Abstract
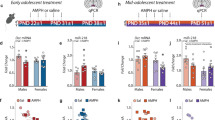
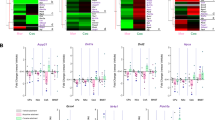
Adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (DG) is strongly influenced by drug-taking behavior and may have a role in the etiology of drug-seeking behavior. However, mechanistic studies on the relationship of neurogenesis on drug seeking are limited. Outbred Wistar rats experienced extended access methamphetamine self-administration and individual differences in drug taking defined animals with higher preferred and lower preferred levels of drug intake. Forced abstinence from higher preferred levels of drug taking enhanced neurogenesis and neuronal activation of granule cell neurons (GCNs) in the DG and produced compulsive-like drug reinstatement. Systemic treatment with the drug Isoxazole-9 (a synthetic small molecule known to modulate neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain) during abstinence blocked compulsive-like context-driven methamphetamine reinstatement. Isoxazole-9 modulated neurogenesis, neuronal activation and structural plasticity of GCNs, and expression of synaptic proteins associated with learning and memory in the DG. These findings identify a subset of newly born GCNs within the DG that could directly contribute to drug-seeking behavior. Taken together, these results support a direct role for the importance of adult neurogenesis during abstinence in compulsive-like drug reinstatement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kitamura O, Wee S, Specio SE, Koob GF, Pulvirenti L . Escalation of methamphetamine self-administration in rats: a dose-effect function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2006; 186: 48–53.
Piazza PV, Deroche-Gamonent V, Rouge-Pont F, Le Moal M . Vertical shifts in self-administration dose-response functions predict a drug-vulnerable phenotype predisposed to addiction. J Neurosci 2000; 20: 4226–4232.
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV . Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 2004; 305: 1014–1017.
Sutton MA, Karanian DA, Self DW . Factors that determine a propensity for cocaine-seeking behavior during abstinence in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; 22: 626–641.
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 2013; 153: 1219–1227.
Garcia AD, Doan NB, Imura T, Bush TG, Sofroniew MV . GFAP-expressing progenitors are the principal source of constitutive neurogenesis in adult mouseforebrain. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 1233–1241.
Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M . Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 2005; 85: 523–569.
Ming GL, Song H . Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 2011; 70: 687–702.
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O'Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS et al. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 2011; 472: 466–470.
Niibori Y, Yu TS, Epp JR, Akers KG, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW . Suppression of adult neurogenesis impairs population coding of similar contexts in hippocampal CA3 region. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 1253.
Park EH, Burghardt NS, Dvorak D, Hen R, Fenton AA . Experience-dependent regulation of dentate gyrus excitability by adult-born granule cells. J Neurosci 2015; 35: 11656–11666.
Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science 2014; 344: 598–602.
Epp JR, Silva Mera R, Kohler S, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW . Neurogenesis-mediated forgetting minimizes proactive interference. Nat Commun 2016; 7: 10838.
Frankland PW, Josselyn SA . Hippocampal neurogenesis and memory clearance. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016; 41: 382–383.
Amaral DG, Witter MP . The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 1989; 31: 571–591.
Snyder JS, Radik R, Wojtowicz JM, Cameron HA . Anatomical gradients of adult neurogenesis and activity: young neurons in the ventral dentate gyrus are activated by water maze training. Hippocampus 2009; 19: 360–370.
Wells AM, Lasseter HC, Xie X, Cowhey KE, Reittinger AM, Fuchs RA . Interaction between the basolateral amygdala and dorsal hippocampus is critical for cocaine memory reconsolidation and subsequent drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Learn Mem 2011; 18: 693–702.
Rogers JL, See RE . Selective inactivation of the ventral hippocampus attenuates cue-induced and cocaine-primed reinstatement of drug-seeking in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2007; 87: 688–692.
Lasseter HC, Xie X, Ramirez DR, Fuchs RA . Sub-region specific contribution of the ventral hippocampus to drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuroscience 2010; 171: 830–839.
Lau JY, Goldman D, Buzas B, Hodgkinson C, Leibenluft E, Nelson E et al. BDNF gene polymorphism (Val66Met) predicts amygdala and anterior hippocampus responses to emotional faces in anxious and depressed adolescents. Neuroimage 2010; 53: 952–961.
Mandyam CD, Koob GF . The addicted brain craves new neurons: putative role for adult-born progenitors in promoting recovery. Trends Neurosci 2012; 35: 250–260.
Canales JJ . Comparative neuroscience of stimulant-induced memory dysfunction: role for neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Behav Pharmacol 2010; 21: 379–393.
Recinto P, Samant AR, Chavez G, Kim A, Yuan CJ, Soleiman M et al. Levels of neural progenitors in the hippocampus predict memory impairment and relapse to drug seeking as a function of excessive methamphetamine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012; 37: 1275–1287.
Koh SH, Liang AC, Takahashi Y, Maki T, Shindo A, Osumi N et al. Differential effects of Isoxazole-9 on neural stem/progenitor cells, oligodendrocyte precursor cells, and endothelial progenitor cells. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0138724.
Bettio LE, Patten AR, Gil-Mohapel J, O'Rourke NF, Hanley RP, Kennedy S et al. ISX-9 can potentiate cell proliferation and neuronal commitment in the rat dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2016; 332: 212–222.
Schneider JW, Gao Z, Li S, Farooqi M, Tang TS, Bezprozvanny I et al. Small-molecule activation of neuronal cell fate. Nat Chem Biol 2008; 4: 408–410.
Petrik D, Jiang Y, Birnbaum SG, Powell CM, Kim MS, Hsieh J et al. Functional and mechanistic exploration of an adult neurogenesis-promoting small molecule. FASEB J 2012; 26: 3148–3162.
Zhang L, Li P, Hsu T, Aguilar HR, Frantz DE, Schneider JW et al. Small-molecule blocks malignant astrocyte proliferation and induces neuronal gene expression. Differentiation 2011; 81: 233–242.
Somkuwar SS, Fannon MJ, Staples MC, Zamora-Martinez ER, Navarro AI, Kim A et al. Alcohol dependence-induced regulation of the proliferation and survival of adult brain progenitors is associated with altered BDNF-TrkB signaling. Brain Struct Funct 2015; 221: 4319–4335.
Collingridge GL, Olsen RW, Peters J, Spedding M . A nomenclature for ligand-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 2009; 56: 2–5.
Shaham Y, Shalev U, Lu L, De Wit H, Stewart J . The reinstatement model of drug relapse: history, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003; 168: 3–20.
Kheirbek MA, Klemenhagen KC, Sahay A, Hen R . Neurogenesis and generalization: a new approach to stratify and treat anxiety disorders. Nat Neurosci 2012; 15: 1613–1620.
Linseman DA, Bartley CM, Le SS, Laessig TA, Bouchard RJ, Meintzer MK et al. Inactivation of the myocyte enhancer factor-2 repressor histone deacetylase-5 by endogenous Ca(2+) //calmodulin-dependent kinase II promotes depolarization-mediated cerebellar granule neuron survival. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 41472–41481.
Irvine EE, von Hertzen LS, Plattner F, Giese KP . alphaCaMKII autophosphorylation: a fast track to memory. Trends Neurosci 2006; 29: 459–465.
Yuan CJ, Quiocho JM, Kim A, Wee S, Mandyam CD . Extended access methamphetamine decreases immature neurons in the hippocampus which results from loss and altered development of neural progenitors without altered dynamics of the S-phase of the cell cycle. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2011; 100: 98–108.
Mandyam CD, Wee S, Crawford EF, Eisch AJ, Richardson HN, Koob GF . Varied access to intravenous methamphetamine self-administration differentially alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 64: 958–965.
Prybylowski K, Chang K, Sans N, Kan L, Vicini S, Wenthold RJ . The synaptic localization of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors is controlled by interactions with PDZ proteins and AP-2. Neuron 2005; 47: 845–857.
Lavezzari G, McCallum J, Lee R, Roche KW . Differential binding of the AP-2 adaptor complex and PSD-95 to the C-terminus of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B regulates surface expression. Neuropharmacology 2003; 45: 729–737.
Watterson LR, Olive MF . Synthetic cathinones and their rewarding and reinforcing effects in rodents. Adv Neurosci (Hindawi) 2014; 2014: 209875.
Acknowledgements
We thank Airee Kim, Ana Mohammad-Zadeh, Phillip Silva and Yanabel Grant for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation (to MHG), National Institute on Drug Abuse (to CDM) and National Institute of Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse (to CDM and MCS). This is manuscript number 29314 from The Scripps Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galinato, M., Lockner, J., Fannon-Pavlich, M. et al. A synthetic small-molecule Isoxazole-9 protects against methamphetamine relapse. Mol Psychiatry 23, 629–638 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.46
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.46
This article is cited by
-
ISX-9 potentiates CaMKIIδ-mediated BMAL1 activation to enhance circadian amplitude
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Prevention of relapse to methamphetamine self-administration by environmental enrichment: involvement of glucocorticoid receptors
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
In vivo reduction of striatal D1R by RNA interference alters expression of D1R signaling-related proteins and enhances methamphetamine addiction in male rats
Brain Structure and Function (2020)
-
Depleting adult dentate gyrus neurogenesis increases cocaine-seeking behavior
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
-
Neuroadaptations in the dentate gyrus following contextual cued reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking
Brain Structure and Function (2018)