Abstract
Banana (Musa acuminata) is one of the most popular fresh fruits. However, the rapid spread of fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) in tropical areas severely affected banana growth and production. Thus, it is very important to identify candidate genes involved in banana response to abiotic stress and pathogen infection, as well as the molecular mechanism and possible utilization for genetic breeding. Heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) are widely known for their common involvement in various abiotic stresses and plant-pathogen interaction. However, no MaHsf has been identified in banana, as well as its possible role. In this study, genome-wide identification and further analyses of evolution, gene structure and conserved motifs showed closer relationship of them in every subgroup. The comprehensive expression profiles of MaHsfs revealed the tissue- and developmental stage-specific or dependent, as well as abiotic and biotic stress-responsive expressions of them. The common regulation of several MaHsfs by abiotic and biotic stress indicated the possible roles of them in plant stress responses. Taken together, this study extended our understanding of MaHsf gene family and identified some candidate MaHsfs with specific expression profiles, which may be used as potential candidates for genetic breeding in banana.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Plant heat shock responses are mediated by heat shock elements (HSEs, nTTCnnGAAnnTTCn), which are widely present in the upstream of the heat shock proteins (HSPs)1,2,3,4,5. The first specific transcription regulator that is responsible for HSE bindng, was characterized and confirmed as heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)6. Thereafter, Hsfs act through the cis-acting element of HSE, thus directly recognize the promoters of HSPs and regulate their transcripts7,8,9.
As evolutionarily conserved transcription factors, Hsfs have some conserved domains. (i) the highly structured N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD), that is responsible for binding HSEs in the promoters of several HSPs; (ii) the oligomerization domain (HR-A/B), that is connected to the DBD by a flexible linker; (iii) nuclear export signal (NES) of motif –LFGV- and nuclear localization signal (NLS), (iv) C-terminal activator motic, also known as AHA motif 8,9,10,11,12. According to the flexible linker of variable length (about 15–80 amino acids) and the oligomerization domain (HR-A/B), plant Hsfs can be divided into at least three types, including class A (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9), class B (B1, B2, B3, B4) and class C (C1, C2)1,2,9,10,11,12.
Plant Hsfs are important regulators of various plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses, including heat, cold, salt, drought, osmotic12,13,14,15,16, as well as bacterial and fungal pathogen infection17,18,19,20. After initially identified in yeast6, plant Hsf gene family has been identified and characterized in more and more plant species, including alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)21, Arabidopsis thaliana22, rice (Oryza sativa L.)23,24, maize (Zea mays L.)25, Medicago truncatula, Populus trichocarpa26, wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)27, soybean (Glycine max)28,29, Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis)10,30, cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)31, pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan), barrel medic (Medicago truncatula)32, pepper (Capsicum annuum L.)33,34, pear (Pyrus bretschneideri)35, Populus euphratica36, strawberry (Fragaria vesca)37, tea plant (Camellia sinensis)38, wild Chinese grapevine (Vitis pseudoreticulata)39, etc.
Banana (Musa acuminata) is one of the most popular fresh fruits worldwide, and cultivated in the subtropical and tropical areas40,41,42,43. To date, many banana varieties have been screen and cultivated in China. For example, BaXi jiao (Musa acuminata L. AAA group cv. Cavendish, BX) is widely cultivated for its high yield, long fingers and long-term storage; Fen jiao (Musa ABB Pisang Awak, FJ) is widely cultivated for its good flavor and good resistant to various abiotic stresses44,45. However, because of the rapid spread of fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) in tropical areas, banana growth and production are severely affected46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58. Thus, it is very important to identify candidate genes involved in banana response to both high temperature and pathogen infection, as well as the molecular mechanism and possible utilization for genetic breeding. Hsfs are widely known for their common involvement in various abiotic stresses including heat stress and plant-pathogen interaction. However, no MaHsf have been identified in banana, as well as their possible roles. In this study, genome-wide identification and expression analysis during development and stress response were performed to extend our understanding and possible utilization of MaHsfs in genetic breeding.
Results
Genome-wide identification of Hsfs in banana
After initial identification using Musa acuminata v1 Phytozome database v10.3 and Plant Transcription Factor Database (PlantTFDB) v3.059 as well as further confirmation using National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)’s conserved domain database (CDD)60 and Pfam database61, 43 MaHsfs were successfully obtained from banana genome (Supplementary Table S1). The amino acid residues, molecular weight (MW) and theoretical isoelectric point (pI) of 43 MaHsf proteins were largely different, ranging from 96 aa/10.25 kDa (MaHsf12) to 547 aa/60.12 kDa (MaHsf8), 4.48 pI (MaHsf8) to 11.84 pI (MaHsf39) (Supplementary Table S1).
Phylogenetic analysis of MaHsfs
To investigate the evolutionary relationship among Hsfs from cassava, Arabidopsis and rice, an un-rooted Neighbor-Joining tree was created based on the coding sequences of 43 MaHsfs, 22 AtHsfs and 25 OsHsfs (Fig. 1). Generally, MaHsfs have closer relationship with OsHsfs in comparison to AtHsfs, in accordance with the current understanding in their evolutionary history. Evolutionary analysis also identified some orthologous Hsfs between cassava and rice, indicating the similar roles of these genes in cassava and Arabidopsis.
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis of MaHsfs
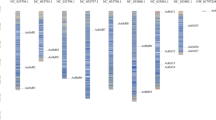
To reveal the structural features of MaHsfs, intron/exon and upstream (5′ UTR)/downstream (3′ UTR) structures were analyzed using Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS) v2.062. The numbers of intron of MaHsfs varied from 1 to 5 (Fig. 2). Most of MaHsfs (29 of 43) have no upstream and downstream sequences, only MaHsf10 and MaHsf11 have both upstream and downstream sequences, and 12 MaHsfs have only downstream sequences (Fig. 2). Moreover, MaHsfs in the same subfamilies exhibited similar exon-intron structure, indicating the link between evolutionary relationship and gene structure. To better understand the functional prediction of MaHsfs, 7 conserved motifs were identified using Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation (MEME) v4.11.0 (Fig. 3). Similarly, MaHsfs in the same subfamilies showed similar motifs, indicating the link between evolutionary relationship and conserved motifs.
Expression analysis of MaHsfs in different banana tissues
The expression levels of MaHsfs are important clues for their possible roles in banana growth and development, and the transcripts of MaHsfs in five-leaf stage leaves, roots and fruits of 80 days after flowering (DAF) were obtained by transcriptomic analysis44,45. Generally, MaHsfs showed similar expression pattern in leaves, roots and fruits of BX and FJ varieties, with litter differences in several genes (14 of 43 genes) (MaHsf8, 27, 17, 4, 43, 12, 16, 21, 14, 19, 24, 20, 36, 42) (Fig. 4). The MaHsfs with similar expression pattern can be clearly shown in the cluster analysis (Fig. 4).
For BX varieties, (i) 16 of 43 MaHsfs displayed higher transcripts in five-leaf stage leaves, relative lower transcripts in roots and fruits (cluster A). (ii) 19 of 43 MaHsfs exhibited relative higher transcripts in roots, and 8 of 43 MaHsfs showed lower transcripts in fruits (cluster B).
For FJ varieties, (i) 11 of 43 MaHsfs displayed higher transcripts in five-leaf stage leaves, relative lower transcripts in roots or fruits (cluster A). (ii) 22 of 43 MaHsfs exhibited relative higher transcripts only in roots, 9 of 43 MaHsfs exhibited relative higher transcripts in both roots and fruits, 1 of 43 MaHsfs showed lower transcripts in fruits (cluster B).
Expression analysis of MaHsfs in different developmental stages of fruit development and ripening of banana
Besides different banana tissues, the transcripts of MaHsfs in different stages of fruit development (0, 20, 80 DAF) and ripening (8 and 14 days (BX) or 3 and 6 days (FJ) postharvest (DPH)) were also analyzed by transcriptomic analysis44,45. Although some slight differences were exhibited, MaHsfs showed similar expression pattern in different stages of fruit development and ripening of BX and FJ varieties, as evidenced by the cluster analysis in the heatmap (Fig. 5). In cluster A, most of MaHsfs exhibited relative higher transcript accumulation in fruit development and ripening, and three MaHsfs (MaHsf23, 25, 43) showed decreased transcripts in later fruit ripening in both BX and FJ varieties (Fig. 5A). In cluster B, most of MaHsfs showed relative lower transcripts in fruit development and ripening in both BX and FJ varieties, while MaHsf39 showed no significant difference in these stages of BX, 6 MaHsfs (MaHsf7, 12, 21, 22, 38, 42) displayed relative higher transcripts in fruit development and early fruit ripening (Fig. 5B).
Gene expression heatmap of MaHsfs in different developmental stages.
The samples of different stages of fruit development and ripening were harvested from fruits of 0, 20, 80 DAF, 8 and 14 days (BX) or 3 and 6 days (FJ) DPH) as Hu et al. (2015b,c) described. The heatmap was constructed using CLUSTER software and Java Treeview software.
Expression analysis of MaHsfs in response to cold, salt and osmotic stresses
To extend our understanding of MaHsfs in response to abiotic stress, the expression patterns of these genes in response to cold, salt and osmotic stresses were also revealed by transcriptomic analysis44,45. Although some similar expression patterns were exhibited (cluster A, B and C), MaHsfs showed complex expression patterns in response to abiotic stress in BX and FJ varieties, as evidenced by the cluster analysis in the heatmap (Fig. 6).
Gene expression heatmap of MaHsfs in response to cold, salt and osmotic stresses.
Five-leaf stage banana seedlings were treated by 4 °C for 22 h, 300 mM NaCl for 7 d, or 200 mM Mannitol for 7 d as Hu et al. (2015b,c) described. The heatmap was constructed using CLUSTER software and Java Treeview software.
For BX varieties, 20, 19 and 13 MaHsfs were regulated by cold stress (16 up-regulated genes and 4 down-regulated genes), osmotic stress (13 up-regulated genes and 6 down-regulated genes) and salt stress (5 up-regulated genes and 8 down-regulated genes), respectively (Figs 6 and 7A). Among these genes, MaHsf31 transcript was commonly up-regulated by cold, salt and osmotic stresses, MaHsf19 and MaHsf36 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by cold and osmotic stresses, MaHsf12, 35, 39 and 43 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by salt and osmotic stresses (Figs 6 and 7A). On the contrary, MaHsf38 transcript was commonly down-regulated by cold and salt stresses, MaHsf20, 21, 22, 24 and 29 transcripts were commonly down-regulated by salt and osmotic stresses (Figs 6 and 7A).
Vene diagram showing the number of overlapping MaHsfs that are differentially expressed under cold, salt and osmotic stresses.
(A,B) Vene diagram showing the number of differentially expressed in response to cold, salt and osmotic stresses in BX variety (A) and FJ variety (B). (C–E) Vene diagram showing the number of differentially expressed in response to cold stress (C), osmotic stress (D) and salt stress (E) in both BX and FJ varieties.
For FJ varieties, 18, 13 and 10 MaHsfs were regulated by cold stress (16 up-regulated genes and 2 down-regulated genes), osmotic stress (11 up-regulated genes and 2 down-regulated genes) and salt stress (7 up-regulated genes and 3 down-regulated genes), respectively (Figs 6 and 7B). Among these genes, MaHsf21 and MaHsf40 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by cold, salt and osmotic stresses, MaHsf6, 9, 18, 22 and 24 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by cold and osmotic stresses, MaHsf16 and MaHsf35 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by cold and salt stresses, MaHsf20 and MaHsf38 transcripts were commonly up-regulated by salt and osmotic stresses (Figs 6 and 7B). On the contrary, MaHsf43 transcript was commonly down-regulated by salt and osmotic stresses (Figs 6 and 7B).
Moreover, we also found the transcripts of some MaHsfs were regulated by the same stress in both BX and FJ varieties (Fig. 7C–E). For cold stress, 12 MaHsfs (MaHsf5, 6, 8, 9, 18, 19, 21, 22, 24, 25, 29, 31) transcripts were up-regulated in both BX and FJ varieties (Fig. 7C). For osmotic stress, MaHsf36 transcript was up-regulated in both BX and FJ varieties (Fig. 7D). For salt stress, MaHsf35 transcript was up-regulated, MaHsf24 and MaHsf29 transcripts were down-regulated in both BX and FJ varieties (Fig. 7E).
Identification of several MaHsfs responsive to Foc1 and Foc 4 inoculation
The rapid spread of fungal pathogen Foc in tropical areas severely affects banana growth and production46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58. To investigate the possible involvement and utilization of MaHsfs in plant-pathogen interaction, the transcriptomic analysis of banana roots in response to control, Foc1 or Foc4 were also obtained50. Totally, 12 of 43 MaHsfs were significantly regulated by Foc infection (Fig. 8). Among these genes, 5 MaHsfs (MaHsf3, 17, 20, 24, 41) were commonly up-regulated by Foc 1 and Foc 4, 2 MaHsfs (MaHsf31, 35) were commonly down-regulated by Foc 1 and Foc 4 (Fig. 8). MaHsf1 and MaHsf6 were first up-regulated and later down-regulated by Foc 1 and Foc 4, whereas MaHsf2 and MaHsf4 were down-regulated by Foc 1, but were up-regulated by Foc 4 (Fig. 8).
Discussion
As one of the most popular fresh fruits worldwide, banana are severally destroyed by various abiotic stress (cold, salt, drought, etc) and biotic stress (especially the fungal pathogen Foc infection) during growth and developmental stages46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58. To solve these questions, the farmers and researchers have increased the planting area and improved cultivated technique, however, the effect is very limited. Because no strong stress-resistant banana variety can be used, it is essential to construct new stress-resistant variety through genetic and molecular breeding46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55. Considering the common involvement of Hsfs in plant stress responses, MaHsfs were chosen for analyzed as candidate genes for further utilization in genetic breeding.
Generally, 43 MaHsfs were genome-wide identified and the phylogenetic evolution of these genes was also revealed. Based on the data of RNA-seq44,45,50, the comprehensive expression profiles of 43 MaHsfs were revealed. To our knowledge, this is the first study extending our understanding of MaHsf gene family. Generally, the expression profiles can be divided to two sections. One is the expression of 43 MaHsfs at developmental stages, or different tissues, this is the basic information of this gene family. We found that the transcripts of some MaHsfs are tissue- and developmental stage-specific or dependent, indicating the possible roles of them in specific growth or developmental stages, such as fruit ripening. The other one gene expression in response to various abiotic and biotic stresses, which intends to identify several candidate genes commonly regulated by various stresses for stress-related genetic breeding.
In this study, multiple of abiotic and biotic stress-responsive MaHsfs were also identified, in accordance with previous studies of Hsf gene family in other plant species1,2,3,4,5. Based on the clues from transcript pattern, the in vivo roles of several plant Hsfs have been revealed. AtHsfA1s, AtHsfA2 and AtHsfA6a confers heat, salt and dehydration stress resistance in Arabidopsis3,5,7,8. OsHSFA2dI is essential for heat stress resistance in rice1, respectively. AtHsfA6a confers salt and dehydration stress resistance in Arabidopsis3. A seed preferential TaHsf confers abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis27, and overexpression of GmHsf-24 increased drought and heat stress resistance in Arabidopsis29. These results provide solid evidence of the protective roles of plant Hsfs in abiotic stress responses. In this study, 12 MaHsfs (12, 19, 20, 21, 22, 24, 29, 31, 35, 36, 39, 43) in BX variety and 10 MaHsfs (6, 9, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 35, 38, 43) in FJ variety were commonly regulated by at least two abiotic stresses (fold change >2), indicating their possible roles in abiotic stress. Thus, these MaHsfs can be further chosen for functional analysis.
Additionally, plant Hsfs are also involved in plant-pathogen interactions17,18,19,20. The activation of OsHsf23 is important for cell death in rice inoculated with rice blast fungus20. AtHsfA1b, AtHsfB1 and AtHsfB2b are involved in plant pathogen resistance and defense gene expression17,19. Thus, the identification of 12 Foc-responsive MaHsfs (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 17, 20, 24, 27, 31, 35, 41) may be further used as potential candidates in disease genetic breeding in banana. Notably, MaHsf31 transcript was commonly up-regulated by cold, salt and osmotic stresses in BX, and was down-regulated by Foc 1 and Foc 4 infection; MaHsf20 and MaHsf24 transcripts were commonly regulated by salt stress, osmotic stress and Foc infection. There are also other MaHsfs that are regulated by both abiotic and biotic stresses, such as MaHsf35. The common regulation of these MaHsfs by abiotic and biotic stress indicated the possible roles of them in plant stress responses, and these MaHsfs may be potential candidates for further functional analysis and genetic breeding in banana. We highlight the possible common involvement of four MaHsfs (MaHsf20, MaHsf24, MaHsf31 and MaHsf35) in both abiotic and biotic stresses. It is just the beginning, further functional analysis will reveal their in vivo roles as well as underlying mechanism.
Taken together, this study is the first study showing MaHsf gene family as well as their specific expression profiles, which may be used as potential candidates for genetic breeding in banana.
Methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
Banana varieties of BX and FJ were used in this study. The five leaf stage seedlings were from Banana Tissue Culture Center (Danzhou city, Hainan province, Institute of Banana and Plantains, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences). Thereafter, the seedlings were cultivated in soil in the greenhouse, which was controlled at 28 °C, with 12 h light/12 h dark cycles and 120–150 μmol quanta m−2 s−1 irradiance.
Genome-wide identification of MaHsfs
The candidate MaHsfs were first searched in Musa acuminata v1 (Banana) Phytozome database v10.3 (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#!info?alias=Org_Macuminata) and PlantTFDB v3.0 (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/index.php)59. Thereafter, the candidate MaHsfs were further checked and confirmed using CDD (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd)60 and Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org)61. Then the detailed information of MaHsfs including sequences, the locus name, chromosome location, gene and amino acid length were downloaded from Musa acuminata v1 (Banana) Phytozome database v10.3, the MW and pI of MaHsfs were analyzed using ProtParam software (http://web.expasy.org/protparam).
Phylogenetic analysis of MaHsfs
Besides the coding sequences of 43 MaHsfs, the coding sequences of 22 AtHsfs and 25 OsHsfs were obtained from hytozome database v10.3 (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html). The phylogenetic tree of these Hsfs was constructed using Clustalx 1.83 software and MEGA 5.05 software by the neighbor-joining method63,64.
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis of MaHsfs
Gene structure analysis of 43 MaHsfs was performed using GSDS v2.0 (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/index.php) by uploading the coding sequences and genomic sequences of these genes62. The conserved motifs of 43 MaHsfs were analyzed using the MEME v4.11.0 (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) by uploading the coding sequences according the instructions.
Expression profile analysis of MaHsfs
The transcriptomic data of two banana varieties (BX and FJ) in different organs, different developmental stages and in response to abiotic stress has been described in Hu et al.44,45. Briefly, the different organs include five-leaf stage leaves, roots and fruits of 80 DAF, different developmental stages include fruits of 0, 20, 80 DAF, 8 and 14 (BX) or 3 and 6 (FJ) DPH, abiotic stress treatment include 4 °C treatment for 22 h, 300 mM NaCl treatment for 7 d and 200 mM Mannitol treatment for 7 d.
The transcriptomic data of roots in response to pathogen fungal pathogen of Foc1 and Foc 4 has been described previously50. For the gene expression assay, sterile tissue cultivated banana roots were inoculated by control, Foc1 or Foc4 for 3 h, 27 h and 51 h.
Hierarchical cluster and gene expression heatmap analysis
The hierarchical cluster analysis of gene expression was performed using CLUSTER software (http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster/software.htm)63, and the heatmap was then constructed using Java Treeview software (http://jtreeview.sourceforge.net)65.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Wei, Y. et al. Heat shock transcription factors in banana: genome-wide characterization and expression profile analysis during development and stress response. Sci. Rep. 6, 36864; doi: 10.1038/srep36864 (2016).
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Cheng, Q. et al. An alternatively spliced heat shock transcription factor, OsHSFA2dI, functions in the heat stress-induced unfolded protein response in rice. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 17, 419–429 (2015).
Giesguth, M., Sahm, A., Simon, S. & Dietz, K. J. Redox-dependent translocation of the heat shock transcription factor AtHSFA8 from the cytosol to the nucleus in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett. 589, 718–725 (2015).
Hwang, S. M. et al. Functional characterization of Arabidopsis HsfA6a as a heat-shock transcription factor under high salinity and dehydration conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 37, 1202–1222 (2014).
Kotak, S., Port, M., Ganguli, A., Bicker, F. & von Koskull-Döring, P. Characterization of C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and identification of a new signature combination of plant class A Hsfs with AHA and NES motifs essential for activator function and intracellular localization. Plant J. 39, 98–112 (2004).
Nishizawa, A. et al. Arabidopsis heat shock transcription factor A2 as a key regulator in response to several types of environmental stress. Plant J. 48, 535–547 (2006).
Sorger, P. K. & Pelham, H. R. B. Yeast heat-shock factor is an essential DNA -binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell 54, 855–864 (1988).
Charng, Y. Y. et al. A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 143, 251–262 (2007).
Nishizawa-Yokoi, A. et al. HsfA1d and HsfA1e involved in the transcriptional regulation of HsfA2 function as key regulators for the Hsf signaling network in response to environmental stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 52, 933–945 (2011).
Singh, A. et al. OsHsfA2c and OsHsfB4b are involved in the transcriptional regulation of cytoplasmic OsClpB (Hsp100) gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Cell Stress Chaperones 17, 243–254 (2012).
Huang, X. Y. et al. Genome-wide identification, classification, and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa pekinensis). Genet. Mol. Res. 14, 2189–2204 (2015).
Shim, D. et al. Orthologs of the class A4 heat shock transcription factor HsfA4a confer cadmium tolerance in wheat and rice. Plant Cell 21, 4031–4043 (2009).
Yabuta, Y. Functions of heat shock transcription factors involved in response to photooxidative stresses in Arabidopsis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 20, 1–10 (2016).
Almoguera, C., Personat, J. M., Prieto-Dapena, P. & Jordano, J. Heat shock transcription factors involved in seed desiccation tolerance and longevity retard vegetative senescence in transgenic tobacco. Planta 242, 461–475 (2015).
Stief, A., Brzezinka, K., Lämke, J. & Bäurle, I. Epigenetic responses to heat stress at different time scales and the involvement of small RNAs. Plant Signal. Behav. 9, e970430 (2014).
Wang, C., Zhang, Q. & Shou, H. X. Identification and expression analysis of OsHsfs in rice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 10, 291–300 (2009).
Yamada, K. & Nishimura, M. Cytosolic heat shock protein 90 regulates heat shock transcription factor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav. 3, 660–662 (2008).
Bechtold, U. et al. Arabidopsis HEAT SHOCK TRANSCRIPTION FACTORA1b overexpression enhances water productivity, resistance to drought, and infection. J Exp. Bot. 64, 3467–3481 (2013).
Daurelio, L. D. et al. Characterization of Citrus sinensis transcription factors closely associated with the non-host response to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. J. Plant Physiol. 170, 934–942 (2013).
Kumar, M. et al. Heat shock factors HsfB1 and HsfB2b are involved in the regulation of Pdf1.2 expression and pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2, 152–165 (2009).
Tanabe, S. et al. The elicitor-responsive gene for a GRAS family protein, CIGR2, suppresses cell death in rice inoculated with rice blast fungus via activation of a heat shock transcription factor, OsHsf23. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 80, 145–151 (2015).
Friedberg, J. N., Bowley, S. R., McKersie, B. D., Gurley, W. B. & Czarnecka-Verner, E. Isolation and characterization of class A4 heat shock transcription factor from alfalfa. Plant Sci. 171, 332–344 (2006).
Guo, J. et al. Genome-wide analysis of heat shock transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. J. Genet. Genomics 35, 105–118 (2008).
Chauhan, H., Khurana, N., Agarwal, P. & Khurana, P. Heat shock factors in rice (Oryza sativa L.): genome-wide expression analysis during reproductive development and abiotic stress. Mol. Genet. Genomics 286, 171–187 (2011).
Jin, G. H., Gho, H. J. & Jung, K. H. A systematic view of rice heat shock transcription factor family using phylogenomic analysis. J. Plant Physiol. 170, 321–329 (2013).
Lin, Y. X. et al. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genomics 12, 76 (2011).
Wang, F. et al. Genome-wide analysis of the heat shock transcription factors in Populus trichocarpa and Medicago truncatula. Mol Biol. Rep. 39, 1877–1886 (2012).
Chauhan, H., Khurana, N., Agarwal, P., Khurana, J. P. & Khurana, P. A seed preferential heat shock transcription factor from wheat provides abiotic stress tolerance and yield enhancement in transgenic Arabidopsis under heat stress environment. PLoS One 8, e79577 (2013).
Chung, E., Kim, K. M. & Lee, J. H. Genome-wide analysis and molecular characterization of heat shock transcription factor family in Glycine max. J. Genet. Genomics 40, 127–135 (2013).
Li, P. S. et al. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsf family in soybean and functional identification of GmHsf-34 involvement in drought and heat stresses. BMC Genomics 15, 1009 (2014).
Song, X. et al. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage. Mol. Genet. Genomics 289, 541–551 (2014).
Wang, J., Sun, N., Deng, T., Zhang, L. & Zuo, K. Genome-wide cloning, identification, classification and functional analysis of cotton heat shock transcription factors in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). BMC Genomics 15, 961 (2014).
Lin, Y. et al. Genome duplication and gene loss affect the evolution of heat shock transcription factor genes in legumes. PLoS One 9, e102825 (2014).
Guo, M. et al. Cloning and expression analysis of heat-shock transcription factor gene CaHsfA2 from pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Genet. Mol. Res. 13, 1865–1875 (2014).
Guo, M. et al. Genome-wide analysis, expression profile of heat shock factor gene family (CaHsfs) and characterisation of CaHsfA2 in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 15, 151 (2015).
Qiao, X. et al. Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and five other Rosaceae species. BMC Plant Biol. 15, 12 (2015).
Shen, Z. et al. Populus euphratica HSF binds the promoter of WRKY1 to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Sci. 235, 89–100 (2015).
Hu, Y. et al. Identification, isolation, and expression analysis of heat shock transcription factors in the diploid woodland strawberry Fragaria vesca. Front Plant Sci. 6, 736 (2015).
Liu, Z. W. et al. Identification, classification, and expression profiles of heat shock transcription factors in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) under temperature stress. Gene 576, 52–59 (2016).
Hu, Y. et al. Identification and expression analysis of heat shock transcription factors in the wild Chinese grapevine (Vitis pseudoreticulata). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 99, 1–10 (2016).
Liu, J. et al. Role for the banana AGAMOUS-like gene MaMADS7 in regulation of fruit ripening and quality. Physiol Plant. 155, 217–231 (2015).
Liu, J. et al. Banana Ovate family protein MaOFP1 and MADS-box protein MuMADS1 antagonistically regulated banana fruit ripening. PLoS One 10, e0123870 (2015).
Xu, Y. et al. A banana aquaporin gene, MaPIP1;1, is involved in tolerance to drought and salt stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 14, 59 (2014).
Zhang, L. et al. The MaASR gene as a crucial component in multiple drought stress response pathways in Arabidopsis. Funct. Integr. Genomics 15, 247–260 (2015).
Hu, W. et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of aquaporin gene family during development and abiotic stress in banana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 19728–19751 (2015).
Hu, W. et al. The auxin response factor gene family in banana: genome-wide identification and expression analyses during development, ripening, and abiotic stress. Front Plant Sci. 6, 742 (2015).
Bai, T. T. et al. Transcriptome and expression profile analysis of highly resistant and susceptible banana roots challenged with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4. PLoS One 8, e73945 (2013).
Deng, G. M. et al. roteomic analysis of conidia germination in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 reveals new targets in ergosterol biosynthesis pathway for controlling Fusarium wilt of banana. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99, 7189–7207 (2015).
Guo, L. et al. Genome and transcriptome analysis of the fungal pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense causing banana vascular wilt disease. PLoS One 9, e95543 (2014).
Li, C. Y. et al. Transcriptome profiling of resistant and susceptible Cavendish banana roots following inoculation with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4. BMC Genomics 13, 374 (2012).
Li, C. et al. Analysis of banana transcriptome and global gene expression profiles in banana roots in response to infection by race 1 and tropical race 4 of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. BMC Genomics 14, 851 (2013).
Li, X., Bai, T., Li, Y., Ruan, X. & Li, H. Proteomic analysis of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4-inoculated response to Fusarium wilts in the banana root cells. Proteome Sci. 11, 41 (2013).
Ploetz, R. C. Fusarium wilt of banana is caused by several pathogens referred to as Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Phytopathology 96, 653–656 (2006).
Ploetz, R. C. Fusarium Wilt of Banana. Phytopathology 105, 1512–1521 (2015).
Ploetz, R. C., Kema, G. H. & Ma, L. J. Impact of diseases on export and smallholder production of banana. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 53, 269–288 (2015).
Silva, P. R. et al. Development of a thematic collection of Musa spp accessions using SCAR markers for preventive breeding against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp cubense tropical race 4. Genet. Mol. Res. 15, doi: 10.4238/gmr.15017765. (2016).
Tan, D. et al. Identification of an endophytic antifungal bacterial strain isolated from the Rubber tree and its application in the biological control of banana Fusarium Wilt. PLoS One 10, e0131974 (2015).
Wang, Z. et al. De novo characterization of the banana root transcriptome and analysis of gene expression under Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense tropical race 4 infection. BMC Genomics 13, 650 (2012).
Wu, Y. et al. Systemic acquired resistance in Cavendish banana induced by infection with an incompatible strain of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. J. Plant Physiol. 170, 1039–1046 (2013).
Jin, J. P., Zhang, H., Kong, L., Gao, G. & Luo, J. C. PlantTFDB 3.0: a portal for the functional and evolutionary study of plant transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D1182–D1187 (2014).
Marchler-Bauer, A. et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D222–D226 (2015).
Finn, R. D. et al. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D279–D285 (2016).
Hu, B. et al. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296–1297 (2015).
Larkin, M. A. et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948 (2007).
Tamura, K. et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739 (2011).
Saldanha, A. J. Java Treeview-extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 20, 3246–3248 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31570249), a central financial support to enhance the comprehensive strength of the central and western colleges and universities, the startup funding and the scientific research foundation of Hainan University (No. kyqd1531) to Haitao Shi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shi H. conceived and directed this study, designed the experiments, wrote and revised the manuscript; Wei Y. performed the experiments, analyzed the data, wrote and revised the manuscript; Hu W. analyzed the data and revised the manuscript; Xia F., Zeng H., Yan Y. and Li X. performed the experiments; He C. designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript and the version to be published.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Hu, W., Xia, F. et al. Heat shock transcription factors in banana: genome-wide characterization and expression profile analysis during development and stress response. Sci Rep 6, 36864 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36864
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36864
This article is cited by
-
Comprehensive genome-wide analysis of calmodulin-binding transcription activator (CAMTA) in Durio zibethinus and identification of fruit ripening-associated DzCAMTAs
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
Generation of fruit postharvest gene datasets and a novel motif analysis tool for functional studies: uncovering links between peach fruit heat treatment and cold storage responses
Planta (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.