Abstract
Aging of biological systems is accompanied by degeneration of mitochondrial functions. Different pathways are active to counteract the processes which lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial dynamics, the fission and fusion of mitochondria, is one of these quality control pathways. Mitophagy, the controlled degradation of mitochondria, is another one. Here we show that these pathways are linked. A double deletion mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which two essential components of the fission and fusion machinery, Dnm1 and Mgm1, are simultaneously ablated, contain wild-type like filamentous mitochondria, but are characterized by impaired respiration, an increased sensitivity to different stressors, increased mitochondrial protein carbonylation and a decrease in mitophagy and replicative lifespan. These data show that a balanced mitochondrial dynamics and not a filamentous mitochondrial morphotype per se is the key for a long lifespan and demonstrate a cross-talk between two different mitochondrial quality control pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Mitochondria are organelles with different essential functions. They are the main site of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation, play a key role in synthesis of iron sulfur clusters and are involved in the control of apoptosis. Mitochondrial function and efficiency are closely associated with the morphology of the organelle which varies between organisms, tissues and under different environmental conditions. Mostly, mitochondria possess a highly dynamic tubular-like or filamentous morphotype. Mitochondrial dynamics is the result of a well-balanced fission and fusion of mitochondrial units, processes which are controlled by a complex fusion and fission machinery1,2. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the two dynamin-related GTPases Fzo1, Mgm13,4 and the outer mitochondrial membrane protein Ugo15 are important components of this machinery. Fzo1 is anchored in the outer mitochondrial membrane via two transmembrane regions. Both, the N-terminal GTPase domain and the C-terminus are facing towards the cytosol6 and form homodimers in an Ugo1-dependent manner7. Besides the interaction of Ugo1 with Fzo1, it also interacts with the inner mitochondrial membrane GTPase Mgm1, representing a linker between the outer and inner membrane fusion machinery8. Mitochondrial fusion is initiated through GTP hydrolysis by Fzo1. Ubiquitination of Fzo1 by the cytosolic F-box protein Mdm30 leads to degradation of Fzo1 which mediates fusion of the outer mitochondrial membrane7. Fusion of the inner mitochondrial membrane is dependent on two isoforms of Mgm1 (‘large’ l-Mgm1 and ‘small’ s-Mgm1)9. The l-Mgm1 protein exhibits an N-terminal transmembrane domain and a C-terminal GTPase region which protrudes into the intermembrane space. The s-Mgm1 form, which lacks the N-terminal transmembrane domain, is associated with l-Mgm1 that is thought to act as an inner membrane receptor of s-Mgm110. The details of the Mgm1-mediated inner membrane fusion are not fully clarified. It has been suggested that Mgm1 forms homo-oligomeric protein bridges and ordered lattices between two inner membranes to ultimately promote fusion by GTP hydrolysis11. Although Mgm1 is believed to control mitochondrial inner membrane fusion, MGM1 deletion mutants are also unable to mediate outer membrane fusion12. Due to this defect in fusion, that does not affect fission, mitochondria are of the fragmented morphotype. In addition, they are respiration deficient (rho0 petites) due to the loss of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)13,14.
The mitochondrial fission machinery of S. cerevisiae is composed of the outer membrane protein Fis1, the WD domain protein Mdv1 and the large GTPase Dnm110,15,16,17,18. Fis1 has been demonstrated to interact with Mdv1, which interacts with Dnm119. Dnm1 can oligomerize to form spirals around mitochondria. Subsequently, GTP hydrolysis by Dnm1 leads to separation of the outer and inner membrane10. Deletion of DNM1 results in fission deficiency and, due to unaffected fusion of mitochondria, to a net-like mitochondrial morphotype16.
The balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission is a major regulator for adaption to environmental situations and an efficient mitochondrial quality control20,21,22. Impairments in mitochondrial dynamics lead to cell death, human diseases23,24 and are associated with aging25,26.
We use S. cerevisiae as an aging model to unravel the role of mitochondrial dynamics in biological aging. In previous work it has been shown, that mitochondria change their morphology during aging from the filamentous to the fragmented morphotype. This age-related fragmentation can be delayed by deletion of DNM1 and leads to an increased replicative lifespan26. Concordantly, deletion of the MGM1 gene accelerates fragmentation and shortens replicative lifespan27. Interestingly, it has previously been shown, that a double deletion strain of DNM1 and MGM1 in which fission and fusion are impaired, retains wild-type like filamentous mitochondria and maintains mtDNA12.
Here we investigated the consequences of the simultaneous disruption of mitochondrial fission and fusion in S. cerevisiae in more detail. We found that, although the mitochondrial morphotype of the double mutant resembles the morphotype of the wild type, mitochondria from the mutant are strongly impaired in respiration and stress resistance and are characterized by a pronounced decrease in replicative lifespan. These adverse effects are linked to a strong reduction of mitophagy representing a mechanism involved in clearance of impaired mitochondria.
Results
Generation and verification of a Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant
In order to generate a Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant, we crossed the two kanamycin resistant BY4741 Δdnm1 and BY4742 Δmgm1 strains. After sporulation of the resulting heterozygous diploid (BY4743), we selected a putative DNM1/MGM1 double deletion strain and verified the correct deletions by PCR.
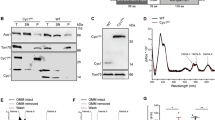
Next we investigated mitochondrial morphology of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain and compared it to the wild type and the single mutants. In this analysis we used strains transformed with a mtGfp fusion gene which encodes GFP with a mitochondrial targeting sequence. Yeast strains were grown to exponential phase, at which most cells are juvenile but also some are of older age including some senescent cells. Analyses of samples from these cultures by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) revealed five distinct mitochondrial morphotypes (Fig. 1a): (i) a filamentous morphotype with long and branched mitochondria, (ii) the network like morphotype in which filamentous mitochondria are fused and form net like structures, (iii) the fragmented morphotype with punctate mitochondria, (iv) the giant mitochondria morphotype with 1–3 huge ellipsoid mitochondria and (v) the linear morphotype with long, unbranched mitochondria. We manually counted mitochondria of the individual morphotypes in the different strains. In concordance with earlier investigations14,26 the vast majority (94%) of mitochondria of the wild type BY4742 displayed a filamentous morphotype while the major morphotype was network-like in the DNM1 deletion strain (69%), fragmented (91%) in the MGM1 deletion strain and filamentous (89%) in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant (Fig. 1b).
Mitochondrial morphotypes in the investigated yeast strains.
The indicated strains were transformed with mitochondrial localized GFP (mtGFP). Z-stacks of individual cells (BY4742 n = 52; Δdnm1 n = 54; Δmgm1 n = 65; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 64) were taken by confocal laser scanning microscopy and individually matched to one of five morphotypes. (a) Representative examples for each morphotype are shown. Scale bars represent 5 μm of length. The proportion of the different morphotypes was determined by counting the above indicated number of cells of each strain. (b) The predominant morphotype in the analyzed strains were: BY4742, 94% filamentous; Δdnm1, 69% network like; Δmgm1, 91% fragmented; Δdnm1Δmgm1, 89% filamentous.
Simultaneous deletion of DNM1 and MGM1 leads to a shortened replicative lifespan linked to increased stress sensitivity
In earlier experiments it has been shown that, compared to the wild type, in which most mitochondria are of the filamentous morphotype, deletion of DNM1 leads to an extension and the deletion of MGM1 to a decrease in replicative lifespan26,27. We now determined the replicative lifespan of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant grown on YPD and compared it to the lifespan of the wild type and the two single deletion mutants, Δdnm1 and Δmgm1, respectively (Fig. 2a). On YPD, the mean lifespan of Δdnm1Δmgm1 (10.8 ± 1.7 generations) was much shorter than that of the Δdnm1 strain (26.8 ± 1.4 generations). Most strikingly, although mitochondria of the double deletion strain are of the wild-type-like morphotype, the lifespan of this strain was shorter than that of the wild type (18.0 ± 1.7 generations). The difference in mean lifespan between this strain and that of the Δmgm1 strain (10.8 vs. 13.2 ± 1.6 generations) is statistically not significant. We next verified the severe effect on lifespan of a simultaneous deletion of DNM1 and MGM1 on non-fermentable medium (Fig. 2b). While lifespans of the single mutants differed when compared to those under fermentable conditions, which are more reminiscent to natural conditions, the double deletion mutant is again characterized by the shortest lifespan.
Replicative lifespan with different carbon sources.
(a) Lifespan of the indicated strains (BY4742 n = 39; Δdnm1 n = 39; Δmgm1 n = 34; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 23) was determined on YPD medium. Strains were cultivated at 30°C and separated from their daughter cells by micromanipulation (mean lifespan: BY4742 = 18 generations; Δdnm1 = 26.8 generations; Δmgm1 = 13.2 generations; Δdnm1Δmgm1 = 10.8 generations). Significance was tested by SPSS with the Log Rank (Mantel-Cox) (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.001; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.01; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.004; Δmgm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.508), Breslow (Generalized Wilcoxon) (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.0005; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.035; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.009; Δmgm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.305) and the Tarone-Ware (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.001; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.021; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.005; Δmgm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.288) test. (b) Lifespan of the indicated strains (BY4742 n = 33; Δdnm1 n = 40; Δmgm1 n = 40; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 34) was determined on SG medium used during the mitophagy assay. Strains were cultivated at 30°C and separated from their daughter cells by micromanipulation (mean lifespan: BY4742 = 24.4 generations; Δdnm1 = 19.3 generations; Δmgm1 = 31.2 generations; Δdnm1Δmgm1 = 15.6 generations). Significance was tested by SPSS with the Log Rank (Mantel-Cox) (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.031; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.008; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.001; Δdnm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.125), Breslow (Generalized Wilcoxon) (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.039; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.027; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.001; Δdnm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.067) and the Tarone-Ware (BY4742/Δdnm1 p = 0.031; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.028; BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.002; Δdnm1/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.082) test.
Differences in lifespan are often related to cellular stress conditions and the ability of the organism to respond to exogenous stress in an effective way. Therefore, we compared the different strains in their ability to respond to UV-light, temperature, paraquat and acetic acid stress on fermentable growth medium (YPD). The used stressors are known to induce DNA damage, affect protein folding, oxidative stress and induce apoptosis, respectively and activate molecular pathways counteracting adverse stress-related effects. We found that the Δmgm1 and Δdnm1Δmgm1 strains are characterized by reduced growth under standard conditions (Fig. 3, control). Oxidative stress (paraquat, 0.5 and 0.75 mM) and heat-stress (37°C, 3.5 hrs) diminished the growth of all strains. All mutants were more sensitive against oxidative- and heat-stress than the wild type. Again both, Δmgm1 and Δdnm1Δmgm1 were most sensitive. UV-stress also reduced growth of all strains. The Δmgm1 and Δdnm1Δmgm1 strains were most affected by UV-stress. Apoptosis induction by acetic acid disclosed an increased resistance of the Δdnm1 strain to apoptotic cell death. Strikingly, the Δdnm1Δmgm1 and the Δmgm1 strain were both highly sensitive to this kind of stress. Taken together, the two strains in which MGM1 is deleted respond very similar to different exogenous stressors and are both strongly reduced in replicative lifespan. These data emphasize the important role of Mgm1 specifically under fermentable growth conditions with increasing stress, conditions as they occur during normal aging. Concordantly, ablation of Mgm1 leads to a reduction of the lifespan of the wild type and of the long-lived DNM1 deletion strain with a reduced sensitivity to apoptosis induction (e.g., via acetic acid).
Resistance of strains against different stresses.
Cells grown to the logarithmic phase were plated in serial dilutions (3 μl drops of a 107–103 cells/ml solution) on YPD medium and treated with different stressors (UV-Stress irradiated at 100 J/m2, Heat-Stress 3.5 hr. at 37°C, 0.5 or 0.75 mM paraquat, 30 or 40 mM acetic acid for 300 min in YPD before plating). Plates were incubated for two days at 30°C.
Oxygenic energy metabolism is affected in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain
Due to the essential role of mitochondria in energy metabolism, we next analyzed the effect on growth of strains on different carbon sources in some more detail. The Δmgm1 strain is ρ0 and therefore cannot grow on non-fermentable media (YPG) (Fig. 4a). The double mutant was not ρ0. The competence to maintain mtDNA and the mtDNA itself, appears to be derived from the Δdnm1 parental strain used in the cross with Δmgm1 to generate the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant. Despite the ability of the double mutant to grow on YPD, growth is decreased when compared to that of the wild type. To analyze growth characteristics of the different investigated strains in some more detail, we studied the time-related cell density in liquid cultures by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (Fig. 4b). In YPD medium, all strains metabolized glucose during the exponential fermentative growth phase. After glucose depletion, the wild type, Δdnm1 and Δdnm1Δmgm1 enter the exponential respiratory phase. In contrast, vegetative propagation of the Δmgm1 strain, which is not capable to respire, ceases after glucose depletion. This behavior is well in concordance with the petite phenotype and the absence of a functional respiration which is needed to metabolize acetate and ethanol produced in the fermentative growth phase. Also, in YPG medium, where glycerol is the only carbon source, Δmgm1 is not viable. In contrast, although strongly decreased in comparison to the wild type and the Δdnm1 strain, the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant propagates in glycerol-containing liquid medium indicating that mitochondria are functional but respiration is inefficient in this strain.
Analysis of energy metabolism.
(a) Samples from a culture grown to the exponential phase were serial diluted and plated onto YPD and YPG plates (3 μl drops of 107–102 cells per ml solution), respectively followed by incubation at 30°C for two days. (b) Cells were grown in liquid YPD (start OD600: 0.08) or YPG (start OD600: 0.02) at 30°C. Samples were taken at different time points and OD600 was measured. (c) High resolution respirometry was performed to determinate the normal respiration capacity and respiration after stepwise addition of the uncoupling reagent FCCP to the indicated strain. Measurements were performed in YPG medium at 30°C. The ground value of all oxidases was taken after edition of antimycin A to inhibit the respiratory chain (complex III) and were subtracted from the measured data of the normal respiration and after addition of FCCP to obtain the Basic and maximal electron transport system capacity (ETS), respectively (BY4742 Basic/Δdnm1Δmgm1 Basic p = 8.5 E-6; BY4742 ETS/Δdnm1Δmgm1 ETS p = 7.3 E-5). Measurements were performed with biological replicates of BY4742 (n = 10), Δdnm1 (n = 4) and Δdnm1Δmgm1 (n = 6). Statistic tests were performed with the ″Students t-test″ and error bars represent the standard error.
In order to unravel the reasons for the inefficient utilization of glycerol in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant, we measured the respiration capacity of this strain and compared it to the wild type and Δdnm1 grown in YPG liquid medium. The respiration capacity (Fig. 4c) was determined by measuring cellular oxygen uptake. The maximal oxygen consumption was determined in cells grown in YPG to which increasing amounts of the uncoupling reagent FCCP were added. Subsequently, background value of oxygen consumption by all cellular oxidases was measured by addition of antimycin A (complex III inhibitor). The background value was subsequently substracted from normal oxygen consumption to obtain the basic respiration (Basic) and from oxygen consumption after addition of FCCP to yield the maximal electron transport system capacity (ETS). In concordance with the results from the growth experiments on solid growth medium (Fig. 4a), respiration of the Δdnm1 strain was not significantly different from that of the wild type, while the basic respiration capacity and the electron transport capacity of Δdnm1Δmgm1 were significantly lower than in the wild type (Fig. 4c).
Increased abundance of oxidized proteins in Δdnm1Δmgm1
The observed differences in energy transduction in the double deletion strain may be due to a reduced mass or a lower quality of mitochondria. To discriminate between these possibilities, we microscopically determined the number of mitochondria of different strains used in this study to which GFP (mtGFP) was targeted to mitochondria. To take the three-dimensional structure of mitochondria into account, we used z-stacks images and normalized the mitochondrial mass to cell size (Fig. 5a). The analyses revealed a lower mitochondrial mass in the Δmgm1 strain than in the other strains in which no significant difference was observed. Thus, a reduced mitochondrial mass cannot account for the observed reduction of the respiration capacity of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain.
Analysis of mitochondrial mass and quality.
(a) Cells expressing mtGFP were analysed by condocal laser scanning microscopy. Mitochondrial area of maximal projected z-stacks (BY4742 n = 52; Δdnm1 n = 54; Δmgm1 n = 65; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 64) was measured with the ImageJ software (BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 0.03). (b) The indicated strains were cultivated in YPG medium at 30°C and subsequently used to inoculate an YPD liquid culture at 30°C. Samples were taken after 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 days for plating on YPDGly medium. The amount of small (petite) and large colonies was determined after 2–3 days. The Δmgm1 strain as a petite mutant is indicated by a straight blue line at 100% petites. (c) For the analysis of protein oxidation, 15 μg of mitochondrial extracts was derivatized with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, followed by western blot analysis. The derivatized carbonyl groups were detected by α-DNPH. The coomassie stained gel was used as a loading control. (d) The relative protein oxidation was calculated for three biological replicates from scans of oxy-blots using an infrared scanner. Error bars represent the standard error (BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 0.022). Statistic tests were performed with the ″Students t-test″ and error bars represent the standard error.
Next, we investigated the quality of mitochondria in the different investigated strains. First we determined the formation of petite cells as a measure of mtDNA loss. In this analysis, strains were cultivated in liquid YPD medium and samples were taken at different time points. The samples were plated onto YPDGly medium, containing a limited amount of the fermentable carbon source glucose (2% glycerol, 0.1% glucose, 2% yeast extract, 1% peptone and 2% agar28). After 2–3 days of growth, the number of small (petite) colonies was determined in relation to normal-sized colonies. The portion of cells forming petite colonies is linked to mtDNA loss in the analyzed mutants (Fig. 5b). These results verified the mtDNA deficiency phenotype of the Δmgm1 strain and revealed a higher mtDNA loss over time in this mutant than in the wild type. Also the Δdnm1 strain showed a significantly higher mtDNA loss compared to the wild type. Most strikingly, the loss of mtDNA of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant is even higher than in the Δdnm1 strain, but, in contrast to the Δmgm1 strain (Fig. 5b, blue line), mtDNA is not completely lost.
Next, as ‘readout’ of mitochondrial oxidative stress, we investigated the oxidation of mitochondrial proteins in the different strains by oxy-blot analysis. After derivatization of carbonyl groups, which result from protein oxidation with 2,2-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH), the resulting dinitrophenylhydrazone groups were detected by a specific DNPH antibody (Fig. 5c). Protein oxidation was quantified using the Odyssey infrared imaging software and normalized to the coomassie stained gels (Fig. 5d). Clearly, the amount of mitochondrial protein carbonylation in the wild type and the single mutants did not differ significantly. However, in the Δmgm1 a shift of oxidized proteins occurs towards higher molecular weight. Most strikingly, in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant relative protein carbonylation is increased by 2.1-fold compared to wild type strongly supporting the idea that the observed impairment in mitochondrial function of the double mutant is the result of the accumulation of oxidative damage.
Impairment in mitochondrial fission and fusion leads to a reduction in mitophagy
The quality of mitochondria is controlled by various mechanisms which act at different levels and are part of a network of interacting pathways29,30. The genes deleted in the mutants investigated in this study are part of this system. They are involved in the control of mitochondrial dynamics and are linked to autophagy and programmed cell death. In particular, selective autophagy of mitochondria, termed mitophagy, which allows clearance of dysfunctional mitochondria within cells, is important in controlling a ‘healthy’ population of mitochondria. We therefore investigated autophagy in the wild type and the different mutants of this study. To measure autophagy and mitophagy rates, we used an alkaline phosphatase-based (ALP) assay described previously31. This colorimetric in-vivo assay allows quantification of autophagy or mitophagy in yeast cells by expressing an inactive proenzyme of alkaline phosphatase that is targeted either to the cytosol (cytALP) or to the mitochondrial matrix (mtALP), respectively. At note, the endogenous alkaline phosphatase gene (PHO8) has to be deleted in tester strains in order to avoid unspecific background activity. Upon delivery of the inactive phosphatase to the vacuole via autophagosomes, these enzymes become processed and activated by vacuolar proteinase A. After cell lysis the specific phosphatase activity can be determined directly reflecting the level of autophagy or mitophagy, respectively. After generation of the corresponding strains, we determined the extent of non-selective autophagy and mitophagy, respectively, prior or after induction with the TOR kinase inhibitor rapamycin. Cells were cultivated in medium containing glycerol as a non-fermentable carbon source to induce respiratory growth (Fig. 6a). Compared to the wild type strain all strains, except for Δmgm1, did not show significant differences for rapamycin-induced rates of general autophagy. The same is true for a strain, in which ATG32, encoding a specific mitophagy receptor protein, is deleted. In sharp contrast, rapamycin-induced mitophagy was significantly decreased in the Δdnm1Δmgm1, the Δatg32 and the Δmgm1 strain compared to wild type. In Δdnm1 no significant effect on mitophagy induction was observed. It should be noted that only the Δmgm1 strain lacks mitochondrial DNA and thus grows very slowly under the applied test conditions. This may partly explain the low induction of rapamycin-induced mitophagy and autophagy in this strain. Proteolytic processing of mtALP and cytALP determined by western blot analysis of total cell extracts was in accordance with the assay results. The two bands representing the inactive ALP proenzyme and the active ALP upon proteolytic processing are visible (Fig. 6b). Overall, the reduction of mitophagy appears to be the key process giving rise to the specific characteristics of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant. As a consequence, mitochondria that resemble the wild-type morphotype, accumulate damage, are less efficient in energy transduction and replicative lifespan of the corresponding mutant is shortened.
Analysis of mitophagy and autophagy.
(a) The indicated strains deleted for endogenous PHO8 and expressing cytALP (marker for autophagy) or mtALP (marker for mitophagy) were analyzed during exponential growth or upon rapamycin treatment (1 μM, 24 h) in glycerol-containing medium. Autophagy and mitophagy were quantified by determination of specific ALP activity upon cell lysis. Specific activities are given as means (n = 4) normalized to the wild type control upon rapamycin treatment. (b) Proteolytic processing of mtALP and cytALP was analyzed by western blotting of total cell extracts and Bmh2 served as a control. Statistic tests were performed with the ″Students t-test″ and error bars represent the standard error (Autophagy: BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 3.8*10−7 Mitophagy: BY4742/Δdnm1Δmgm1 p = 3.2*10−8; BY4742/Δatg32 p = 3.6*10−10; BY4742/Δmgm1 p = 1.5*10−8).
Discussion
Since mitochondrial dynamics has been discovered in 191432 the importance of this pathway for biological systems has been repeatedly demonstrated. This impact is emphasized by different diseases including Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A33, Optic atrophy34, or Congenital microcephaly, lactic acidosis sudden death35 which result from impairments in mitochondrial fission or fusion. Also, biological aging is linked to mitochondrial dynamics. For instance, in the filamentous fungus Podospora anserina an increase in DNM1 transcripts and a shift from filamentous to fragmented mitochondria was observed during aging of this aging model. The deletion of DNM1 in both P. anserina and yeast let to an increased resistance to apoptosis induction and an increased ‘healthy’ lifespan of both aging models26. Subsequently, the deletion of MGM1 in yeast was found to cause a striking reduction in chronological and replicative lifespan27. The MGM1 deletion strain is respiratory incompetent and only viable on fermentable carbon sources. Since P. anserina is a strict aerobe, deletion of the corresponding gene is not possible in this system.
In the current study, we therefore addressed the question of the consequences of a simultaneous impairment of both, mitochondrial fission and fusion and thus ‘freezing’ of mitochondrial dynamics, in S. cerevisiae. The corresponding Δdnm1Δmgm1 double deletion strain is characterized by mitochondrial morphotypes that resemble those in the wild type with 89% and 94% filamentous mitochondria in the double mutant and the wild type, respectively. This morphotype results from the generation of the double mutant by crossing the two single mutants. In the resulting heterozygous diploid the defects of the single mutants complement each other leading to mitochondria of the wild-type morphotype. After sporulation, this morphotype remains stable because both fission and fusion are impaired in the haploid double deletion offspring. Our results are consistent with data from a basic characterization of such a strain in an earlier study in which the double mutant was shown to maintain mtDNA, is able to utilize non-fermentable media but is affected mitochondrial dynamics12. Despite the similarity in morphology of the wild type and Δdnm1Δmgm1 double deletion strain, our analyses revealed that mitochondrial functions and characteristics differ in the two strains. Impairments in respiration in the double deletion strain correlate with increased protein oxidation and mtDNA instability, change in growth, stress resistance and replicative lifespan. In fact, we found that replicative lifespan is strongly reduced emphasizing that a well-balanced fusion and fission of mitochondria is important to keep a ‘healthy’ population of mitochondria. In particular, fusion of mitochondria appears to be important because it allows mixing of the content of mitochondria of different quality to improve the overall quality of fusion products23,36,37. Concordantly, we found a strong effect when fusion was affected by deletion of MGM1. The ablation of Mgm1 resulted in a fragmented mitochondria morphotype and negatively affected oxygenic energy metabolism, reduced the ability to efficiently deal with exogenous stress and shortened replicative lifespan. Such a strong effect is not only observed in the wild-type genetic background but also in the DNM1 deletion strain. Strikingly, although mitochondria are of the wild-type like filamentous morphotype, replicative lifespan and stress response of the double deletion strain is similar to the Δmgm1 demonstrating that, concerning physiological effects, the MGM1 deletion is more important than the deletion of DNM1 on glucose-rich medium. This is not the case when cultivated on glycerol-rich medium where growth and also lifespan were more comparable to the DNM1 deletion strain.
One of the key problems in the Δmgm1 strain is certainly the loss of the mtDNA. This loss leads to the inability of mitochondrial biogenesis and remodeling of impaired mitochondrial components, in particular those of the respiratory chain which are encoded by the mtDNA. Strikingly, in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 double mutant the loss of mtDNA is not as severe as in the Δmgm1 strain, allowing the double mutant to utilize non-fermentable carbon sources. However, for yet unknown reasons, growth of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain on glycerol-containing solid medium is more efficient than in the corresponding liquid medium.
One of the most intriguing results of our study is the effect of the simultaneous ablation of essential components of the mitochondrial fission and fusion machinery on mitophagy. While, compared to the wild type, general autophagy is not affected in the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain, the selective degradation of mitochondria is reduced by 56%. Concordantly, we found a 2.1-fold increase in oxidized proteins in mitochondria of this strain that, together with the increased instability of the mtDNA, seem to be responsible for the short-lived phenotype of this strain. We also demonstrate in this study that it is not the mitochondrial morphotype a priori that is important for a ‘healthy’ function of mitochondria since filamentous mitochondria of the wild type and the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain strongly differ in quality. It is rather a well-balanced dynamics of mitochondria in which fission and fusion is controlled according to the physiological needs and to the fitness of mitochondria. The importance of this flexibility has been recently suggested from mathematical modeling in which mitochondrial dynamics, mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy and mitochondrial damage were analyzed. This study revealed that the deceleration of fission and fusion appears to be beneficial for an organism when mitochondrial damage passed specific threshold levels36,38. The elucidation of the underlying mechanisms controlling such flexibility including the sensing of impairments and imbalances and the induction of potential compensatory mechanisms certainly holds the key for understanding the complex network of pathways involved in lifespan control, aging and the development of mitochondrial diseases.
Methods
Yeast strains, media and plasmids
BY4742 (MAT α) wild type cells, BY4742 Δdnm1 (ΔYLL001W, MAT α), BY4741 Δdnm1 (ΔYLL001W, MAT a), BY4742 Δmgm1 (ΔYOR211C, MAT α), BY4742 Δatg32 (ΔYIL146C, MAT α) and BY4742 Δpho8 (Δ YDR481C, MAT α) cells were obtained from EUROSCARF clone collection, Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Crossing of BY4741 Δdnm1 with BY4742 Δmgm1 resulted in a diploid BY4743 Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain. Sporulation and selection of the four spores due to their kanamycin resistance was performed (crossing of strains and splitting of spores was done by Dr. Peter Kötter). Offspring's with a splitting of 2/2 (two sensitive/two resistant spores) were tested by PCR for double deletion of DNM1 and MGM1. PHO8 was deleted by PCR-based gene disruption and replaced with a HIS cassette amplified from pFA6aHISMX6 using the oligonucleotides PHO8-KO1 (5′-TCGTGCTCCACATTTTGCCAGCAAGTGGCTACATAAACATTTACACGTACGCTGCAGGTCGAC-3′) and PHO8-KO2 (5′-TGCACTCCGAAACGAAATGCGATACAGTACGTGTCATGCGGTTAGATCGATGAATTCGAGCTC-3′). BY4742 wild type and mutant strains Δdnm1, Δmgm1 and Δdnm1Δmgm1 were transformed with plasmid pVT100U-mtGFP for GFP fluorescence labeling of mitochondria. For cultivation, standard YPD (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose), YPG (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 3% glycerol) or YPDGly (2% glycerol, 0.1% glucose, 2% yeast extract, 1% peptone) media were used. For growth of plasmid containing strains, SC medium was used (0.17% yeast nitrogen base, 2% glucose, 0.5% ammonium sulfate and amino acids). For a solid growth media, 2% agar was added. Strains were cultured using standard methods at 30°C.
PCR Amplification
Genomic DNA was isolated according to39. PCR reactions were performed with 5 ng purified genomic DNA. For verification of DNM1 deletion, the oligonucleotides DNM1-A1 (5′-GAGGAAGGCGCAATAGAAGC-3′) and K1-A (5′-GGATGTATGGGCTAAATGTACG-3′) as well as K2-A (5′-CATCATCTGCCCAGATGCG-3′) and DNM1-A4 (5′-CCATGTAGAAGGTCTATCTGC-3′) were used. For verification of MGM1 deletion, the oligonucleotides MGM1-A1 (5′-CATCGACAAGTAAGCTGTTC-3′) and K1-A as well as K2-A and MGM1-A4 (5′-GGATGAAGGTACTGCATTGTC-3′) were used. After amplification, the samples were separated in 1% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide (1 μg/ml).
Confocal laser scanning microscopy
Strains, possessing the pVT100U-mtGFP plasmid40 were grown on SC medium 3 days before analysis at 30°C. For the assay, cells were transferred in 100 μl YPD media containing 1% low melting agar. 2 μl of the cell suspension was covered on a microscopy slide with a cover slip. Fluorescence was recorded with a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM, TCS SP5, Leica) with a 63x magnification objective lens (PL FL 63x/0.70). Z-Stacks of individual cells were taken and a maximum projection (ImageJ) was generated. The amount of mitochondrial morphotypes was determined by counting. Mitochondrial mass was calculated by measuring the area of GFP signal in the maximum projection in relation to the area of the particular cell (ImageJ). For calculation of morphotype and mitochondrial mass, individual cells were inspected (BY4742 n = 52; Δdnm1 n = 54; Δmgm1 n = 65; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 64).
Determination of replicative lifespan
Exponentially growing cells (BY4742 n = 39; Δdnm1 n = 39; Δmgm1 n = 34; Δdnm1Δmgm1 n = 23) were placed on a Petri dish using a micromanipulator (MSM Manual, Singer instruments, Roadwater, UK). Cells were allowed to bud once and the mother was subsequently discarded. Thereafter, the buds produced by the remaining virgin mother cells were removed and every division was recorded. Lifespan was analyzed with the statistic program IBM SPSS 19 for significance by the Log Rank (Mantel-Cox), Breslow (Generalized Wilcoxon) and the Tarone-Ware test.
Stress test
Cells were grown to logarithmic phase and serial diluted as indicated on YPD media. For acetic acid stress, the cells were treated 200 min with 30 or 40 mM acetic acid, respectively, in YPD media before plating. Heat stress was carried out by incubating the cells after plating at 37°C for 3 h. For UV-stress, plated cells were irradiated with 80 J/m2 after plating. For paraquat stress induction, cells were plated onto YPD medium containing 0.5 or 0.75 mM paraquat, respectively. Plates were then incubated two days at 30°C. Three biological replicates were analyzed with comparable results.
Growth determination
Growth on YPD and YPG medium was tested by plating cells in the logarithmic phase in serial dilutions on solid medium. Subsequently, the cells were incubated two days at 30°C before observation. For determination of the growth rate, a YPD liquid pre-culture was grown to exponential phase. A new liquid culture was inoculated (YPD OD600 0.06–0.09; YPG OD600 0.01–0.02) and the OD600 was measured at different time points with an Ultrospec 2100 pro photometer.
Respiration measurement
For measurement of respiration, cells were incubated in YPG at 30°C. After 1 h cells were transferred into a test chamber of a high resolution respirometer (Oxygraph-2k, Oroboros) filled with oxygen saturated YPG. By stepwise addition (1 μM) of the uncoupling agent carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP) respiration was increased to its maximum. Subsequently, antimycin A was added (2 μM) to inhibit respiration at complex III. The remaining respiration after inhibition of complex III represents all cellular oxidases and was used as background. The background was subtracted from respiration before and after addition of FCCP to obtain the ″Basic″ and ″ETS″ respiration, respectively. The data were normalized to the amount of cells within the chamber, counted after the experiment with a Thoma cell counting chamber.
mtDNA loss quantification
Cells were grown on YPG medium and transferred in a YPD liquid culture at 30°C. At different time points (1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 days), samples were poured on a YPDGly agar plate. After incubation of the plate for 3 days at 30°C, the relation between small (petite) and big (able to respire) colonies was counted.
Isolation of highly purified Mitochondria
Isolation of mitochondria was performed as described in Meisinger et al. (2006)41. DTT Buffer was used with 50 mM instead of 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT) to prevent protein oxidation after isolation.
OxyBlot analysis
Protein oxidations were detected using the OxyBlot Protein Oxidation Detection Kit (Millipore). Protein separation was performed using standard protocols for SDS-Page in a 10% polyacrylamide gel, followed by transfer of the proteins onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Immobilon-FL, Millipore). Blocking and incubation with antibodys was performed according to the Odyssey ‘Western Blot Analysis’ handbook (LI-COR). Primary α-DNPH rabbit antibody was used according to the OxyBlot Protein Oxidation Detection Kit manual. As a secondary antibody, infrared dye IRDye 800 CW (LI-COR) conjugated with a goat anti rabbit antibody was used (antibody dilution: 1:15,000). For detection and quantification, the Odyssey infrared Imaging System (LI-COR) was used according to the manufacturer's guide. For OxyBlot analysis, three biological replicates were analyzed.
Alkaline-phosphatase-based (ALP) Assay for mitophagy and autophagy
For analysis of mitophagy or autophagy rates, yeast strains deleted for endogenous PHO8 were transformed with mtALP- or cytALP-expression plasmids, respectively. Cells were cultivated in respiratory glycerol-containing medium (SG medium) and kept in the exponential growth phase for at least four generations. Mitophagy and autophagy were induced by addition of 1 μM rapamycin and cells were harvested after 24 hours of growth. Untreated control cells were analyzed in parallel. Cell lysis and ALP enzyme activity assay were carried out as described previously31. Cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blotting.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of western blot, oxygen consumption, mitochondrial mass, protein oxidation, mitophagy and autophagy the two-tailed Students t-test was used. In order to take different characteristics of curve progressions of lifespans into account, the results were analyzed by SPSS 19 (IBM) with three independent statistical tests (Log Rank (Mantel-Cox), Breslow (Generalized Wilcoxon) and the Tarone-Ware). According all results, a p-value < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
References
Okamoto, K. & Shaw, J. M. Mitochondrial morphology and dynamics in yeast and multicellular eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 39, 503–536 (2005).
Westermann, B. Mitochondrial dynamics in model organisms: what yeasts, worms and flies have taught us about fusion and fission of mitochondria. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 542–549 (2010).
Hermann, G. J. et al. Mitochondrial fusion in yeast requires the transmembrane GTPase Fzo1p. J. Cell Biol. 143, 359–373 (1998).
Jones, B. A. & Fangman, W. L. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in yeast requires a protein containing a region related to the GTP-binding domain of dynamin. Genes Dev. 6, 380–389 (1992).
Sesaki, H. & Jensen, R. E. UGO1 encodes an outer membrane protein required for mitochondrial fusion. J. Cell Biol. 152, 1123–1134 (2001).
Rojo, M., Legros, F., Chateau, D. & Lombes, A. Membrane topology and mitochondrial targeting of mitofusins, ubiquitous mammalian homologs of the transmembrane GTPase Fzo. J. Cell Sci. 115, 1663–1674 (2002).
Anton, F. et al. Ugo1 and Mdm30 act sequentially during Fzo1-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane fusion. J. Cell Sci. 124, 1126–1135 (2011).
Sesaki, H. & Jensen, R. E. Ugo1p links the Fzo1p and Mgm1p GTPases for mitochondrial fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 28298–28303 (2004).
Herlan, M., Vogel, F., Bornhovd, C., Neupert, W. & Reichert, A. S. Processing of Mgm1 by the rhomboid-type protease Pcp1 is required for maintenance of mitochondrial morphology and of mitochondrial DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 27781–27788 (2003).
Hoppins, S., Lackner, L. & Nunnari, J. The machines that divide and fuse mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 751–780 (2007).
Abutbul-Ionita, I., Rujiviphat, J., Nir, I., McQuibban, G. A. & Danino, D. Membrane tethering and nucleotide-dependent conformational changes drive mitochondrial genome maintenance (Mgm1) protein-mediated membrane fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 36634–36638 (2012).
Sesaki, H., Southard, S. M., Yaffe, M. P. & Jensen, R. E. Mgm1p, a dynamin-related GTPase, is essential for fusion of the mitochondrial outer membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 2342–2356 (2003).
Shepard, K. A. & Yaffe, M. P. The yeast dynamin-like protein, Mgm1p, functions on the mitochondrial outer membrane to mediate mitochondrial inheritance. J. Cell Biol. 144, 711–720 (1999).
Wong, E. D. et al. The dynamin-related GTPase, Mgm1p, is an intermembrane space protein required for maintenance of fusion competent mitochondria. J. Cell Biol. 151, 341–352 (2000).
Dohm, J. A., Lee, S. J., Hardwick, J. M., Hill, R. B. & Gittis, A. G. Cytosolic domain of the human mitochondrial fission protein fis1 adopts a TPR fold. Proteins 54, 153–156 (2004).
Otsuga, D. et al. The dynamin-related GTPase, Dnm1p, controls mitochondrial morphology in yeast. J. Cell Biol. 143, 333–349 (1998).
Mozdy, A. D., McCaffery, J. M. & Shaw, J. M. Dnm1p GTPase-mediated mitochondrial fission is a multi-step process requiring the novel integral membrane component Fis1p. J. Cell Biol. 151, 367–380 (2000).
Fekkes, P., Shepard, K. A. & Yaffe, M. P. Gag3p, an outer membrane protein required for fission of mitochondrial tubules. J. Cell Biol. 151, 333–340 (2000).
Tieu, Q., Okreglak, V., Naylor, K. & Nunnari, J. The WD repeat protein, Mdv1p, functions as a molecular adaptor by interacting with Dnm1p and Fis1p during mitochondrial fission. J. Cell Biol. 158, 445–452 (2002).
Knorre, D. A., Popadin, K. Y., Sokolov, S. S. & Severin, F. F. Roles of mitochondrial dynamics under stressful and normal conditions in yeast cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 139491 (2013).
Westermann, B. Mitochondrial membrane fusion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1641, 195–202 (2003).
Ono, T., Isobe, K., Nakada, K. & Hayashi, J. I. Human cells are protected from mitochondrial dysfunction by complementation of DNA products in fused mitochondria. Nat. Genet. 28, 272–275 (2001).
Chen, H. & Chan, D. C. Mitochondrial dynamics--fusion, fission, movement and mitophagy--in neurodegenerative diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, R169–R176 (2009).
Archer, S. L. Mitochondrial dynamics--mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 2236–2251 (2013).
Braun, R. J. & Westermann, B. Mitochondrial dynamics in yeast cell death and aging. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 39, 1520–1526 (2011).
Scheckhuber, C. Q. et al. Reducing mitochondrial fission results in increased life span and fitness of two fungal ageing models. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9, 99–105 (2007).
Scheckhuber, C. Q., Wanger, R. A., Mignat, C. A. & Osiewacz, H. D. Unopposed mitochondrial fission leads to severe lifespan shortening. Cell Cycle 10, 3105–3110 (2011).
Deutsch, J. et al. Mitochondrial genetics. VI. The petite mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: interrelations between the loss of the p+ factor and the loss of the drug resistance mitochondrial genetic markers. Genetics 76, 195–219 (1974).
Osiewacz, H. D. & Bernhardt, D. Mitochondrial quality control: impact on aging and life span - a mini-review. Gerontology 59, 413–420 (2013).
Fischer, F., Hamann, A. & Osiewacz, H. D. Mitochondrial quality control: An integrated network of pathways. Trends Biochem. Sci. 37, 284–292 (2012).
Mendl, N. et al. Mitophagy in yeast is independent of mitochondrial fission and requires the stress response gene WHI2. J. Cell Sci. 124, 1339–1350 (2011).
Lewis, M. R. & Lewis, W. H. Mitochondria in tissue culture. Science 39, 330–333 (1914).
Zuchner, S. et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 2A. Nat. Genet. 36, 449–451 (2004).
Olichon, A. et al. Mitochondrial dynamics and disease, OPA1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1763, 500–509 (2006).
Waterham, H. R. et al. A lethal defect of mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 1736–1741 (2007).
Figge, M. T., Reichert, A. S., Meyer-Hermann, M. & Osiewacz, H. D. Deceleration of fusion-fission cycles improves mitochondrial quality control during aging. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8, e1002576 (2012).
Detmer, S. A. & Chan, D. C. Functions and dysfunctions of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 870–879 (2007).
Figge, M. T., Osiewacz, H. D. & Reichert, A. S. Quality control of mitochondria during aging: Is there a good and a bad side of mitochondrial dynamics? Bioessays 35, 314–322 (2013).
Harju, S., Fedosyuk, H. & Peterson, K. R. Rapid isolation of yeast genomic DNA: Bust n' Grab. BMC. Biotechnol. 4, 8 (2004).
Westermann, B. & Neupert, W. Mitochondria-targeted green fluorescent proteins: convenient tools for the study of organelle biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 16, 1421–1427 (2000).
Meisinger, C., Pfanner, N. & Truscott, K. N. Isolation of yeast mitochondria. Methods Mol. Biol. 313, 33–39 (2006).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) through the GerontoMitoSys project (FKZ0315584) to HDO and ASR and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft project RE-1575/1-2 (MM and ASR). We thank Dr. Peter Kötter (Goethe University, Molecular Genetics and Cellular Microbiology, Max-von-Laue-Straße 9, 60438 Frankfurt, Germany) for selection of the Δdnm1Δmgm1 strain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.B. and M.M. performed the experiments and analyzed data. H.D.O. and D.B. wrote the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript. H.D.O. and A.R. initiated and supervised the work of this study.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
Supplement
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder in order to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Bernhardt, D., Müller, M., Reichert, A. et al. Simultaneous impairment of mitochondrial fission and fusion reduces mitophagy and shortens replicative lifespan. Sci Rep 5, 7885 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07885
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07885
This article is cited by
-
The potency of mitochondria enlargement for mitochondria-mediated terpenoid production in yeast
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2024)
-
Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease: mechanisms and potential targets
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Increased peroxisome proliferation is associated with early yeast replicative ageing
Current Genetics (2022)
-
Mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the tip of the iceberg
Heart Failure Reviews (2021)
-
Cell organelles and yeast longevity: an intertwined regulation
Current Genetics (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.