Abstract
To explore the latitudinal variation of stomatal traits from species to community level and their linkage with net primary productivity (NPP), we investigated leaf stomatal density (SDL) and stomatal length (SLL) across 760 species from nine forest ecosystems in eastern China and calculated the community-level SD (SDC) and SL (SLC) through species-specific leaf area index (LAI). Our results showed that latitudinal variation in species-level SDL and SLL was minimal, but community-level SDC and SLC decreased clearly with increasing latitude. The relationship between SD and SL was negative across species and different plant functional types (PFTs), but positive at the community level. Furthermore, community-level SDC correlated positively with forest NPP and explained 51% of the variation in NPP. These findings indicate that the trade-off by regulating SDL and SLL may be an important strategy for plant individuals to adapt to environmental changes and temperature acts as the main factor influencing community-level stomatal traits through alteration of species composition. Importantly, our findings provide new insight into the relationship between plant traits and ecosystem function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Changes in the environment can affect ecosystem processes and function directly through influences on abiotic controls and indirectly through influences on the physiology, morphology, behavior of individual plants, the structure of populations and the composition of communities1,2,3. Recent studies have suggested that the spatial and temporal variation of ecosystem functions is difficult to be explained sufficiently by classical climatological or biogeographical approaches and plant traits have the potential to advance the understanding in this field2,4. Plant traits have been well recognized as important determinants of ecosystem function2,5 and it is possible to aggregate functional traits measured on organisms to explain the function of populations, communities, ecosystems and beyond2,4,5,6. Thus, understanding plant traits and their controlling factors at a large scale is of importance to explore how organisms and environmental conditions collectively shape the variation of ecosystem function in space and time2 and to predict ecosystem function in response to environmental changes.
Spatial and temporal variation of ecosystem function, such as net primary productivity (NPP), evapotranspiration and water use efficiency, has received much attention to date2,7,8. Some studies have demonstrated that leaf traits, including leaf size, specific leaf area (SLA) and tissue nitrogen and phosphorus concentration, are strongly correlated with ecosystem productivity2,3,5. Abiotic factors (e.g., soil, climate and disturbance) may exert indirect effects on the variation of NPP through regulating leaf area and duration of photosynthetic season3. Leaf stomata regulate gas exchange between plants and the atmosphere and thus control the balance between water loss and CO2 uptake to some extent9. Compared with leaf morphological and chemical traits, stomatal traits are more useful indicators to investigate the process of photosynthesis and evapotranspiration. Among stomatal traits, stomatal density (SD) and stomatal size (or length, SL) are considered as key morphological traits to jointly determine stomatal conductance of leaves to CO2 and H2O9,10,11.
Biogeography and variability of stomatal traits of leaves at a large scale are highly important but currently poorly understood. Most of previous studies used short-term control experiments to investigate the responses of stomatal morphological traits to changing environments, such as CO2 concentration12, light intensity13, temperature14 and water status15,16. The response of SD to elevated temperature is inconsistent, as it increases17, decreases14, or remains unchanged18. Furthermore, SD is also affected by water availability and moderate water deficits have a positive effect on SD15,16. These observations focus on the responses or plasticity of stomatal traits to controlled stresses at the local scale, but they can’t clarify the variation of stomatal traits at a large scale as a result of long-term adaption to changing environments19. Recently, Yang et al.20 reported that lower temperature and higher insolation led to higher SL but lower SD of grassland species in the Tibetan Plateau compared to Inner Mongolia. Stenstrom et al.21 found that the SD of Carex increased and SL decreased with increasing temperature and precipitation in arctic Eurasia. However, how to scale up the stomatal traits from species to community level and how to establish the relationship between these traits and ecosystem function are still important challenges.
At the leaf level, short-term field measurements have suggested that a positive relationship exists between the maximum stomatal conductance (determined by the size and density of stomata) and the photosynthetic capacity9. Given that ecosystem function is manifested through the plant community rather than individual plants or species, it is expected that ecosystem NPP is closely related to community-level stomatal traits. In this study, through an investigation of SD and SL across 760 common species (to differentiate from community-level stomatal traits, we used SDL and SLL to represent leaf or species-level stomatal traits thereafter) in nine typical forests, ranging from tropical monsoon rainforest to cold-temperate coniferous forest along the north-south transect of eastern China (NSTEC, Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table S1), we explored the latitudinal patterns of leaf stomatal traits and their main controlling factors at the species and community levels. Furthermore, we tested the assumption that stomatal traits at the community level (SDC and SLC) would be closely related to NPP in forests at a large scale.
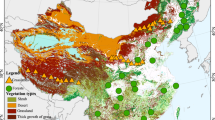
Geographic locations and vegetation types of the sampling sites.
JF, Jianfengling; DH, Dinghu; JL, Jiulian; SN, Shennongjia; TY, Taiyue; DL, Dongling; CB, Changbai; LS, Liangshui; HZ, Huzhong. The north-south transect of eastern China (NSTEC) is highlighted with different colors representing different vegetation types32. The map is generated using ArcGIS 10.0 software.
Results
Overall statistics of stomatal traits
Across all 760 species, the mean values of species-level SDL and SLL were 219.15 stomata mm–2 and 28.16 μm, with the range from 24.82 to 1,371.93 stomata mm–2 for SDL and 9.34–93.76 μm for SLL, respectively (Fig. 2). Moreover, the variation of SDL was larger than that of SLL (coefficient of variation, CV = 0.70 vs. 0.38, Fig. 2). For nine forest communities, the mean values of community-level SDC and SLC were 1,497.09 stomata mm−2 and 36,032.13 μm mm–2 (see Supplementary Table S2), with CVs of 0.55 and 0.49, respectively.
SDL and SLL varied markedly across different plant functional types (PFTs) (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. S1). Compared with shrubs and herbs, the leaves of trees had denser but smaller stomata (F = 234.80, P < 0.001 for SDL; F = 185, P < 0.001 for SLL). Among trees, broadleaves had higher SDL and lower SLL than conifers (F = 13.48, P < 0.001 for SDL; F = 11.73, P = 0.001 for SLL) and evergreen broadleaves had higher SDL and less SLL than those of deciduous counterparts (F = 24.10, P < 0.001 for SDL; F = 57.83, P < 0.001 for SLL).
Box plots of stomatal density (SDL, (A)) and stomatal length (SLL, (B)) across different plant functional types (PFTs).
The solid and dashed lines across the middle of the box are mean and median values, respectively. N, species number. Statistical differences (P < 0.05) are denoted by different letters using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Relationships between SD and SL at the species and community levels
Strong negative relationship between SDL and SLL was observed across species (Fig. 4A) and different PFTs (Fig. 5), in which SLL decreased linearly with the increase in SDL (after log10 transformation). The results of standardized major axis (SMA) tests showed that the slopes differed significantly among growth forms (P < 0.05, Fig. 5A and Supplementary Table S3) and the slope for herbs was steeper than those of trees or shrubs. SMA tests for common slopes revealed no significant difference between evergreen and deciduous trees (P > 0.05), but difference was observed in the y-axis intercept, with higher SLL at any given SDL in deciduous trees than that in evergreen trees (P < 0.05, Fig. 5B and Supplementary Table S3).
Standardized major axis (SMA) regressions between species-level stomatal density (SDL) and stomatal length (SLL) across different growth types (A) and leaf habits (B). “Slope”, difference in SMA slopes; “Elevation”, difference in SMA elevations (i.e. y-axis intercept); *significantly different (P < 0.05); NS, not significantly different (P > 0.05). Sample size and results of regression analyses are presented in Supplementary Table S3.
In contrast to the results at the species and PFT levels, a significantly positive relationship between SDC and SLC was observed at the community level (R2 = 0.97, P < 0.001, Fig. 4B).
Latitudinal variation in stomatal traits and their influencing factors
At the species level, plant species at lower latitudes had higher SDL than those distributed in higher latitudes (R2 = 0.08, P < 0.001, Fig. 6A), whereas the observed latitudinal trend of SLL was opposite (R2 = 0.07, P < 0.001, Fig. 6A). When scaling up to the community level, SDC and SLC decreased nonlinearly with increasing latitude (R2 = 0.83, P < 0.05 for SDC; R2 = 0.76, P < 0.05 for SLC, Fig. 6B).
Mixed-effect models were used to explain the effects of environmental factors and PFT on the stomatal traits (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S5). At the species level, the best model for SDL included PFT, mean annual temperature (MAT), soil N and their interactions as predictors; the best model for SLL only included PFT and MAT (Supplementary Table S5). PFT could explain the largest part of the variation in SDL and SLL (15.3–22.8%) at the species level and the environmental variables accounted for only a small proportion (4.7–5.4%, Table 1), although the relationships between MAT or soil N and stomatal traits were significant (Fig. 7A–C). In addition, the interactions among PFT, MAT and soil N accounted for a large proportion of the variation in SDL (16.6–17.9%, Table 1).
Relationships between stomatal traits and environmental variables.
SDL, SLL, SDC and SLC are the stomatal density and length at the species and community levels, respectively. Environmental variables include mean annual temperature (MAT), mean annual precipitation (MAP) and soil N. n, number of observations. Error bars in panels (D) and (E) represent ± 1 standard error.
To partition the variance of SDL and SLL into among-site and within-site components, the data were further analyzed through nested random-effect analysis of variance (ANOVA), with species nested within sites. We found that >50% of the variance in SDL and SLL existed within sites and 10.3–13% of variance occurred across sites (Supplementary Table S6).
At the community level, both SDC and SLC increased significantly with the increase in MAT (P < 0.05, Fig. 7D,E). The best models of SDC and SLC only included MAT (Supplementary Table S5), which accounted for 35.2–36.7% of total variation (Table 1). Furthermore, the site explained 30.9% and 45.9% of the variation in SDC and SLC, respectively (Table 1).
Relationships between community-level stomatal traits and NPP
Community-level SDC and SLC were closely correlated with forest NPP (Fig. 8). NPP increased linearly with increasing SDC and SLC (P < 0.05, Fig. 8). Moreover, in the general linear model analysis, SDC explained 51% of the total variation in forest NPP at the large scale (Supplementary Table S7), whereas SLC did not have a significant effect on NPP (P > 0.05, Supplementary Table S7), probably because of the high self-correlation between SDC and SLC (R2 = 0.97, Fig. 4B).
Discussion
This study is the first to explore the latitudinal variation in stomatal traits at the species and community levels from tropical monsoon rainforest to cold-temperate coniferous forest. Furthermore, our findings establish a relationship between stomatal traits and the spatial variation in ecosystem NPP and thus provide useful biological information for modeling ecosystem carbon and water cycles under global changes.
As expected, community-level stomatal traits were closely related to forest NPP in our study (Fig. 8). In previous studies, tight relationships between aboveground NPP and other community-aggregated traits (such as SLA and leaf N) have been documented5,22. Community structure is the basis for scaling up plant traits from species to community level5. Furthermore, leaf area index (LAI) has been widely considered as an important parameter controlling the interception of light and water, transpiration, photosynthesis, carbon and nutrient cycles3. In this study, we developed a new methodology to determine community-level stomatal traits through leaf-level measurements weighted by species-specific LAI. Such defined community-level stomatal traits were useful to qualify the total stomatal number and length per unit ground surface area within communities and could reflect the potential to exchange water vapor and CO2 between plant community and the atmosphere. The results from Fig. 8 and Supplementary Table S7 showed that community-level SDC positively correlated with forest NPP and accounted for 51% of spatial variation in NPP along the NSTEC. These findings suggest that the stomatal data measured at the species level may be associated with NPP through community structure, which provides new evidence for the linkage between plant traits and ecosystem function2. Moreover, community-level SDC can better characterize the capacity of CO2 and H2O exchange between plant community and atmosphere and thus may be a new ecological parameter in modeling CO2 and H2O exchange at the community scale.
Because of measurement difficulties and other limitations, few studies have systematically analyzed the biogeographical variation in stomatal traits across wide gradients of environmental factors. In this study, we found that latitudinal variation in species-level SDL and SLL was minimal (R2 ranging from 0.07 to 0.08, Fig. 6A) and environmental variables weakly modulated stomatal traits (4.7–5.4%, Table 1). The main reason for these weak correlations was that a substantial proportion of the variation in SDL and SLL was observed within sites (>50%, Supplementary Table S6) and thus resulted in relatively weak spatial patterns of species-level stomatal traits along the large-scale environmental gradients. Similarly, high within-site variation is normal for global-scale analyses of plant morphological, chemical, anatomical and physiological traits23,24. The large variance explained by within-site differences implies that site scale (or community level) is of particular relevance when studying mechanisms of species assembly25.
Changes in PFTs were dominant factors influencing the biogeographic distribution of species-level stomatal traits, explaining the largest part of the variation in species-level SDL and SLL (Table 1). Considerable variation was observed among different PFTs (Fig. 3), reflecting the differences in adaptive strategies of PFTs to their external environment. For example, smaller and denser stomata in trees are associated with higher stomatal conductance and transpiration rates10,26, which benefits water and nutrient transmission through longer xylem pathways in woody plants27. In contrast, large stomata are critical for herbs to optimize light capture in the light-limited environment9. Differences in stomatal traits between broadleaves and conifers reflect the differences in leaf vascular architecture, where broadleaved angiosperms reach high stomatal conductance with numerous small stomata and conifers obtain lower stomatal conductance with fewer large stomata28. Compared with deciduous trees, evergreen broadleaves with high leaf SDL can likely acquire high diffusive conductance for water vapor or CO2, thereby meeting the high transpiration requirement and simultaneously providing efficient cooling of the leaf9,29. Thus, changes in PFTs along environmental gradients contributed substantially to generating the observed variation in SDL and SLL.
Shifts of PFTs accounted for the major part of the latitudinal variation in SDL and SLL; however, climate and soil, especially MAT and soil N (Fig. 7A–C), may directly or indirectly influence stomatal traits by shaping the vegetation biogeography (changes in species composition)3,30. In this study, the interactive effect of MAT and PFT accounted for 16.6% of the variation in SDL and that of PFT and soil N explained another 17.9% of the variation (Table 1).
In this study, the latitudinal trends of SDC and SLC were significant at the community level (P < 0.05, Fig. 6B). Both SDC and SLC decreased with latitude (Fig. 6B) and could be explained largely by MAT (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S5). These results indicated that through regulation of species composition and PFTs within a community, temperature acted as the main environmental factor driving the latitudinal patterns of community-level stomatal traits, even though the influence was moderate at the species level. On the one hand, evergreen broad-leaved forests with higher LAI and SDL also have higher community-level SDC and SLC, allowing them to attain effectively high stomatal conductance to meet the high requirements of transpiration and photosynthesis at low latitudes3. On the other hand, coniferous forests dominate at high latitude and cold habitats with low SDL (thus low SDC and SLC) that allows them to minimize water loss by transpiration and mitigate water-deficit stress resulting from low air and soil temperature31.
Stomatal morphological traits and behaviors collectively determine the balance of CO2 uptake for plant photosynthesis against water loss by transpiration9. In addition to the short-term dynamics resulting from altering the width of the stomatal pore apertures, plants can respond to environmental change by adjusting their stomatal morphology via long-term evolution and development. In this study, SLL correlated negatively with SDL across all species and PFTs (Figs 4A and 5), which was consistent with a general relationship reported by previous studies across multiple species and geological time scales9,10,11. The trade-off between SDL and SLL can be partially explained by physical and energetic constraints11. The physical (space) constraints hypothesis assumes that plants adjust their stomatal size and density to optimize stomatal conductance while satisfying a given stomata-to-pavement cell ratio and thus the allocation of leaf epidermal space to stomata is limited. The second plausible hypothesis for the trade-off between SDL and SLL is the energetic constraint, which emphasizes maximizing the return in terms of stomatal conductance and photosynthesis for a given investment in the construction of stomatal complexes11. High stomatal conductance may be related to increased metabolic cost, which may explain why some species revert to producing fewer but larger stomata, particularly for plants grown in low light or low nitrogen availability with a low requirement for stomatal conductance and photosynthesis11.
The negative relationship between SDL and SLL governs short-term (plastic) and long-term (evolutionary) adaptations of plant physiological activities to the environment11. In contrast, a positive relationship between SDC and SLC was observed at the community level, indicating that the general trade-off between species-level SDL and SLL did not exist between the community-level SDC and SLC. Therefore, we assume that the trade-off mechanism through regulation of SDL and SLL may be an important strategy at the species level for adaptation to the external environment, while the adaptation of community-level stomatal traits is achieved mainly through the modulation of community composition. This mechanism could compensate for the limitation of biological conservatism resulting from the trade-off between leaf SDL and SLL at the species level.
In conclusion, community-level SDC and SLC decreased significantly as latitude increased, although latitudinal variation in species-level SDL and SLL was minimal. The adaptive strategies of stomatal traits to the external environment may be different between the species and community levels. We assume that the trade-off between SDL and SLL represents adaptive mechanism of leaf stomata to respond to environmental changes at the species level. While community-level stomatal traits regulate species composition to maximize ecosystem productivity in a given environment and to some extent compensate for the limitation of biological conservatism resulting from the trade-off between SDL and SLL. More importantly, SDC could explain 51% of the variation in forest NPP, which bridges stomatal traits to ecosystem function. Finally, the new framework, which scales up stomatal traits from species to community level weighted by LAI, makes it possible to better parameterize the complex models pertaining to ecosystem carbon and water cycles in the future.
Methods
Site description
The NSTEC is a unique forest belt driven mainly by a thermal gradient and includes almost all forest types found in the northern hemisphere32 (Fig. 1); therefore, it offers an ideal condition to test the ecological and evolutionary responses of plants to environmental changes32. Nine natural forests along the NSTEC were selected to conduct field sampling, including Jianfengling (JF), Dinghu (DH), Jiulian (JL), Shennongjia (SN), Taiyue (TY), Dongling (DL), Changbai (CB), Liangshui (LS) and Huzhong (HZ) (Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table S1). These ecosystems span latitudes from 18.7 to 51.8 °N, with MAT ranging from −3.67 to 23.15 °C and mean annual precipitation (MAP) ranging from 472.96 to 2265.80 mm. The soil type varies from tropical red soils with low organic matter to brown soils with high organic matter. Correspondingly, vegetation type varies among tropical monsoon rainforest, subtropical evergreen forest, temperate deciduous forest and cold-temperate coniferous forest. To minimize anthropogenic disturbances, we set up the sampling plots within well-protected national nature reserves in each forest type, where the vegetation is relatively homogenous and is strongly representative of the given forest ecosystems.
Field sampling and measurement
The field survey was conducted during July and August of 2013. Three or four experimental plots (30 × 40 m) were set up in each forest ecosystem. The geographic information (latitude, longitude and altitude), plant species identity and community structure were determined for each plot. The number, height, diameter at breast height (DBH) of all trees with DBH ≥ 2 cm (basal stem diameter for shrubs) and aboveground live-biomass of all herbs were measured. Subsequently, 20 fully expanded sun leaves were collected from four individuals of each plant species using a long chain saw or by two professional climbers and all of the leaf samples for a given plant species from one plot were mixed together as a replicate. Collected fresh leaves were stored in sealed plastic bags and scanned to determine leaf area within 4–8 h after collection. In total, 904 species-at-site combinations, consisting of 760 plant species from 427 genera and 154 families, were collected. Species were also grouped in different PFTs by the possible groups: growth form (herbs, shrubs and trees), leaf type (coniferous vs. broadleaved trees) and leaf habit (evergreen vs. deciduous broadleaved trees). At each plot, soil samples (0–10 cm) were collected randomly from 30–50 points using a 6-cm-diameter auger and then mixed thoroughly.
We randomly selected ten fresh leaves for each plant species and scanned them using a scanner (CanoScan LiDE 110, Japan), then measured the area by using Photoshop CS (Adobe Systems, San Jose, USA). Finally, the leaves were oven-dried at 70 °C for 48 h and then weighed to calculate SLA (m2 kg−1)33.
Leaf SDL (stomata mm–2) and SLL (μm) were measured from surface impressions of the mid-blade abaxial leaf surface made with clear nail polish (methods described in Wang et al.34). All stomatal measurements were conducted with electronic image analysis equipment (COIC XSZ-HS3 and MIPS software, Optical Instrument Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China). In total, 4284 leaf cuticle images were obtained (see examples in Supplementary Fig. S1).
Calculation of community-level stomatal traits
Here, we defined the total stomata number per unit ground surface area within a community as community-level SDC (stomata mm–2) and total stomatal length per unit land area as community-level SLC (μm mm–2). Community-level stomatal values were calculated as the sum of species-specific SDLi and SLLi weighted by their LAI (m2 m–2) in each plot (30 × 40 m). To estimate LAI, we firstly calculated the foliar biomass of woody species based on the mean DBH (basal stem diameter for shrubs) and height through allometric equations, which were obtained from Chinese Ecosystem Research Net (CERN) database (http://159.226.111.42/pingtai/cernc/index.jsp), published studies and our previous field measurements (unpublished data) (available in Supplementary Table S8). The use of species-specific equations is preferred in the calculation of foliar biomass; however, this is virtually unrealistic in practice, especially for tropical rainforests. Therefore, we used the biomass equations from the same genera, similar PFT, or mixed-species equations of a forest to estimate species’ foliar biomass when their allometric equations were unavailable. In total, 246 species-specific equations with R2-values ranging from 0.52 to 1.00 were used in this study. For herbs, the foliar biomass was represented by aboveground biomass. Then, species-specific foliar biomass multiplied by SLA was used to calculate the LAIi35. Finally, community-level SDC and SLC were calculated according to equations (1) and (2). The frameworks to scale up stomatal traits from species to community level were also illustrated in Supplementary Fig. S2.


Ecosystem NPP
The ecosystem NPP (g C m–2 yr–1) used in this study was derived from Luo36, who estimated the biomass and NPP of 668 stands from 7 major forest types in China. In Luo’s published dataset, NPP was computed as the sum of the annual net increment of root, stem, branch and leaf components of trees and those of shrubs and herbs. For trees, the annual net increments of stems, branches and roots were obtained by multiplication of the biomass of different components and their growth rate. The annual net increment of leaves was estimated as the leaf biomass divided by leaf age of different trees. The average NPP of the shrub and herb layers was estimated by dividing their biomass by average stand age. A more detailed description to estimate forest NPP is presented in Ni et al.35 and Luo36. From this dataset, we extracted NPP data based on latitude, longitude and forest type. Because NPP data in Luo’s dataset was based on dry matter, the dry matter was converted into units of C, using a conversion factor of 0.537.
To test the accuracy of these data, we compared ecosystem NPP and LAI with the MODIS products in a 1 × 1 km grid (http://daac.ornl.gov/cgi-bin/MODIS/GLBVIZ_1_Glb/modis_subset_order_global_col5.pl). MODIS NPP data from 2000 to 2010 and LAI data from July to August of 2013 for nine sampling sites were selected. The observed closely relationships between measured NPP and LAI and MODIS products proved our data reliable to some extent (Supplementary Fig. S3).
Climate data
The climatic variables in this study, including MAT and MAP, were extracted from the meteorological database produced by CERN38. The climate dataset at a 1 × 1 km spatial resolution was generated from the data of 740 climate stations of the China Meteorological Administration during 1961 and 2007, using the interpolation software of ANUSPLIN.
The monthly averaged insolation (kWh m–2 day–1) of nine sampling sites over a 22-year period (1983–2004) was obtained from the NASA Surface Meteorology and Solar Energy dataset (http://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/sse/) to represent light intensity in this study.
Analysis of soil properties
Soil water content (SWC, %) was determined after fresh soil was dried at 105 °C for 24 h. Other fresh soil samples were air-dried and sieved with the roots removed by hand, then ground to pass through a 2-mm sieve. Soil total N concentration (mg g–1) was analyzed using an elemental analyzer (Vario MAX CN Elemental Analyzer, Germany). Soil total P concentration (mg kg–1) was measured by the ammonium molybdate method using a continuous-flow analyzer (AutoAnalyzer3 Continuous-Flow Analyzer; Bran Luebbe, Germany) after H2SO4-H2O2-HF digestion39.
Data analysis
Stomatal data were log10-transformed prior to analyses to obtain the approximate normality and homogeneity of residuals. We analyzed stomatal traits at the species level (averaged within species at each site) and community level (weighted by species-specific LAI), respectively.
One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test was used to compare differences in species-level SDL and SLL among different PFTs. Then, the bivariate analyses of SDL–SLL and SDC–SLC relationships were performed using ordinary least squares (OLS) linear regressions and differences in the slopes and elevations of SDL–SLL relationships among PFTs were evaluated by SMA estimation with the R package smatr. In SMA analyses, we tested the heterogeneity of regression slopes and estimated the common slopes when non-heterogeneity of the slopes was demonstrated (P > 0.05). Then, differences in the elevation of regression slopes (i.e. y-axis intercept) were tested using ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc tests.
To explore the latitudinal patterns of stomatal traits and their environmental drivers, we performed regression analyses between stomatal traits and latitude at the species and community levels, respectively. Then, we analyzed each of the stomatal traits using linear mixed-effect models with the residual maximum likelihood (REML) method in the R package lme4. In these analyses, we treated environmental variables and PFT as fixed effects and the random-effect term for site was included to account for the non-independence of species occurring at the same site23. This term also allowed us to determine how variance in stomatal traits was partitioned within and across sites. To avoid problems of collinearity among the environmental variables, only variables with insignificant Pearson’s correlation (P > 0.05, Supplementary Table S4) were included. The environmental variables that had significant effects (P < 0.05) on stomatal traits and interaction terms between PFT and the environmental variables were included in the final model (Supplementary Table S5). Models with lower Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) values were chosen as the final best-fit models40.
Finally, linear regressions were performed to describe the relationships between ecosystem NPP and community-level SDC and SLC and the relative contributions to the spatial variation of NPP were assessed by a general linear model.
All analyses were conducted using SPSS 13.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, 2004) and R software (version 2.15.2, R Development Core Team 2012).
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Wang, R. et al. Latitudinal variation of leaf stomatal traits from species to community level in forests: linkage with ecosystem productivity. Sci. Rep. 5, 14454; doi: 10.1038/srep14454 (2015).
References
Suding, K. N. et al. Scaling environmental change through the community-level: a trait-based response-and-effect framework for plants. Global Change Biol. 14, 1125–1140 (2008).
Reichstein, M., Bahn, M., Mahecha, M. D., Kattge, J. & Baldocchi, D. D. Linking plant and ecosystem functional biogeography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 13697–13702 (2014).
Chapin III, F. S., Matson, P. A. & Mooney, H. A. Principles of terrestrial ecosystem ecology (Springer, New York, 2002).
Violle, C., Reich, P. B., Pacala, S. W., Enquist, B. J. & Kattge, J. The emergence and promise of functional biogeography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 13690–13696 (2014).
Garnier, E. & Navas, M. L. A trait-based approach to comparative functional plant ecology: concepts, methods and applications for agroecology. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 365–399 (2012).
Andersen, K. M., Endara, M. J., Turner, B. L. & Dalling, J. W. Trait-based community assembly of understory palms along a soil nutrient gradient in a lower montane tropical forest. Oecologia 168, 519–531 (2012).
Yu, G. R. et al. High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the East Asian monsoon region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 4910–4915 (2014).
Zhu, X. J. et al. Spatiotemporal variations of T/ET (the ratio of transpiration to evapotranspiration) in three forests of Eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 52, 411–421 (2015).
Hetherington, A. M. & Woodward, F. I. The role of stomata in sensing and driving environmental change. Nature 424, 901–908 (2003).
Franks, P. J. & Beerling, D. J. Maximum leaf conductance driven by CO2 effects on stomatal size and density over geologic time. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 10343–10347 (2009).
Franks, P. J., Drake, P. L. & Beerling, D. J. Plasticity in maximum stomatal conductance constrained by negative correlation between stomatal size and density: an analysis using Eucalyptus globulus. Plant Cell Environ. 32, 1737–1748 (2009).
Engineer, C. B. et al. Carbonic anhydrases, EPF2 and a novel protease mediate CO2 control of stomatal development. Nature 513, 246–250 (2014).
Al Afas, N., Marron, N. & Ceulemans, R. Variability in Populus leaf anatomy and morphology in relation to canopy position, biomass production and varietal taxon. Ann. Forest Sci. 64, 521–532 (2007).
Luomala, E. M., Laitinen, K., Sutinen, S., Kellomaki, S. & Vapaavuori, E. Stomatal density, anatomy and nutrient concentrations of Scots pine needles are affected by elevated CO2 and temperature. Plant Cell Environ. 28, 733–749 (2005).
Fraser, L. H., Greenall, A., Carlyle, C., Turkington, R. & Friedman, C. R. Adaptive phenotypic plasticity of Pseudoroegneria spicata: response of stomatal density, leaf area and biomass to changes in water supply and increased temperature. Ann. Bot. 103, 769–775 (2009).
Xu, Z. & Zhou, G. Responses of leaf stomatal density to water status and its relationship with photosynthesis in a grass. J. Exp. Bot. 59, 3317–3325 (2008).
Ferris, R., Nijs, I., Behaeghe, T. & Impens, I. Elevated CO2 and temperature have different effects on leaf anatomy of perennial ryegrass in spring and summer. Ann. Bot. 78, 489–497 (1996).
Zheng, Y. P. et al. Effects of experimental warming on stomatal traits in leaves of maize (Zea may L.). Ecol. Evol. 3, 3095–3111 (2013).
Wang, R. Z. et al. Anatomical and physiological plasticity in Leymus chinensis (Poaceae) along large-scale longitudinal gradient in northeast China. PLoS One 6, e26209 (2011).
Yang, X. et al. Large-scale patterns of stomatal traits in Tibetan and Mongolian grassland species. Basic. Appl. Ecol. 15, 122–132 (2014).
Stenstrom, A., Jonsdottir, I. S. & Augner, M. Genetic and environmental effects on morphology in clonal sedges in the Eurasian Arctic. Am. J. Bot. 89, 1410–1421 (2002).
Garnier, E. et al. Plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during secondary succession. Ecology 85, 2630–2637 (2004).
Moles, A. T. et al. Which is a better predictor of plant traits: temperature or precipitation? J. Veg. Sci. 25, 1167–1180 (2014).
Kazakou, E. et al. Are trait-based species rankings consistent across data sets and spatial scales? J. Veg. Sci. 25, 235–247 (2014).
Liu, G. F. et al. Coordinated variation in leaf and root traits across multiple spatial scales in Chinese semi-arid and arid ecosystems. New Phytol. 188, 543–553 (2010).
Drake, P. L., Froend, R. H. & Franks, P. J. Smaller, faster stomata: scaling of stomatal size, rate of response and stomatal conductance. J. Exp. Bot. 64, 495–505 (2013).
Woodward, F. I. Do plants really need stomata? J. Exp. Bot. 49, 471–480 (1998).
Lammertsma, E. I. et al. Global CO2 rise leads to reduced maximum stomatal conductance in Florida vegetation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4035–4040 (2011).
Eamus, D. Ecophysiological traits of deciduous and evergreen woody species in the seasonally dry tropics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 14, 11–16 (1999).
Han, W. X., Fang, J. Y., Reich, P. B., Woodward, F. I. & Wang, Z. H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 14, 788–796 (2011).
Luo, J. X., Zang, R. G. & Li, C. Y. Physiological and morphological variations of Picea asperata populations originating from different altitudes in the mountains of southwestern China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 221, 285–290 (2006).
Zhang, X. S. & Yang, D. A. Allocation and study on global change transects in China. Quatern. Sci. 1, 43–52 (1995).
Cornelissen, J. H. C. et al. A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 51, 335–380 (2003).
Wang, R. L. et al. Elevation-related variation in leaf stomatal traits as a function of plant functional type: evidence from Changbai Mountain, China. PLoS One 9, e115395 (2014).
Ni, J., Zhang, X. S. & Scurlock, J. M. O. Synthesis and analysis of biomass and net primary productivity in Chinese forests. Ann. Forest. Sci. 58, 351–384 (2001).
Luo, T. X. Patterns of biological production and its mathematical models for main forest types of China. PhD thesis, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1996).
Lieth, H. & Whittaker, R. H. Primary productivity of the biosphere (Springer, New York, 2012).
He, H. L. et al. Large-scale estimation and uncertainty analysis of gross primary production in Tibetan alpine grasslands. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 119, 466–486 (2014).
Zhao, N. et al. The altitudinal patterns of leaf C:N:P stoichiometry are regulated by plant growth form, climate and soil on Changbai Mountain, China. PLoS One 9, e95196 (2014).
Aho, K., Derryberry, D. & Peterson, T. Model selection for ecologists: the worldviews of AIC and BIC. Ecology 95, 631–636 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff in nine forest ecosystem research stations for access to their study sites. We are grateful to Dali Guo and Shuli Niu for their valuable comments on the manuscript and to Shinichi Nakagawa for his help on data analysis. This work was partially supported by the Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31290221), the Chinese Academy of Sciences Strategic Priority Research Program (XDA05050702) and the Program for “Kezhen” Distinguished Talents in Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS (2013RC102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.Y., N.H., Q.W. and J.G. designed the research. R.W. analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. R.W., N.Z. and Z.X. performed the field experiments. R.W., N.H. and G.Y. revised and edited the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Yu, G., He, N. et al. Latitudinal variation of leaf stomatal traits from species to community level in forests: linkage with ecosystem productivity. Sci Rep 5, 14454 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14454
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14454
This article is cited by
-
Eco-physiological trait variation in widely occurring species of Western Himalaya along elevational gradients reveals their high adaptive potential in stressful conditions
Photosynthesis Research (2024)
-
Relationships of stomatal morphology to the environment across plant communities
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Functional traits and habitat heterogeneity explain tree growth in a warm temperate forest
Oecologia (2023)
-
Leaf phenotypic plasticity and integration balance plant adaptation to water table decline: a mesocosm experiment
Plant and Soil (2023)
-
Perennials have evolved a greater resistance to exogenous H2O2 than annuals, consistent with the oxidative stress theory of aging
Biologia (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.