Abstract
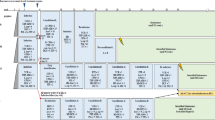
Modern treatment strategies, consisting of intensive chemotherapy and cranial irradiation, have remarkably improved the prognosis for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. However, patients with a potential for cure are at risk of severe acute and late adverse effects of treatment. Furthermore, in 25–30% of patients treatment still fails. The objectives of the DCLSG study ALL 8 were to decrease the toxicity and to increase the effectivity of BFM-oriented treatment. Decrease of toxicity was aimed at by confirmation of the results of the previous DCLSG study ALL-7, showing that the majority (94%) of children with ALL can succesfully be treated with BFM-oriented therapy without cranial irradiation, and by reduction of treatment for standard risk (SRG) patients. To increase the cure rate in medium risk (MRG) patients the efficacy of high doses of intravenous 6-mercaptopurine (HD-6MP) during protocol M and in SRG patients the efficacy of high doses of L-asparaginase (HD-L-ASP) during maintenance treatment was studied in randomized studies. Patient stratification and treatment were identical to protocol ALL-BFM90, with the following differences: no prophylactic cranial irradiation, SRG patients received only phase 1 of protocol I. Four hundred and sixty-seven patients entered the protocol: 170 SRG, 241 MRG and 56 HRG patients. The 5 years event-free survival rate for all patients was 73% (s.e. 2%); for SRG, MRG and HRG patients 85% (s.e. 3%), 73% (s.e. 3%) and 39% (s.e. 7%), respectively. In patients >1 year of age at diagnosis unfavorable prognostic factors were male sex, >25% blasts in the bone marrow at day 15 and initial white blood cell count (WBC) >50 × 109/l. The cumulative risk of CNS relapse rate was 5% (s.e. 1%) at 5 years. These results confirm that the omission of cranial irradiation in BFM-oriented treatment does not jeopardize the overall good treatment results, nor does early reduction of chemotherapy in SRG patients. No benefit was observed from treatment intensification with HD-L-ASP in SRG patients, nor from HD-6MP in MRG patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riehm H, Feickert HJ, Schrappe M, Henze G, Schellong G . Therapy results in five ALL-BFM studies since 1970. Complications of risk factors for prognosis Haematol Blood Transfus 1987 30: 139–146
Kamps WA, Bökkerink JPM, Hählen K, Van den Berg-de Ruiter E, Smets LA, De Vaan GAM, Weening RS, Van Weerden JF, Van Wering ER, Van der Does-van den Berg A . Intensive treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia according to ALL-BFM 86 without cranial radiotherapy: results of DCLSG Protocol ALL-7 (1988–1991) Blood 1999 94: 1226–1236
Schrappe M, Reiter A, Ludwig W-D, Harbott J, Zimmermann M, Hiddemann W, Niemeyer Ch, Henze G, Feldges A, Zintl F, Kornhuber B, Ritter J, Welte K, Gadner H, Riehm H . Improved outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia despite reduced use of anthracyclines and cranial radiotherapy: results of trial ALL-BFM 90 Blood 2000 95: 3310–3322
Masera G, Gadner H, Kamps WA, Otten J, Philippe N, Schuler D, Riehm H . The treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Int J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol 1998 5: 141–144
Rizzari C, Valsecchi MG, Aricò M, Conter V, Testi A, Barisone E, Casale F, Lo Nigro L, Rondelli R, Basso G, Santoro N, Masera G . Effect of protracted high-dose L-asparaginase given as a second exposure in a Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster-based treatment: results of the randomized 9102 Intermediate-Risk Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Study – a report from the Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica J Clin Oncol 2001 19: 1297–1303
Van der Does-van den Berg A, Bartram CR, Basso G, Benoit A, Haas OA, Harbott J, Kamps WA, Köller U, Lampert F, Ludwig W-D, Niemeyer CM, van Wering ER . Minimal requirements for the diagnosis, classification and evaluation of the treatment of childhood ALL in the ‘BFM Family’ Cooperative Group Med Pediatr Oncol 1992 20: 497–505
Veerman AJP, Huismans DR, Van Zantwijk CH . Storage of cerebrospinal fluid samples at room temperature Acta Cytol 1985 9: 188–189
Van Wering ER, Veerman AJP, Van der Linden-Schrever BEM . Diagnosis of meningeal involvement in childhood acture lymphoblastic leukemia: cytomorphology and TdT Eur J Haematol 1988 40: 250–255
Langermann HJ, Henze G, Wulf M, Riehm H . Abschätzung der Tumorzellmasse bei der akuten lymphoblastischen Leukämie im Kindersalter: prognostische Bedeutung und praktische Anwendung Klin Pädiat 1982 194: 209–213
Van Wering ER, Brederoo P, Van Staalduinen GJ, Van der Meulen J, Van der Linden-Schrever BEM, Van Dongen JJM . Contribution of electronmicroscopy to the classification of the minimally differentiated leukemias in children Recent Res Cancer Res 1993 131: 77–87
Slater RM, Smeets DFCM, Hagemeijer A, De Jong B, Beverstock CG, Geraedts JPM, Van der Does-van den Berg A, Van Wering ER, Veerman AJP . Update of the cytogenetic study of childhood non-high-risk acute lymphocytic leukemia at diagnosis in protocol VI of the Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group Haematol Blood Transfus 1990 33: 169–173
Matthews DE, Farewell VT . Understanding and Using Medical Statistics, 3rd edn Karger: Basel 1996
Klein JP, Moeschberger ML . Survival Analysis Springer: Berlin 1997
Statsoft, Inc. Statistica for Windows (computer manual) Tulsa, OK 1998
Smith M, Arthur D, Camitta B, Carroll AJ, Crist W, Gaynon P, Gelber R, Heerema N, Korn EL, Link M, Murphy S, Pui-C-H, Pullen J, Reaman G, Sallan SE, Sather H, Shuster J, Simon R, Trigg M, Tubergen D, Uckun F, Ungerleider R . Uniform approach to risk classification and treatment assignment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 18–24
Conter V, Aricò M, Valsecchi MG, Rizzari C, Testi A, Miniero R, Di Tullio MT, Lo Nigro L, Pession A, Rondelli R, Messina C, Santoro N, Mori PG, De Rossi G, Tamaro T, Silvestri D, Biondi A, Basso G, Masera G . Intensive BFM chemotherapy for childhood ALL: interim analysis of the AEIOP-ALL91 study Haematologica 1998 83: 791–799
Pui CH, Schrappe M, Camitta B (co-ordinators). Spotlight on long-term results of pediatric ALL clinical trials from 12 study groups worldwide Leukemia 2000 14: 2193–2320
Stark B, Sharon R, Rechavi G, Attias D, Ballin A, Cividalli G, Burstein Y, Sthoeger D, Abramov A, Zaizov R . Effective preventive central nervous system therapy with extended triple intrathecal therapy and the modified ALL-BFM 86 chemotherapy program in an enlarged non-high risk group of children and adolescents with non-B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Cancer 2000 88: 205–216
Tubergen DG, Gilchrist GS, O'Brien T, Coccia PF, Sather HN, Waskerwitz MJ, Hammond GD . Improved outcome with delayed intensification for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and intermediate presenting features; a Childrens Cancer Group phase III Trial J Clin Oncol 1993 3: 527–537
Vilmer E, Suciu S, Ferster A, Bertrand Y, Cavé H . Thyss A, Benoit Y, Dastugue N, Fournier M, Souillet G, Manel A-M, Robert A, Nelken B, Millot F, Lutz P, Rialland X, Mechinaud F, Boutard P, Behar C, Chantraine J-M, Plouvier E, Laureys G, Brock P, Uyttebroeck A, Marqueritte G, Plantaz D, Norton L, Francotte N, Gyselinck J, Waterkeyn C, Solbu G, Phillipe N, Otten J. Long term results of three randomized trials (58831, 58832 58881) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a CLCG-EORTC report Leukemia 2000 14: 2257–2266
Manera R, Ramirez I, Mullins J, Pinkel D . Pilot studies of species-specific chemotherapy of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia using genotype and immunophenotype Leukemia 2000 14: 1354–1361
Conter V, Schrappe M, Aricò M, Reiter A, Rizzari C, Dördelmann M, Valsecchi MG, Zimmermann M, Ludwig W-D, Basso G, Masera G, Riehm H for the Associazone Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pedriatrica and the Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster Groups. Role of cranial radiotherapy for childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with high WBC count and good response to prednisone J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 2786–2791
Silverman LB, Gelber RD, Kimball Dalton V, Asselin BL, Barr RD, Clavell LA, Hurwitz CA, Moghrabi A, Samson Y, Schorin MA, Arkin S, Declerck L, Cohen HJ, Sallan SE . Improved outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of Dana-Farber Consortium Protocol 91–01 Blood 2001 97: 1211–1218
Paolucci G, Vecchi V, Favre C, Miniero R, Madon E, Pession A, Rondelli R, De Rossi G, LoNigro L, Porta F, Santoro N, Indolfi P, Basso G, Conter V, Aricò M . Treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: long-term results of the AIEOP-ALL 87 study Haematologica 2001 86: 478–484
Asselin BL, Whitin JC, Coppola DJ, Rupp IP, Sallan SE, Cohen HJ . Comparative pharmacokinetic studies of three asparaginase preparations J Clin Oncol 1993 11: 1780–1786
Reiter A, Schrappe M, W-D Ludwig Hiddemann W, Sauter S, Henze G, Zimmermann M, Odenwald E, Ritter J, Mann G, Welte K, Gadner H, Riehm H . Chemotherapy in 998 unselected childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Results and conclusions of the multicenter trial ALL-BFM 86 Blood 1994 84: 3122–3133
Chessells JM, Richards SM, Bailey CC, Lilleyman JS, Eden OB . Gender and treatment outcome in childhood 0lymphoblastic leukemia: report from the MRC UKALL trials Br J Haematol 1995 89: 364–372
Shuster JJ, Wacker P, Pullen J, Humbert J, Land VJ, Mahoney DH Jr, Lauer S, Look T, Borowitz MJ, Caroll AJ, Camitta B . Prognostic significance of sex in childhood B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 2854–2863
Pui C-H, Boyett JM, Relling MV, Harrison PL, Rivera GK, Behm FG, Sandlund JT, Ribeiro RC, Rubnitz JE, Gajjar A, Evans WE . Sex differences in prognosis for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 818–824
Kaspers GJL, Pieters R, van Zantwijk CH, van Wering ER, Veerman AJP . Clinical and cell biological features related to cellular drug resistance of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells Leuk Lymphoma 1995 19: 407–416
Dibenedetto SP, Guardabasso V, Ragusa R, De Cataldo A, Miraglia V, D'Amico S, Ippolito AM . 6-Mercaptopurine cumulative dose. A critical factor of maintenance therapy in average risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Ped Hematol Oncol 1994 11: 251–258
Riehm H, Gadner H, Henze G, Kornhuber B, Lampert F, Niethammer D, Reiter A, Schellong G . Results and significance of six randomized trials in four consecutive ALL-BFM studies Haematol Blood Transfus 1990 33: 439–450
Gajjar A, Ribeiro R, Hancock ML, Rivera GK, Mahmoud H, Sandlund JT, Crist WM, Pui C-H . Persistence of circulating blasts after 1 week of multiagent chemotherapy confers a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1995 86: 1292–1295
Steinherz PG, Gaynon PS, Breneman JC, Cherlow JM, Grossmann NJ, Kersey JH, Johnstone HS, Sather HN, Trigg ME, Chappel R, Hammond D, Bleyer WA . Cytoreduction and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. The importance of early marrow response. Report from the Children's Cancer Group J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 389–398
Van Dongen JJM, Seriu T, Panzer-Grümayer R, Biondi A, Pongers-Willemse MJ, Corral L, Stolz F, Schrappe M, Masera G, Kamps WA, Gadner H, van Wering ER, Ludwig W-D, Basso G, de Bruijn MAC, Cazzaniga G, Hettinger K, Van der Does-van den Berg A, Hop WCJ, Riehm H, Bartram C . Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood Lancet 1998 352: 1731–1738
Kaspers GJL, Veerman AJP, Pieters R, Van Zantwijk CH, Smets LA, Van Wering ER, Van der Does-van den Berg A . In vitro cellular drug resistance and prognosis in newly diagnosed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1997 90: 2723–2729
Davies HA, Lennard L, Lilleyman JS . Variable mercaptopurine metabolism in children with leukaemia: a problem of non-compliance? Br Med J 1993 306: 1239–1240
Veerman AJP, Hählen K, Kamps WA, Van Leeuwen EF, De Vaan GAM, Solbu G, Suciu S, Van Wering ER, Van der Does-van den Berg A . High cure rate with a moderately intensive treatment regiment in non-high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of protocol ALL VI from the Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 911–918
Kamps WA, Veerman AJP, van Wering ER, van Weerden JF, Slater R, Van der Does-van den Berg A . Long-term follow up of Dutch Childhood Leukemia Study Group (DCLSG) protocols for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, 1984–1991 Leukemia 2000 14: 2240–2246
Sluis van der IM, Heuvel van den MM, Hählen K, Krenning EP, Muinck Keizer-Schrama de SMPF . Bone mineral density, body composition, and height in long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood Med Pediatr Oncol 1999 33: 247 (Abstr.)
Tan ML, Kardos G, Veerman AJP, Van der Does-van den Berg A, Kamps WA . Avascular osteonecrosis as side effect of treatment in childhood ALL may not be dependent upon dexemethasone dose Med Pediatr Oncol 1999 33: 246 (Abstr.)
Acknowledgements
The DCLSG thanks the I-BFM-SG members Prof dr H-J Riehm (Hannover), Prof dr H Gadner (Vienna), Prof dr G Masera (Monza) and Dr M Schrappe (Hannover) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
DCLSG Board Members 1991: W A Kamps, P J van Dijken, K Hählen, F A E Nabben, A Postma, J A Rammeloo, G A M de Vaan, Eth. Korthof, A J P Veerman
NWKGC Members 1991: R Slater (Amsterdam), A Hagemeijer-Hausman (Rotterdam), E van den Berg (Groningen), A Hamers (Maastricht), C G Beverstock (Leiden), A Geurts van Kessel (Nijmegen), D E M Olde Weghuis (Utrecht), W Kroes (Amsterdam), M Blij-Philipsen (Veldhoven)
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamps, W., Bökkerink, J., Hakvoort-Cammel, F. et al. BFM-oriented treatment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia without cranial irradiation and treatment reduction for standard risk patients: results of DCLSG protocol ALL-8 (1991–1996). Leukemia 16, 1099–1111 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402489
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402489
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Flowcytometric evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid in childhood ALL identifies CNS involvement better then conventional cytomorphology
Leukemia (2021)
-
Progress against childhood and adolescent acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in the Netherlands, 1990–2015
Leukemia (2021)
-
Reduced vs. standard dose native E. coli-asparaginase therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: long-term results of the randomized trial Moscow–Berlin 2002
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2019)
-
High STAP1 expression in DUX4-rearranged cases is not suitable as therapeutic target in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Neurotoxicity after high-dose methotrexate (MTX) is adequately explained by insufficient folinic acid rescue
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (2017)