Volume 13
-
No. 12 December 2012
Activation of type I interferon by c-di-GMP and c-di-AMP depends on the adaptor STING. Cheng and colleagues show that these bacterial secondary messengers are detected by the helicase DDX41, which forms a complex with STING ((p 1155 and News & Views by Bowie, p 1137). The original image by Rosane Teles shows weak colocalization of c-di-GMP (red) with STING (green) in 293T cells transfected with Myc-STING and biotinylated c-di-GMP. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 11 November 2012
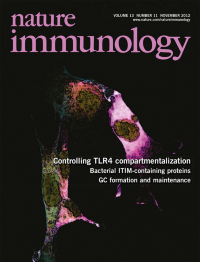
Signaling by ligand-bound TLR4 transitions from plasma membraneassociated MyD88-TIRAP complexes to endosomal TRAM-TRIF complexes. Vanhaesebroeck and colleagues (p 1045; News and Views by Siegemund & Sauer, p 1031) show that the phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase p110d regulates this switch by inducing dissociation of TIRAP from the membrane and degradation of TIRAP. The original confocal microscopic image by Ezra Aksoy shows PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 lipid (magenta), p110δ (yellow) and F-actin (turquoise) in mouse fibroblasts. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 10 October 2012
Like walking on a tightrope, immune responses balance the eradication of pathogens and collateral damage to the host. This month's Focus features a series of specially commissioned articles that discuss the cellular and molecular mechanisms that regulate this fine balance (http://www.nature.com/ni/focus/checksandbalances/). Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 9 September 2012
Antifungal responses are primarily mediated by members of the C-type lectin receptor family. Hardison & Brown (p 817) review recent advances in our understanding of the roles and mechanisms of these multifunctional receptors and explore how they orchestrate antifungal immunity. Original image courtesy of Sarah Hardison and Floyd Wormley shows deadly cryptococcoma forming in mouse cerebrum after a disseminated pulmonary infection with Cryptococcus neoformans. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 8 August 2012
Intestinal microfold (M) cells sample the contents of the gut lumen and capture antigens for presentation in gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Ohno and colleagues (p 729) show that the transcription factor Spi-B is required for the generation of M cells. The original image by Takashi Kanaya and Hiroshi Ohno shows whole-mount staining of a mouse Peyer's patch with M cells positive for the M cell–specific molecule GP2 (green) scattered in the follicle-associated epithelium; the architecture of that epithelium (center) and surrounding villi is visualized by staining for F-actin (blue). Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 7 July 2012
B cells recruit dendritic cells to initiate type 2 immune responses. Lund and colleagues (p 681; News and Views by Cannons, Lu & Schwartzberg, p 630) show that dendritic cells (green) localize to the central T cell area of lymph nodes after infection with influenza virus (top). In contrast, dendritic cells accumulate outside the T cell zone in close proximity to B cell follicles (red) after infection with the nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus (bottom). Original images by Beatriz León. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 6 June 2012
Costimulatory signaling via CD28 is required for the deletion of autoreactive thymocytes. Singer and colleagues (p 569; News and Views by Stritesky & Hogquist, p 528) show that autoreactive cells that survive negative selection differentiate into TCRexpressing CD4-CD8- double-negative thymocytes that leave the thymus to become CD8aa+ intraepithelial lymphocytes. The original image by Xuguang Tai, Jingjing Zhang and Michael Kruhlak is an overlay of staining of the thymus for the maturation marker CD80 (green) and keratin 14 (red). Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 5 May 2012
Periodontitis is associated with aging and more neutrophil-mediated tissue pathology. Hajishengallis and colleagues show an inverse correlation between interleukin-17 (IL-17) expression and Del-1 expression in gingival tissues, with Del-1 protecting tissues from neutrophil infiltration (p 465; and News and Views by Khader, p 433). The original image by Ravi Jotwani shows local expression of IL-17 (red) and recruitment of neutrophils (green) to the gingival tissue in the absence of Del-1. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 4 April 2012
Magnetic resonance imaging of magnetic nanoparticles allows monitoring of disease progression in type 1 diabetes. Mathis and colleagues (p 361; and News and Views by Chervonsky, p 311) use this approach to predict diabetes onset and identify a pathway important in the regulation of disease progression. The original image is a coronal view of an anesthetized mouse visualized by magnetic resonance imaging with a 4.7-Tesla microimaging system. Artwork by Lewis Long.
Focus
-
No. 3 March 2012
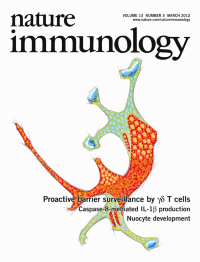
Dendritic epidermal T cells residing in the basal epidermis extend apical processes to the tight junctions of squamous keratinocytes; these steady-state interactions are driven by Vγ5 T cell antigen receptors in immunological synapse–like structures, as reported by Zal and colleagues (p 272; and News and Views by Hayday & Tigelaar, p 209). The original three-dimensional confocal microscopy image shows a γδ dendritic epidermal T cell in a biopsy of healthy skin. Original image by Grzegorz Chodaczek and Tomasz Zal. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 2 February 2012
Under homeostatic conditions, B cell–helper neutrophils colonize the perifollicular area of the spleen to stimulate antibody diversification and production in marginal zone B cells, as reported by Puga and colleagues (p 170; and News & Views by Tangye & Brink, p 111). The original confocal microscopy image shows splenic B cell–helper neutrophils forming neutrophil extracellular trap–like B cell–interacting projections that express the pattern-recognition receptor CEACAM1 (green) and the glycoprotein CD15 (red). DAPI (blue) stains DNA. Original image by Linda Cassis. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 1 January 2012
The transendothelial migration of effector lymphocytes can be mediated by vesicle-stored intraendothelial chemokines, as reported by Alon and colleagues (p 67, and News and Views by Constantin and Laudanna, p 15). The secretion of chemokines into sub-micrometer contacts between the lymphocyte and the endothelial cell promotes the formation of numerous ventral protrusions essential for lymphocyte crossing. Original scanning electron microscopy image by Ziv Shulman and Eugenia Klein. Artwork by Lewis Long.