
Read our April issue
Featuring Articles on lunar mantle overturn and fluorinated chemical pollution, a Review of anthropogenic impacts on mud, a Collection on mantle heterogeneity, and more.

Featuring Articles on lunar mantle overturn and fluorinated chemical pollution, a Review of anthropogenic impacts on mud, a Collection on mantle heterogeneity, and more.

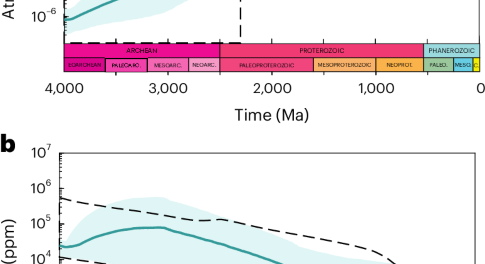
There are no good models for the chemical evolution of the Earth’s surface over the planet’s lifetime, because models typically overlook the progressive build-up of carbonate rocks in the crust. A new model that includes this accumulation enables the reconstruction of major oxygen and temperature trends throughout Earth’s history.
