Our April issue presents:
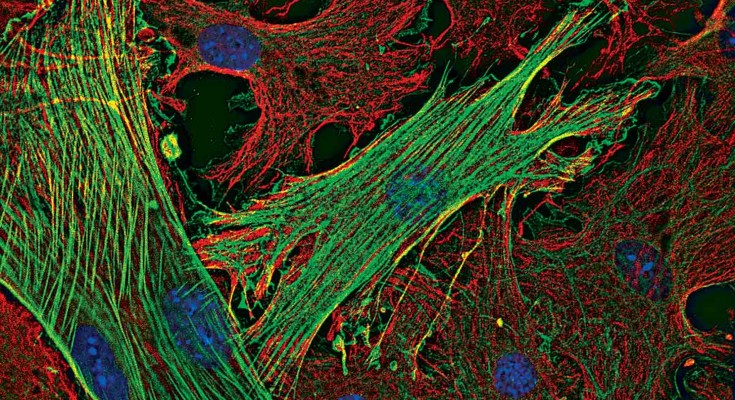
New online tool BulkECexplorer, how histone H1.0 regulates myofibroblast activation, the effectiveness of GLP-1RA and SGLT2i for CV risk reduction in a clinical study, and more!

New online tool BulkECexplorer, how histone H1.0 regulates myofibroblast activation, the effectiveness of GLP-1RA and SGLT2i for CV risk reduction in a clinical study, and more!
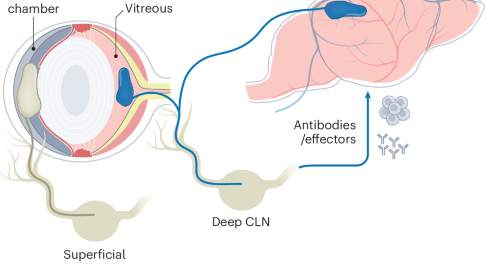
The eye and the brain are both recognized as immune-privileged sites. Research now indicates that responses in the eye mirror those in the central nervous system (CNS), offering major implications for the treatment of CNS cancers and infections.