Abstract
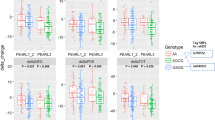
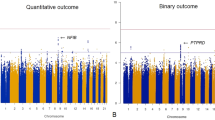
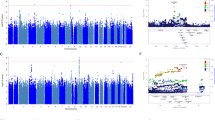
Clinical trial data were evaluated for the association between 22 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and response in acutely ill patients diagnosed with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or schizophreniform disorder, who were treated with oral risperidone. All patients in the exploratory (78 African Americans) and validation (65 whites) data sets received risperidone 2–6 mg per day over 2–12 weeks. Two SNPs were found to have significant associations with response to risperidone over 2–12 weeks in both African-American and white patients and had a consistent direction of effect in both cohorts. Metabotropic glutamate receptor (GRM3) SNP, rs724226, was associated with a change in the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) total response. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) SNP, rs165599, was moderately associated with a change in the PANSS Negative score. The greater prevalence of poor-responder GRM3 and COMT alleles in white versus African-American patients might have a clinical significance in evaluating the ethnic-specific response to risperidone.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arranz MJ, de Leon J . Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia: a review of last decade of research. Mol Psychiatry 2007; 12: 707–747.
Ascher-Svanum H, Nyhuis AW, Faries DE, Kinon BJ, Baker RW, Shekhar A . Clinical, functional, and economic ramifications of early nonresponse to antipsychotics in the naturalistic treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2008; 34: 1163–1171.
Kinon BJ, Chen L, Ascher-Svanum H, Stauffer VL, Kollack-Walker S, Sniadecki JL et al. Predicting response to atypical antipsychotics based on early response in the treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2008; 102: 230–240.
Schäfer M, Rujescu D, Giegling I, Guntermann A, Erfuth A, Bondy B et al. Association of short-term response to haloperidol treatment with a polymorphism in the dopamine D2 receptor gene. Am J Psychiatry 2001; 158: 802–804.
Yamanouchi Y, Iwata N, Suzuki T, Kitajima T, Ikeda M, Ozaki N . Effect of DRD2, 5-HT2A, and COMT genes on antipsychotic response to risperidone. Pharmacogenomics J 2003; 3: 356–361.
Perlis RH, Fijal B, Adams DH, Sutton VK, Trivedi MH, Houston JP . COMT variants associated with duloxetine response: a candidate gene association analysis of a randomized clinical treatment trial for major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2009; 65: 785–791.
Weickert TW, Goldberg TE, Mishara A, Apud JA, Kolachana BS, Egan MF et al. Catechol-O-methyltransferase val108/158met genotype predicts working memory response to antipsychotic medications. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56: 677–682.
Lane HY, Lee CC, Chang YC, Lu CT, Huang CH, Chang WH . Effects of dopamine D2 receptor Ser311Cys polymorphism and clinical factors on risperidone efficacy for positive and negative symptoms and social function. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2004; 7: 461–470.
Lencz T, Robinson DG, Xu K, Ekholm J, Sevy S, Gunduz-Bruce H et al. DRD2 promoter region variation as a predictor of sustained response to antipsychotic medication in first-episode schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 529–531.
Adams DH, Close S, Farmen M, Downing AM, Breier A, Houston JP . Dopamine receptor D3 genotype association with greater acute positive symptom remission with olanzapine therapy in predominantly Caucasian patients with chronic schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 2008; 23: 267–274.
Lane HY, Hsu SK, Liu YC, Chang YC, Huang CH, Chang WH . Dopamine D3 receptor Ser9Gly polymorphism and risperidone response. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2005; 25: 6–11.
Bishop JR, Ellingrod VL, Moline J, Miller D . Association between the polymorphic GRM3 gene and negative symptom improvement during olanzapine treatment. Schizophr Res 2005; 77: 253–260.
Lane HY, Chang YC, Chiu CC, Chen ML, Hsieh MH, Chang WH . Association of risperidone treatment response with a polymorphism in the 5-HT2A receptor gene. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 1593–1595.
Kim B, Choi EY, Kim CY, Song K, Joo YH . Could HTR2A T102C and DRD3 Ser9Gly predict clinical improvement in patients with acutely exacerbated schizophrenia? Results from treatment responses to risperidone in a naturalistic setting. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 2008; 23: 61–67.
Arranz MJ, Munro J, Owen MJ, Spurlock G, Sham PC, Zhao J et al. Evidence for association between the polymorphisms in the promoter and coding regions of the 5-HT2A receptor gene and response to clozapine. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 61–66.
Sodhi MS, Arranz MJ, Curtis D, Ball DM, Sham P, Roberts GW et al. Association between clozapine resistance and allelic variation in the 5-HT2C receptor gene. Neuroreport 1995; 7: 169–172.
Lane HY, Lin CC, Huang CH, Chang YC, Hsu SK, Chang WH . Risperidone response and 5-HT6 receptor gene variance: Genetic association analysis with adjustment for nongenetic confounders. Schizophr Res 2004; 67: 63–70.
Predicting Response to Risperidone Treatment Through Identification of Early-Onset of Antipsychotic Drug Action in Schizophrenia. Approved 30 Jan 2006. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00373321.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA . The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987; 13: 261–276.
Jurinke C, van den Boom D, Cantor CR, Koster H . Automated genotyping using the DNA MassArray technology. Methods Mol Biol 2002; 187: 179–192.
Andreasen NC, Carpenter Jr WT, Kane JM, Lasser RA, Marder SR, Weinberger DR . Remission in schizophrenia: proposed criteria and rationale for consensus. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162: 441–449.
Bray NJ, Buckland PR, Williams NM, Williams HJ, Norton N, Owen MJ et al. A haplotype implicated in schizophrenia susceptibility is associated with reduced COMT expression in human brain. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 152–161.
Shifman S, Bronstein M, Sternfeld M, Pisanté-Shalom A, Lev-Lehman E, Weizman A et al. A highly significant association between a COMT haplotype and schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1296–1302.
Chan RC, Chen RY, Chen EY, Hui TC, Cheung EF, Cheung HK et al. The differential clinical and neurocognitive profiles of COMT SNP rs165599 genotypes in schizophrenia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2005; 11: 202–204.
Berrettini WH, Wileyto EP, Epstein L, Restine S, Hawk L, Shields P et al. Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene variants predict response to bupropion therapy for tobacco dependence. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 61: 111–118.
Bishop JR, Ellingrod VL . Neuropsychiatric pharmacogenetics: moving toward a comprehensive understanding of predicting risks and response. Pharmacogenomics 2004; 5: 463–477.
Correll CU, Malhotra AK, Kaushik S, McMeniman M, Kane JM . Early prediction of antipsychotic response in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 2063–2065.
Leucht S, Busch R, Kissling W, Kane JM . Early prediction of antipsychotic nonresponse among patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 2007; 68: 352–360.
Leucht S, Shamsi SA, Busch R, Kissling W, Kane JM . Predicting antipsychotic drug response—replication and extension to six weeks in an international olanzapine study. Schizophr Res 2008; 101: 312–319.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of Virginia M Peschke of Medical Communication Consultants in the preparation of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fijal, B., Kinon, B., Kapur, S. et al. Candidate-gene association analysis of response to risperidone in African-American and white patients with schizophrenia. Pharmacogenomics J 9, 311–318 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2009.24
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2009.24