Abstract
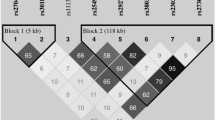
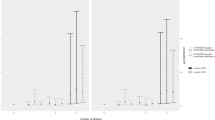
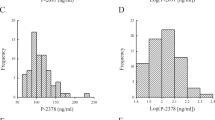
Abnormal matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 levels may have a role in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. We examined whether MMP-9 genetic polymorphisms (g.−1562C>T and g.−90(CA)13−25) modify plasma MMP-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 levels and the responses to antihypertensive therapy in 214 patients with preeclampsia (PE), 185 patients with gestational hypertension (GH) and a control group of 214 healthy pregnant (HP). Alleles for the g.−90(CA)13−25 polymorphism were grouped L (low) (<21 CA repeats) or H (high) (⩾21 CA repeats). Plasma MMP-9 and TIMP-1 concentrations were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Plasma MMP-9 concentrations were not affected by genotypes or haplotypes in HP and PE groups, except for the g.−90(CA)13−25 polymorphism: GH patients with the LH genotype for this polymorphism have higher MMP-9 levels than those with other genotypes. The T allele for the g.−1562C>T polymorphism and the H4 haplotype (combining T and H alleles) are associated with GH and lack of responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in GH. The H2 haplotype (combining C and H alleles) was associated with lack of responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in PE, but not in GH. In conclusion, our results show that MMP-9 genetic variants are associated with GH and suggest that MMP-9 haplotypes affect the responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maynard S, Epstein FH, Karumanchi SA . Preeclampsia and angiogenic imbalance. Annu Rev Med 2008; 59: 61–78.
Myers J, Mires G, Macleod M, Baker P . In preeclampsia, the circulating factors capable of altering in vitro endothelial function precede clinical disease. Hypertension 2005; 45: 258–263.
Roberts JM, Gammill HS . Preeclampsia: recent insights. Hypertension 2005; 46: 1243–1249.
Leik CE, Walsh SW . Neutrophils infiltrate resistance-sized vessels of subcutaneous fat in women with preeclampsia. Hypertension 2004; 44: 72–77.
Visse R, Nagase H . Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 2003; 92: 827–839.
Narumiya H, Zhang Y, Fernandez-Patron C, Guilbert LJ, Davidge ST . Matrix metalloproteinase-2 is elevated in the plasma of women with preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 2001; 20: 185–194.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Cavalli RC, Tanus-Santos JE . Comparative assessment of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, and their inhibitors, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2 in preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Clin Biochem 2008; 41: 875–880.
Tayebjee MH, Karalis I, Nadar SK, Beevers DG, MacFadyen RJ, Lip GY . Circulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1 and -2 levels in gestational hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2005; 18: 325–329.
Kolben M, Lopens A, Blaser J, Ulm K, Schmitt M, Schneider KT et al. Proteases and their inhibitors are indicative in gestational disease. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996; 68: 59–65.
Montagnana M, Lippi G, Albiero A, Scevarolli S, Salvagno GL, Franchi M et al. Evaluation of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and their inhibitors in physiologic and pre-eclamptic pregnancy. J Clin Lab Anal 2009; 23: 88–92.
Isaka K, Usuda S, Ito H, Sagawa Y, Nakamura H, Nishi H et al. Expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in human trophoblasts. Placenta 2003; 24: 53–64.
Shimonovitz S, Hurwitz A, Dushnik M, Anteby E, Geva-Eldar T, Yagel S . Developmental regulation of the expression of 72 and 92 kd type IV collagenases in human trophoblasts: a possible mechanism for control of trophoblast invasion. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994; 171: 832–838.
Chow AK, Cena J, Schulz R . Acute actions and novel targets of matrix metalloproteinases in the heart and vasculature. Br J Pharmacol 2007; 152: 189–205.
Jeyabalan A, Novak J, Doty KD, Matthews J, Fisher MC, Kerchner LJ et al. Vascular matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates the inhibition of myogenic reactivity in small arteries isolated from rats after short-term administration of relaxin. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 189–197.
Sankaralingam S, Arenas IA, Lalu MM, Davidge ST . Preeclampsia: current understanding of the molecular basis of vascular dysfunction. Expert Rev Mol Med 2006; 8: 1–20.
Van den Steen PE, Dubois B, Nelissen I, Rudd PM, Dwek RA, Opdenakker G . Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2002; 37: 375–536.
Zhang B, Ye S, Herrmann SM, Eriksson P, de Maat M, Evans A et al. Functional polymorphism in the regulatory region of gelatinase B gene in relation to severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 1999; 99: 1788–1794.
Peters DG, Kassam A, St Jean PL, Yonas H, Ferrell RE . Functional polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-9 promoter as a potential risk factor for intracranial aneurysm. Stroke 1999; 30: 2612–2616.
Shimajiri S, Arima N, Tanimoto A, Murata Y, Hamada T, Wang KY et al. Shortened microsatellite d(CA)21 sequence down-regulates promoter activity of matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene. FEBS Lett 1999; 455: 70–74.
Demacq C, Vasconcellos VB, Marcaccini AM, Gerlach RF, Machado AA, Tanus-Santos JE . A genetic polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) affects the changes in circulating MMP-9 levels induced by highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV patients. Pharmacogenomics J 2009; 9: 265–273.
Coolman M, de Maat M, Van Heerde WL, Felida L, Schoormans S, Steegers EA et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene −1562C/T polymorphism mitigates preeclampsia. Placenta 2007; 28: 709–713.
Palei AC, Sandrim VC, Duarte G, Cavalli RC, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE . Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 genotypes and haplotypes in preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. Clin Chim Acta 2010; 411: 874–877.
Report of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000; 183: S1–S22.
Demacq C, de Souza AP, Machado AA, Gerlach RF, Tanus-Santos JE . Genetic polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 does not affect plasma MMP-9 activity in healthy subjects. Clin Chim Acta 2006; 365: 183–187.
Demacq C, Vasconcellos VB, Marcaccini AM, Gerlach RF, Silva Jr WA, Tanus-Santos JE . Functional polymorphisms in the promoter of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) gene are not linked with significant plasma MMP-9 variations in healthy subjects. Clin Chem Lab Med 2008; 46: 57–63.
Lacchini R, Jacob-Ferreira AL, Luizon MR, Coeli FB, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Gasparini S et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 gene haplotypes affect left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients. Clin Chim Acta 2010; 411: 1940–1944.
Lacchini R, Metzger IF, Luizon M, Ishizawa M, Tanus-Santos JE . Interethnic differences in the distribution of matrix metalloproteinases genetic polymorphisms are consistent with interethnic differences in disease prevalence. DNA Cell Biol 2010; 29: 649–655.
Sandrim VC, Palei AC, Luizon MR, Izidoro-Toledo TC, Cavalli RC, Tanus-Santos JE . eNOS haplotypes affect the responsiveness to antihypertensive therapy in preeclampsia but not in gestational hypertension. Pharmacogenom J 2010; 10: 40–45.
Donnelly R, Collinson DJ, Manning G . Hypertension, matrix metalloproteinases and target organ damage. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1627–1630.
Chappell S, Morgan L . Searching for genetic clues to the causes of pre-eclampsia. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006; 110: 443–458.
Podymow T, August P . Update on the use of antihypertensive drugs in pregnancy. Hypertension 2008; 51: 960–969.
Martinez ML, Lopes LF, Coelho EB, Nobre F, Rocha JB, Gerlach RF et al. Lercanidipine reduces matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in patients with hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2006; 47: 117–122.
Zervoudaki A, Economou E, Pitsavos C, Vasiliadou K, Aggeli C, Tsioufis K et al. The effect of Ca2+ channel antagonists on plasma concentrations of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 273–276.
Zervoudaki A, Economou E, Stefanadis C, Pitsavos C, Tsioufis K, Aggeli C et al. Plasma levels of active extracellular matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in patients with essential hypertension before and after antihypertensive treatment. J Hum Hypertens 2003; 17: 119–124.
Marcal DM, Rizzi E, Martins-Oliveira A, Ceron CS, Guimaraes DA, Gerlach RF et al. Comparative study on antioxidant effects and vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 downregulation by dihydropyridines in renovascular hypertension. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2011; 383: 35–44.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Sao Paulo (FAPESP), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palei, A., Sandrim, V., Amaral, L. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 polymorphisms affect plasma MMP-9 levels and antihypertensive therapy responsiveness in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Pharmacogenomics J 12, 489–498 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.31
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Associations of polymorphisms of CYP2D6 and CYP2C9 with early onset severe pre-eclampsia and response to labetalol therapy
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2018)
-
Gene–gene interactions in the NAMPT pathway, plasma visfatin/NAMPT levels, and antihypertensive therapy responsiveness in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy
The Pharmacogenomics Journal (2017)
-
An update on the pharmacogenetics of treating hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2015)
-
Functional polymorphisms in the promoter region of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and susceptibility to obstructive sleep apnea
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Is there any genetic predisposition of MMP-9 gene C1562T and MTHFR gene C677T polymorphisms with essential hypertension?
Cytotechnology (2015)