Volume 19
-
No. 12 December 2013
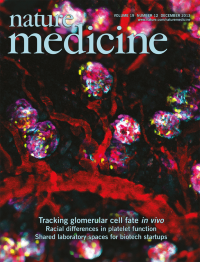
Improved methods for identifying and tracking single podocytes in the intact kidney could improve our understanding of the mechanisms of glomerular injury and regeneration. In this issue (p 1661), Janos Peti-Peterdi and his colleagues describe the use of Podocin-Confetti mice to image podocytes in vivo. The cover shows podocytes labeled in one of four colors (blue, green, yellow or red) and the renal vasculature.
-
No. 11 November 2013
In this issue, we are proud to feature a collection of reviews on targeted cancer therapies (pp 13801464). Cover image: Plato's Cave by Katie Merz (katiemerz.com).
-
No. 10 October 2013
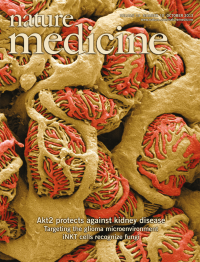
In this issue (p 1288), Fabiola Terzi and her team show that the protein kinase Akt2 is crucial for podocyte survival and function during chronic kidney disease. The cover shows a pseudocolored scanning electron micrograph of rat glomerulus. Image courtesy of Thomas Deerinck, NCMIR/UCSD.
-
No. 9 September 2013
Many people who suffer from migraines experience a suite of visual and sensory disturbances before their headaches[mdash]a phenomenon known as aura. A News Feature on page 1083 by Elie Dolgin explores efforts to find a reliable aura trigger, allowing neuroscientists to provoke auras in the laboratory and study them in action. Cover illustration by Sydney Smith (www.sydneydraws.com).
-
No. 8 August 2013
Eosinophilic esophagitis is a food allergyassociated inflammatory disease characterized by esophageal eosinophilia. In this issue (p 1005), David Artis and his colleagues establish a role for basophils and TSLP in this condition. The cover shows a computer-enhanced color electron micrograph of a TSLP-elicited basophil, courtesy of the authors and the University of Pennsylvania Electron Microscopy Resource Laboratory.
-
No. 7 July 2013
This month Nature Medicine features a collection of Reviews that highlight recent progress on the development of effective strategies to prevent and treat hepatitis. The cover shows an electron micrograph of hepatitis B virus particles. Credit: Eye of Science / Science Source.
-
No. 6 June 2013
Toxoplasma gondii infects the mouse gut and induces an inflammatory response mediated by neutrophils that damages the intestinal tissue and leads to proliferation and translocation of commensal bacteria. In this issue, Grainger et al. report that commensal bacteria help temper the inflammation caused by T. gondii by stimulating inflammatory monocytes to release prostaglandin E2, which dampens neutrophil activity. The cover depicts commensal bacteria in blue and intestinal villi in red in mice infected with T. gondii. Image credit: Lily Y. Koo and Michael J. Molloy.
-
No. 5 May 2013
In this issue (p 576), Stanley Hazen and his colleagues identify a mechanistic link between gut microbiota-dependent metabolism of carnitine, a nutrient that is abundant in red meat, and atherosclerosis. The cover shows gut microbes dining on a carnitinerich spread of red meats. Artwork courtesy of David Schumick(Cleveland Clinic).
-
No. 4 April 2013
In this issue (p 473), Huaxi Xu and colleagues identify a role for sorting nexin 27 in the pathogenesis of Down's syndrome. The cover shows Golgi staining of the mouse forebrain. Image courtesy of Huaxi Xu (Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute).
-
No. 3 March 2013
Lobbying efforts by patient advocacy organizations have created a contest for tax dollars that pits one disease against another. A News Feature on page 257 by Virginia Hughes explores how this 'disease Olympics' affects both decision-making at federal funding agencies and the biomedical research enterprise. Cover illustration by Sydney Smith (www.sydneydraws.com/).
-
No. 2 February 2013
Results from a recent malaria vaccine trial have posed new challenges to the field. This month we feature a collection of Reviews and Perspectives on how to tackle the public health threat posed by malaria and on new therapeutic efforts to control it. The cover shows an Anopheles stephensi mosquito, a malaria vector, in flight after a blood meal. Image credit: Hugh Sturrock, Wellcome Images.
-
No. 1 January 2013
In this issue (p 74), Hyung Chun and his coworkers uncover an apelinmiRNAfibroblast growth factor signaling axis in endothelial cells that is disrupted in pulmonary arterial hypertension. The cover shows a remodeled pulmonary blood vessel from an individual with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Red, smooth muscle actin; cyan, von Willebrand factor; blue, DAPI.