Volume 6
-
No. 12 December 2011
Computer-aided reconstruction of a lineage tree from time-lapse phase-contrast microscopy image sequence data. Shown in grayscale is a single image frame with automated segmentation and tracking results. The lineage tree showing patterns of population growth is overlaid in color. Image adapted from the protocol by Winter et al.
-
No. 11 November 2011
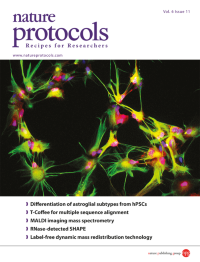
Human astrocytes with functional properties and regional specificity are generated by the protocol described in this issue through the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells to the gliogenic stage. These astrocytes have a star-like appearance, express the glial progenitor marker S100β (red), and at mature stages form filaments expressing GFAP (green). Image taken from the protocol by Krencik & Zhang.
-
No. 10 October 2011
The orientation of helices across RNA junctions is specified using three interhelical Euler angles that define rotations around helices (γh and αh) and an interhelical bend angle (βh). The angles can be visualized using 3D plots. Shown in gray are the topologically allowed interhelical orientations across a dinucleotide bulge junction. Image taken from protocol by Al-Hashimi et al.
-
No. 9 September 2011
A monkey prefrontal layer III pyramidal cell injected with Lucifer yellow and imaged at high resolution on a confocal microscope. Final rendition is the product of tiling multiple 3D stacks. Image from the protocol by Dumitriu et al. (High throughput, detailed, cell-specific neuroanatomy of dendritic spines using microinjection and confocal microscopy. DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2011.389), in collaboration with J. Hao and TheVisualMD. Cover design by Jamel Wooten.
-
No. 8 August 2011
Astrocytes generated at physiological oxygen tension from human embryonic stem cellderived neural precursors. Immature astrocytes express vimentin (green), whereas a more mature subpopulation also expresses glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, red). Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). The protocol describes efficient neural precursor cell, motor neuron and dopaminergic neuron generation at 3% oxygen.
-
No. 7 July 2011
Hanging drop culture. Embryoid bodies for the differentiation of embryonic stem cells in the embryonic stem cell test are generated by pipetting a single-cell suspension onto the lid of a cell culture dish. The cells aggregate at the bottom of the drop by gravitational force, thereby forming the embryoid body.
-
No. 6 June 2011
A confocal image of FGF-2induced corneal new blood vessels (CD31, red) and lymphatic vessels (LYVE-1, green). Corneal lymphatic networks comprise large-diameter vessels with blunt-ended vascular sprouts, whereas blood vessel networks are composed of smaller microvessels at higher densities relative to lymphatics.
-
No. 5 May 2011
A transgenic Cynops pyrrhogaster newt at swimming larva stage showing EGFP expression evenly in the whole body. Shown approximately 4 weeks after co-injection of a DNA construct and I-SceI meganuclease into a fertilized egg.
-
No. 4 April 2011
Triple fluorescence co-detection of sterols (red), the cytokinesis-specific KNOLLE syntaxin (cyan) and an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) fusion of the small GTPase ARF1 (ARF1-EGFP) in dividing root epidermal cells of Arabidopsis thaliana. The protocol visualizes fluorescent filipin-sterol complexes in plants expressing ARF1-EGFP by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cover design by Jamel Wooten.
-
No. 3 March 2011
Life depends on specific interactions between molecules, exemplified here by binding of IP3 to the receptor through which it evokes calcium signals. Rossi and Taylor describe a protocol that uses fluorescence polarization to allow nondisruptive measurement of the association of a fluorescent ligand with a larger molecule. Image from the protocol by Rossi and Taylor. Cover design by Jamel Wooten.
-
No. 2 February 2011
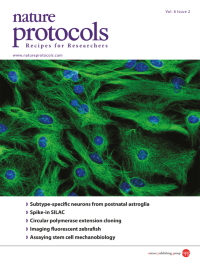
A confocal micrograph showing astroglia from the early postnatal mouse cerebral cortex in culture. The cells are immunostained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, green) and with DAPI to show nuclei (blue). Image from the protocol by Heinrich et al. Cover design by Jamel Wooten.
-
No. 1 January 2011
Soybean hypernodulating mutant plants are fed aqueous plant extracts with the petiole-feeding technique. The technique is an effective tool for the delivery of solutions that allow the investigation of the physiological and morphological development of the plant in response to the presence of bioactive compounds. Image is from the protocol by Lin et al. on p. 36. Cover design by Jamel Wooten.