Abstract
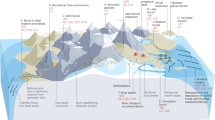
The large-scale use of organophosphate esters (OPEs) as flame retardants and plasticizers has led to their prevalence in the environment, with still unknown broader impacts. This Review describes the transport and occurrence of OPEs in marine systems and summarizes emerging evidence of their biogeochemical and ecosystem impacts. Long-range environmental transport via the atmosphere and ocean currents distributes OPEs from industrialized regions to the open ocean. OPEs are most prevalent in coastal regions, but notable concentrations are also found in the Arctic and regions far from shore. Air–water interactions are important for the transport of OPEs to remote oceans and polar regions. Processes such as degradation and sinking of particle-bound compounds modulate the properties and fate of OPEs in the water column, where they are potentially a non-accounted source of anthropogenic organic phosphorus for microbial communities. Some OPEs have toxic effects in marine species and are found in measurable quantities in fish and other aquatic organisms. However, there is conflicting evidence on the potential for bioaccumulation and biomagnification of OPEs. Future work must constrain the large-scale impact of OPEs on marine biota and biogeochemistry to support more effective regulation and mitigation.
Key points
-
Higher concentrations of organophosphate esters (OPEs) occur in coastal seas near populated and industrial areas than in the open ocean.
-
OPEs are transported to the ocean from terrestrial sources via both atmospheric transport and riverine discharge. Air–water exchange and atmospheric deposition affect the cycling of OPEs.
-
Transport via ocean currents and, potentially, biodegradation control the vertical distribution and sedimentation of OPEs.
-
Re-emission from melting snow and ice in polar regions can impact OPE levels in the High Arctic and the Southern Ocean water columns.
-
OPEs and their transformation products are emerging concerns for marine ecosystems, especially related to their presence in marine mammals and fish.
-
International strategies are needed to manage their environmental emissions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$99.00 per year
only $8.25 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Veen, I. & de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88, 1119–1153 (2012).
Suhring, R. et al. Organophosphate esters in Canadian Arctic air: occurrence, levels and trends. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 7409–7415 (2016).
Makinen, M. S. E. et al. Respiratory and dermal exposure to organophosphorus flame retardants and tetrabromobisphenol A at five work environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 941–947 (2009).
Brommer, S., Harrad, S., Van den Eede, N. & Covaci, A. Concentrations of organophosphate esters and brominated flame retardants in German indoor dust samples. J. Environ. Monit. 14, 2482–2487 (2012).
Gravel, S. et al. Halogenated flame retardants and organophosphate esters in the air of electronic waste recycling facilities: evidence of high concentrations and multiple exposures. Environ. Int. 128, 244–253 (2019).
Akram, R. et al. Trends of electronic waste pollution and its impact on the global environment and ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 16923–16938 (2019).
Lee, D., Offenhuber, D., Duarte, F., Biderman, A. & Ratti, C. Monitour: tracking global routes of electronic waste. Waste Manag. 72, 362–370 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Distribution of flame retardants in smartphones and identification of current-use organic chemicals including three novel aryl organophosphate esters. Sci. Total Environ. 693, 133654 (2019).
Ghimire, H. & Ariya, P. A. E-wastes: bridging the knowledge gaps in global production budgets, composition, recycling and sustainability implications. Sustain. Chem. 1, 154–182 (2020).
Perkins, D. N., Drisse, M. N. B., Nxele, T. & Sly, P. D. E-waste: a global hazard. Ann. Glob. Health 80, 286–295 (2014).
Marklund, A., Andersson, B. & Haglund, P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in Swedish sewage treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 7423–7429 (2005).
Meyer, J. & Bester, K. Organophosphate flame retardants and plasticisers in wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Monit. 6, 599–605 (2004).
Zeng, X. et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in wastewater treatment plant sludges from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 33, 1720–1725 (2014).
Kim, U. J. & Kannan, K. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate flame retardants/plasticizers in surface waters, tap water, and rainwater: implications for human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 5625–5633 (2018).
Fries, E. & Puttmann, W. Monitoring of the three organophosphate esters TBP, TCEP and TBEP in river water and ground water (Oder, Germany). J. Environ. Monit. 5, 346–352 (2003).
Salamova, A., Hermanson, M. H. & Hites, R. A. Organophosphate and halogenated flame retardants in atmospheric particles from a European Arctic site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 6133–6140 (2014).
Moeller, A. et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in airborne particles over the Northern Pacific and Indian Ocean toward the polar regions: evidence for global occurrence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 3127–3134 (2012).
Rodgers, T. F. M., Truong, J. W., Jantunen, L. M., Helm, P. A. & Diamond, M. L. Organophosphate ester transport, fate, and emissions in Toronto, Canada, estimated using an updated multimedia urban model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 12465–12474 (2018).
Suhring, R., Scheringer, M., Rodgers, T. F. M., Jantunen, L. M. & Diamond, M. L. Evaluation of the OECD POV and LRTP screening tool for estimating the long-range transport of organophosphate esters. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 22, 207–216 (2020).
Wei, G. L. et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers: sources, occurrence, toxicity and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 196, 29–46 (2015).
Nguyen, L. V. et al. Exposure of Canadian electronic waste dismantlers to flame retardants. Environ. Int. 129, 95–104 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. Measuring exposure of e-waste dismantlers in Dhaka Bangladesh to organophosphate esters and halogenated flame retardants using silicone wristbands and T-shirts. Sci. Total Environ. 720, 137480 (2020).
Zeng, Y. et al. Organophosphate esters (OPEs) in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in urban, e-waste, and background regions of South China. J. Hazard. Mater. 385, 121583 (2020).
Wang, R. M. et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in 40 rivers draining into the Bohai Sea, north China. Environ. Pollut. 198, 172–178 (2015).
Schmidt, N., Castro-Jiménez, J., Fauvelle, V., Ourgaud, M. & Sempéré, R. Occurrence of organic plastic additives in surface waters of the Rhône River (France). Environ. Pollut. 257, 113637 (2020).
Schmidt, N. et al. The Amazon River: a major source of organic plastic additives to the tropical North Atlantic? Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 7513–7521 (2019).
Fu, L. F. et al. Tracing the occurrence of organophosphate ester along the river flow path and textile wastewater treatment processes by using dissolved organic matters as an indicator. Sci. Total Environ. 722, 137895 (2020).
Li, J. et al. Inference of organophosphate ester emission history from marine sediment cores impacted by wastewater effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 8767–8775 (2019).
Li, H. R. et al. Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants along a sediment transect encompassing the Guiyu, China e-waste recycling zone. Sci. Total Environ. 646, 58–67 (2019).
Casal, P., Castro-Jiménez, J., Pizarro, M., Katsoyiannis, A. & Dachs, J. Seasonal soil/snow-air exchange of semivolatile organic pollutants at a coastal Arctic site (Tromsø, 69°N). Sci. Total Environ. 636, 1109–1116 (2018).
Castro-Jiménez, J. & Sempéré, R. Atmospheric particle-bound organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in a North African Mediterranean coastal city (Bizerte, Tunisia). Sci. Total Environ. 642, 383–393 (2018).
Paluselli, A., Fauvelle, V., Galgani, F. & Sempéré, R. Phthalate release from plastic fragments and degradation in seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 166–175 (2019).
Fauvelle, V. et al. Organic additive release from plastic to seawater is lower under deep-sea conditions. Nat. Commun. 12, 4426 (2021).
Castro, V., Montes, R., Quintana, J. B., Rodil, R. & Cela, R. Determination of 18 organophosphorus flame retardants/plasticizers in mussel samples by matrix solid-phase dispersion combined to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 208, 120470 (2020).
Schmidt, N., Castro-Jiménez, J., Oursel, B. & Sempéré, R. Phthalates and organophosphate esters in surface water, sediments and zooplankton of the NW Mediterranean Sea: Exploring links with microplastic abundance and accumulation in the marine food web. Environ. Pollut. 272, 115970 (2021).
Sutton, R., Chen, D., Sun, J., Greig, D. J. & Wu, Y. Characterization of brominated, chlorinated, and phosphate flame retardants in San Francisco Bay, an urban estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 652, 212–223 (2019).
Ma, Y. X., Xie, Z. Y., Lohmann, R., Mi, W. Y. & Gao, G. P. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in ocean sediments from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 3809–3815 (2017).
Nigar, A. et al. Environmental occurrence of phthalate and organophosphate esters in sediments across the Gulf of Lion (NW Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 760, 143412 (2021).
Castro-Jiménez, J., González-Fernández, D., Fornier, M., Schmidt, N. & Sempéré, R. Macro-litter in surface waters from the Rhone River: plastic pollution and loading to the NW Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 146, 60–66 (2019).
Lebreton, L. C. M. et al. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 8, 15611 (2017).
Bollmann, U. E., Moeler, A., Xie, Z., Ebinghaus, R. & Einax, J. W. Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in coastal and marine surface waters. Water Res. 46, 531–538 (2012).
Wolschke, H. et al. Atmospheric occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizer at the German coast. Atmos. Environ. 137, 1–5 (2016).
Suhring, R. et al. Organophosphate esters in the Canadian Arctic Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 304–312 (2021).
Gong, P. et al. Persistent organic pollutant cycling in forests. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2, 182–197 (2021).
Wania, F., Haugen, J.-E., Lei, Y. D. & Mackay, D. Temperature dependence of atmospheric concentrations of semivolatile organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 1013–1021 (1998).
Octaviani, M., Stemmler, I., Lammel, G. & Graf, H. F. Atmospheric transport of persistent organic pollutants to and from the Arctic under present-day and future climate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 3593–3602 (2015).
European Communities. Tris(2-chloro-1-methylethyl) phosphate (TCPP): EU risk assessment report (European Communities, 2008).
Zhang, X. et al. Novel flame retardants: estimating the physical-chemical properties and environmental fate of 94 halogenated and organophosphate PBDE replacements. Chemosphere 144, 2401–2407 (2016).
Liu, Y. C. et al. Heterogeneous OH initiated oxidation: a possible explanation for the persistence of organophosphate flame retardants in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 1041–1048 (2014).
Moeller, A., Xie, Z., Caba, A., Sturm, R. & Ebinghaus, R. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the atmosphere of the North Sea. Environ. Pollut. 159, 3660–3665 (2011).
Salamova, A., Ma, Y., Venier, M. & Hites, R. A. High levels of organophosphate flame retardants in the Great Lakes atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 1, 8–14 (2014).
Castro-Jiménez, J., Berrojalbiz, N., Pizarro, M. & Dachs, J. Organophosphate ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in the open Mediterranean and Black Seas atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 3203–3209 (2014).
Cheng, W. H. et al. Organophosphorus esters in the oceans and possible relation with ocean gyres. Environ. Pollut. 180, 159–164 (2013).
Li, J. et al. Organophosphate esters in air, snow, and seawater in the North Atlantic and the Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 6887–6896 (2017).
Chokwe, T. B., Abafe, O. A., Mbelu, S. P., Okonkwo, J. O. & Sibali, L. L. A review of sources, fate, levels, toxicity, exposure and transformations of organophosphorus flame-retardants and plasticizers in the environment. Emerg. Contam. 6, 345–366 (2020).
Castro-Jiménez, J. et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the global oceanic atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 12831–12839 (2016).
Na, G. S. et al. Occurrence, distribution, air-seawater exchange and atmospheric deposition of organophosphate esters (OPEs) from the Northwestern Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 157, 111243 (2020).
Jurado, E. et al. Wet deposition of persistent organic pollutants to the global oceans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 2426–2435 (2005).
Jurado, E. et al. Atmospheric dry deposition of persistent organic pollutants to the Atlantic and inferences for the global oceans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 5505–5513 (2004).
Hallanger, I. et al. Organophosphorous flame retardants in biota from Svalbard, Norway. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 101, 442–447 (2015).
McDonough, C. A. et al. Dissolved organophosphate esters and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in remote marine environments: Arctic surface water distributions and net transport through fram strait. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 6208–6216 (2018).
Lohmann, R. & Dachs, J. in World Seas: A Environmental Evaluation 2nd edn Vol. III Ch. 15 (ed. Sheppard, C.) 269–282 (Academic, 2019).
Gallban-Malagon, C. J., Del Vento, S., Cabrerizo, A. & Dachs, J. Factors affecting the atmospheric occurrence and deposition of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Southern Ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13, 12029–12041 (2013).
Wang, Y. et al. Occurrence, distribution, and air-water exchange of organophosphorus flame retardants in a typical coastal area of China. Chemosphere 211, 335–344 (2018).
Li, J. et al. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of organophosphate esters in air above the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 89–97 (2018).
Zhang, L. et al. Atmospheric deposition, seasonal variation, and long-range transport of organophosphate esters on Yongxing Island, South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 806, 150673 (2022).
Lai, S. C. et al. Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles over the northern South China Sea. Chemosphere 127, 195–200 (2015).
Regnery, J. & Puttmann, W. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in rain and snow from middle Germany. Clean Soil Air Water 37, 334–342 (2009).
Casas, G., Martinez-Varela, A., Vila-Costa, M., Jiménez, B. A. & Dachs, J. Rain amplification of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 12961–12972 (2021).
Casal, P. et al. Snow amplification of persistent organic pollutants at coastal Antarctica. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 8872–8882 (2019).
Zhang, Z. G. et al. Occurrence, behavior, and fate of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in subtropical paddy field environment: a case study in Nanning City of South China. Environ. Pollut. 267, 115675 (2020).
Xie, Z. Y. et al. Occurrence of legacy and emerging organic contaminants in snow at Dome C in the Antarctic. Sci. Total Environ. 741, 140200 (2020).
Cheng, W. H. et al. Detection and distribution of Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate on the East Antarctic ice sheet. Chemosphere 92, 1017–1021 (2013).
Cabrerizo, A., Muir, D. C. G., Teixeira, C., Lamoureux, S. F. & Lafreniere, M. J. Snow deposition and melting as drivers of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in Arctic rivers, lakes, and ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 14377–14386 (2019).
Gustafsson, O. et al. Observations of the PCB distribution within and in-between ice, snow, ice-rafted debris, ice-interstitial water, and seawater in the Barents Sea marginal ice zone and the North Pole area. Sci. Total Environ. 342, 261–279 (2005).
Herbert, B. M. J., Halsall, C. J., Villa, S., Jones, K. C. & Kallenborn, R. Rapid changes in PCB and OC pesticide concentrations in Arctic snow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 2998–3005 (2005).
Zhao, Z. et al. Distribution and long-range transport of polyfluoroalkyl substances in the Arctic, Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic coast. Environ. Pollut. 170, 71–77 (2012).
Sun, Y. X. et al. Glacial melt inputs of organophosphate ester flame retardants to the largest High Arctic lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 2734–2743 (2020).
Zhong, M. et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the Bohai, Yellow and East China seas. Sci.Total Environ. 741, 140434 (2020).
Chen, M. et al. Temporal and seasonal variation and ecological risk evaluation of flame retardants in seawater and sediments from Bohai Bay near Tianjin, China during 2014 to 2017. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 146, 874–883 (2019).
Regnery, J. & Puttmann, W. Seasonal fluctuations of organophosphate concentrations in precipitation and storm water runoff. Chemosphere 78, 958–964 (2010).
Regnery, J. & Puttmann, W. Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in urban and remote surface waters in Germany. Water Res. 44, 4097–4104 (2010).
Xiao, K. Y. et al. Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in surface seawater of the West Pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 170, 112691 (2021).
Barnes, D. K. A., Galgani, F., Thompson, R. C. & Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 364, 1985–1998 (2009).
Cristale, J. et al. Role of oxygen and DOM in sunlight induced photodegradation of organophosphorous flame retardants in river water. J. Hazard. Mater. 323, 242–249 (2017).
Li, X. M. et al. Organophosphate diesters (Di-OPEs) play a critical role in understanding global organophosphate esters (OPEs) in fishmeal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 12130–12141 (2020).
Strobel, A., Wilimore, W. G., Sonne, C., Dietz, R. & Letcher, R. J. Organophosphate esters in East Greenland polar bears and ringed seals: adipose tissue concentrations and in vitro depletion and metabolite formation. Chemosphere 196, 240–250 (2018).
Liu, Y. X. et al. Organophosphate (OP) diesters and a review of sources, chemical properties, environmental occurrence, adverse effects, and future directions. Environ. Int. 155, 106691 (2021).
Li, Y. et al. Occurrence and ecological implications of organophosphate triesters and diester degradation products in wastewater, river water, and tap water. Environ. Pollut. 259, 113810 (2020).
Xu, L. et al. Occurrence and spatio-seasonal distribution of organophosphate tri- and di-esters in surface water from Dongting Lake and their potential biological risk. Environ. Pollut. 282, 117031 (2021).
Liang, C. et al. Organophosphate diesters in urban river sediment from South China: call for more research on their occurrence and fate in field environment. ACS EST Water 1, 871–880 (2021).
Saeger, V. W. et al. Environmental fate of selected phosphate-esters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13, 840–844 (1979).
Abe, K. et al. Haloalkylphosphorus hydrolases purified from Sphingomonas sp. strain TDK1 and Sphingobium sp. strain TCM1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 5866–5873 (2014).
Takahashi, S., Katanuma, H., Abe, K. & Kera, Y. Identification of alkaline phosphatase genes for utilizing a flame retardant, tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate, in Sphingobium sp. strain TCM1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 101, 2153–2162 (2017).
Takahashi, S., Abe, K. & Kera, Y. in Environmental Biotechnology: New Approaches and Prospective Applications Ch. 5 (IntechOpen, 2013).
Latip, W. et al. Microbial phosphotriesterase: structure, function, and biotechnological applications. Catalysts 9, 671 (2019).
Takahashi, S. et al. Isolation and identification of persistent chlorinated organophosphorus flame retardant-degrading bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76, 5292–5296 (2010).
Kera, Y., Abe, K., Kasai, D., Fukuda, M. & Takahashi, S. Draft genome sequences of Sphingobium sp. strain TCM1 and Sphingomonas sp. strain TDK1, haloalkyl phosphate flame retardant- and plasticizer-degrading bacteria. Microbiol. Res. Announc. 4, e00668-16 (2016).
Liu, Y. et al. Biodegradation of tricresyl phosphate isomers by Brevibacillus brevis: degradation pathway and metabolic mechanism. Chemosphere 232, 195–203 (2019).
Wei, K., Yin, H., Peng, H., Lu, G. N. & Dang, Z. Bioremediation of triphenyl phosphate by Brevibacillus brevis: degradation characteristics and role of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase. Sci. Total Environ. 627, 1389–1395 (2018).
Wang, J. H. et al. Characterization and 16S metagenomic analysis of organophosphorus flame retardants degrading consortia. J. Hazard. Mater. 380, 120881 (2019).
Kawagoshi, Y., Nakamura, S., Nishio, T. & Fukunaga, S. Isolation of aryl-phosphate ester-degrading bacterium from leachate of a sea-based waste disposal site. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 98, 464–469 (2004).
Vila-Costa, M., Cerro-Gálvez, E., Martínez-Varela, A., Casas, G. & Dachs, J. Anthropogenic disolved organic carbon and marine microbiomes. ISME J. 14, 2646–2648 (2020).
Nemergut, D. R. et al. Global patterns in the biogeography of bacterial taxa. Environ. Microbiol. 13, 135–144 (2011).
Thomson, B. et al. Relative importance of phosphodiesterase vs. phosphomonoesterase (alkaline phosphatase) activities for dissolved organic phosphorus hydrolysis in epi- and mesopelagic waters. Front. Earth Sci. 8, 560893 (2020).
Wang, X. et al. A review of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in the environment: analysis, occurrence and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 731, 139071 (2020).
Zhao, J. P. et al. Novel brominated flame retardants in West Antarctic atmosphere (2011–2018): temporal trends, sources and chiral signature. Sci. Total Environ. 720, 137557 (2020).
Cheng, W. et al. Response of polar regions to emerging organic pollutant organophosphorus esters (OPEs), a review. Adv. Polar Sci. 28, 13–22 (2017).
Han, X. et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in the air and soils of Ny-Ålesund and London Island, Svalbard, Arctic. Environ. Pollut. 263, 114495 (2020).
Rohler, L. et al. Non-target and suspect characterisation of organic contaminants in Arctic air – Part 2: application of a new tool for identification and prioritisation of chemicals of emerging Arctic concern in air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 20, 9031–9049 (2020).
Wang, C. et al. Atmospheric organophosphate esters in the Western Antarctic Peninsula over 2014–2018: occurrence, temporal trend and source implication. Environ. Pollut. 267, 115428 (2020).
Andresen, J. A., Grundmann, A. & Bester, K. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticisers in surface waters. Sci. Total Environ. 332, 155–166 (2004).
Bester, K. Comparison of TCPP concentrations in sludge and wastewater in a typical German sewage treatment plant — comparison of sewage sludge from 20 plants. J. Environ. Monit. 7, 509–513 (2005).
Fries, E. & Puttmann, W. Occurrence of organophosphate esters in surface water and ground water in Germany. J. Environ. Monit. 3, 621–626 (2001).
Lian, M. S. et al. Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution, and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in the water of the Yellow River to the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 787, 147528 (2021).
Aznar-Alemany, Ò. et al. Halogenated and organophosphorus flame retardants in European aquaculture samples. Sci. Total Environ. 612, 492–500 (2018).
Hu, M. et al. Regional distribution of halogenated organophosphate flame retardants in seawater samples from three coastal cities in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 86, 569–574 (2014).
Lai, N. L. S. et al. Assessment of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in aquatic environments of China (Pearl River Delta, South China Sea, Yellow River Estuary) and Japan (Tokyo Bay). J. Hazard. Mater. 371, 288–294 (2019).
Zhong, M. et al. Occurrence and spatial distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 121, 331–338 (2017).
Gao, X. et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants and persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic contaminants in Arctic seawaters: on-board passive sampling coupled with target and non-target analysis. Environ. Pollut. 253, 1–10 (2019).
Gao, X. Z. et al. Occurrences, sources, and transport of hydrophobic organic contaminants in the waters of Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Environ. Pollut. 241, 950–958 (2018).
Esteban, S. et al. Presence of endocrine disruptors in freshwater in the northern Antarctic Peninsula region. Environ. Res. 147, 179–192 (2016).
Zhong, M. et al. Occurrences and distribution characteristics of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in the sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Sci. Total Environ. 615, 1305–1311 (2018).
Mo, L. et al. Legacy and emerging contaminants in coastal surface sediments around Hainan Island in South China. Chemosphere 215, 133–141 (2019).
Zeng, X. et al. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants/plasticizers in coastal sediments from the Taiwan Strait in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 151, 110843 (2020).
Brandsma, S. H., Leonards, P. E. G., Leslie, H. A. & de Boer, J. Tracing organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants and plasticizers in an estuarine food web. Sci. Total Environ. 505, 22–31 (2015).
Choi, W., Lee, S., Lee, H.-K. & Moon, H.-B. Organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in sediment and bivalves along the Korean coast: occurrence, geographical distribution, and a potential for bioaccumulation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 156, 111275 (2020).
Wang, Y. et al. Organophosphate esters in sediment cores from coastal Laizhou Bay of the Bohai Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 607, 103–108 (2017).
Bekele, T. G., Zhao, H., Wang, Q. & Chen, J. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of emerging organophosphate flame retardants in the marine food webs of Laizhou Bay, North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 13417–13426 (2019).
Zhang, R. et al. Occurrence, phase distribution, and bioaccumulation of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in mariculture farms of the Beibu Gulf, China: a health risk assessment through seafood consumption. Environ. Pollut. 263, 114426 (2020).
Liao, C. Y., Kim, U. J. & Kannan, K. Occurrence and distribution of organophosphate esters in sediment from northern Chinese coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 704, 135328 (2020).
Tan, X.-X. et al. Distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants in sediments from the Pearl River Delta in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 544, 77–84 (2016).
Harino, H., Yatsuzuka, E., Yamao, C., Ueno, M. & Ohji, M. Current status of organophosphorus compounds contamination in Maizuru Bay, Japan. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 94, 43–49 (2014).
Gao, X. Z. et al. Distribution, sources and transport of organophosphorus flame retardants in the water and sediment of Ny-Ålesund, Svalbard, the Arctic. Environ. Pollut. 264, 114792 (2020).
Marklund, A., Andersson, B. & Haglund, P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in air from various indoor environments. J. Environ. Monit. 7, 814–819 (2005).
Marklund, A., Andersson, B. & Haglund, P. Traffic as a source of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in snow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 3555–3562 (2005).
Sundkvist, A. M., Olofsson, U. & Haglund, P. Organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in marine and fresh water biota and in human milk. J. Environ. Monit. 12, 943–951 (2010).
Letcher, R. J. et al. Legacy and new halogenated persistent organic pollutants in polar bears from a contamination hotspot in the Arctic, Hudson Bay Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 610, 121–136 (2018).
Kim, J.-W. et al. Levels and distribution of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in fishes from Manila Bay, the Philippines. Environ. Pollut. 159, 3653–3659 (2011).
Garcia-Garin, O. et al. Assessment of organophosphate flame retardants in Mediterranean Boops boops and their relationship to anthropization levels and microplastic ingestion. Chemosphere 252, 126569 (2020).
Sala, B. et al. Organophosphate ester plasticizers in edible fish from the Mediterranean Sea: marine pollution and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 292, 118377 (2022).
Fernie, K. J. et al. Spatiotemporal patterns and relationships among the diet, biochemistry, and exposure to flame retardants in an apex avian predator, the peregrine falcon. Environ. Res. 158, 43–53 (2017).
Papachlimitzou, A. et al. Organophosphorus flame retardants (PFRs) and plasticisers in harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) stranded or bycaught in the UK during 2012. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 98, 328–334 (2015).
Sala, B., Gimenez, J., de Stephanis, R., Barcelo, D. & Eljarrat, E. First determination of high levels of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in dolphins from Southern European waters. Environ. Res. 172, 289–295 (2019).
Ding, Y. et al. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of organophosphate esters in tropical marine food web, South China Sea. Environ. Int. 143, 105919 (2020).
Song, H. et al. Inhibitory effects of tributyl phosphate on algal growth, photosynthesis, and fatty acid synthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 24009–24018 (2016).
Liu, Q. et al. Toxic effect and mechanism of tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl)phosphate (TDCPP) on the marine alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Chemosphere 252, 126467 (2020).
Liu, Q. et al. ROS changes are responsible for tributyl phosphate (TBP)-induced toxicity in the alga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 208, 168–178 (2019).
Wu, H. F. et al. Biological effects of tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TCPP) on immunity in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 61, 102–106 (2018).
Noyes, P. D., Haggard, D. E., Gonnerman, G. D. & Tanguay, R. L. Advanced morphological — behavioral test platform reveals neurodevelopmental defects in embryonic zebrafish exposed to comprehensive suite of halogenated and organophosphate flame retardants. Toxicol. Sci. 145, 177–195 (2015).
Sun, L. et al. Developmental exposure of zebrafish larvae to organophosphate flame retardants causes neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 55, 16–22 (2016).
Dishaw, L. V., Hunter, D. L., Beth, P., Stephanie, P. & Stapleton, H. M. Developmental exposure to organophosphate flame retardants elicits overt toxicity and alters behavior in early life stage zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. 142, 445–454 (2014).
Jarema, K. A., Hunter, D. L., Shaffer, R. M., Behl, M. & Padilla, S. Acute and developmental behavioral effects of flame retardants and related chemicals in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 52, 194–209 (2015).
Vila-Costa, M. et al. Microbial consumption of organophosphate esters in seawater under phosphorus limited conditions. Sci. Rep. 9, 233 (2019).
Okeme, J. O., Rodgers, T. F. M., Jantunen, L. M. & Diamond, M. L. Examining the gas-particle partitioning of organophosphate esters: how reliable are air measurements? Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 13834–13844 (2018).
Su, G. Y., Crump, D., Letcher, R. J. & Kennedy, S. W. Rapid in vitro metabolism of the flame retardant triphenyl phosphate and effects on cytotoxicity and mrna expression in chicken embryonic hepatocytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 13511–13519 (2014).
Zhang, Q., Yu, C., Fu, L. L., Gu, S. J. & Wang, C. New insights in the endocrine disrupting effects of three primary metabolites of organophosphate flame retardants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 4465–4474 (2020).
Blum, A. et al. Organophosphate ester flame retardants: are they a regrettable substitution for polybrominated diphenyl ethers? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 6, 638–649 (2019).
Rao, W. H., Liao, W., Wang, H., Zhao, H. B. & Wang, Y. Z. Flame-retardant and smoke-suppressant flexible polyurethane foams based on reactive phosphorus-containing polyol and expandable graphite. J. Hazard. Mater. 360, 651–660 (2018).
Liu, L., Gao, Y. P., Liu, H. P., Du, J. M. & Xia, N. Electrochemical-chemical-chemical redox cycling triggered by thiocholine and hydroquinone with ferrocenecarboxylic acid as the redox mediator. Electrochim. Acta 139, 323–330 (2014).
Liu, Q. F. et al. Experimental study of OH-initiated heterogeneous oxidation of organophosphate flame retardants: kinetics, mechanism, and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 14398–14408 (2019).
Wolschke, H., Suhring, R., Massei, R., Tang, J. H. & Ebinghaus, R. Regional variations of organophosphorus flame retardants: fingerprint of large river basin estuaries/deltas in Europe compared with China. Environ. Pollut. 236, 391–395 (2018).
Castro-Jiménez, J. & Ratola, N. An innovative approach for the simultaneous quantitative screening of organic plastic additives in complex matrices in marine coastal areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27, 11450–11457 (2020).
Fu, J. et al. Long-range transport, trophic transfer, and ecological risks of organophosphate esters in remote areas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 10192–10209 (2021).
Fu, J. et al. Occurrence and trophic magnification of organophosphate esters in an Antarctic ecosystem: insights into the shift from legacy to emerging pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 396, 122742 (2020).
Evenset, A. et al. Screening of New Contaminants in Samples from the Norwegian Arctic (Akvaplan, 2009).
Zheng, G. et al. Legacy and emerging semi-volatile organic compounds in sentinel fish from an Arctic formerly used defense site in Alaska. Environ. Pollut. 259, 113872 (2020).
Verreault, J., Letcher, R. J., Gentes, M. L. & Braune, B. M. Unusually high Deca-BDE concentrations and new flame retardants in a Canadian Arctic top predator, the glaucous gull. Sci. Total Environ. 639, 977–987 (2018).
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to D. Muir for his detailed and constructive internal review on the manuscript. They thank W. Cheng and R. Zhang for providing the data on OPEs in air, snow and marine organisms. They thank Q. Meng, L. Mi and J. Li for technical support in creating Figs 1–4. Z.X. acknowledges the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 689443 via project iCUPE (Integrative and Comprehensive Understanding on Polar Environments). They thank the researchers who contributed original research for OPEs in environmental and biological matrices and modelling predictions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.X. initiated the project and assembled the authorship team. P.W., X.W., C.L., J.C.-J., M.V.-C., J.D. and Z.X. researched the data and drafted the manuscript and figures. R.K., W.M. and R.L. contributed to writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment thanks Wilhelm Püttmann, Roxana Sühring and Gan Zhang for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Wang, P., Wang, X. et al. Organophosphate ester pollution in the oceans. Nat Rev Earth Environ 3, 309–322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00277-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00277-w
This article is cited by
-
Herbicide leakage into seawater impacts primary productivity and zooplankton globally
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Unbalanced Pollution and Ecological Risk of Organophosphate Esters in Chinese Surface Water and Land Use Under Multiple Driving Factors
Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2023)
-
Dermal Uptake is an Important Pathway for the Bioconcentration of Hydrophobic Organic Compounds by Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2023)
-
Effective degradation of organophosphate ester flame retardants and plasticizers in coastal sediments under high urban pressure
Scientific Reports (2022)