Abstract
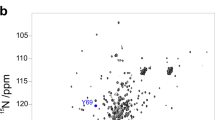
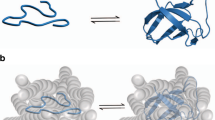
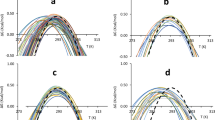
Multidimensional NMR studies of proteins in unfolded and partially folded states give unique insights into their structures and dynamics and provide new understanding of protein folding and function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyson, H.J. & Wright, P.E. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 47, 369–395 (1996).
Dobson, C.M. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 504–507 (1998).
Roder, H., Elöve, G.A. & Englander, S.W. Nature 335, 700– 704 (1988).
Udgaonkar, J.B. & Baldwin, R.L. Nature 335, 694–699 (1988).
Braun, D., Wider, G. & Wüthrich, K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 8466– 8469 (1994).
Zhang, O., Forman-Kay, J.D., Shortle, D. & Kay, L.E. J. Biomol. NMR 9, 181–200 (1997).
Logan, T.M., Thériault, Y. & Fesik, S.W. J. Mol. Biol. 236, 637– 648 (1994).
Alexandrescu, A.T., Abeygunawardana, C. & Shortle, D. Biochemistry 33, 1063– 1072 (1994).
Eliezer, D., Yao, J., Dyson, H.J. & Wright, P.E. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 148–155 ( 1998).
Baum, J., Dobson, C.M., Evans, P.A. & Hanley, C. Biochemistry 28, 7–13 ( 1989).
Dyson, H.J. & Wright, P.E. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 20, 519–538 ( 1991).
Wright, P.E., Dyson, H.J. & Lerner, R.A. Biochemistry 27, 7167– 7175 (1988).
Wishart, D.S. & Sykes, B.D. Meth. Enz. 239, 363–392 (1994).
Smith, L.J. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 255, 494– 506 (1996).
Smith, L.J., Fiebig, K.M., Schwalbe, H. & Dobson, C.M. Folding & Design 1, R95–R106(1996).
Zhang, O. & Forman-Kay, J.D. Biochemistry 36 , 3959–3970 (1997).
Pan, H., Barbar, E., Barany, G. & Woodward, C. Biochemistry 34, 13974–13981 ( 1995).
Dyson, H.J., Merutka, G., Waltho, J.P., Lerner, R.A. & Wright, P.E. J. Mol. Biol. 226, 795–817 (1992).
Dyson, H.J. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 226, 819– 835 (1992).
Zhang, O., Kay, L.E., Shortle, D. & Forman-Kay, J.D. J. Mol. Biol. 272, 9–20 ( 1997).
Hughson, F.M., Wright, P.E. & Baldwin, R.L. Science 249, 1544– 1548 (1990).
Schulman, B.A., Kim, P.S., Dobson, C.M. & Redfield, C. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 630–634 ( 1997).
Jennings, P.A. & Wright, P.E. Science 262, 892–896 (1993).
Harding, M.M., Williams, D.H. & Woolfson, D.N. Biochemistry 30, 3120– 3128 (1991).
Neri, D., Billeter, M., Wider, G. & Wüthrich, K. Science 257, 1559–1563 ( 1992).
Gillespie, J.R. & Shortle, D. J. Mol. Biol. 268, 158–169 ( 1997).
Gillespie, J.R. & Shortle, D. J. Mol. Biol. 268, 170–184 ( 1997).
Brutscher, B., Brüschweiler, R. & Ernst, R.R. Biochemistry 36, 13043– 13053 (1997).
Farrow, N.A., Zhang, O., Forman-Kay, J.D. & Kay, L.E. Biochemistry 36, 2390–2402 (1997).
Frank, M.K., Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. Prot. Sci. 4, 2605– 2615 (1995).
Alexandrescu, A.T. & Shortle, D. J. Mol. Biol. 242, 527–546 ( 1994).
Plaxco, K.W. & Gross, M. Nature 386, 657–659 (1997).
Daughdrill, G.W., Hanely, L.J. & Dahlquist, F.W. Biochemistry 37, 1076– 1082 (1998).
Penkett, C.J., Redfield, C., Dodd, I., et al. J. Mol. Biol. 274, 152– 159 (1997).
Radhakrishnan, I. et al. Cell 91, 741–752 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Eliezer, P. Jennings and S. Cavagnero for assistance with preparation of the figures. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dyson, H., Wright, P. Equilibrium NMR studies of unfolded and partially folded proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 5 (Suppl 7), 499–503 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/739
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/739
This article is cited by
-
Using azobenzene photocontrol to set proteins in motion
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2021)
-
Role of ORF4 in Hepatitis E virus regulation: analysis of intrinsically disordered regions
Journal of Proteins and Proteomics (2021)
-
Zn2+-binding in the glutamate-rich region of the intrinsically disordered protein prothymosin-alpha
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2018)
-
Resonance assignment of disordered protein with repetitive and overlapping sequence using combinatorial approach reveals initial structural propensities and local restrictions in the denatured state
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2016)
-
Evolutionary Pareto-optimization of stably folding peptides
BMC Bioinformatics (2008)