Abstract
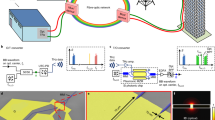
In communications, the frequency range 0.1–30 THz is essentially terra incognita. Recently, research has focused on this terahertz gap, because the high carrier frequencies promise unprecedented channel capacities1. Indeed, data rates of 100 Gbit s−1 were predicted2 for 2015. Here, we present, for the first time, a single-input and single-output wireless communication system at 237.5 GHz for transmitting data over 20 m at a data rate of 100 Gbit s−1. This breakthrough results from combining terahertz photonics and electronics, whereby a narrow-band terahertz carrier is photonically generated by mixing comb lines of a mode-locked laser in a uni-travelling-carrier photodiode. The uni-travelling-carrier photodiode output is then radiated over a beam-focusing antenna. The signal is received by a millimetre-wave monolithic integrated circuit comprising novel terahertz mixers and amplifiers. We believe that this approach provides a path to scale wireless communications to Tbit s−1 rates over distances of >1 km.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleine-Ostmann, T. & Nagatsuma, T. A review on terahertz communications research. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 32, 143–171 (2011).
Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nature Photon. 1, 97–105 (2007).
International Telcommunications Union. ITU Recommendation P.676-9, Attenuation by Atmospheric Gases (ITU, 2012).
Su, K., Moeller, L., Barat, R. B. & Federici, J. F. Experimental comparison of performance degradation from terahertz and infrared wireless links in fog. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29, 179–184 (2012).
Su, K., Moeller, L., Barat, R. B. & Federici, J. F. Experimental comparison of terahertz and infrared data signal attenuation in dust clouds. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29, 2360–2366 (2012).
Kanno, A. et al. Optical and millimeter-wave radio seamless MIMO transmission based on a radio over fiber technology. Opt. Express 20, 29395–29403 (2012).
Li, X. et al. Fiber-wireless transmission system of 108 Gb/s data over 80 km fiber and 2 × 2 multiple-input multiple-output wireless links at 100 GHz W-band frequency. Opt. Lett. 37, 5106–5108 (2012).
Pang, X. et al. 100 Gbit/s hybrid optical fiber-wireless link in the W-band (75–110 GHz). Opt. Express 19, 24944–24949 (2011).
Federici, J. & Moeller, L. Review of terahertz and subterahertz wireless communications. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 111101 (2010).
Song, H. J. & Nagatsuma, T. Present and future of terahertz communications. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Tech. 1, 256–263 (2011).
Schneider, G. J., Murakowski, J. A., Schuetz, C. A., Shi, S. & Prather, D. W. Radiofrequency signal-generation system with over seven octaves of continuous tuning. Nature Photon. 7, 118–122 (2013).
Stöhr, A. et al. Millimeter-wave photonic components for broadband wireless systems. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 58, 3071–3082 (2010).
Lin, C.-T. et al. 31 Gbps RoF system employing adaptive bit-loading OFDM modulation at 60 GHz. in Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, paper OWT7 (Optical Society of America, 2011).
Chien, H-C., Chowdhury, A., Jia, Z., Hsueh, Y-T. & Chang, G-K. 60 GHz millimeter-wave gigabit wireless services over long-reach passive optical network using remote signal regeneration and upconversion. Opt. Express 17, 3016–3024 (2009).
Kanno, A. et al. 20-Gb/s QPSK W-band (75-110 GHz) wireless link in free space using radio-over-fiber technique. IEICE Electron. Express 8, 612–617 (2011).
Kanno, A. et al. 40 Gb/s W-band (75-110 GHz) 16-QAM radio-over-fiber signal generation and its wireless transmission. Opt. Express 19, B56–B63 (2011).
Hirata, A. et al. 120-GHz-band millimeter-wave photonic wireless link for 10-Gb/s data transmission. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 54, 1937–1944 (2006).
Hirata, A. et al. Transmission characteristics of 120-GHz-band wireless link using radio-on-fiber technologies. J. Lightwave Technol. 26, 2338–2344 (2008).
Song, H. J. et al. 8 Gbit/s wireless data transmission at 250 GHz. Electron. Lett. 45, 1121–1122 (2009).
Song, H. J. et al. 24 Gbit/s data transmission in 300 GHz band for future terahertz communications. Electron. Lett. 48, 953–954 (2012).
Lopez-Diaz, D. et al. A subharmonic chipset for gigabit communication around 240 GHz. Proceedings of IEEE International Microwave Symposium http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MWSYM.2012.6258404 (2012).
Lopez-Diaz, D. et al. A 240 GHz quadrature and transmitter for data transmission up to 40 Gbit/s. in Proceedings of European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference, paper EuMC/EuMIC06-4 (IEEE, 2013).
Leuther, A. et al. Metamorphic HEMT technology for submillimeter-wave MMIC applications. in Proceedings of International Conference on Indium Phosphide & Related Materials, 1–6 (IEEE, 2010).
Tessmann, A., Leuther, A., Massler, H. & Seelmann-Eggebert, M. A high gain 600 GHz amplifier TMIC using 35 nm metamorphic HEMT technology. in Proceedings of Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium, 1–4 (IEEE, 2012).
Schmogrow, R. et al. Real-time software-defined multiformat transmitter generating 64 QAM at 28 GBd. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 22, 1601–1603 (2010).
Ito, H., Furuta, T., Muramoto, Y., Ito, T. & Ishibashi, T. Photonic millimetre- and sub-millimetrewave generation using J-band rectangular waveguide-output uni-travelling-carrier photodiode module. Electron. Lett. 42, 1424–1425 (2006).
Ip, E., Lau, A. P. T., Barros, D. J. F. & Kahn, J. M. Coherent detection in optical fiber systems. Opt. Express 16, 753–791 (2008).
Ly-Gagnon, D., Tsukamoto, S., Katoh, K. & Kikuchi, K. Coherent detection of optical quadrature phase-shift keying signals with carrier phase estimation. J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 12–21 (2006).
Proakis, J. Digital Communications 3rd edn (McGraw-Hill, 2012).
Korn, D. et al. First monolithic GaAs IQ electro-optic modulator, demonstrated at 150 Gbit/s with 64-QAM. in Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, postdeadline paper PDP5C.4 (Optical Society of America, 2013).
Fish, G. Heterogeneous photonic integration for microwave photonic applications. in Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, paper OW3D.5 (Optical Society of America, 2013).
Schmogrow, R. et al. Error vector magnitude as a performance measure for advanced modulation formats. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 24, 61–63 (2012); erratum 24, 2198 (2012).
Chang, F., Onohara, K. & Mizuochi, T. Forward error correction for 100 G transport networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48, S48–S55 (2010).
Hirata, A. et al. Low-phase noise photonic millimeter-wave generator using an AWG integrated with a 3-dB combiner. IEICE Trans. Electron. E88-C, 1458–1464 (2005).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank NTT Electronics (NEL) for providing the UTC-PD for this experiment, and W. Schroeder from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) for the artwork in Fig. 1. The authors also acknowledge support from the MILLILINK project (Millimeterwellen-Drahtlos-Links in optischen Kommunikationsnetzwerken) funded by the German Federal Ministry of Research and Education (BMBF; grant 01BP1023), the Karlsruhe School of Optics & Photonics (KSOP), the Helmholtz International Research School for Teratronics (HIRST) at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the Agilent University Relation Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.K. developed the concept, designed and performed the experiments, implemented the photonic transmitter, characterized the MMIC receiver module, analysed the data and wrote the paper. D.L.-D. designed the MMIC receiver chip and characterized the MMIC receiver module. R.H. packaged the MMIC receiver chip and provided the horn antennas. A.T. simulated and designed the MMIC amplifiers. A.L. developed the 35 nm mHEMT MMIC technology. J.A., F.B., R.S., D.H. and R.P. assisted in performing the experiments and analysing the data. T.Z., C.K., W.F., O.A., J.L. and I.K. developed the concept and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2343 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koenig, S., Lopez-Diaz, D., Antes, J. et al. Wireless sub-THz communication system with high data rate. Nature Photon 7, 977–981 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.275
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.275
This article is cited by
-
Design of a binary programmable transmitarray based on phase change material for beam steering applications in D-band
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Recent advances in MXene for terahertz applications
Optoelectronics Letters (2024)
-
Millimeter-wave to near-terahertz sensors based on reversible insulator-to-metal transition in VO2
Communications Materials (2023)
-
Conformal leaky-wave antennas for wireless terahertz communications
Communications Engineering (2023)
-
Intense multicycle THz pulse generation from laser-produced nanoplasmas
Scientific Reports (2023)