Abstract
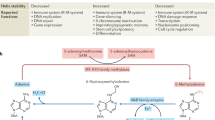
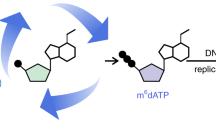
The DNA-adenine modification N6-methyladenine (6mA), initially thought to be mainly restricted to prokaryotes and certain unicellular eukaryotes, has recently been found in metazoans. Proposed functions vary from gene activation to transposon suppression. However, since most metazoan genomes possess 5-methylcytosine (5mC) as a dominant epigenetic mark, it raises the question of why 6mA is required. This Perspective summarizes the latest discoveries and suggests potential functional roles for 6mA in metazoan genomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiseman, H. & Halliwell, B. Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem. J. 313, 17–29 (1996).
Klose, R.J. & Bird, A.P. Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem. Sci. 31, 89–97 (2006).
Wion, D. & Casadesús, J. N6-methyl-adenine: an epigenetic signal for DNA-protein interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 183–192 (2006).
Gorovsky, M.A., Hattman, S. & Pleger, G.L. (6N)methyl adenine in the nuclear DNA of a eucaryote, Tetrahymena pyriformis . J. Cell Biol. 56, 697–701 (1973).
Hattman, S. DNA-[adenine] methylation in lower eukaryotes. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 70, 550–558 (2005).
Ratel, D., Ravanat, J.L., Berger, F. & Wion, D. N6-methyladenine: the other methylated base of DNA. BioEssays 28, 309–315 (2006).
Vanyushin, B.F., Alexandrushkina, N.I. & Kirnos, M.D. N6-Methyladenine in mitochondrial DNA of higher plants. FEBS Lett. 233, 397–399 (1988).
Adams, R.L., McKay, E.L., Craig, L.M. & Burdon, R.H. Methylation of mosquito DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 563, 72–81 (1979).
Fedoreyeva, L.I. & Vanyushin, B.F.N. N(6)-Adenine DNA-methyltransferase in wheat seedlings. FEBS Lett. 514, 305–308 (2002).
Huang, W. et al. Determination of DNA adenine methylation in genomes of mammals and plants by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. RSC Advances 5, 64046–64054 (2015).
Luo, G.Z., Blanco, M.A., Greer, E.L., He, C. & Shi, Y. DNA N6-methyladenine: a new epigenetic mark in eukaryotes? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 705–710 (2015).
Fu, Y. et al. N6-methyldeoxyadenosine marks active transcription start sites in Chlamydomonas. Cell 161, 879–892 (2015). This work revealed the genomic distribution and functional implications of 6mA in positioning nucleosomes in eukaryotes for the first time.
Greer, E.L. et al. DNA methylation on N6-adenine in C. elegans . Cell 161, 868–878 (2015). This work provided comprehensive evidence showing the presence of 6mA in metazoans for the first time. It also implies that 6mA is an inheritable DNA mark.
Zhang, G. et al. N6-methyladenine DNA modification in Drosophila . Cell 161, 893–906 (2015). This group discovered 6mA in a metazoan ( Drosophila ) at the same time as the two publications described in refs. 12 and 13 and proposed a potential 6mA demethylase.
O'Brown, Z.K. & Greer, E.L. N6-Methyladenine: a conserved and dynamic DNA mark. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 945, 213–246 (2016).
Koziol, M.J. et al. Identification of methylated deoxyadenosines in vertebrates reveals diversity in DNA modifications. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 23, 24–30 (2016). This work reported the presence of 6mA in vertebrates. It showed very low levels of 6mA that are depleted at transcription start sites.
Wu, T.P. et al. DNA methylation on N6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Nature 532, 329–333 (2016). This work studied 6mA in mouse embryonic stem cells by combining antibody-based 6mA enrichment with SMRT sequencing. It showed that 6mA deposition could silence LINE-1 transposons.
Liu, J. et al. Abundant DNA 6mA methylation during early embryogenesis of zebrafish and pig. Nat. Commun. 7, 13052 (2016). This work reported a significant elevation of the DNA 6mA level during early embryogenesis of vertebrates. The dynamic changes of 6mA may play critical roles in facilitating early embryo development.
Pfeifer, G.P. Epigenetics: an elusive DNA base in mammals. Nature 532, 319–320 (2016).
Schiffers, S. et al. Quantitative LC-MS provides no evidence for m6dA or m4dC in the genome of mouse embryonic stem cells and tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 10.1002/anie.201700424 (2017).
Suzuki, M.M. & Bird, A. DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 465–476 (2008).
Jones, P.A. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 484–492 (2012).
Pratt, K. & Hattman, S. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylation and chromatin organization in Tetrahymena thermophila . Mol. Cell. Biol. 1, 600–608 (1981).
Bromberg, S., Pratt, K. & Hattman, S. Sequence specificity of DNA adenine methylase in the protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila . J. Bacteriol. 150, 993–996 (1982).
Luo, G.Z. et al. Characterization of eukaryotic DNA N(6)-methyladenine by a highly sensitive restriction enzyme-assisted sequencing. Nat. Commun. 7, 11301 (2016).
Messerschmidt, D.M., Knowles, B.B. & Solter, D. DNA methylation dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the germline and preimplantation embryos. Genes Dev. 28, 812–828 (2014).
Smith, Z.D. & Meissner, A. DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 204–220 (2013).
Kohli, R.M. & Zhang, Y. TET enzymes, TDG and the dynamics of DNA demethylation. Nature 502, 472–479 (2013).
Wang, X. et al. Structural basis of N6-adenosine methylation by the METTL3–METTL14 complex. Nature 534, 575–578 (2016).
Śledź, P. & Jinek, M. Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)A writer complex. eLife 5, e18434 (2016).
Yue, Y., Liu, J. & He, C. RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev. 29, 1343–1355 (2015).
Wang, P., Doxtader, K.A. & Nam, Y. Structural basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 63, 306–317 (2016).
Iyer, L.M., Zhang, D. & Aravind, L. Adenine methylation in eukaryotes: apprehending the complex evolutionary history and functional potential of an epigenetic modification. BioEssays 38, 27–40 (2016).
Jia, G. et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 885–887 (2011).
Zheng, G. et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol. Cell 49, 18–29 (2013).
Liu, F. et al. ALKBH1-mediated tRNA demethylation regulates translation. Cell 167, 1897 (2016).
Jones, P.L. et al. Methylated DNA and MeCP2 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nat. Genet. 19, 187–191 (1998).
Viré, E. et al. The Polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 439, 871–874 (2006).
Tsumura, A. et al. Maintenance of self-renewal ability of mouse embryonic stem cells in the absence of DNA methyltransferases Dnmt1, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. Genes Cells 11, 805–814 (2006).
Wenzel, D., Palladino, F. & Jedrusik-Bode, M. Epigenetics in C. elegans: facts and challenges. Genesis 49, 647–661 (2011).
Tweedie, S. et al. Vestiges of a DNA methylation system in Drosophila melanogaster? Nat. Genet. 23, 389–390 (1999).
Heyn, H. & Esteller, M. An adenine code for DNA: a second life for N6-methyladenine. Cell 161, 710–713 (2015).
Helbock, H.J. et al. DNA oxidation matters: the HPLC-electrochemical detection assay of 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine and 8-oxo-guanine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 288–293 (1998).
Olarerin-George, A.O. & Hogenesch, J.B. Assessing the prevalence of mycoplasma contamination in cell culture via a survey of NCBI's RNA-seq archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 2535–2542 (2015).
Hattman, S., Kenny, C., Berger, L. & Pratt, K. Comparative study of DNA methylation in three unicellular eucaryotes. J. Bacteriol. 135, 1156–1157 (1978).
Feng, S. et al. Conservation and divergence of methylation patterning in plants and animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 8689–8694 (2010).
Liu, J. et al. A METTL3–METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10, 93–95 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, GZ., He, C. DNA N6-methyladenine in metazoans: functional epigenetic mark or bystander?. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24, 503–506 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3412
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3412
This article is cited by
-
A DNA adenine demethylase impairs PRC2-mediated repression of genes marked by a specific chromatin signature
Genome Biology (2023)
-
Genome-wide deposition of 6-methyladenine in human DNA reduces the viability of HEK293 cells and directly influences gene expression
Communications Biology (2023)
-
METTL4-mediated nuclear N6-deoxyadenosine methylation promotes metastasis through activating multiple metastasis-inducing targets
Genome Biology (2022)
-
Context-dependent DNA polymerization effects can masquerade as DNA modification signals
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Bacterial N4-methylcytosine as an epigenetic mark in eukaryotic DNA
Nature Communications (2022)