Special Issues
2020
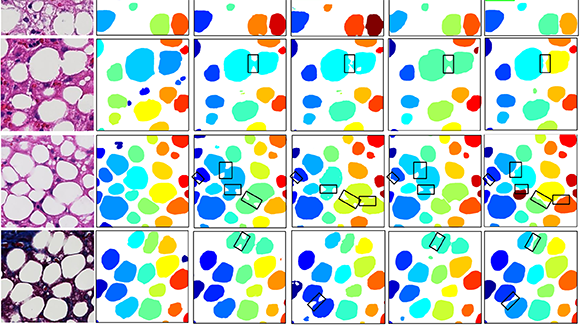
Computational Pathology
TRP ion channels in the pathobiology of disease
 Transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels serve as cellular sensors that respond to a range of physical and chemical stimuli. Twenty-eight mammalian TRP ion channels have been reported, which belong to six subfamilies (TRPV, TRPM, TRPC, TRPA, TRPP, and TRPML). This collection of articles from Laboratory Investigation describes the roles of various TRP ion channels in inflammation, fibrosis and cancer.
Transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels serve as cellular sensors that respond to a range of physical and chemical stimuli. Twenty-eight mammalian TRP ion channels have been reported, which belong to six subfamilies (TRPV, TRPM, TRPC, TRPA, TRPP, and TRPML). This collection of articles from Laboratory Investigation describes the roles of various TRP ion channels in inflammation, fibrosis and cancer.
Techniques and Models
2019
Neurodegenerative Diseases
 The growing burden of neurodegenerative diseases on patients, their families, and health care providers has also stimulated some exciting new developments in the field. This issue of Laboratory Investigation provides a broad view of the field of neurodegenerative diseases with diverse papers focusing on basic research, clinicopathological correlation, neuropathological diagnosis.
The growing burden of neurodegenerative diseases on patients, their families, and health care providers has also stimulated some exciting new developments in the field. This issue of Laboratory Investigation provides a broad view of the field of neurodegenerative diseases with diverse papers focusing on basic research, clinicopathological correlation, neuropathological diagnosis.
Pathophysiological Basis of Vascular Disease
 This collection of LI papers focuses on developments in our understanding of the underlying pathophysiological processes that contribute to cardiovascular disease.
This collection of LI papers focuses on developments in our understanding of the underlying pathophysiological processes that contribute to cardiovascular disease.
2018
The Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase Superfamily: State of the Art
 Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPK), encoded by NME (NM23) genes, control intracellular nucleotide homeostasis. In this collection, the authors discuss three major cellular processes that involve members of the multi-functional NME/NDPK family: cancer and metastasis dissemination, membrane remodeling and nucleotide channeling, and protein histidine phosphorylation.
Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPK), encoded by NME (NM23) genes, control intracellular nucleotide homeostasis. In this collection, the authors discuss three major cellular processes that involve members of the multi-functional NME/NDPK family: cancer and metastasis dissemination, membrane remodeling and nucleotide channeling, and protein histidine phosphorylation.
2017
Cancer Stem Cells and Pluripotent/multipotent cells

Malignant Melanoma: from causes to cures

The Translational Pathology of Melanoma

2016
WNT Signalling in Fibrosis, Inflammation and Cancer

2015
Imaging Advances

