Abstract
Electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots are good candidates of quantum bits for quantum information processing. Basic operations of the qubit have been realized in recent years: initialization, manipulation of single spins, two qubit entanglement operations and readout. Now it becomes crucial to demonstrate scalability of this architecture by conducting spin operations on a scaled up system. Here, we demonstrate single-electron spin resonance in a quadruple quantum dot. A few-electron quadruple quantum dot is formed within a magnetic field gradient created by a micro-magnet. We oscillate the wave functions of the electrons in the quantum dots by applying microwave voltages and this induces electron spin resonance. The resonance energies of the four quantum dots are slightly different because of the stray field created by the micro-magnet and therefore frequency-resolved addressable control of each electron spin resonance is possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) have relatively long coherence times in solid state devices1,2,3,4 and potential scalability by utilizing current extensive semiconductor fabrication techniques. Considered good candidates for quantum bits5 in quantum information processing6,7, the required elementary operations on the spin-1/2 qubits for quantum information processing have been demonstrated recently. The spin states are initialized and read out using the Pauli spin blockade (PSB)8 or tunneling to the leads from Zeeman split energy levels9,10. Rotation of single spins has been realized by electron spin resonance (ESR)11. Addressability and the speed of single spin rotation are improved by micro-magnet (MM) induced ESR12,13. High-fidelity single-spin rotation decoupled from the fluctuating nuclear spin environment was demonstrated14. Entanglement operations of two spins are realized by utilizing exchange interaction and fast two qubit operations have been demonstrated15,16,17,18. This scheme for the spin-1/2 qubit is applicable to a wide variety of materials including Si, which has a long spin coherence time3,4.
Scale up of the QD system is crucial to realize larger scale quantum gate operations and also explore multi-spin physics. To this end, spin qubit experiments on multiple QDs have been reported in recent years. In triple QDs, PSB has been observed19,20 and the exchange only qubit utilizing a triple QD as a single qubit has been demonstrated21,22,23,24. Towards three spin-1/2 qubits25, ESR in a triple QD was recently realized26. Experiments on quadruple QDs (QQDs) have also been started27,28 and a QQD is utilized for realization of two qubit operations on singlet-triplet qubits29. For four spin-1/2 qubits, the precise charge state control in a tunnel coupled QQD has been demonstrated in the few-electron regime30.
In this paper, we demonstrate four distinctly addressable electron spin resonances in a QQD. First, we realize few-electron charge states in a QQD required to observe PSB. Second, we observe PSB for readout of ESR signals. The blocked triplet components are created by singlet-triplet mixing induced by the nuclear spins and the MM. Finally, we observe four ESR signals corresponding to the four individual spins in the QQD.
Results
Device and Charge states
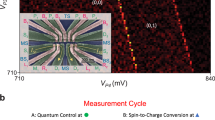
Figure 1(a) shows a scanning electron micrograph of the device. By applying negative voltages on the gate electrodes, which appear light gray in the picture, a QQD and two QD charge sensors31 are formed at the lower and the upper sides, respectively. The QD charge sensors are connected to RF resonators formed by the inductors L1 and L2 and the stray capacitances Cp1 and Cp2 (resonance frequency fres1 = 298 MHz, fres2 = 207 MHz) for the RF reflectometry31,32,33. The number of electrons in each QD n1, n2, n3 and n4 is monitored by the intensity of the reflected RF signal Vrf1 and Vrf2. A change in the electrostatic environment around the sensing dots changes their conductance, shifts the tank circuit resonance and modifies Vrf1 and Vrf2 measured at fres1 and fres2. A MM is deposited on the shaded region on the top of the device, which creates local magnetic fields to induce ESR. The external magnetic field is applied in the plane along the z axis to induce Zeeman splitting and magnetizes the MM. The shape of the MM is specially designed to realize strong driving of the electron spin rotations by the large field gradient and splitting of the ESR frequencies by the Zeeman field differences between the dots34. Thanks to this MM, we can realize a stable magnetic field which is difficult to achieve by the fluctuating nuclear spins and the scheme is material independent.
(a) Scanning electron micrograph of the device and the schematic of the measurement setup. A QQD is formed at the lower side and the charge states are probed by the charge sensor QDs at the upper side. The charge sensors are connected to resonators formed by the inductors L1 and L2 and the stray capacitances Cp1 and Cp2 for the RF reflectometry. A MM is deposited on the shaded region on the top of the device, which creates local magnetic fields to induce ESR. The external magnetic field is applied in plane along the z axis. (b) Vrf1 as a function of VP4 and VP1. Changes of the charge states are observed. The number of the electrons in each QD is shown as n1, n2, n3, n4. (c) Calculated charge stability diagram of a QQD. The experimental result (b) is reproduced by considering the capacitively coupled QQD model. n1, n2, n3, n4 are shown in the figure.
Figure 1(b) is the charge stability diagram of the QQD. We measured Vrf1 as a function of the plunger gate voltages of QD4 VP4 and QD1 VP1. We observe the change of Vrf1, as the result of the charge states in the QQD. Charge transition lines with four different slopes are observed reflecting the different electrostatic coupling of the QQD to VP4 and VP1. n1, n2, n3 and n4 are assigned as shown in Fig. 1(b) by counting the number of charge transition lines from the fully depleted condition [n1, n2, n3, n4] = [0, 0, 0, 0]. Figure 1(c) shows the calculated charge state of the QQD. By considering the capacitively coupled QQD model30,35, we reproduce the observed charge stability diagram. We find the characteristic “goggle” structure, which is formed by the charge transition lines around [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0, 1] and [1, 0, 1, 1] charge states. In the [1, 1, 1, 1] state, each dot contains a single electron and this state is useable as a four qubit system of the spin-1/2 qubit.
Spin blockade
To readout the spin states of the qubits, PSB8 is a powerful tool. If the triplet spin states are formed in the neighboring QDs, the charge transition [1, 1, 0, 1] → [2, 0, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 1, 1] → [1, 0, 0, 2]) is forbidden because of Pauli exclusion principle. In the stability diagrams in Fig. 1(b,c), the spin blockade can be expected around the charge transition lines between [1, 1, 0, 1] and [2, 0, 0, 1] and between [1, 0, 1, 1] and [1, 0, 0, 2]. Note that charge boundaries between [1, 1, 1, 1] → [2, 0, 1, 1] and [1, 1, 1, 1] → [1, 1, 0, 2], which is required to observe PSB around the [1, 1, 1, 1] state, never coexist on a single VP1 − VP4 plane and we need to switch into VP1 − VP2 and VP3 − VP4 planes30. For experimental simplicity, we choose [1, 1, 0, 1] → [2, 0, 0, 1] and [1, 0, 1, 1] → [1, 0, 0, 2] boundaries to demonstrate PSB in this work.
We apply voltage pulses on VP1 and VP4 to observe spin blocked states. The operation schematics are shown in Fig. 2(a,c). We apply an external magnetic field of 0.5 T to induce Zeeman splitting. We start from the ground singlet state in QD1 S2001 (in QD4 10S02). The triplet plus component T+1101 in QD1 and QD2 (10T+11 in QD3 and QD4) is populated at the operation point O by using the singlet-triplet mixing S1101 ⇔ T+1101 (10S11 ⇔ 10T+11) induced by the nuclear spins and the MM stray magnetic fields36. At the measurement point M, the triplet components stay in the [1, 1, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 1, 1]) charge state because of PSB and the singlet components relax to the [2, 0, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 0, 2]) charge state. Then, this blockade can be observed as the change of Vrf1 (Vrf2).
(a,c) Energy diagrams and schematics of the pulse operation to observe PSB in QD1 and QD2 (QD3 and QD4). The T+1101 (10T+11) component is populated at the operation point O by using the S1101 ⇔ T+1101 (10S11 ⇔ 10T+11) mixing. The triplet component is observed as the [1, 1, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 1, 1]) charge state at the measurement point M. (b,d) Observed Vrf1 (Vrf2) as a function of VP4 and VP1. The pulse sequences are indicated by lines in the figures. The change of Vrf1 (Vrf2) as the result of the spin blocked signals are observed around M.
Figure 2(b,d) show the observed Vrf1 (Vrf2) as a function of VP4 and VP1. The operation pulses are cycled constantly at each point of the graph. We apply voltage pulses with fixed amplitudes as shown as lines in Fig. 2(b,d). The directions of the pulses on the stability diagrams are chosen to modulate the detuning, the energy difference of the levels between QD1 and QD2 (between QD3 and QD4). Note that we are also able to control QD2 and QD3 by VP1 and VP4 because of the finite capacitive coupling. Sensor 1 is used for Fig. 2(b) (Sensor 2 for Fig. 2(d)) to maximize the charge sensitivity. The changes of Vrf1 (Vrf2) are observed around M when the operation point O hits the singlet-triplet mixing point. These correspond to the spin blocked signals.
Electron spin resonance
Next, we apply a microwave voltage on gate R to induce ESR (with the frequency fESR). The operation schematics are shown in Fig. 3(a,c). In the present device, the Zeeman field difference ΔBz between QD1 and QD2 (QD3 and QD4) by the MM will be larger than the singlet-triplet splitting at the operation point O and the eigenstates are ↓↑1101 and ↑↓1101 (10↓↑11 and 10↑↓11), not S1101 and T0 1101 (10S11 and 10T0 11) (see Supplementary Information). We prepare the states ↓↑1101 in QD1 and QD2 (10↓↑11 in QD3 and QD4) by adiabatically pulsing from S2001 (10S02). Then, we apply microwaves at the operation point O. These applied microwaves create an oscillating electric field around the gate R and thus induce movements of the QD electron’s wave functions. These oscillations of the wave functions are converted into oscillating magnetic fields along the x axis perpendicular to the external magnetic field in the field gradient created by the MM and ESR is induced12,13. The triplet components T+1101 or T−1101 (10T+11 or 10T−11) are populated by ESR and detected as the [1, 1, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 1, 1]) charge states.
(a,c) Schematics of the energy diagrams and the pulse operations to observe ESR in QD1 and QD2 (QD3 and QD4). States are prepared as ↓↑1101 (10↓↑11) due to ΔBz between QD1 and QD2 (QD3 and QD4) by the MM, which is larger than the singlet-triplet splitting at the operation point O. The states evolve into T+1101 or T−1101 (10T+11 or 10T−11) states by ESR. The created triplet components are observed as [1, 1, 0, 1] ([1, 0, 1, 1]) charge states at the measurement point M. (b,d) Observed PS as a function of fESR and Bext. ESR occurs when the applied microwave frequency matches the external magnetic field plus the stray field created by the micro-magnet hfESR = gμ(Bext + BMMz). (e) Observed PS as a function of Bext at fESR = 3265 MHz. Dips of PS are observed when ESR occurs. The circles (triangles) show the results measured in QD1 and QD2 (QD3 and QD4). The traces are Gaussian eye guides.
Figure 3(b,d) show the singlet return probability PS as a function of fESR and the external magnetic field Bext. PS is calculated from Vrf1 (Vrf2) by using the method reported in the refs 23,37. The measurement time is 30 μs and set shorter than the relaxation time T1 > 100 μs. We can see the decrease of PS when the applied microwave frequency matches the external magnetic field plus the z component of the stray field created by the MM hfESR = gμ(Bext + BMMz). The ESR dips of PS are also observed in Fig. 3(e), which show PS as a function of Bext at fESR = 3265 MHz.
Discussion
The slopes of the ESR lines in Fig. 3(b,d) give a value of the g-factor as |g| = 0.37 ± 0.03 that is consistent with reported values in previous experiments38,39,40.
We realize addressable control of the operation by choosing appropriate Bext and fESR such that the separation of the ESR dips is larger than their width as in Fig. 3(e). From Fig. 3(e), the local Zeeman field differences between the quantum dots BMMz12, BMMz13, BMMz14 are evaluated as BMMz12 = 28 mT, BMMz13 = 9 mT, BMMz14 = 73 mT. If there is no misalignment of the QD positions, BMMz12 < BMMz13 < BMMz14 is expected from the design of the MM34. This discrepancy is attributed to the misalignment of the QD positions from the center of the MM. The observed values of the local Zeeman field are explained by shifts of the QD positions of around 100 nm in the z direction, which is possible in this QQD device (see Supplementary Information). The unexpected position-shift might be compensated by additional tuning of the gate voltages or removing inhomogeneous potentials by using undoped device structures41,42,43.
In conclusion, we have demonstrated formation of few-electron charge states and observed spin blockade and four distinct ESR signals in a QQD. The four observed ESR dips are well separated and we are able to individually address spins by choosing the appropriate Bext and fESR. These results will be important for four or more spin-1/2 qubits, multiple qubit operations and demonstration of larger scale quantum gate operations. These also contribute to exploring multi-spin physics in controlled artificial systems.
Methods
Device structure and measurement
The device was fabricated from a GaAs/AlGaAs heterostructure wafer with an electron sheet carrier density of 2.0 × 1015 m−2 and a mobility of 110 m2/Vs at 4.2 K, measured by Hall-effect in the van der Pauw geometry. The two-dimensional electron gas is formed 90 nm under the wafer surface. We patterned a mesa by wet-etching and formed Ti/Au Schottky surface gates by metal deposition, which appear light gray in Fig. 1(a). All measurements were conducted in a dilution fridge cryostat at a temperature of 13 mK.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Otsuka, T. et al. Single-electron Spin Resonance in a Quadruple Quantum Dot. Sci. Rep. 6, 31820; doi: 10.1038/srep31820 (2016).
References
Bluhm, H. et al. Dephasing time of GaAs electron-spin qubits coupled to a nuclear bath exceeding 200 μs. Nat. Phys. 7, 109–113 (2011).
Shulman, M. D. et al. Suppressing qubit dephasing using real-time Hamiltonian estimation. Nat. Commun. 5, 5156 (2014).
Kawakami, E. et al. Electrical control of a long-lived spin qubit in a Si/SiGe quantum dot. Nat. Nano. 9, 666–670 (2014).
Veldhorst, M. et al. An addressable quantum dot qubit with fault-tolerant control-fidelity. Nat. Nano. 9, 981–985 (2014).
Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120–126 (1998).
Nielsen, M. A. & Chuang, I. L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. (Cambridge University Press, 2000).
Ladd, T. D. et al. Quantum computers. Nature 464, 45–53 (2010).
Ono, K. et al. Current Rectification by Pauli Exclusion in a Weakly Coupled Double Quantum Dot System. Science 297, 1313–1317 (2002).
Elzerman, J. M. et al. Single-shot read-out of an individual electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 430, 431–435 (2004).
Nowack, K. C. et al. Single-Shot Correlations and Two-Qubit Gate of Solid-State Spins. Science 333, 1269–1272 (2011).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006).
Tokura, Y. et al. Coherent Single Electron Spin Control in a Slanting Zeeman Field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 047202 (2006).
Pioro-Ladriere, M. et al. Electrically driven single-electron spin resonance in a slanting Zeeman field. Nat. Phys. 4, 776–779 (2008).
Yoneda, J. et al. Fast Electrical Control of Single Electron Spins in Quantum Dots with Vanishing Influence from Nuclear Spins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 267601 (2014).
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent Manipulation of Coupled Electron Spins in Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Brunner, R. et al. Two-Qubit Gate of Combined Single-Spin Rotation and Interdot Spin Exchange in a Double Quantum Dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 146801 (2011).
Maune, B. M. et al. Coherent singlet-triplet oscillations in a silicon-based double quantum dot Nature 481, 344–347 (2012).
Veldhorst, M. et al. A two-qubit logic gate in silicon Nature 526, 410–414 (2015).
Kobayashi, T. et al. Cooperative Lifting of Spin Blockade in a Three-Terminal Triple Quantum Dot. arXiv:1311.6582 (2013).
Amaha, S. et al. Two- and Three-Electron Pauli Spin Blockade in Series-Coupled Triple Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 016803 (2013).
Laird, E. A. et al. Coherent spin manipulation in an exchange-only qubit Phys. Rev. B 82, 075403 (2010).
Gaudreau, L. et al. Coherent control of three-spin states in a triple quantum dot Nature Physics 8, 54–58 (2012).
Medford, J. et al. Self-consistent measurement and state tomography of an exchange-only spin qubit Nature Nanotech 8, 654–659 (2013).
Eng, K. et al. Science Advances. 1, e1500214 (2015).
Takakura, T. et al. Triple quantum dot device designed for three spin qubits Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 212104 (2010).
Noiri, A. et al. Coherent electron-spin-resonance manipulation of three individual spins in a triple quantum dot. Appl. Phys. Lett 108, 153101 (2016).
Thalineau, R. et al. A few-electron quadruple quantum dot in a closed loop. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 103102 (2012).
Takakura, T. et al. Single to quadruple quantum dots with tunable tunnel couplings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 113109 (2014).
Shulman, M. D. et al. Demonstration of Entanglement of Electrostatically Coupled Singlet-Triplet Qubits Science 336, 202–205 (2012).
Delbecq, M. R. et al. Full control of quadruple quantum dot circuit charge states in the single electron regime. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 183111 (2014).
Barthel, C. et al. Fast sensing of double-dot charge arrangement and spin state with a radio-frequency sensor quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 81, 161308 (2010).
Schoelkopf, R. J. et al. The Radio-Frequency Single-Electron Transistor (RF-SET): A Fast and Ultrasensitive Electrometer. Science 280, 1238–1242 (1998).
Reilly, D. J., Marcus, C. M., Hanson, M. P. & Gossard, A. C. Fast single-charge sensing with a rf quantum point contact. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 162101 (2007).
Yoneda, J. et al. Robust micromagnet design for fast electrical manipulations of single spins in quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Exp. 8, 084401 (2015).
van der Wiel, W. G. et al. Electron transport through double quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 75, 1–22 (2002).
Chesi, S. et al. Single-spin manipulation in a double quantum dot in the field of a micromagnet. Phys. Rev. B 90, 235311 (2014).
Barthel, C., Reilly, D. J., Marcus, C. M., Hanson, M. P. & Gossard, A. C. Rapid Single-Shot Measurement of a Singlet-Triplet Qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 160503 (2009).
Potok, R. M. et al. Spin and Polarized Current from Coulomb Blockaded Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 016802 (2003).
Hanson, R. et al. Zeeman Energy and Spin Relaxation in a One-Electron Quantum Dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 196802 (2003).
van Beveren, L. H. W. et al. Spin filling of a quantum dot derived from excited-state spectroscopy. New J. Phys. 7, 182 (2005).
Borselli, M. G. et al. Pauli spin blockade in undoped Si/SiGe two-electron double quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 063109 (2011).
See, A. M. et al. Impact of Small-Angle Scattering on Ballistic Transport in Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 196807 (2012).
MacLeod, S. J. et al. Hybrid architecture for shallow accumulation mode AlGaAs/GaAs heterostructures with epitaxial gates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 012105 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Beil, J. Medford, F. Kuemmeth, C. M. Marcus, D. J. Reilly, K. Ono, RIKEN CEMS Emergent Matter Science Research Support Team and Microwave Research Group in Caltech for fruitful discussions and technical supports. Part of this work is supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 25800173, 26220710, 26709023, 26630151, 16H00817), CREST, JST, ImPACT Program of Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (Cabinet Office, Government of Japan), Strategic Information and Communications R&D Promotion Programme, RIKEN Incentive Research Project, Yazaki Memorial Foundation for Science and Technology Research Grant, Japan Prize Foundation Research Grant, Advanced Technology Institute Research Grant, the Murata Science Foundation Research Grant, Izumi Science and Technology Foundation Research Grant, TEPCO Memorial Foundation Research Grant and IARPA project “Multi-Qubit Coherent Operations” through Copenhagen University. A.L. and A.D.W. acknowledge support of Mercur Pr-2013-0001, DFG-TRR160, BMBF - Q.com-H 16KIS0109 and the DFH/UFA CDFA-05-06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.O., T.N., M.R.D., S.A., J.Y., K.T., G.A. and S.T. planned the project; T.O., T.N., M.R.D., S.A., A.L. and A.D.W. performed device fabrication; T.O., T.N., M.R.D., S.A., J.Y., K.T., G.A., T.I., R.S., A.N. and S.T. conducted experiments and data analysis; all authors discussed the results; T.O., T.N., M.R.D., S.A., J.Y., K.T., G.A. and S.T. wrote the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Otsuka, T., Nakajima, T., Delbecq, M. et al. Single-electron Spin Resonance in a Quadruple Quantum Dot. Sci Rep 6, 31820 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31820
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31820
This article is cited by
-
Review of performance metrics of spin qubits in gated semiconducting nanostructures
Nature Reviews Physics (2022)
-
Angular momentum transfer from photon polarization to an electron spin in a gate-defined quantum dot
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Detection and control of charge states in a quintuple quantum dot
Scientific Reports (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.