Abstract
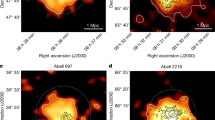
THE distances and velocities of 400 elliptical galaxies1, out to redshifts equivalent to recession velocities of ∼6,000 kms−1, suggest that the peculiar velocities obtained by subtraction of the general cosmological expansion are best fitted by a flow induced by a 'great attractor'2, a large mass of 5.4 x 1016 M⊙ and centred on galactic longitude l = 307° and latitude b = 9° at a distance Rm =4,350 ±350 kms−1. A redshift survey of ∼900 galaxies3 shows that the excess galaxy number counts in this direction are due to two substantial concentrations of galaxies at recession velocities v ≈ 3,000 kms∼1 and 4,500 kms−1. Here we show that in roughly the same direction there is also a very rich concentration of galaxy clusters which may have a considerable dynamical influence. The estimated redshift distances of these clusters range from 3,000 to 20,000 km s−1, with a main complex at v ≈ 14,000 km s−1. The barycentre of this concentration lies ∼25° away from the cosmic microwave background dipole4, and ∼10° away from the latest reported position of the Great Attractor5,6.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dressler, A. et al., Astrophys. J. 313, L37–L42 (1987).
Lynden-Bell, D. et al., Astrophys. J. 326, 19–49 (1988).
Dressler, A. Astrophys. J. 329, 519–526 (1988).
Lubin, P. & Villela, T. in Galaxy Distances and Deviations from Universal Expansion, (eds Madore, B. F. & Tully, R. B.) 169–175 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1986).
Faber, S. M. & Burstein, D. in Large Scale Motions in the Universe (eds Coyne, G. & Rubin, V. C.) (Pontificial Academy of Sciences, Vatican City, in the press).
Burstein, D. in Large Scale Structure and Motions in the Universe (eds Mardirossian, F. et al.) (Reidel, Dordrecht, in the press).
Collins, C. A., Joseph, R. D. & Robertson, N. A. Nature 320, 506–508 (1986).
Aaronson, M., Huchra, J., Mould, J., Schommer, R. & Cornell, M. Astrophys. J. 302, 536–563 (1986).
Yahil, A., Walker, D. & Rowan-Robinson, M. Astrophys. J. 301, L1–L5 (1986).
Meiksin, A. & Davis, M. Astr. J. 91, 191–198 (1986).
Villumsen, J. V. & Strauss, M. A. Astrophys. J. 322, 37–47 (1987).
Harmon, R. T., Lahav, O. & Meurs, E. J. A. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 228, 5P–10P (1987).
Abell, G. O., Corwin, H. G. Jr & Olowin, R. P. Astrophys. J. Suppl. (in the press).
Bahcall, N. A. & Soneira, R. M. Astrophys. J. 277, 27–37 (1984).
Shanks, T., Stevenson, P. R. F., Fong, R. & McGillivray, H. T. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 206, 767–800 (1984).
Vettolani, G., Baiesi-Pillastrini, G., Scaramella, R., Zamorani, G. & Chincarini, G. in Large Scale Structure and Motions in the Universe (eds Mardirossian, F. et al.) (Reidel, Dordrecht, in the press).
Postman, M., Geller, M. J. & Huchra, J. P. Astr. J. 95, 267–283 (1988).
Peebles, P. J. E. The Large Scale Structure of the Universe (Princeton Univ. Press, 1980).
Lilje, P., Yahil, A. & Jones, B. T. J. Astrophys. J. 307, 91–96 (1986).
Lahav, O., Rowan-Robinson, M. & Lynden-Bell, D. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 234, 677–701 (1988).
Merritt, D. Astrophys. J. 313, 121–135 (1987).
Seldner, M. & Peebles, P. J. E. Astrophys. J. 215, L1–L4 (1977).
Liljie, P. & Efstathiou, G. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 231, 635–655 (1988).
Struble, M. A. & Rood, H. J. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 63, 555–613 (1987).
Kaiser, N. & Lahav, O., in Large Scale Motions in the Universe (eds Coyne, G. & Rubin, V. C.) (Pontificial Academy of Sciences, Vatican City, in the press).
Melnick, J. & Moles, M. Rev. Mex. Astr. Astrof. 14, 72–76 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scaramella, R., Baiesi-Pillastrini, G., Chincarini, G. et al. A marked concentration of galaxy clusters: is this the origin of large-scale motions?. Nature 338, 562–564 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/338562a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/338562a0
This article is cited by
-
The dipole repeller
Nature Astronomy (2017)
-
Large-scale structure: Going with the flow
Nature Astronomy (2017)
-
Clusters of Galaxies and the Cosmic Web with Square Kilometre Array
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2016)
-
“Dark energy” in the Local Void
Astrophysics and Space Science (2012)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.