Abstract
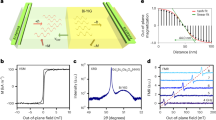
The rich internal degrees of freedom of magnetic domain walls make them an attractive complement to electron charge for exploring new concepts of storage, transport and processing of information. Here we use the tunable internal structure of a domain wall in a perpendicularly magnetized GaMnAsP/GaAs ferromagnetic semiconductor and demonstrate devices in which piezoelectrically controlled magnetic anisotropy yields up to 500% mobility variations for an electrical-current-driven domain wall. We observe current-induced domain wall motion over a wide range of current-pulse amplitudes and report a direct observation and the piezoelectric control of the Walker breakdown separating two regimes with different mobilities. Our work demonstrates that in spin–orbit-coupled ferromagnets with weak extrinsic domain wall pinning, the piezoelectric control allows one to experimentally assess the upper and lower boundaries of the characteristic ratio of adiabatic and non-adiabatic spin-transfer torques in the current-driven domain wall motion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chappert, C., Fert, A. & Dau, F. N. V. The emergence of spin electronics in data storage. Nature Mater. 6, 813–823 (2007).
Parkin, S. S. P., Hayshi, M. & Thomas, L. Magnetic domain-wall racetrack memory. Science 320, 190–194 (2008).
Allwood, D. A. et al. Magnetic domain-wall logic. Science 309, 1688–1692 (2005).
Berger, L. Exchange interaction between ferromagnetic domain wall and electric current in very thin metallic films. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 1954–1956 (1984).
Freitas, P. P. & Berger, L. Observation of s- d exchange force between domain walls and electric current in very thin permalloy films. J. Appl. Phys. 57, 1266–1269 (1985).
Yamaguchi, A. et al. Real-space observation of current-driven domain wall motion in submicron magnetic wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 077205 (2004).
Mougin, A., Cormier, M., Adam, J. P., Metaxas, P. J. & Ferre, J. Domain wall mobility, stability and walker breakdown in magnetic nanowires. Europhys. Lett. 78, 57007 (2007).
Ralph, D. C., Stiles, M. D. & Bader, S. (eds) Current perspectives: Spin transfer torques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1190–1216 (2008).
Vanhaverbeke, A. & Viret, M. Simple model of current-induced spin torque in domain walls. Phys. Rev. B 75, 024411 (2007).
Fernández-Rossier, J., Núñez, A. S., Abolfath, M. & MacDonald, A. H. Optical spin transfer in ferromagnetic semiconductors. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/cond-mat/0304492 (2003).
Nemec, P. et al. Experimental observation of the optical spin transfer torque. Nature Phys. 8, 411–415 (2012).
Berger, L. Emission of spin waves by a magnetic multilayer traversed by a current. Phys. Rev. B 54, 9353–9358 (1996).
Slonczewski, J. C. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, L1–L7 (1996).
Zhang, S. & Li, Z. Roles of nonequilibrium conduction electrons on the magnetization dynamics of ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 127204 (2004).
Garate, I., Gilmore, K., Stiles, M. D. & MacDonald, A. H. Non-adiabatic spin transfer torque in real materials. Phys. Rev. B 79, 104416 (2009).
Hals, K. M. D., Nguyen, A. K. & Brataas, A. Intrinsic coupling between current and domain wall motion in (Ga,Mn)As. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 256601 (2009).
Adam, J. et al. Nonadiabatic spin-transfer torque in (Ga,Mn)As with perpendicular anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 80, 193204 (2009).
Curiale, J., Lemaitre, A., Ulysse, C., Faini, G. & Jeudy, V. Spin drift velocity, polarization, and current-driven domain-wall motion in (Ga,Mn)(As,P). Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 076604 (2012).
Yamanouchi, M., Chiba, D., Matsukura, F. & Ohno, H. Current-induced domain-wall switching in a ferromagnetic semiconductor structure. Nature 428, 539–542 (2004).
Yamanouchi, M., Chiba, D., Matsukura, F., Dietl, T. & Ohno, H. Velocity of domain-wall motion induced by electrical current in a ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 096601 (2006).
Wunderlich, J. et al. Local control of magnetocrystalline anisotropy in (Ga,Mn)As microdevices: Demonstration in current-induced switching. Phys. Rev. B 76, 054424 (2007).
Thiaville, A., Nakatani, Y., Miltat, J. & Suzuki, Y. Micromagnetic understanding of current-driven domain wall motion in patterned nanowires. Europhys. Lett. 69, 990–996 (2005).
Metaxas, P. J. et al. Creep and flow regimes of magnetic domain-wall motion in ultrathin Pt/Co/Pt films with perpendicular anisotropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 217208 (2007).
Koyama, T. et al. Observation of the intrinsic pinning of a magnetic domain wall in a ferromagnetic nanowire. Nature Mater. 10, 194–197 (2011).
Wang, K. Y. et al. Current-driven domain wall motion across a wide temperature range in a (Ga,Mn)(As,P) device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 262102 (2010).
De Ranieri, E. et al. Lithographically and electrically controlled strain effects on anisotropic magnetoresistance in (Ga,Mn)As. New J. Phys. 10, 065003 (2008).
Zemen, J., Kucera, J., Olejnik, K. & Jungwirth, T. Magneto crystalline anisotropies in (Ga,Mn)As: A systematic theoretical study and comparison with experiment. Phys. Rev. B 80, 155203 (2009).
Roy, P. E. & Wunderlich, J. In-plane magnetic anisotropy dependence of critical current density, walker field and domain-wall velocity in a stripe with perpendicular anisotropy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 122504 (2011).
Rushforth, A. W. et al. Voltage control of magnetocrystalline anisotropy in ferromagnetic–semiconductor/piezoelectric hybrid structures. Phys. Rev. B 78, 085314 (2008).
Tatara, G. et al. Threshold current of domain wall motion under extrinsic pinning, β-term and nonadiabaticity. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 75, 064708 (2006).
Miron, I. M. et al. Fast current-induced domain-wall motion controlled by the Rashba effect. Nature Mater. 10, 419–423 (2011).
Fang, D. et al. Spin-orbit driven ferromagnetic resonance. Nature Nanotech. 6, 413–417 (2011).
Liu, X. & Furdyna, J. K. Ferromagnetic resonance in Ga1−xMnxAs dilute magnetic semiconductors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 18, R245–R279 (2006).
Jungwirth, T., Sinova, J., Mašek, J., Kučera, J. & MacDonald, A. H. Theory of ferromagnetic (III,Mn)V semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 809–864 (2006).
Schellekens, A. J., van den Brink, A., Franken, J. H., Swagten, H. J. M. & Koopmans, B. Electric-field control of domain wall motion in perpendicularly magnetized materials. Nature Commun. 3, 848 (2012).
Chiba, D. et al. Electric-field control of magnetic domain-wall velocity in ultrathin cobalt with perpendicular magnetization. Nature Commun. 3, 888 (2012).
Dourlat, A., Jeudy, V., Lemaitre, A. & Gourdon, C. Field-driven domain-wall dynamics in (Ga,Mn)As films with perpendicular anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 78, 161303(R) (2008).
Novák, V. et al. Curie point singularity in the temperature derivative of resistivity in (Ga,Mn)As. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 077201 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from EU grants ERC Advanced Grant 268066-0MSPIN and FP7-215368 SemiSpinNet, and from Czech Republic grant Praemium Academiae, from the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic, Grant No. LM2011026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.D.R., J.W., P.E.R. and E.K.V. developed the experimental set-up, and performed the measurements. P.E.R., T.J., J.W. and E.D.R. performed the theoretical analysis and modelling. R.P.C. and B.L.G. grew and supplied the GaMnAsP films. E.D.R., A.C.I., D.H., E.K.V. and J.W. designed and fabricated the devices. E.D.R., D.F. and A.C. characterized the magnetic properties of the DW devices and unpatterned films. T.J., J.W., E.D.R. and P.E.R. wrote the paper. J.W., E.D.R. and P.E.R. planned the project. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 1282 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Ranieri, E., Roy, P., Fang, D. et al. Piezoelectric control of the mobility of a domain wall driven by adiabatic and non-adiabatic torques. Nature Mater 12, 808–814 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3657
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3657
This article is cited by
-
Self-assembly of Co/Pt stripes with current-induced domain wall motion towards 3D racetrack devices
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Domain wall dynamics in cubic magnetostrictive materials subject to Rashba effect and nonlinear dissipation
Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik (2023)
-
Vector analysis of electric-field-induced antiparallel magnetic domain evolution in ferromagnetic/ferroelectric heterostructures
Journal of Advanced Ceramics (2021)
-
Strain-mediated propagation of magnetic domain-walls in cubic magnetostrictive materials
Ricerche di Matematica (2021)
-
Shear-band affected zone revealed by magnetic domains in a ferromagnetic metallic glass
Nature Communications (2018)