Abstract
Previous studies have documented that decompression led to endothelial dysfunction with controversial results. This study aimed to clarify the relationship between endothelial dysfunction, bubble formation and decompression rate. Rats were subjected to simulated air dives with one of four decompression rates: one slow and three rapid. Bubble formation was detected ultrasonically following decompression for two hours, before measurement of endothelial related indices. Bubbles were found in only rapid-decompressed rats and the amount correlated with decompression rate with significant variability. Serum levels of ET-1, 6-keto-PGF1α, ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and MDA, lung Wet/Dry weight ratio and histological score increased, serum NO decreased following rapid decompression. Endothelial-dependent vasodilatation to Ach was reduced in pulmonary artery rings among rapid-decompressed rats. Near all the above changes correlated significantly with bubble amounts. The results suggest that bubbles may be the causative agent of decompression–induced endothelial damage and bubble amount is of clinical significance in assessing decompression stress. Furthermore, serum levels of ET-1 and MDA may serve as sensitive biomarkers with the capacity to indicate endothelial dysfunction and decompression stress following dives.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Bubble formation in tissues and circulating blood due to inadequate decompression is a causative factor in the pathogenesis of decompression sickness (DCS)1. Damage to vascular endothelial cells by decompression stress has been reported in a number of studies2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Animal experiments have demonstrated that simulated diving could cause endothelium-stripping and a reduction in endothelial-dependent vasorelaxation of pulmonary arteries in animals2,3,4,7. Circulating microparticles (MPs), which serve as sensitive markers of activation and dysfunction of endothelia, were also increased in humans and mice5,6,8,9. Incidence of DCS has been decreased by administration of short-acting nitric oxide (NO) donors and simvastatin, which have protective effects on endothelia in rats and pigs10,11,12. The above evidence strongly supports the hypothesis that endothelial cells are targets of DCS.
However, the etiology of endothelial injury after decompression is controversial. Some studies found that damage was caused by direct bubble-endothelia interaction, others suggested bubbles were not the primary causative agent of endothelial damage and showed that alternative factors such as increased formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused by high oxygen partial pressure (ppO2) during diving compromised endothelial function13,14,15,16,17. It is generally acknowledged that circulating decompression bubbles mainly exist in the venous system, will be trapped in the pulmonary circulation and should have little effect upon the arterial system18,19. However, in healthy divers either single or repeated dives reduced the flow-mediated dilation (FMD) of the brachial artery20,21,22,23. Decompression was also reported to lead to measurable endothelial dysfunction even when no venous bubbles were detected in rats24. Although a correlation between bubble abundance and DCS has been shown, the relationship between bubble amount and endothelial damage remains uncertain19,21,25,26.
The aim of the present study was to clarify the relationship between bubble formation, decompression rate and endothelial dysfunction by observing changes in endothelial parameters following different decompression profiles in rats, and to screen possible biomarkers which may have potential clinical significance in assessing decompression injuries.
Methods
Animals
A total of 64 male rats (Sprague-Dawley strain) weighing 290–310 g were used for the experiments. The experiment protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Second Military Medical University and the methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines, including any relevant details. Rats were housed in a controlled environment with a 12/12-h light/dark cycle, constant temperature (23 ± 1 °C) and relative humidity (54 ± 2%), with ad libitum access to a pelleted rodent diet and water.
Grouping and treatment
The rats were randomly divided into three groups: rapid decompression (RD), slow decompression (SD) and normal control (NC). The RD rats were further divided into 3 subgroups according to decompression rates. The SD and RD rats were subjected to a simulated air dive and bubbles flowing through the pulmonary artery were determined ultrasonically for analysis after surfacing. The NC rats were sham exposed (normobaric air) for the same length of time. Surviving rats in the SD and RD groups and the NC rats were anesthetized and sacrificed following bubble detection for measurement of endothelial related parameters. To avoid the possible interference on entothelial function by blood sampling, the study was separated into two parts: one for biochemical investigation including pulmonary edema and histological study, the other for pulmonary artery function. The experimental design and exact number of animals in each group are shown in Fig. 1.
Simulated diving
The SD and RD rats were compressed with air to 7 absolute atmospheres (ATA) in 5 min and maintained for 90 min before decompression in a transparent hyperbaric rodent chamber (Type RDC150-300-6, SMMU, Shanghai, China). Compression was performed at an increasing rate from 1 ATA/min to 1.5 ATA/min to minimize middle ear squeeze in the animals. Decompression was carried out linearly to ambient pressure in 12 min (0.5 ATA/min) for SD rats and in 3, 4, 5 min for RD3, RD4 and RD5 subgroups (2.0 ATA/min, 1.5 ATA/min, 1.2 ATA/min), respectively.
Bubble detection and grading
Immediately after surfacing, the SD and RD rats were anaesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate (3 mL/kg body weight) (Sinopharm Chemical Regent Co., Shanghai, China) intraperitoneally and were lain supine on a thermo-regulating pad (32 °C). The fur on the chest was removed. The cross-section at the root of the pulmonary artery was monitored for bubbles using an ultrahigh frequency (18 MHz) detector connected to an ultrasonic scanner (Mylab30cv, Esaote, Italy). All the manipulation before attaching the detector to the pulmonary artery was finished within 5 min, and detection was repeated at 5, 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90 and 120 min after decompression, each lasting for 60 s. Data were stored and played back in slow motion for analysis. The number of bubbles was scored according to the grading system described elsewhere25.
Measurement of endothelial indices
Venous blood was drawn from the right ventricle under anesthesia. Blood was transfused into 2-ml Eppendorf tubes without any anticoagulation and placed in room temperature for 2 h. Then the samples were centrifuged at 1000 g at 4 °C for 20 min. The supernatant was stored at −80 °C until determination. The serum levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), 6-keto-PGF1α, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) were assayed by ELISA (Elabscience Biotechnology, Wuhan, China). Levels of nitric oxide (NO) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were detected by chemical colorimetry using commercial assay kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). All assays were performed following the respective manufacturer’s instructions.
Lung wet-dry weight and histology were also measured. The weight of the lung tissue was determined from a less than 1 g section of the left lung. The tissue was weighed (wet weight), incubated at 120 °C for 3 days and then weighed again (dry weight). Lung W/D weight ratio was used to estimate the severity of pulmonary edema. Samples from right upper lung were paraffin embedded by conventional procedures, sectioned into slices of 5-μm thickness. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was conducted and morphological changes were observed under a microscope. Ten different areas were selected randomly from each specimen and examined using a computer image analysis system (Smart Scape, Furi Science & Technology Co., ltd, Shanghai, China). Histological scoring was scaled as described previously12. Briefly, score 0 represents normal histology; score 1 represents slight leukocyte infiltration and capillary congestion; score 2 represents mild leukocyte infiltration, perivascular edema, partial damage of pulmonary structures, and hemorrhage; score 3 represents intense leukocyte infiltration and destruction of pulmonary structures.
Pulmonary artery tension measurement
The chest of each rat in the pulmonary artery analysis group was opened under anesthesia, the heart and lungs were harvested and immediately immersed in cold Krebs-Henseleit solution [K-H solution, composition (mM): NaCl, 118.0; KCl, 4.7; MgSO4, 1.2; KH2PO4, 1.2; CaCl2, 2.5; NaHCO3, 25.0; and glucose, 11.1; pH 7.4]. The second branch of the right pulmonary artery was gently dissected and the connective tissue and fat carefully removed. The vessels were cut into 3 mm long rings, mounted on two L-shaped metal prongs and lowered into a temperature-controlled (37 °C) tissue bath containing K-H solution. The solution was aerated continuously with a mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2. Changes in tension were recorded by isometric transducers connected to a data acquisition system (ALCB10, MPA-2000, Alcott Biotech, China). The solution was changed every 15 min. Rings were stretched progressively to a basal tension of 0.5 g and allowed to equilibrate for 1 h. The contractile capacity of each vessel segment was measured by exposure to a potassium-rich (60 mM) K-Krebs buffer solution that had the same composition as the Na-Krebs buffer solution except that some of the NaCl was replaced by an equimolar concentration of KCl. For relaxation measurement the rings were pre-contracted with phenylephrine (PE) at a concentration of 10−5 M. When the PE-induced contraction reached a plateau level, acetylcholine (ACh, 10−9‒10−5 M) was added in cumulative concentration. The resultant relaxation response indicated how severely the endothelial layer was damaged by bubbles. The performance of the smooth muscle layer was examined with cumulative doses of sodium nitroprusside (SNP, 10−10‒10−5 M). Changes in tension induced by ACh or SNP were expressed as percentages of the initial contraction induced by PE.
Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise stated, all data are presented as mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Student Newman–Keuls tests or post hoc Dunnett’s tests were used for multiple comparisons between means. Lung histological scores between RD and SD rats and the difference in dependent correlations were compared using Student’s t-test. Relaxation responses of arterial rings are expressed as percentage reversal of the phenylephrine contraction. Pearson correlation and Spearman correlation were used for correlation analysis between endothelial indices and bubble counts and between endothelial indices and decompression rate, respectively. The threshold for significance was accepted at P < 0.05.
Results
Bubble formation
Immediately after decompression, bubble detection was performed at the root of the pulmonary artery. Gas bubbles were seen as moving bright spots in ultrasound images of the pulmonary artery in RD rats only. The relative bubble count increased gradually after decompression, reaching a maximum at around 20 min in all subgroups. Faster decompressed rats showed greater total bubble count represented by the area under the curve, 286.5 ± 103.1, 184.4 ± 85.0, 92.5 ± 75.8 for RD3, RD4 and RD5, respectively (P < 0.01 for RD3 vs. RD4 or RD5, P < 0.05 for RD4 vs. RD5, Fig. 2A). Linear regression revealed a significant positive relationship between decompression rate and bubble formation (Fig. 2B). However, bubble counts showed wide dispersion even among rats decompressed at the same rate, with coefficients of variation (CV) of 34%, 44% and 79% for RD3, RD4 and RD5 respectively.
Bubble formation in rats decompressed with different rates (A) and correlation between bubble formation and decompression rate (B). Rats were exposed to 7 ATA air for 90 min and decompressed to atmospheric pressure in 3, 4, or 5 min (RD3, RD4, and RD5). Bubbles were detected and scored at 8 time points following decompression. Total bubble count for each rat was calculated as the area under the curve. Error bars are standard deviation to the mean. n = 12 for each of the RD group. Some dots overlap in Panel B.
Endothelial indices
No difference was found between the NC and SD rats. Rapid decompression induced a significant increase in serum ET-1, 6-keto-PGF1α, ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and MDA levels, lung Wet/Dry weight ratio, and a significant decrease in serum NO level (Fig. 3, P < 0.01 RD vs. SD or NC group). Significant decreases in NO correlated negatively with bubble counts (P < 0.01) and decompression rates (P < 0.05), while all the increases of the other parameters correlated positively with bubble counts (P < 0.01) and decompression rates (P < 0.05) with exception of 6-keto-PGF1α and VCAM-1, which showed no correlation with decompression rate (Figs 4 and 5).
Decompression induced changes in endothelial biomarkers.
All parameters were determined at 2 h after decompression from a simulated air dive (7 ATA-90 min) in 12 min (SD) or 3, 4 or 5 min (RD). n = 8 for NC and SD group, n = 24 for SD group, which included the 3 subgroups (n = 8 per subgroup). Error bars are standard deviation to the mean. *P < 0.01 RD vs. NC rats respectively, #P < 0.05 RD vs. SD rats.
Correlation analysis between the endothelial damage and total bubble amount.
Endothelial indices and bubbles were detected in rats rapidly decompressed from a simulated dive (7 ATA-90 min) in 3, 4 and 5 min. Total bubble count is represented by the area under the curve showed in Fig. 2A. n = 24 and some dots overlap.
Correlation between endothelial biomarkers and decompression rate.
Rats were exposed to 7 ATA air for 90 min and decompressed to atmospheric pressure in rate of 1.2, 1.5, or 2.0 ATA/min (RD5, RD4, and RD3) and the endothelial indices were determined 2 h after decompress. n = 8 for each decompression rate and some dots overlap.
Lung morphological changes
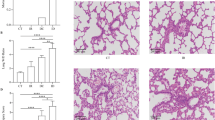
Rapid decompression caused injuries including edema, capillary expansion and congestion, hemorrhage, leukocyte infiltration, disruption of the structure (Fig. 6A) and RD3 rats scored highest (Fig. 6B). The score in RD lungs correlated positively with bubble counts and decompression rates (P < 0.01) (Fig. 6C,D).
Photomicrographs and histological score of lung biopsies and correlation with decompression rate and bubble counts.
Tissues were sampled from normal control (NC, (A)) slow decompressed (SD, (B)) and rapid decompressed (RD, (C)) rats. The higher the histological score, the greater severity of the injury. One of the dots is overlapped in panel D. Error bars are standard deviation to the mean. *P < 0.001 RD vs. SD, n = 5 in NC or SD group, n = 15 in RD group.
Changes in pulmonary artery tension
Concentration-response relaxation curves were obtained by adding Ach (10−9–10−5 mol/L) or SNP (10−10–10−5 mol/L) cumulatively (Fig. 7A,B). The percentages of relaxation of artery rings differed when stimulated at different concentrations. The concentration at which 50% of the response (EC50) to Ach was observed increased significantly in RD rings compared with NC or SD rings (P < 0.01, Fig. 7C). There was no difference in the EC50 to SNP among the three groups (P > 0.05, Fig. 7D). The -logEC50 to Ach correlated negatively with bubble counts (Fig. 7E) or decompression rate (Fig. 7F), indicating positive correlations among endothelial dysfunction, bubble counts and decompression rates.
Concentration-response relaxation in isolated rat pulmonary artery rings and the correlation with decompression rate or bubble count.
The Ach and SNP induced relaxation (A,B) and the EC50 values (C,D) were determined on isolated rings from the second branch of the pulmonary arteries in rats rapid decompressed (RD) or slow decompressed (SD) from a simulated air dive to 7 ATA for 90 min. The correlation between -logEC50 with decompression rate (E) or total bubble count (F). NC stands for normal control. The EC50 to Ach or SNP were the concentrations that produced 50% relative responses. Error bars are standard deviation to the mean. *P < 0.01 RD vs. NC rings, #P < 0.05 RD vs. SD rings. n = 4 in NC or SD group, n = 12 in RD group. Some dots in Panel F overlap.
Discussion
DCS is a potential problem for a growing population of professional and recreational divers1. There is a common agreement that bubble formation is associated with DCS1,27. Evidence points to vascular endothelial cells as a target for damage by decompression stress2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,28. However, the cause of endothelial injury after decompression is controversial13,15,16. Elucidating the correlation between bubble amount, decompression rate and endothelial dysfunction will help to understand the etiology of endothelial damage after decompression and identify reliable methods for assessing decompression stress.
To induce different amounts of decompression bubbles in rats, three different decompression rates were adopted. According to our preliminary study, for a 7 ATA-90 min simulated air dive, 12 min decompression duration would not induce observable bubble formation for rats weighing around 300 g; while 3–5 min decompression causes a variety of DCS symptoms (further verified by the present results)12,29. In the three RD subgroups, faster decompression produced greater amounts of bubbles. However, bubble formation showed significant variability even among rats with low weight variation and with decompression at the same rate, with coefficient of variation ranging from 34% to 79% between the three subgroups. This finding coincides with observations that individual variation in DCS susceptibility exists in divers19,30.
A series of endothelia related indices were measured in the present study. Among these determined parameters, the lung Wet/Dry weight ratio is an indicator of lung microvascular permeability; VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 are sensitive biomarkers with the capacity to reflect endothelial damage directly; NO, ET-1 and 6-keto-PGF1α are vasoactive substances secreted by endothelial cells; lung morphology reflects the general injuries caused by bubbles; and in vitro vasodilatation determination is considered to be a reliable method for evaluating endothelial and smooth muscle function. Rapid decompression induced significant changes in all these parameters. Slow decompression did not induce detectable bubbles and none of the determined indices changed, compared with normal controls, which suggests that neither the high ppO2 nor hyperbaric exposure per se exerted any discernable effects in this scenario. Increased ppO2 during diving has been proposed as a cause of endothelial dysfunction16. Linear regression revealed that all observed changes correlated well with bubble amounts in a dose-dependent manner. This is in accordance with previous studies which found reduction of endothelial-dependent vasodilation was related to the amount of bubbles2,4. These findings suggest that intravascular bubbles may be the causative agents of endothelial damage following diving decompression, and bubble score may be sensitive to predict decompression-induced endothelial dysfunction. Among the serum parameters measured in this study, ET-1 and MDA presented better sensitivity and reliability as demonstrated in the relatively large changes and high correlation shown in Figs 2 and 3. These serum indices could be valuable biomarkers for decompression stress but it remains to be tested if they are equally sensitive in other species and/or other dive profiles. Further studies in a swine DCS model and divers are underway. While 7 out of the 9 measured biomarker levels correlated with decompression rate, the mean correlation coefficient was not as high as the mean correlation between the indices and bubbles (0.552 ± 0.207 vs. 0.846 ± 0.086). As bubbles cause endothelial injury, the result also reflects the significant variability of bubble formation at the same decompression rate. Accordingly, we recommend future rat research incorporate bubble measurement into the study design, rather than just vary the rate of decompression and compare groups based on dive profile instead of between bubble score outcomes.
During inadequate decompression from a diving or hyperbaric exposure, bubbles will form in supersaturated tissue, converge into the venous system, and move with blood flow to the right heart and thence the pulmonary artery for sequestration in the lung vasculature. Decompression bubbles therefore mainly exist in the venous system18,19. In this study, no bubbles were found in the left heart and aorta. However, the present results could not determine whether injuries to endothelia were only from the venous system or from both sides. Because tiny moving microbubbles cannot be detected by current ultrasound techniques, the possibility remains that bubbles could have existed in the arterial system. In human divers, even large venous bubbles do cross to systemic arteries via right-to-left shunts including patent foramen ovale20 and, although bubble detection was not performed, insults to arterial smooth muscle have been reported in a rat DCS model while endothelial function remained unchanged31,32.
Circulating bubbles can act on the endothelial lining of vessels directly or via increased shear stress, resulting in perturbations, activation or even stripping of endothelial cells25. As with foreign material, bubbles can initiate biochemical cascades including activation of coagulation, platelet aggregation, inflammatory responses, and lead ultimately to endothelial damage13,33. No matter how bubbles injure endothelia, the indices measured in this study herald endothelial activation and dysfunction, and are sensitive markers of decompression stress, especially for the assessment of divers with subclinical manifestations. Furthermore, some substances released from injured endothelia will initiate further endothelial injury at remote sites13,20, making the etiology of this protean disease more complicated. This may also be a possible cause of arterial dysfunction in divers who have not obviously violated decompression rules8. This possibility deserves further study.
In this study, the relaxation of pulmonary artery rings from rapidly decompressed rats remained unchanged with SNP (a vasodilator acting directly on smooth muscles) but was hampered with Ach (a vasodilator acting via endothelia), indicating that vascular smooth muscle was not affected (Fig. 6). Similar findings have been previously reported3,4. However, a study on divers showed both endothelium dependent and independent vascular function were altered after a single air scuba dive, and vascular smooth muscle was postulated to be involved21. Another study on rats showed that vascular smooth muscle function was progressively impaired with increased decompression stress with no modification of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation31. The different amount and size of bubbles formed, type of vessels and other predisposing factors could offer possible explanation4,34.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that endothelial dysfunction following decompression is mainly caused by bubbles in a linearly correlated relationship. The results further support the notion that bubble amount is a sensitive marker of decompression stress. Some of the endothelial indices together with bubble count may serve as sensitive or specific markers with the capacity to reflect decompression stress. Further studies are warranted to reveal the mechanisms of decompression induced bubbles affecting endothelial integrity and function.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Zhang, K. et al. Endothelial dysfunction correlates with decompression bubbles in rats. Sci. Rep. 6, 33390; doi: 10.1038/srep33390 (2016).
References
Vann, R. D., Butler, F. K., Mitchell, S. J. & Moon, R. E. Decompression illness. Lancet . 377, 153–164 (2011).
Nossum, V., Hjelde, A., Bergh, K. & Brubakk, A. O. Lack of effect of anti-C5a monoclonal antibody on endothelial injury by gas bubbles in the rabbit after decompression. Undersea Hyperb Med. 27, 27–35 (2000).
Nossum, V., Hjelde, A. & Brubakk, A. O. Small amounts of venous gas embolism cause delayed impairment of endothelial function and increase polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration. Eur J Appl Physiol. 86, 209–214 (2002).
Nossum, V., Koteng, S. & Brubakk, A. O. Endothelial damage by bubbles in the pulmonary artery of the pig. Undersea Hyperb Med. 26, 1–8 (1999).
Thom, S. R. et al. Association of microparticles and neutrophil activation with decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol (1985). 119, 427–434 (2015).
Thom, S. R., Yang, M., Bhopale, V. M., Huang, S. & Milovanova, T. N. Microparticles initiate decompression-induced neutrophil activation and subsequent vascular injuries. J Appl Physiol (1985). 110, 340–351 (2011).
Warren, B., Philp, R. & Inwood, M. The ultrastructural morphology of air embolism: platelet adhesion to the interface and endothelial damage. Br J Exp Pathol. 54, 163–172 (1973).
Madden, L. A. et al. Endothelial Function and Stress Response After Simulated Dives to 18 msw Breathing Air or Oxygen. Aviat Space Environ Med. 81, 41–45 (2010).
Thom, S. R. et al. Microparticle production, neutrophil activation, and intravascular bubbles following open-water SCUBA diving. J Appl Physiol (1985). 112, 1268–1278 (2012).
Møllerløkken, A., Berge, V. J., Jørgensen, A., Wisløff, U. & Brubakk, A. O. Effect of a short-acting NO donor on bubble formation from a saturation dive in pigs. J Appl Physiol (1985). 101, 1541–1545 (2006).
Wisløff, U., Richardson, R. S. & Brubakk, A. O. Exercise and nitric oxide prevent bubble formation: a novel approach to the prevention of decompression sickness? J Physiol . 555, 825–829 (2004).
Zhang, K. et al. Simvastatin decreases incidence of decompression sickness in rats. Undersea Hyperb Med. 42, 115–123 (2014).
Chrismas, B. et al. Acute antioxidant pre-treatment attenuates endothelial microparticle release after decompression. Diving Hyperb Med. 40, 184–188 (2010).
Ferrer, M. D. et al. Scuba diving enhances endogenous antioxidant defenses in lymphocytes and neutrophils. Free Radic Res. 41, 274–281 (2007).
Klinger, A. L., Pichette, B., Sobolewski, P. & Eckmann, D. M. Mechanotransductional basis of endothelial cell response to intravascular bubbles. Integr Biol (Camb) . 3, 1033–1042 (2011).
Madden, L. A. & Laden, G. Gas bubbles may not be the underlying cause of decompression illness–The at-depth endothelial dysfunction hypothesis. Med hypotheses. 72, 389–392 (2009).
Obad, A. et al. Antioxidant pretreatment and reduced arterial endothelial dysfunction after diving. Aviat Space Environ Med. 78, 1114–1120 (2007).
Lambrechts, K. et al. Effect of decompression-induced bubble formation on highly trained divers microvascular function. Physiol Rep. 1, e00142, 10.1002/phy2.142 (2013).
Levett, D. & Millar, I. Bubble trouble: a review of diving physiology and disease. Postgrad Med J. 84, 571–578 (2008).
Brubakk, A. O. et al. A single air dive reduces arterial endothelial function in man. J Physiol. 566, 901–906 (2005).
Lambrechts, K. et al. Effect of a single, open-sea, air scuba dive on human micro-and macrovascular function. Eur J Appl Physiol. 113, 2637–2645 (2013).
Marinovic, J. et al. Effects of successive air and nitrox dives on human vascular function. Eur J Appl Physiol. 112, 2131–2137 (2012).
Theunissen, S. et al. Nitric oxide-related endothelial changes in breath-hold and scuba divers. Undersea Hyperb Med. 40, 135–144 (2013).
Rasdal, K. V., Hjelde, A., Møllerløkken, A., Lundset, N. & Brubakk, A. O. Aortic Function in Rats After Decompression Without Ultrasonically Detectable Bubble Formation. Aviat Space Environ Med. 80, 1006–1011 (2009).
Eftedal, O. S., Lydersen, S. & Brubakk, A. O. The relationship between venous gas bubbles and adverse effects of decompression after air dives. Diving Hyperb Med. 45, 105–110 (2007).
Gardette, B. Correlation between decompression sickness and circulating bubbles in 232 divers. Undersea Biomed Res. 6, 99–107 (1979).
Madden, L. A. & Laden, G. Endothelial microparticles in vascular disease and as a potential marker of decompression illness. Diving Hyperb Med. 37, 156–161 (2007).
Brubakk, A. O. & Mollerlokken, A. The role of intra-vascular bubbles and the vascular endothelium in decompression sickness. Diving Hyperb Med. 39, 162–169 (2009).
Ni, X. et al. Protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline on decompression sickness in rats. Aviat Space Environ Med. 82, 604–609 (2011).
Hills, B. The variation in susceptibility to decompression sickness. Int J Biometeorol. 12, 343–349 (1968).
Mazur, A. et al. Influence of decompression sickness on vasomotion of isolated rat vessels. Int J Sports Med. 35, 551–558 (2014).
Mazur, A. et al. Influence of decompression sickness on vasocontraction of isolated rat vessels. J Appl Physiol (1985). 120, 784–791 (2016).
Schellart, N. A., Rozložník, M. & Balestra, C. Relationships between plasma lipids, proteins, surface tension and post-dive bubbles. Undersea Hyperb Med. 42, 133–141 (2015).
Pontier, J. M., Guerrero, F. & Castagna, O. Bubble formation and endothelial function before and after 3 months of dive training. Aviat Space Environ Med. 80, 15–19 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to Yanan Zhang for her excellent technical assistance and Qi Chen for his expertise help in the statistical analysis. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 81571846.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.X. and K.Z. designed and K.Z., D.W., Z.J. and X.N. conducted the experiments. W.X., K.Z. and P.B. wrote the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Wang, D., Jiang, Z. et al. Endothelial dysfunction correlates with decompression bubbles in rats. Sci Rep 6, 33390 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33390
This article is cited by
-
Effect of angiotensin II on irradiation exacerbated decompression sickness
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Establishment of a fish model to study gas-bubble lesions
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Endothelia-Targeting Protection by Escin in Decompression Sickness Rats
Scientific Reports (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.