Abstract
Perception of olfactory stimuli is mediated by distinct populations of olfactory sensory neurons, each with a characteristic set of morphological as well as functional parameters. Beyond two large populations of ciliated and microvillous neurons, a third population, crypt neurons, has been identified in teleost and cartilaginous fishes. We report here a novel, fourth olfactory sensory neuron population in zebrafish, which we named kappe neurons for their characteristic shape. Kappe neurons are identified by their Go-like immunoreactivity and show a distinct spatial distribution within the olfactory epithelium, similar to, but significantly different from that of crypt neurons. Furthermore, kappe neurons project to a single identified target glomerulus within the olfactory bulb, mdg5 of the mediodorsal cluster, whereas crypt neurons are known to project exclusively to the mdg2 glomerulus. Kappe neurons are negative for established markers of ciliated, microvillous and crypt neurons, but appear to have microvilli. Kappe neurons constitute the fourth type of olfactory sensory neurons reported in teleost fishes and their existence suggests that encoding of olfactory stimuli may require a higher complexity than hitherto assumed already in the peripheral olfactory system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Two main types of olfactory sensory neurons are employed by the vertebrate olfactory system for detection of odors, ciliated neurons that express olfactory receptors of the OR and TAAR gene families and microvillous neurons that express V1R and V2R genes1,2,3. Both types are present in tetrapods as well as teleost fish4. Additionally, fish employ a third type of olfactory sensory neuron, the crypt neurons, named for their conspicuous shape and possessing cilia and microvilli within the same cell4. The three cell types are intermingled within a single sensory surface in fishes, but can be distinguished by their characteristic shape and spatial position: a slender dendrite and a basal soma for ciliated neurons, a plump cell body and an intermediate soma position for microvillous neurons and a large globose soma with an apical position for crypt neurons5,6. Moreover, all three types have been defined by the presence of characteristic molecular markers, OMP for ciliated neurons7, TRPC2 for microvillous neurons7 and TrkA- as well as S100-like immunoreactivity (TrkA-ir, S100-ir) for crypt neurons8,9, see5,6 for clarification. Crypt neurons have recently been shown to express a single olfactory receptor, ORA45 and to project to a single target glomerulus in the olfactory bulb, mdg2 of the mediodorsal cluster6. On the other side, a recent report has suggested that some of the neurons innervating another glomerulus of the mediodorsal cluster, mdg5 and identified by Go-ir, show crypt neuron-like morphology10. This was an intriguing suggestion because it implied that neurons innervating a single glomerulus could be morphologically and presumably functionally heterogenous – a violation of the well-established rule of axonal convergence of same receptor-expressing neurons into a homogenous glomerulus11. The question remained unanswered, though, because neither quantitative assessment of shape and spatial position nor double labeling with a crypt neuron marker had been reported. Here we performed a thorough quantitative analysis of several morphological parameters, together with double-labeling experiments for established molecular markers of ciliated, microvillous and crypt neurons. We find that the neuronal population identified by Go-ir does not overlap with crypt, ciliated and microvillous neurons, using established molecular markers for the latter three types of olfactory sensory neurons. Furthermore, cell shape and spatial position are unique for Go-ir-positive neurons and significantly different from either crypt, ciliated or microvillous neurons. We conclude that Go-ir-positive neurons constitute a novel, fourth type of olfactory sensory neurons. This suggests a higher complexity than so far assumed already in the peripheral olfactory system.
Results
A homogenous population of olfactory sensory neurons with characteristic shape and spatial position is labeled by Go antibody
Go-ir-positive neurons have been described as a morphologically heterogenous population including cells with the globose shape typical of crypt neurons10. We suspected that at least part of this heterogeneity might be due to different sectioning angles of the labelled cells. Therefore we engaged in analysis of distributions for different cell shape and position parameters, as opposed to focusing on single cell properties. In our experience the former approach is much more powerful and allows to distinguish homogenous from heterogenous cell populations with high sensitivity and accuracy5,6,12.
We report here that Go-ir labels a sparse population of pear- or bottle-shaped cells with a characteristic cap of intense Go-ir at the apical end of the cells (Fig. 1a, b, c). We have used the ratio of horizontal to vertical diameter of these cells as measure of their shape cf.5,6. A value of 1 would correspond to a perfectly circular shape, with decreasing values pointing to increasingly elongated shapes. We find a median value of 0.66 for Go-ir-positive neurons, distinctly lower than that of crypt neurons5 and see below, but also much larger than that of ciliated neurons6 and see below. The distribution of diameter ratios is narrow (Fig. 1f), consistent with a homogenous population. Importantly, the empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) of the diameter ratio is a single sigmoid curve (Fig. 1g), indicative of a homogenous population (a mix of different populations would result in either a step or quasi-linear function, cf.6.
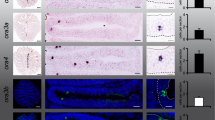
Go-like immunoreactivity reveals a distinct population of sparse, pear-shaped sensory neurons in zebrafish olfactory epithelium.
(a) Go-ir (green) is seen in a sparse population of pear-shaped cells in horizontal sections of the olfactory epithelium (short-fixed), using DAPI as counter-stain (blue); r, radial distance. Top right inset at higher magnification shows a Go-ir-positive cell (green), co-labeled with zns2 (red) and visible nucleus (DAPI, blue). Bottom left inset at higher magnification shows a Go-ir-positive cell with initial axon segment (ax) and cap (cp). (b) At higher magnification the apical position of Go-ir-positive cells (green) is clearly visible. øv, vertical cell diameter; øh, horizontal cell diameter; h, laminar height; dotted half-circle, the apical dendritic part of Go-ir-positive olfactory sensory neurons resembles a cap. (c) Nine Go-ir-positive cells show the typical range of morphologies for these neurons. (d) Whole mount of adult zebrafish olfactory bulb double-labeled with anti- Go and anti-zns2 antibodies, dorsal view. Zns2 labels all glomeruli, whereas Go-ir labels a single medial glomerulus (yellow).The olfactory nerves were cut at the entrance to the olfactory bulb before staining. (e) Horizontal vibrotome cross-section (100 μm) reveals the extremely dorsal position of the Go-immunoreactive glomerulus in each olfactory bulb. A single, thick axon bundle is seen entering the glomerulus. (f,g) One shape parameter and three spatial parameters were quantified for the Go-ir-positive cell population and shown as histogram (f) and empirical cumulative distribution function, ECDF (g). From left to right: ratio of horizontal to vertical diameter, laminar height (normalized to maximal height), radial distance (normalized to maximal radius) and number of cells per 10 μm horizontal cross section of the olfactory epithelium; x axis units and labels are valid for both (f) and (g). Scale bars correspond to 50 μm (a), 5 μm (b) and 100 μm (d, e).
Beyond a characteristic shape, Go-ir-positive neurons also have a very conspicuous position within the olfactory epithelium. It is known that such restricted spatial distributions are characteristic parameters for particular subpopulations, e.g. olfactory sensory neurons expressing a particular receptor6,13,14. Across a lamella, Go-ir-positive neurons tend to lie very apical, close to the lumen and far away from the basal lamina. We quantified this parameter as relative height (hrel = hsoma center/thickness of sensory layer; 0, basal; 1, apical). The histogram shows a rather narrow peak and the ECDF exhibits a sigmoidal shape, indicative of a homogenous population (Fig. 1f, g).
Within a lamella, the distance of Go-ir-positive cells to the median raphe, the center of the epithelium, is generally rather small, compared to the full extent of the sensory epithelium. We quantified this coordinate as relative radius (rrel = rsoma center/length of the lamella; 0, innermost; 1, outermost, cf.13. The histogram of radial distance values shows a steep and narrow peak and the corresponding ECDF exhibits a sigmoidal shape consistent with a homogenous population (Fig. 1f, g). Within the epithelium, a third axis is defined by the series of horizontal sections. Here, the majority of Go-ir-positive cells were concentrated in a few sections close to the opening of the cup-shaped epithelium and far away from the basal region containing the olfactory nerve bundles (Fig. 1f, g).
Taken together, we have quantified four different morphological and spatial parameters for Go-ir-positive cells. All four distributions are consistent with the presence of a single, homogenous cell population. Go-ir-positive cells are also labeled by zns2-immunostaining, a general marker for sensory neurons and in high magnification initial axon segments are visible, suggesting that Go-ir-positive cells are indeed neurons (Fig. 1a).
Furthermore, whole mount immunohistochemistry of the olfactory bulb using Go antibody results in the labeling of a single, bilateral symmetric glomerulus (Fig. 1 d, e), confirming that these cells are sensory neurons that convey information to the brain. Comparison with zns2-immunostaining, which labels the entire glomerular pattern, allows to identify the Go-ir-positive glomerulus as mdg5, consistent with a previous report10. Between 200 to 500 Go-ir-positive neurons are present in a single olfactory epithelium, which is well within the range expected to innervate a single glomerulus, cf.11.
Go-ir-positive neurons are different from crypt neurons
The apical laminar position of Go-ir-positive neurons is roughly similar to that of crypt neurons6, even though their shape is generally somewhat more slender than that of crypt neurons cf.5,6. However, cells with morphology similar to that of crypt neurons have been reported in the Go-ir-positive cell population10. Therefore we have used the Go antibody in parallel with an established crypt neuron marker, S100-ir, to examine a potential overlap between these two markers. We report here that Go-ir and S100-ir label mutually exclusive cell populations (Fig. 2a–c, f). Also, as shown above, Go-ir-positive neuron terminals in the olfactory bulb innervate a different glomerulus, mdg5, compared to mdg2, the crypt neuron glomerulus6.
Go-ir-positive neuron population is different from crypt neurons.
(a) Double labeling with anti-Go antibody (green) and anti-S100 antibody (red, marker for crypt neurons) in cryostat sections of short-fixed olfactory epithelium reveals two mutually exclusive sensory neuron populations. Insets, single neurons at higher magnifications. Note the differences in morphology of these two cell populations; arrow in top right insert, the cap-like structure typical for Go-ir-positive neurons. (b–c) Higher magnifications show the typical shapes of Go-ir-positive neurons (pear-shaped) and crypt neurons (globose), indicated by filled arrow heads and open arrow heads, respectively. (d–e, g–h) One shape parameter and three spatial parameters (see Fig. 1b for graphical explanation) were quantified for the TrkA-ir-positive cell population and the corresponding empirical cumulative distribution function, ECDF, was compared with that of Go-ir-positive neurons; ***, distributions of TrkA-ir and Go-ir cells are significantly different (p < 10−6), as assessed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of the unbinned distributions. (d), ratio of horizontal to vertical diameter [diameter ratio (øh/øv)], (e), laminar height normalized to maximal height is shown. (f), Absence of co-label for Go-ir and TrkA-ir cell populations. (g) Relative radial distance of labeled cells is shown. (h) Number of cells per 10 μm horizontal cross section of the olfactory epithelium was analysed for Go-ir and TrkA-ir-positive neurons. (i) Maximal vertical distance (Δ max) of distributions as indicated; ø ratio, diameter ratio; height, normalized laminar height; radius, normalized radial distance; z axis, section number (ordinal). Vertical distance can range between 0 (identical curves) and 1 (no overlap of x value range). Scale bars correspond to 100 μm (a) and 10 μm (b, c).
Furthermore, we have examined the shape and spatial distribution of Go-ir-positive and crypt neurons identified by a second marker, TrkA-ir, in alternating sections to obtain a stringent comparison of the properties of both cell populations. We find subtle, but highly significant (p < 10−6) differences in relative height and relative radius between the two populations (Fig. 2e, g). Go-ir-positive neurons are even more apically situated within the lamella than TrkA-ir-positive neurons (maximal difference between the distributions 25%) and they are found closer to the median raphe than crypt neurons (maximal difference between the distributions 22%). Within the entire olfactory epithelium, Go-ir-positive neurons are found in more apical sections closer to the opening of the cup-shaped olfactory organ, compared to TrkA-ir-positive neurons (Fig. 2h). Finally the comparison of cell shapes shows the largest difference between both populations (54%), with Go-ir-positive neurons significantly (p < 10−6) less globose than crypt neurons (Fig. 2d).
Taken together, Go-ir-positive neurons differ significantly in all morphological parameters analysed from crypt neurons. Next, we examined, whether Go-ir-positive neurons might belong to either microvillous or ciliated neuron populations.
Go-ir-positive neurons are different from ciliated and microvillous neurons
Ciliated neurons in teleosts specifically express the olfactory marker protein (OMP) and a transgenic line is available, in which the OMP promoter faithfully drives expression of a red fluorescent protein (RFP), Tg(OMP:lynRFP)7. We performed Go immunostaining with transgenic epithelia and report here that almost all Go-ir-positive neurons (98%) are negative for RFP (Fig. 3a, f). This suggests that Go-ir-positive neurons do not belong to the population of ciliated neurons.
Go-ir-positive neurons do not co-localize with established markers for ciliated and microvillous neurons.
(a–d), Double labeling of Go-ir-positive cells with different markers is analysed in horizontal cryostat sections of olfactory epithelia; dashed line, basal border; dotted line, apical border of the sensory layer; scale bar, 20 μm. (a) Double fluorescent labeling of anti-Go antibody (green) with RFP (red) expressed in ciliated neurons in Tg(OMP:lyn-mRFP) shows absence of co-localization; filled grey arrowhead, Go-ir-positive cell; open arrowhead, RFP-positive cell. (b) Double fluorescent labeling of anti-Go antibody with Venus expressed in microvillous neurons in Tg(TRPC2:Venus) line shows absence of co-localization. Go-ir signal is set to green, Venus signal is set to red; filled arrowhead, Go -ir-positive cell; open arrowhead, Venus-positive cell. (c) Double fluorescent labeling of anti- Go antibody (green) with in situ hybridisation signal from TRPC2 probe5 shows absence of co-localization; filled grey arrowhead, Go-ir-positive cell; open arrowhead, TRPC2-positive cell. (d) Double fluorescent labeling of anti-Go antibody (green) with anti-calretinin antibody (red) shows absence of co-localization; filled grey arrowhead, Go-ir-positive cell; open arrowhead, calretinin-positive cell. (e) The empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) for a cell shape parameter (diameter ratio) shows distributions for TRPC2 and OMP-positive cells to be different from each other as well as from Go-ir and TrkA-ir, shown for comparison here. (f) Quantification of co-label for Go-ir and markers for microvillous, ciliated and crypt neurons (as indicated) shows 0 to 2% co-label (yellow) in Go-ir-positive neurons. Such small percentages amount to a handful of cells in an entire olfactory epithelium and are likely to accrue from the dense packing of cells, dendrites, cilia and microvilli, at the limit of light-microscopic resolution. (g) The empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) for a cell localisation parameter (laminar height) shows distributions for TRPC2 and OMP-positive cells to be different from each other as well as from Go-ir and TrkA-ir-positive cells, shown for comparison here. (h) Maximal vertical distance (Δ max) of distributions as indicated; ø ratio, diameter ratio; height, normalized laminar height. Significance of distribution differences is assessed by Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of the unbinned distributions; a, p < 10−6; b, p > 0.6.
Moreover, a comparison of cell shape and preferred laminar position within the lamella shows highly significant differences between Go-ir-positive and OMP-positive neurons. Ciliated neurons tend to have a very slender shape and rather basal cell bodies, whereas Go-ir-positive neurons are mostly pear-shaped and are found at extreme apical positions within the lamella, even more apical than crypt neurons (Fig. 3e, g, h). Only 1–2% overlap are observed between Go-ir and OMP distributions (Fig. 3h).
Next, we investigated, whether Go-ir-positive neurons might express the microvillous neuronal marker TRPC27. First, we employed a transgenic line, which largely reproduces the endogenous TRPC2 pattern, Tg(TRPC2:gap-Venus)7. We report that Go-ir-positive cells were negative for Venus fluorescence (Fig. 3b, f). Secondly, we also performed direct double labeling in wildtype zebrafish, detecting Go-ir by immunostaining and TRPC2 by in situ hybridization. Again, almost all Go-ir-positive cells (>98%) were negative for TRPC2 signals (Fig. 3c, f), suggesting that Go-ir-positive neurons are different from microvillous neurons.
Furthermore, a comparison of cell shape and preferred laminar position within the lamella shows highly significant differences between Go-ir-positive and TRPC2-positive neurons (p < 10−6). Microvillous neurons are somewhat slender in shape and their cell bodies are preferentially located more basal than crypt neuron somata, whereas Go-ir-positive neurons are mostly pear-shaped and are found at extreme apical positions within the lamella, more apical than crypt neurons (Fig. 3c, e, g, h).
Finally we have examined a potential overlap of Go-ir-positive neurons with the calretinin-positive population of olfactory sensory neurons. Calretinin appears to label subpopulations of ciliated and microvillous neurons10,15,16. Again we observe no co-localisation for Go-ir and calretinin (<1%, Fig. 3d, f), confirming the results for ciliated and microvillous neuron markers (OMP and TRPC2, respectively). We note that both cell shape and laminar height distribution of calretinin-positive neurons are identical to the respective distributions of OMP-positive neurons, which itself show nearly no overlap with those of TRPC2-positive neurons (Fig. 3e, g, h). These results are consistent with calretinin-positive neurons being ciliated neurons, cf.10. In summary, Go-ir-positive neurons exhibit a conspicuous distinct shape and preferred laminar position, significantly different from the morphology and location observed for the three known populations of olfactory sensory neurons. Moreover, molecular markers for ciliated, microvillous and crypt neurons are absent in Go-ir-positive neurons. We conclude that Go-ir-positive neurons do not belong to the three known populations, but constitute a fourth type of olfactory sensory neuron. Due to their conspicuous 'cap' (German: Kappe) we suggest to name this novel population kappe neurons.
Kappe neurons are tubulin-negative and actin-positive
We performed immunostaining with anti-tubulin and anti-actin antibodies together with Go antibody to further characterize kappe neurons. We report that tubulin staining mostly does not overlap with Go-ir (Fig. 4a, c). Rare cases of overlap may be due to technical reasons, since tubulin-positive cilia of ciliated neurons are densely packed in the apical layer, cf. (Fig. 4a). Since tubulin is an essential component of cilia17 we conclude that kappe neurons do not possess cilia. Microvilli, on the other hand, require actin as essential component18. We observe nearly complete co-labeling of Go-ir and actin (Fig. 4c), with the actin antibody consistently labeling a small apical spot within the cap of kappe neurons (Fig. 4b). Although immuno-EM studies will be required to draw a firm conclusion, these results suggest that kappe neurons may possess microvilli.
Kappe neurons are tubulin-negative and actin-positive.
Double labeling of Go-ir-positive cells with anti-tubulin or anti-actin antibody is analysed in horizontal cryostat sections of olfactory epithelia. (a) Double fluorescent labeling of Go-ir (green) and tubulin (red) shows absence of co-localization; scale bar 10 μm. The insets represent magnified images of single neurons taken at 100× magnification, 0.1 μm optical sections. (b) Double fluorescent labeling of Go-ir (green) and actin (red) shows co-localization: Go-ir positive neurons exhibit highly localized actin staining at the apical surface of their cell bodies, the expected position for microvilli. Scale bar 10 μm. The insets show single neurons, images taken at 100× magnification, 0.1 μm optical sections. (c) Quantification of co-label for Go-ir and actin or tubulin, respectively, shows over 90% co-label (yellow) for actin, but less than 10% co-label for tubulin. The small number of Go-ir/tubulin co-labeled cells is likely to result from the dense packing of cells, dendrites, cilia and microvilli, at the limit of light-microscopic resolution. (d) Schematic representation of four types of olfactory sensory neurons with their laminar position. Ciliated neurons (orange) have round somata and slender dendrites that terminate in bundles of cilia on the epithelial surface. They constitue the most basal layer of olfactory sensory neuron. Microvillous neurons (blue) have bundles of microvilli on their apical surface. Crypt neurons (red) are globular-shaped and carry both microvilli and cilia on their apical surface. They are located more apical than microvillous neurons. Go-ir-positive kappe neurons (green) are pear-shaped with an apical appendage resembling a cap (German: Kappe), have no cilia and are located even more apical than crypt neurons. Kappe neurons (green) constitute a novel olfactory sensory neuron population.
Discussion
Three different types of olfactory sensory neurons are known in the vertebrate sense of smell, ciliated, microvillous and crypt neurons4. Here we report the presence of a fourth type of olfactory sensory neurons, kappe neurons, identified by the presence of Go-ir10, which do not express the molecular markers commonly accepted as defining ciliated, microvillous and crypt neurons. We used a population-based quantitative approach to characterize kappe neurons and show them to be highly significantly different in shape and spatial location from each of the three previously known populations of olfactory sensory neurons. Kappe neurons are a rare cell population with a few hundred cells per olfactory organ, consistent with the expression of only one or very few olfactory receptor genes in this type of sensory neurons. Thus, it is conceivable that additional such populations of olfactory sensory neurons might exist, cf.19,20, but they would presumably only come into view after identification of a molecular marker specific for such a population.
It is not clear, whether Go-ir labels the same type of kappe neurons in other teleost fish species. Different patterns of Go immunoreactivity have been reported for different fish species, both for sparse neuron populations described as crypt-like neurons21,22,23 and for frequent neuron populations of undefined16 or microvillous21,24 phenotype. It is conceivable that in the absence of knowledge about kappe neurons, some may have been mistaken as crypt neurons in those earlier studies, since kappe neurons are more similar to crypt neurons than to the other two populations, ciliated and microvillous neurons. In any case, the observed species differences preclude the use of Go-ir as a defining criterion of kappe neurons in other fish species.
Kappe neurons project to a single glomerulus in the mediodorsal cluster, mdg5 (this manuscript, see also10). With the identification of kappe neurons two of the six glomeruli in this cluster have been shown to be innervated by distinct populations of olfactory neurons, mdg5 by kappe neurons and mdg2 by crypt neurons. It will be interesting to see, whether this observation will be generalizable to the remaining four glomeruli in this cluster. Indeed, all six mediodorsal glomeruli are negative for ciliated and microvillous markers7 in the double transgenic line also used here.
The presence of Go-like immunoreactivity in kappe neurons could suggest Go as a possible signal transduction molecule for these neurons. However, the subcellular distribution of Go-ir in dendrite, cytoplasm, axon and axon terminals is unexpectedly broad. Additionally, in situ hybridization with Go shows a large and broadly distributed cell population25, inconsistent with the small and spatially restricted population of Go-ir-positive neurons. Thus, we cannot exclude that Go-ir in kappe neurons might be caused by a cross-reacting antigen, reminescent of the situation for standard molecular markers of crypt neurons, S100-ir5 and TrkA-ir6.
Kappe neurons feature a dot of intense actin signal somewhat recessed on their apical cap, suggesting the presence of microvilli in these neurons. However, in all other aspects investigated (shape, location, molecular markers), kappe neurons are highly significantly different from microvillous neurons and in particular they do not express TRPC2, the accepted molecular marker and signal transduction molecule of microvillous neurons.
The functional role of kappe neurons is not known so far, but their sheer existence shows an astonishing complexity of odor representation already in the periphery of the olfactory system.
Methods
Antibodies, tissue and animal handling
Primary antibodies used were anti-S100 antibody (rabbit IgG; 1:500; catalog no. Z0311, Dako), anti- Go (K-20) antibody (rabbit IgG; 1:50; sc-387, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-TrkA (763) antibody (rabbit IgG; 1:100; sc-118, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-zns2 (monoclonal mouse IgG1;1:50; supernatant, Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA), anti-calretinin (mouse IgG; 1:200; Swant (Bellinzona, Switzerland), anti-tubulin (mouse monoclonal antibody IgG, 1:300; G712, Promega) and beta-actin (mouse monoclonal antibody; A5441; 1:300; Sigma). Secondary antibodies used were donkey anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 (A21206, Invitrogen), goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (A11012, Invitrogen) and goat anti-mouse conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (A11005, Invitrogen).
Adult wild type zebrafish (Ab/Tü strain, 8–12 months old) were maintained at 28°C on 14/10-hour light/dark cycle. Adult fish were sacrificed by decapitation during anesthesia with MS-222 (ethyl 3-aminobenzoate, Sigma). Those experiments were approved by the governmental animal care and use office (Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz Nordrhein- Westfalen, Recklinghausen, Germany, Protocol No. 8.87-51.05.20.10.217) and were in accordance with the German Animal Welfare Act as well as with the General Administrative Directive for the Execution of the Protection of Animals Act. Tissues were embedded in 5% low melting agarose and sectioned by vibratome (Pelco 101) or embedded in TissueTek O.C.T. compound (Sakura) and cut by cryostat (Leica CM1900) at −20°C. Fluorescence was analysed using a wide field fluorescence microscope (Keyence BZ-9000) for sections and whole mounts. Transgenic zebrafish lines for ciliated neurons, Tg(OMP:lyn-mRFP-S) and microvillous neurons, Tg(TRPC2:gap-Venus), were used in this study.
Whole mount olfactory bulb immunohistochemistry
The dorsal cranium was removed, exposed brains were fixed by immersion in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA, pH 7.4) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.5) overnight at 4°C and olfactory bulbs were dissected out, keeping their connection to the telencephalon intact. Staining was performed according to6. After blocking, samples were incubated with primary antibodies anti-Go and anti-zns2 either single or in mixture at 4°C for 20 to 25 days on a vertical rotator (5 sec/round), followed by several washes over a period of 3 hours at room temperature. Subsequently, the olfactory bulbs were incubated with secondary antibodies for 7 days at 4°C, followed by several washes at room temperature. Tissue was cleared as described6. Both primary and secondary antibodies were used at a final dilution of 1:100 in blocking reagent. For detailed examination 100 μm vibratome sections were analysed.
Immunohistochemistry on cryosections
Heads were either pre-incubated before dissection in cold freshly prepared 4% PFA in PBS for 5 min (pre-fixed tissue) or dissected directly (fresh-frozen tissue). We found that a short fixation step of 5 min does not impair the specificity of the S100 antibody for crypt neurons, in contrast to long fixation times, cf.5. Horizontal cryosections (8 μm) of the olfactory epithelia were thaw-mounted onto Superfrost Plus slide glasses (Thermo), incubated in acetone at −20°C for 15 min, washed several times in PBST and blocked in 5% normal goat serum in PBST (blocking solution) for 1 hour at room temperature.
In order to overcome the limitations arising from same species antibodies in double labeling, the Fc portion of the anti-S100 antibody was covalently conjugated with fluorescein (Thermo Scientific, 53029) as described26. For double labeling, the slides were overnight incubated at 4°C with anti-Go antibody (1:50 dilution in blocking solution), washed 3 times in PBST to remove unbound anti-Go antibody and incubated for 2 hours at room temperature with the first of the two secondary antibodies (anti-rabbit alexa fluor 488). Slides were further washed 3 times in PBST, incubated for 1 hour in blocking solution, followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with flu-labeled anti-S100 (second primary antibody), washed 3 times for 10 min each and incubated for 2 hours at room temperature with alkaline phosphatase (AP) conjugated anti-fluorescein (the second of the two secondary antibodies). S100-labeled cells were visualized by enzymatic reaction of AP with HNPP Fluorescent Detection Set (Roche). The slides were washed in PBS and mounted with VectaShield containing DAPI (Vector).
Immunohistochemistry combined with in situ hybridization
TRPC2 cRNA riboprobe was prepared as described5. Pretreatment of sections, probe hybridization and stringent washing were performed as described previously13, except that Proteinase K treatment was omitted. For high stringency conditions the final washes were performed at 65°C in 0.2× SSC. Afterward, sections were blocked in 1% blocking reagent (Roche) in PBS for 1 h. The slides were then incubated with sheep anti-DIG Fab fragments conjugated with alkaline phosphatase (AP, Roche; 1:200) together with rabbit anti-Go antibody (1:50) in the blocking solution at 4°C overnight. After washing three times in PBS, sections were treated with the secondary antibody (1:200) in PBS for 2 h at room temperature. Hybridized probes were visualized by enzymatic reaction of AP with HNPP Fluorescent Detection Set (Roche). After evaluating the success of the staining, slides were washed in PBS, mounted with VectaShield with DAPI (Vector) and observed and photographed with a fluorescent microscope (BZ-9000, Keyence).
Quantification and statistical evaluation
Spatial coordinates were measured in arbitrary units and normalized. Horizontal cell diameter was determined as maximal cell width, i.e. parallel to the basal lamina and vertical diameter was determined as maximal cell length perpendicular to the basal lamina (soma and dendrite, if any), see Fig. 1b. For laminar height in the olfactory epithelium the distance between center of the cell soma and basal border of the epithelial layer (see Fig. 1b) was normalized to the distance between basal and apical border of the epithelial layer at the position of the cell to be measured. Thus the range of values is between 0 (most basal) and 1 (most apical). Radial distance was measured from the apex of the lamellar 'curve', i.e. closest to the median raphe, to the cell soma center (see Fig. 1b) and normalized to the distance between the central position and the border of the epithelial section. Finally, the cardinal number of sections served as z axis coordinate. One hundred to several hundred cells were measured for each marker and spatial coordinate.
Distributions are depicted as histograms or as the corresponding empirical cumulative distribution function (ECDF) of the unbinned distributions27,28.
To estimate whether two spatial or shape distributions were significantly different, we performed Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests on the unbinned distributions as described29. This test is particularly suitable for continuous distributions and makes no assumptions about the nature of the distributions investigated, which is essential because the skewness of the observed distributions shows that these are not Gaussian. Due to the sensitive nature of the test on large distributions (n > 100), we selected P < 0.01 as cutoff criterion for significant difference. Results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test were confirmed by permutation analysis30 without exception.
References
Mombaerts, P. et al. Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87, 675–86 (1996).
Johnson, M. A. et al. Neurons expressing trace amine-associated receptors project to discrete glomeruli and constitute an olfactory subsystem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109, 13410–5 (2012).
Wagner, S., Gresser, A. L., Torello, A. T. & Dulac, C. A multireceptor genetic approach uncovers an ordered integration of vno sensory inputs in the accessory olfactory bulb. Neuron 50, 697–709 (2006).
Hansen, A. & Zeiske, E. The peripheral olfactory organ of the zebrafish, danio rerio: An ultrastructural study. Chem Senses 23, 39–48 (1998).
Oka, Y., Saraiva, L. R. & Korsching, S. I. Crypt neurons express a single v1r-related ora gene. Chem Senses 37, 219–27 (2012).
Ahuja, G. et al. Zebrafish crypt neurons project to a single, identified mediodorsal glomerulus. Sci Rep 3, 2063 (2013).
Sato, Y., Miyasaka, N. & Yoshihara, Y. Mutually exclusive glomerular innervation by two distinct types of olfactory sensory neurons revealed in transgenic zebrafish. J Neurosci 25, 4889–97 (2005).
Germana, A. et al. S100 protein-like immunoreactivity in the crypt olfactory neurons of the adult zebrafish. Neurosci Lett 371, 196–8 (2004).
Catania, S. et al. The crypt neurons in the olfactory epithelium of the adult zebrafish express trka-like immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett 350, 5–8 (2003).
Braubach, O. R., Fine, A. & Croll, R. P. Distribution and functional organization of glomeruli in the olfactory bulbs of zebrafish (danio rerio). J Comp Neurol 520, 2317–39, Spc1 (2012).
Mombaerts, P. Axonal wiring in the mouse olfactory system. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22, 713–37 (2006).
Syed, A. S., Sansone, A., Nadler, W., Manzini, I. & Korsching, S. I. Ancestral amphibian v2rs are expressed in the main olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110, 7714–9 (2013).
Weth, F., Nadler, W. & Korsching, S. Nested expression domains for odorant receptors in zebrafish olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93, 13321–6 (1996).
Conzelmann, S. et al. A novel brain receptor is expressed in a distinct population of olfactory sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci 12, 3926–34 (2000).
DeMaria, S. et al. Role of a ubiquitously expressed receptor in the vertebrate olfactory system. J Neurosci 33, 15235–47 (2013).
Gayoso, J. A., Castro, A., Anadon, R. & Manso, M. J. Differential bulbar and extrabulbar projections of diverse olfactory receptor neuron populations in the adult zebrafish (danio rerio). J Comp Neurol 519, 247–76 (2011).
Arikawa, K. & Williams, D. S. Acetylated alpha-tubulin in the connecting cilium of developing rat photoreceptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34, 2145–9 (1993).
Arikawa, K., Hicks, J. L. & Williams, D. S. Identification of actin filaments in the rhabdomeral microvilli of drosophila photoreceptors. J Cell Biol 110, 1993–8 (1990).
Brechbuhl, J., Klaey, M. & Broillet, M. C. Grueneberg ganglion cells mediate alarm pheromone detection in mice. Science 321, 1092–5 (2008).
Elsaesser, R. & Paysan, J. The sense of smell, its signalling pathways and the dichotomy of cilia and microvilli in olfactory sensory cells. BMC Neurosci 8 Suppl 3, S1 (2007).
Hansen, A. & Zielinski, B. S. Diversity in the olfactory epithelium of bony fishes: Development, lamellar arrangement, sensory neuron cell types and transduction components. J Neurocytol 34, 183–208 (2005).
Hansen, A. et al. Correlation between olfactory receptor cell type and function in the channel catfish. J Neurosci 23, 9328–39 (2003).
Hansen, A., Anderson, K. T. & Finger, T. E. Differential distribution of olfactory receptor neurons in goldfish: Structural and molecular correlates. J Comp Neurol 477, 347–59 (2004).
Ferrando, S. et al. Immunolocalization of g protein alpha subunits in the olfactory system of polypterus senegalus (cladistia, actinopterygii). Neurosci Lett 499, 127–31 (2011).
Oka, Y. & Korsching, S. I. Shared and unique g alpha proteins in the zebrafish versus mammalian senses of taste and smell. Chem Senses 36, 357–65 (2011).
Korsching, S. & Thoenen, H. Two-site enzyme immunoassay for nerve growth factor. Methods Enzymol 147, 167–85 (1987).
Wilk, M. B. & Gnanadesikan, R. Probability plotting methods for the analysis of data. Biometrika 55, 1–17 (1968).
Feller, W. An introduction to probability theory and its applications. (Vol. II., New York: Wiley, 1966).
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T. & Flannery, B. P. Numerical recipes in c: The art of scientific computing. (Cambridge university press, cambridge. Vol. Second, 1992).
Manly, B. F. J. Randomization, bootstrap and monte carlo methods in biology, (London: Chapman and Hall/CRC, London, 1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank Walter Nadler for implementing the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and the permutation analysis, Priyanka Maiti for technical help and Mehmet Saltürk for taking good care of the zebrafish. We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the German Science foundation (grant KO 1046/7-1 to S.I.K.) and the International Graduate School IGSDHD (G.A., V.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experiments were designed by S.I.K. and G.A. and performed by G.A., V.S., D.K. and Y.O. Illustrations were drafted by V.Z., G.A. and S.I.K. Data analysis was done by S.I.K., S.B. and G.A. S.I.K. wrote the paper.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Ahuja, G., Nia, S., Zapilko, V. et al. Kappe neurons, a novel population of olfactory sensory neurons. Sci Rep 4, 4037 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04037
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04037
This article is cited by
-
Calcium imaging of adult olfactory epithelium reveals amines as important odor class in fish
Cell and Tissue Research (2024)
-
Spatial organization of olfactory receptor gene choice in the complete V1R-related ORA family of zebrafish
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A comprehensive structural, lectin and immunohistochemical characterization of the zebrafish olfactory system
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Neural pathways of olfactory kin imprinting and kin recognition in zebrafish
Cell and Tissue Research (2021)
-
Diving into the streams and waves of constitutive and regenerative olfactory neurogenesis: insights from zebrafish
Cell and Tissue Research (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.