoy L et al. (2006). The nuclear receptor LRH-1 critically regulates extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in the intestine. J Exp Med 203: 2057–2062.
Noti M, Sidler D, Brunner T . (2009). Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in the intestinal epithelium: more than a drop in the ocean? Semin Immunopathol 31: 237–248.
Pages F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R et al. (2005). Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 353: 2654–2666.
Parker KL, Rice DA, Lala DS, Ikeda Y, Luo X, Wong M et al. (2002). Steroidogenic factor 1: an essential mediator of endocrine development. Recent Prog Horm Res 57: 19–36.
Pazirandeh A, Xue Y, Rafter I, Sjovall J, Jondal M, Okret S . (1999). Paracrine glucocorticoid activity produced by mouse thymic epithelial cells. FASEB J 13: 893–901.
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU . (2000). How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev 21: 55–89.
Schoonjans K, Dubuquoy L, Mebis J, Fayard E, Wendling O, Haby C et al. (2005). Liver receptor homolog 1 contributes to intestinal tumor formation through effects on cell cycle and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 2058–2062.
Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ et al. (2001). IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 410: 1107–1111.
Smyth MJ, Thia KY, Street SE, Cretney E, Trapani JA, Taniguchi M et al. (2000). Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells. J Exp Med 191: 661–668.
Takeda Y, Miyamori I, Yoneda T, Iki K, Hatakeyama H, Blair IA et al. (1994). Synthesis of corticosterone in the vascular wall. Endocrinology 135: 2283–2286.
Vacchio MS, Papadopoulos V, Ashwell JD . (1994). Steroid production in the thymus: implications for thymocyte selection. J Exp Med 179: 1835–1846.
van den Broek ME, Kagi D, Ossendorp F, Toes R, Vamvakas S, Lutz WK et al. (1996). Decreased tumor surveillance in perforin-deficient mice. J Exp Med 184: 1781–1790.
Wahl SM, Wen J, Moutsopoulos N . (2006). TGF-beta: a mobile purveyor of immune privilege. Immunol Rev 213: 213–227.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mario Noti, Pamela Bianchi, Andrea Hirsch, Gabi Hofer and Andreas Kappeler for technical help and advice, the members of the Division of Clinical Histopathology for preparation of tissue sections, and Sam Okret and Kristina Schoonjans for reagents. This work was supported by research grants from Oncosuisse (OCS-02025-02-2007) and the Swiss National Science Foundation (310000-121854) to TB. DS was supported by an MD-PhD fellowship from the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidler, D., Renzulli, P., Schnoz, C. et al. Colon cancer cells produce immunoregulatory glucocorticoids. Oncogene 30, 2411–2419 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.629
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.629
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The cancer-immune dialogue in the context of stress
Nature Reviews Immunology (2024)
-
Liver receptor homolog-1: structures, related diseases, and drug discovery
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Delineating the role of nuclear receptors in colorectal cancer, a focused review
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
Human lung carcinomas synthesize immunoregulatory glucocorticoids
Genes & Immunity (2023)
-
Association of body-shape phenotypes with imaging measures of body composition in the UK Biobank cohort: relevance to colon cancer risk
BMC Cancer (2021)