Abstract
Study design:
Psychometrics study.
Objectives:
To assess the reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) and Modified Tardieu Scale (MTS) in patients with spinal cord injuries (SCIs).
Setting:
Inpatient rehabilitation clinics at two state hospitals.
Methods:
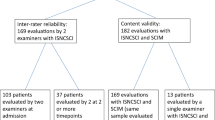
The study included 65 participants aged between 18 and 88 years with SCI with spasticity. All participants were at least 6 months after injury and had an American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale grade of A–D. The MAS and MTS scores were collected from the right hip adductor and hip extensor muscles, right knee extensor and knee flexor muscles and right plantar flexor muscles. Each participant was assessed twice by two experienced physiatrists 1 week apart. The raters were blinded to each other’s scores.
Results:
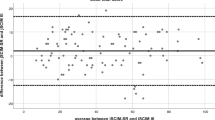
Inter-rater and test–retest agreement for the MAS scores (κ=0.531–0.774) was moderate to substantial. Inter-rater and test–retest agreement for the MTS X scores (κ=0.692–0.917) was substantial to almost perfect. Inter-rater reliability and test–retest reliability of the MTS R2−R1 was excellent (intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) 0.874–0.973, confidence interval (CI): 0.79–0.98) for all muscles tested. Inter-rater reliability of the MTS R2 for the hip adductor and knee extensor muscles was poor (ICC 0.248, CI: −0.00 to 0.47 and ICC 0.094, CI: −0.16 to 0.34, respectively). The test–retest reliability of the MTS R2 was also poor for the knee extensor muscles (ICC 0.318, CI: −0.06 to 0.53).
Conclusion:
MAS has adequate reliability for determining lower-extremity spasticity in patients with SCI. The demonstration of excellent inter-rater reliability and test–retest reliability of the MTS R2−R1 suggests its utility as a complementary tool for informing treatment decisions in patients with SCI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lance JW. Symposium synopsis. In: Feldman RG, Young PR, Koella WP (eds). Spasticity: Disordered Motor Control. Yearbook Medical Publishers: Chicago, IL, USA, 1980, pp 485–494.
Fleuren JF, Voerman GE, Snoek GJ, Nene AV, Rietman JS, Hermens HJ . Perception of lower limb spasticity in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2009; 47: 396–400.
Pandyan AD, Gregoric M, Barnes MP, Wood D, Van Wijck F, Burridge J et al. Spasticity: clinical perceptions, neurological realities and meaningful measurement. Review. Disabil Rehabil 2005; 27: 2–6.
Burns AS, Lanig I, Grabljevec K, New PW, Bensmail D, Ertzgaard P et al. Optimizing the management of disabling spasticity following spinal cord damage-The Ability Network-an international initiative. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2016; 97: 2222–2228.
Maynard FM, Karunas RS, Waring WP . Epidemiology of spasticity following traumatic spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990; 71: 566–569.
Sköld C, Levi R, Seiger A . Spasticity after traumatic spinal cord injury: nature, severity, and location. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1999; 80: 1548–1557.
Hitzig SL, Tonack M, Campbell KA, McGillivray CF, Boschen KA, Richards K et al. Secondary health complications in an aging Canadian spinal cord injury sample. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2008; 87: 545–555.
Walter JS, Sacks J, Othman R, Rankin AZ, Nemchausky B, Chintam R et al. A database of self-reported secondary medical problems among VA spinal cord injury patients: its role in clinical care and management. J Rehabil Res Dev 2002; 39: 53–61.
Haas BM, Bergström E, Jamous A, Bennie A . The inter rater reliability of the original and of the modified Ashworth scale for the assessment of spasticity in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1996; 34: 560–564.
Smith AW, Jamshidi M, Lo SK . Clinical measurement of muscle tone using a velocity-corrected modified Ashworth scale. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2002; 81: 202–206.
Tederko P, Krasuski M, Czech J, Dargiel A, Garwacka-Jodzis I, Wojciechowska A . Reliability of clinical spasticity measurements in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 2007; 9: 467–483.
Craven BC, Morris AR . Modified Ashworth scale reliability for measurement of lower extremity spasticity among patients with SCI. Spinal Cord 2010; 48: 207–213.
Baunsgaard CB, Nissen UV, Christensen KB, Biering-Sørensen F . Modified Ashworth scale and spasm frequency score in spinal cord injury: reliability and correlation. Spinal Cord 2016; 54: 702–708.
Patrick E, Ada L . The Tardieu Scale differentiates contracture from spasticity whereas the Ashworth Scale is confounded by it. Clin Rehabil 2006; 20: 173–182.
Fleuren JF, Voerman GE, Erren-Wolters CV, Snoek GJ, Rietman JS, Hermens HJ et al. Stop using the Ashworth Scale for the assessment of spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2010; 81: 46–52.
Haugh AB, Pandyan AD, Johnson GR . A systematic review of the Tardieu Scale for the measurement of spasticity. Disabil Rehabil 2006; 28: 899–907.
Tardieu G, Shentoub S, Delarue R . A la recherche d'une technique de measure de la spasticité. Revue de Neurologie (Paris). [Research on a technique for measurement of spasticity]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1954; 91: 143–144.
Held JP, Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Reeducation Motrice des Affections Neurologiques. JB Bailiere et Fils: Paris, France, 1969, pp 31–42.
Boyd R, Graham H . Objective measurement of clinical findings in the use of botulinum toxin type A for the management of children with cerebral palsy. Eur J Neurol 1999; 6: S23–S35.
Alhusaini AA, Dean CM, Crosbie J, Shepherd RB, Lewis J . Evaluation of spasticity in children with cerebral palsy using Ashworth and Tardieu Scales compared with laboratory measures. J Child Neurol 2010; 25: 1242–1247.
Mehrholz J, Wagner K, Meissner D, Grundmann K, Zange C, Koch R et al. Reliability of the Modified Tardieu Scale and the Modified Ashworth Scale in adult patients with severe brain injury: a comparison study. Clin Rehabil 2005; 19: 751–759.
Waninge A, Rook RA, Dijkhuizen A, Gielen E, van der Schans CP . Feasibility, test-retest reliability, and interrater reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in persons with profound intellectual and multiple disabilities. Res Dev Disabil 2011; 32: 613–620.
Ben-Shabat E, Palit M, Fini NA, Brooks CT, Winter A, Holland AE . Intra- and interrater reliability of the Modified Tardieu Scale for the assessment of lower limb spasticity in adults with neurologic injuries. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013; 94: 2494–2501.
Hsieh JT, Wolfe DL, Miller WC, Curt A, SCIRE Research Team. Spasticity outcome measures in spinal cord injury: psychometric properties and clinical utility. Spinal Cord 2008; 46: 86–95.
Pandyan AD1, Johnson GR, Price CI, Curless RH, Barnes MP, Rodgers H . A review of the properties and limitations of the Ashworth and modified Ashworth Scales as measures of spasticity. Clin Rehabil 1999; 13: 373–383.
Bohannon RW, Smith MB . Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther 1987; 67: 206–207.
Fosang AL, Galea MP, McCoy AT, Reddihough DS, Story I . Measures of muscle and joint performance in the lower limb of children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2003; 45: 664–670.
Li F, Wu Y, Li X . Test-retest reliability and inter-rater reliability of the Modified Tardieu Scale and the Modified Ashworth Scale in hemiplegic patients with stroke. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2014; 50: 9–15.
Yam WKL, Leung MSM . Interrater reliability of Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in children with spastic cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol 2006; 21: 1031–1035.
Landis JR, Koch GG . The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977; 33: 159–174.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Statistical measures of reliability. In: Portney LG, Watkins MP (eds). Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice. Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000, pp 557–586.
Cicchetti DV . Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol Assessment 1994; 6: 284–290.
Gracies JM, Burke K, Clegg NJ, Browne R, Rushing C, Fehlings D et al. Reliability of the Tardieu Scale for assessing spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2010; 91: 421–428.
Benz EN, Hornby TG, Bode RK, Scheidt RA, Schmit BD . A physiologically based clinical measure for spastic reflexes in spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005; 86: 52–59.
Akpinar P, Atici A, Ozkan FU, Aktas I, Kulcu DG, Kurt KN Reliability of the spinal cord assessment tool for spastic reflexes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil (e-pub ahead of print 12 October 2016; doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2016.09.119).
Priebe M . Assessment of spinal cord injury spasticity in clinical trials. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 2006; 11: 69–77.
Acknowledgements
We thank the participants of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akpinar, P., Atici, A., Ozkan, F. et al. Reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in patients with spinal cord injuries. Spinal Cord 55, 944–949 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2017.48
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2017.48
This article is cited by
-
A portable system to measure knee extensor spasticity after spinal cord injury
Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation (2024)
-
A pilot, randomized, placebo-controlled study of mindfulness meditation in treating insomnia in multiple sclerosis
BMC Neurology (2023)
-
Risk factors for hospital acquired pressure injury in patients with spinal cord injury during first rehabilitation: prospective cohort study
Spinal Cord (2022)
-
Spasticity distribution and severity in individuals with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis
Journal of NeuroVirology (2021)
-
The beneficial aspects of spasticity in relation to ambulatory ability in mice with spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2020)