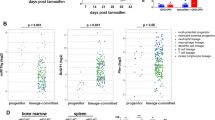
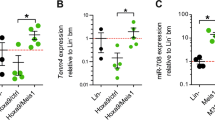
Abstract
MiR-125 is a highly conserved microRNA throughout many different species from nematode to humans. In humans, there are three homologs (hsa-miR-125b-1, hsa-miR-125b-2 and hsa-miR-125a). Here we review a recent research on the role of miR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Its high expression in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) enhances self-renewal and survival. Its expression in specific subtypes of myeloid and lymphoid leukemias provides resistance to apoptosis and blocks further differentiation. A direct oncogenic role in the hematopoietic system has recently been demonstrated by several mouse models. Targets of miR-125b include key proteins regulating apoptosis, innate immunity, inflammation and hematopoietic differentiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Filipowicz W . Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms? Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 118–126.
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP . Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010; 466: 835–840.
Breving K, Esquela-Kerscher A . The complexities of microRNA regulation: mirandering around the rules. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2010; 42: 1316–1329.
Guo L, Lu Z . Global expression analysis of miRNA gene cluster and family based on isomiRs from deep sequencing data. Comput Biol Chem 2010; 34: 165–171.
Yu J, Wang F, Yang GH, Wang FL, Ma YN, Du ZW et al. Human microRNA clusters: genomic organization and expression profile in leukemia cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 349: 59–68.
Corcoran DL, Pandit KV, Gordon B, Bhattacharjee A, Kaminski N, Benos PV . Features of mammalian microRNA promoters emerge from polymerase II chromatin immunoprecipitation data. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5279.
Long YS, Deng GF, Sun XS, Yi YH, Su T, Zhao QH et al. Identification of the transcriptional promoters in the proximal regions of human microRNA genes. Mol Biol Rep 2011; 38: 4153–4157.
Ozsolak F, Poling LL, Wang Z, Liu H, Liu XS, Roeder RG et al. Chromatin structure analyses identify miRNA promoters. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 3172–3183.
Wang X, Xuan Z, Zhao X, Li Y, Zhang MQ . High-resolution human core-promoter prediction with CoreBoost_HM. Genome Res 2009; 19: 266–275.
Jansen BJ, Sama IE, Eleveld-Trancikova D, van Hout-Kuijer MA, Jansen JH, Huynen MA et al. MicroRNA genes preferentially expressed in dendritic cells contain sites for conserved transcription factor binding motifs in their promoters. BMC Genomics 2011; 12: 330.
Monteys AM, Spengler RM, Wan J, Tecedor L, Lennox KA, Xing Y et al. Structure and activity of putative intronic miRNA promoters. RNA 2010; 16: 495–505.
Baskerville S, Bartel DP . Microarray profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA 2005; 11: 241–247.
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L, Chen C . Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics 2007; 8: 166.
Lin KY, Zhang XJ, Feng DD, Zhang H, Zeng CW, Han BW et al. miR-125b, a target of CDX2, regulates cell differentiation through repression of the core binding factor in hematopoietic malignancies. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 38253–38263.
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B et al. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5082–5089.
Zhou R, Hu G, Liu J, Gong AY, Drescher KM, Chen XM . NF-kappaB p65-dependent transactivation of miRNA genes following Cryptosporidium parvum infection stimulates epithelial cell immune responses. PLoS Pathog 2009; 5: e1000681.
Zhou R, Hu G, Gong AY, Chen XM . Binding of NF-kappaB p65 subunit to the promoter elements is involved in LPS-induced transactivation of miRNA genes in human biliary epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38: 3222–3232.
Gutierrez O, Berciano MT, Lafarga M, Fernandez-Luna JLA . Novel pathway of TEF regulation mediated by MicroRNA-125b contributes to the control of actin distribution and cell shape in fibroblasts. PLoS One 2011; 6: e17169.
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Lodygin D, Epanchintsev A, Menssen A et al. Differential regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and G1-arrest. Cell Cycle 2007; 6: 1586–1593.
Chang TC, Yu D, Lee YS, Wentzel EA, Arking DE, West KM et al. Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 43–50.
Androulidaki A, Iliopoulos D, Arranz A, Doxaki C, Schworer S, Zacharioudaki V et al. The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity 2009; 31: 220–231.
Shi XB, Xue L, Yang J, Ma AH, Zhao J, Xu M et al. An androgen-regulated miRNA suppresses Bak1 expression and induces androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19983–19988.
Shi XB, Xue L, Ma AH, Tepper CG, Kung HJ, White RW . miR-125b promotes growth of prostate cancer xenograft tumor through targeting pro-apoptotic genes. Prostate 2011; 71: 538–549.
O'Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA, Rao DS, Gibson WS, Balazs AB, Baltimore D . MicroRNAs enriched in hematopoietic stem cells differentially regulate long-term hematopoietic output. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14235–14240.
Ooi AG, Sahoo D, Adorno M, Wang Y, Weissman IL, Park CY . MicroRNA-125b expands hematopoietic stem cells and enriches for the lymphoid-balanced and lymphoid-biased subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21505–21510.
Bousquet M, Harris MH, Zhou B, Lodish HF . MicroRNA miR-125b causes leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21558–21563.
Surdziel E, Cabanski M, Dallmann I, Lyszkiewicz M, Krueger A, Ganser A et al. Enforced expression of miR-125b affects myelopoiesis by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Blood 2011; 117: 4338–4348.
Klusmann JH, Li Z, Bohmer K, Maroz A, Koch ML, Emmrich S et al. miR-125b-2 is a potential oncomiR on human chromosome 21 in megakaryoblastic leukemia. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 478–490.
Bousquet M, Quelen C, Rosati R, Mansat-De Mas V, La Starza R, Bastard C et al. Myeloid cell differentiation arrest by miR-125b-1 in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia with the t(2;11)(p21;q23) translocation. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2499–2506.
Gururajan M, Haga CL, Das S, Leu CM, Hodson D, Josson S et al. MicroRNA 125b inhibition of B cell differentiation in germinal centers. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 583–592.
Malumbres R, Sarosiek KA, Cubedo E, Ruiz JW, Jiang X, Gascoyne RD et al. Differentiation stage-specific expression of microRNAs in B lymphocytes and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2009; 113: 3754–3764.
Rossi RL, Rossetti G, Wenandy L, Curti S, Ripamonti A, Bonnal RJ et al. Distinct microRNA signatures in human lymphocyte subsets and enforcement of the naive state in CD4(+) T cells by the microRNA miR-125b. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 796–803.
Chaudhuri AA, So AY, Sinha N, Gibson WS, Taganov KD, O'Connell RM et al. MicroRNA-125b potentiates macrophage activation. J Immunol 2011; 187: 5062–5068.
Rajaram MV, Ni B, Morris JD, Brooks MN, Carlson TK, Bakthavachalu B et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipomannan blocks TNF biosynthesis by regulating macrophage MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) and microRNA miR-125b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 17408–17413.
Murphy AJ, Guyre PM, Pioli PA . Estradiol suppresses NF-kappa B activation through coordinated regulation of let-7a and miR-125b in primary human macrophages. J Immunol 2010; 184: 5029–5037.
Orom UA, Nielsen FC, Lund AH . MicroRNA-10a binds the 5'UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol Cell 2008; 30: 460–471.
Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA . Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 2007; 318(5858): 1931–1934.
Izraeli S . Leukaemia—a developmental perspective. Br J Haematol 2004; 126: 3–10.
Votavova H, Grmanova M, Dostalova Merkerova M, Belickova M, Vasikova A, Neuwirtova R et al. Differential expression of microRNAs in CD34+ cells of 5q- syndrome. J Hematol Oncol 2011; 4: 1.
Hussein K, Theophile K, Busche G, Schlegelberger B, Gohring G, Kreipe H et al. Aberrant microRNA expression pattern in myelodysplastic bone marrow cells. Leuk Res 2010; 34: 1169–1174.
Cammarata G, Augugliaro L, Salemi D, Agueli C, La Rosa M, Dagnino L et al. Differential expression of specific microRNA and their targets in acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol 2010; 85: 331–339.
Enomoto Y, Kitaura J, Hatakeyama K, Watanuki J, Akasaka T, Kato N et al. Emu/miR-125b transgenic mice develop lethal B-cell malignancies. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1849–1856.
Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, Mi S, Zhang H, Luo RT et al. Distinct microRNA expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 15535–15540.
Zhang H, Luo XQ, Zhang P, Huang LB, Zheng YS, Wu J et al. MicroRNA patterns associated with clinical prognostic parameters and CNS relapse prediction in pediatric acute leukemia. PLoS One 2009; 4: e7826.
Sonoki T, Iwanaga E, Mitsuya H, Asou N . Insertion of microRNA-125b-1, a human homologue of lin-4, into a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene locus in a patient with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2005; 19: 2009–2010.
Chapiro E, Russell LJ, Struski S, Cave H, Radford-Weiss I, Valle VD et al. A new recurrent translocation t(11;14)(q24;q32) involving IGH@ and miR-125b-1 in B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2010; 24: 1362–1364.
Tassano E, Acquila M, Tavella E, Micalizzi C, Panarello C, Morerio C . MicroRNA-125b-1 and BLID upregulation resulting from a novel IGH translocation in childhood B-Cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2010; 49: 682–687.
Gefen N, Binder V, Zaliova M, Linka Y, Morrow M, Novosel A et al. Hsa-mir-125b-2 is highly expressed in childhood ETV6/RUNX1 (TEL/AML1) leukemias and confers survival advantage to growth inhibitory signals independent of p53. Leukemia 2010; 24: 89–96.
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Moqadam FA, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C et al. MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2011; 96: 703–711.
Zhou Y, Chen L, Barlogie B, Stephens O, Wu X, Williams DR et al. High-risk myeloma is associated with global elevation of miRNAs and overexpression of EIF2C2/AGO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 7904–7909.
Lionetti M, Biasiolo M, Agnelli L, Todoerti K, Mosca L, Fabris S et al. Identification of microRNA expression patterns and definition of a microRNA/mRNA regulatory network in distinct molecular groups of multiple myeloma. Blood 2009; 114: e20–e26.
Kumar M, Lu Z, Takwi AA, Chen W, Callander NS, Ramos KS et al. Negative regulation of the tumor suppressor p53 gene by microRNAs. Oncogene 2011; 30: 843–853.
Elton TS, Sansom SE, Martin MM . Trisomy-21 gene dosage over-expression of miRNAs results in the haploinsufficiency of specific target proteins. RNA Biol 2010; 7: 540–547.
Kuhn DE, Nuovo GJ, Martin MM, Malana GE, Pleister AP, Jiang J et al. Human chromosome 21-derived miRNAs are overexpressed in down syndrome brains and hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 370: 473–477.
Malinge S, Izraeli S, Crispino JD . Insights into the manifestations, outcomes, and mechanisms of leukemogenesis in Down syndrome. Blood 2009; 113: 2619–2628.
Le MT, Teh C, Shyh-Chang N, Xie H, Zhou B, Korzh V et al. MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative regulator of p53. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 862–876.
Sinha AU, Kaimal V, Chen J, Jegga AG . Dissecting microregulation of a master regulatory network. BMC Genomics 2008; 9: 88.
Xia HF, He TZ, Liu CM, Cui Y, Song PP, Jin XH et al. MiR-125b expression affects the proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells by targeting Bmf. Cell Physiol Biochem 2009; 23: 347–358.
Zhou M, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Liu H, Xi Y et al. MicroRNA-125b confers the resistance of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through suppression of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1 (Bak1) expression. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 21496–21507.
Villeneuve LM, Kato M, Reddy MA, Wang M, Lanting L, Natarajan R . Enhanced levels of microRNA-125b in vascular smooth muscle cells of diabetic db/db mice lead to increased inflammatory gene expression by targeting the histone methyltransferase Suv39h1. Diabetes 2010; 59: 2904–2915.
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Iuliano R, Cimmino A, Aqeilan R et al. MicroRNA fingerprints during human megakaryocytopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 5078–5083.
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K . An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009; 139: 693–706.
Guo S, Lu J, Schlanger R, Zhang H, Wang JY, Fox MC et al. MicroRNA miR-125a controls hematopoietic stem cell number. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14229–14234.
Gerrits A, Walasek MA, Olthof S, Weersing E, Ritsema M, Zwart E et al. Genetic screen identifies microRNA cluster 99b/let-7e/125a as a regulator of primitive hematopoietic cells. Blood 2012; 119: 377–387.
Zhao X, Tang Y, Qu B, Cui H, Wang S, Wang L et al. MicroRNA-125a contributes to elevated inflammatory chemokine RANTES levels via targeting KLF13 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 3425–3435.
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M, Taccioli C, Rossi S et al. Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 136–146.
Baffa R, Fassan M, Volinia S, O'Hara B, Liu CG, Palazzo JP et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of human metastatic cancers identifies cancer gene targets. J Pathol 2009; 219: 214–221.
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007; 297: 1901–1908.
Song T, Xia W, Shao N, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y et al. Differential miRNA expression profiles in bladder urothelial carcinomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2010; 11: 905–911.
Veerla S, Lindgren D, Kvist A, Frigyesi A, Staaf J, Persson H et al. MiRNA expression in urothelial carcinomas: important roles of miR-10a, miR-222, miR-125b, miR-7 and miR-452 for tumor stage and metastasis, and frequent homozygous losses of miR-31. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 2236–2242.
Guan Y, Yao H, Zheng Z, Qiu G, Sun K . MiR-125b targets BCL3 and suppresses ovarian cancer proliferation. Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 2274–2283.
Nelson PT, Baldwin DA, Kloosterman WP, Kauppinen S, Plasterk RH, Mourelatos Z . RAKE and LNA-ISH reveal microRNA expression and localization in archival human brain. RNA 2006; 12: 187–191.
Scott GK, Goga A, Bhaumik D, Berger CE, Sullivan CS, Benz CC . Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 1479–1486.
Rajabi H, Jin C, Ahmad R, McClary C, Joshi MD, Kufe D . Mucin1 oncoprotein expression is suppressed by the mir-125b oncomir. Genes Cancer 2010; 1: 62–68.
Glud M, Rossing M, Hother C, Holst L, Hastrup N, Nielsen FC et al. Downregulation of miR-125b in metastatic cutaneous malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res 2010; 20: 479–484.
Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Wallace TA, Howe TM, Yfantis HG et al. Expression of microRNAs and protein-coding genes associated with perineural invasion in prostate cancer. Prostate 2008; 68: 1152–1164.
Shi L, Zhang J, Pan T, Zhou J, Gong W, Liu N et al. MiR-125b is critical for the suppression of human U251 glioma stem cell proliferation. Brain Res 2010; 1312: 120–126.
Mohri T, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Komagata S, Yokoi T . MicroRNA regulates human vitamin D receptor. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 1328–1333.
Zhang Y, Yan LX, Wu QN, Du ZM, Chen J, Liao DZ et al. miR-125b is methylated and functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating the ETS1 proto-oncogene in human invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3552–3562.
Xu N, Brodin P, Wei T, Meisgen F, Eidsmo L, Nagy N et al. MiR-125b, a microRNA downregulated in psoriasis, modulates keratinocyte proliferation by targeting FGFR2. J Invest Dermatol 2011; 131: 1521–1529.
Acknowledgements
We thank Y Kirschenbaum for reading and correcting the manuscript. This work was supported by the German Israeli Foundation (SI and AB), ISF-Legacy program (SI), Children with Leukemia UK (SI), Waxman Cancer Foundation NY (SI), the National Institutes of Health (SI), Wolfson foundation (SI), i-CORE (SI), and the WLBH Foundation (SI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The study is partial fulfillment of the requirements for completing a PhD degree (Lital Shaham) for Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan, Israel.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaham, L., Binder, V., Gefen, N. et al. MiR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 26, 2011–2018 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.90
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.90
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The accumulation of miR-125b-5p is indispensable for efficient erythroblast enucleation
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Rs12976445 polymorphism is associated with the risk of post-SAH re-bleeding by modulating the expression of microRNA-125 and ET-1
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Micro-RNA-125a mediates the effects of hypomethylating agents in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Clinical Epigenetics (2021)
-
Circular RNAs as important players in human gastric cancer
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
miR-125-5p inhibits thyroid cancer growth and metastasis by suppressing the ERK/PI3K/AKT signal pathway
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2021)