Dendritic cells as orchestrators of immune responses
Learn more about this and other topics in our April issue

Learn more about this and other topics in our April issue

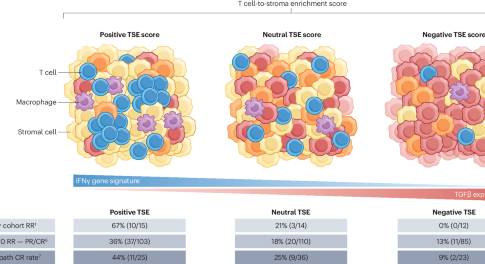
T cell infiltration in the tumour microenvironment (TME) is a prerequisite for sustained antitumour immune responses. However, identifying predictive biomarkers that quantify T cell infiltration and the presence of proinflammatory TMEs associated with immune-checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) response for clinical implementation has proved challenging. Here, we highlight a study that validates a T cell-to-stroma enrichment score generated from RNA sequencing data as a novel biomarker for ICI response in patients with urothelial carcinoma.