Abstract
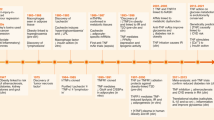
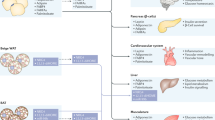
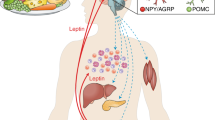
Adiponectin, first described in the mid-1990s, is one of the most widely studied adipokines to date. Studies of its regulation, biogenesis and physiological effects have yielded great insight and improved understanding of the mechanisms that ensure systemic metabolic homeostasis. Here, we provide a brief overview of the current state of the adiponectin field, describing adiponectin’s history, sites and mechanisms of action, and the critical questions that must be addressed in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg, A. H., Combs, T. P., Du, X., Brownlee, M. & Scherer, P. E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 7, 947–953 (2001).
Yamauchi, T. et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 7, 941–946 (2001).
Rutkowski, J. M. et al. Adiponectin promotes functional recovery after podocyte ablation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 24, 268–282 (2013).
Ye, R. et al. Adiponectin is essential for lipid homeostasis and survival under insulin deficiency and promotes β-cell regeneration. eLife 3, e03851 (2014).
Okamoto, Y. et al. Adiponectin reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation 106, 2767–2770 (2002).
Qi, Y. et al. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat. Med. 10, 524–529 (2004).
Oshima, K. et al. Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 331, 520–526 (2005).
Takemura, Y., Walsh, K. & Ouchi, N. Adiponectin and cardiovascular inflammatory responses. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 9, 238–243 (2007).
Halberg, N. et al. Systemic fate of the adipocyte-derived factor adiponectin. Diabetes 58, 1961–1970 (2009).
Stern, J. H., Rutkowski, J. M. & Scherer, P. E. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metab. 23, 770–784 (2016).
Ye, R. & Scherer, P. E. Adiponectin, driver or passenger on the road to insulin sensitivity? Mol. Metab. 2, 133–141 (2013).
Scherer, P. E. Adiponectin: basic and clinical aspects. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 28, 1–2 (2014).
Scherer, P. E., Williams, S., Fogliano, M., Baldini, G. & Lodish, H. F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26746–26749 (1995).
Hu, E., Liang, P. & Spiegelman, B. M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 10697–10703 (1996).
Maeda, K. et al. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 221, 286–289 (1996).
Nakano, Y., Tobe, T., Choi-Miura, N. H., Mazda, T. & Tomita, M. Isolation and characterization of GBP28, a novel gelatin-binding protein purified from human plasma. J. Biochem. 120, 803–812 (1996).
Arita, Y. et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 79–83 (1999).
Berg, A. H., Combs, T. P. & Scherer, P. E. ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 84–89 (2002).
Shapiro, L. & Scherer, P. E. The crystal structure of a complement-1q family protein suggests an evolutionary link to tumor necrosis factor. Curr. Biol. 8, 335–338 (1998).
Maeda, N. et al. Diet-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking adiponectin/ACRP30. Nat. Med. 8, 731–737 (2002).
Kubota, N. et al. Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 25863–25866 (2002).
Ma, K. et al. Increased beta-oxidation but no insulin resistance or glucose intolerance in mice lacking adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 34658–34661 (2002).
Xia, J. Y. et al. Acute loss of adipose tissue-derived adiponectin triggers immediate metabolic deterioration in mice. Diabetologia 61, 932–941 (2018).
Hotta, K. et al. Circulating concentrations of the adipocyte protein adiponectin are decreased in parallel with reduced insulin sensitivity during the progression to type 2 diabetes in rhesus monkeys. Diabetes 50, 1126–1133 (2001).
Weyer, C. et al. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1930–1935 (2001).
Yamauchi, T. et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 423, 762–769 (2003).
Yamauchi, T. et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 13, 332–339 (2007).
Okada-Iwabu, M. et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature 503, 493–499 (2013).
Tanabe, H. et al. Crystal structures of the human adiponectin receptors. Nature 520, 312–316 (2015).
Vasiliauskaite-Brooks, I. et al. Structural insights into adiponectin receptors suggest ceramidase activity. Nature 544, 120–123 (2017).
Holland, W. L. et al. Receptor-mediated activation of ceramidase activity initiates the pleiotropic actions of adiponectin. Nat. Med. 17, 55–63 (2011).
Holland, W. L. & Scherer, P. E. Structural biology: receptors grease the metabolic wheels. Nature 544, 42–44 (2017).
Scherer, P. E. The multifaceted roles of adipose tissue-therapeutic targets for diabetes and beyond: the 2015 Banting lecture. Diabetes 65, 1452–1461 (2016).
Hotta, K. et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20, 1595–1599 (2000).
Spranger, J. et al. Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 361, 226–228 (2003).
Ouchi, N. et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 100, 2473–2476 (1999).
Pischon, T. et al. Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 291, 1730–1737 (2004).
Turer, A. T. & Scherer, P. E. Adiponectin: mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Diabetologia 55, 2319–2326 (2012).
Maeda, N. et al. PPARγ ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes 50, 2094–2099 (2001).
Kusminski, C. M. et al. MitoNEET-driven alterations in adipocyte mitochondrial activity reveal a crucial adaptive process that preserves insulin sensitivity in obesity. Nat. Med. 18, 1539–1549 (2012).
Kim, J. Y. et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 2621–2637 (2007).
Makowski, L. et al. Lack of macrophage fatty-acid-binding protein aP2 protects mice deficient in apolipoprotein E against atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 7, 699–705 (2001).
Elmasri, H. et al. Fatty acid binding protein 4 is a target of VEGF and a regulator of cell proliferation in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 23, 3865–3873 (2009).
Shan, T., Liu, W. & Kuang, S. Fatty acid binding protein 4 expression marks a population of adipocyte progenitors in white and brown adipose tissues. FASEB J. 27, 277–287 (2013).
Wang, Y. et al. Cardiomyocyte-derived adiponectin is biologically active in protecting against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 298, E663–E670 (2010).
Shafiei, M. S., Shetty, S., Scherer, P. E. & Rockey, D. C. Adiponectin regulation of stellate cell activation via PPARγ-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Am. J. Pathol. 178, 2690–2699 (2011).
Ding, X. et al. The roles of leptin and adiponectin: a novel paradigm in adipocytokine regulation of liver fibrosis and stellate cell biology. Am. J. Pathol. 166, 1655–1669 (2005).
Jasinski-Bergner, S., Büttner, M., Quandt, D., Seliger, B. & Kielstein, H. Adiponectin and its receptors are differentially expressed in human tissues and cell lines of distinct origin. Obes. Facts 10, 569–583 (2017).
Das, K., Lin, Y., Widen, E., Zhang, Y. & Scherer, P. E. Chromosomal localization, expression pattern, and promoter analysis of the mouse gene encoding adipocyte-specific secretory protein Acrp30. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 280, 1120–1129 (2001).
Wang, Q. A. et al. Distinct regulatory mechanisms governing embryonic versus adult adipocyte maturation. Nat. Cell Biol. 17, 1099–1111 (2015).
Segawa, K. et al. Identification of a novel distal enhancer in human adiponectin gene. J. Endocrinol. 200, 107–116 (2009).
Wang, Z. V., Deng, Y., Wang, Q. A., Sun, K. & Scherer, P. E. Identification and characterization of a promoter cassette conferring adipocyte-specific gene expression. Endocrinology 151, 2933–2939 (2010).
Kim, H. B. et al. NFATc4 and ATF3 negatively regulate adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetes 55, 1342–1352 (2006).
Park, S. K. et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein and nuclear factor-Y regulate adiponectin gene expression in adipose tissue. Diabetes 53, 2757–2766 (2004).
Iwaki, M. et al. Induction of adiponectin, a fat-derived antidiabetic and antiatherogenic factor, by nuclear receptors. Diabetes 52, 1655–1663 (2003).
Seo, J. B. et al. Adipocyte determination- and differentiation-dependent factor 1/sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c regulates mouse adiponectin expression. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 22108–22117 (2004).
Combs, T. P. et al. Induction of adipocyte complement-related protein of 30 kilodaltons by PPARγ agonists: a potential mechanism of insulin sensitization. Endocrinology 143, 998–1007 (2002).
Fasshauer, M., Klein, J., Neumann, S., Eszlinger, M. & Paschke, R. Hormonal regulation of adiponectin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290, 1084–1089 (2002).
Halleux, C. M. et al. Secretion of adiponectin and regulation of apM1 gene expression in human visceral adipose tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 288, 1102–1107 (2001).
Wang, Z. V. & Scherer, P. E. DsbA-L is a versatile player in adiponectin secretion. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18077–18078 (2008).
Kondo, H. et al. Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 51, 2325–2328 (2002).
Kadowaki, T. et al. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1784–1792 (2006).
Pajvani, U. B. et al. Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Implications fpr metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 9073–9085 (2003).
Holland, W. L. et al. Inducible overexpression of adiponectin receptors highlight the roles of adiponectin-induced ceramidase signaling in lipid and glucose homeostasis. Mol. Metab. 6, 267–275 (2017).
Tsuchida, A. et al. Insulin/Foxo1 pathway regulates expression levels of adiponectin receptors and adiponectin sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 30817–30822 (2004).
Hug, C. et al. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 10308–10313 (2004).
Yamauchi, T., Iwabu, M., Okada-Iwabu, M. & Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin receptors: a review of their structure, function and how they work. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 28, 15–23 (2014).
Uhlén, M. et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347, 1260419 (2015).
Matsuda, K. et al. Positive feedback regulation between adiponectin and T-cadherin impacts adiponectin levels in tissue and plasma of male mice. Endocrinology 156, 934–946 (2015).
Kelesidis, I., Kelesidis, T. & Mantzoros, C. S. Adiponectin and cancer: a systematic review. Br. J. Cancer 94, 1221–1225 (2006).
Barb, D., Williams, C. J., Neuwirth, A. K. & Mantzoros, C. S. Adiponectin in relation to malignancies: a review of existing basic research and clinical evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 86, s858–s866 (2007).
Taliaferro-Smith, L. et al. LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6K axis and inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28, 2621–2633 (2009).
Landskroner-Eiger, S. et al. Proangiogenic contribution of adiponectin toward mammary tumor growth in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 3265–3276 (2009).
Denzel, M. S. et al. Adiponectin deficiency limits tumor vascularization in the MMTV-PyV-mT mouse model of mammary cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 3256–3264 (2009).
Masamoto, Y. et al. Adiponectin enhances antibacterial activity of hematopoietic cells by suppressing bone marrow inflammation. Immunity 44, 1422–1433 (2016).
Mandal, P., Pratt, B. T., Barnes, M., McMullen, M. R. & Nagy, L. E. Molecular mechanism for adiponectin-dependent M2 macrophage polarization: link between the metabolic and innate immune activity of full-length adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 13460–13469 (2011).
Ohashi, K. et al. Adiponectin promotes macrophage polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 6153–6160 (2010).
Combs, T. P. et al. A transgenic mouse with a deletion in the collagenous domain of adiponectin displays elevated circulating adiponectin and improved insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology 145, 367–383 (2004).
Marangoni, R. G. et al. Adiponectin is an endogenous anti-fibrotic mediator and therapeutic target. Sci. Rep. 7, 4397 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. Adiponectin inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced vascular inflammatory response via caveolin-mediated ceramidase recruitment and activation. Circ. Res. 114, 792–805 (2014).
Vasiliauskaité-Brooks, I. et al. Structure of a human intramembrane ceramidase explains enzymatic dysfunction found in leukodystrophy. Nat. Commun. 9, 5437 (2018).
Kupchak, B. R., Garitaonandia, I., Villa, N. Y., Smith, J. L. & Lyons, T. J. Antagonism of human adiponectin receptors and their membrane progesterone receptor paralogs by TNFα and a ceramidase inhibitor. Biochemistry 48, 5504–5506 (2009).
Sharma, A. X. & Holland, W. L. Adiponectin and its hydrolase-activated receptors. J. Nat. Sci. 3, e396 (2017).
Schmitz-Peiffer, C., Craig, D. L. & Biden, T. J. Ceramide generation is sufficient to account for the inhibition of the insulin-stimulated PKB pathway in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells pretreated with palmitate. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 24202–24210 (1999).
Holland, W. L. & Summers, S. A. Sphingolipids, insulin resistance, and metabolic disease: new insights from in vivo manipulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 29, 381–402 (2008).
Hosch, S. E., Olefsky, J. M. & Kim, J. J. APPLied mechanics: uncovering how adiponectin modulates insulin action. Cell Metab. 4, 5–6 (2006).
Mao, X. et al. APPL1 binds to adiponectin receptors and mediates adiponectin signalling and function. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 516–523 (2006).
Mitsuuchi, Y. et al. Identification of a chromosome 3p14.3-21.1 gene, APPL, encoding an adaptor molecule that interacts with the oncoprotein-serine/threonine kinase AKT2. Oncogene 18, 4891–4898 (1999).
Zhou, L. et al. Adiponectin activates AMP-activated protein kinase in muscle cells via APPL1/LKB1-dependent and phospholipase C/Ca2+/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 22426–22435 (2009).
Iwabu, M. et al. Adiponectin and AdipoR1 regulate PGC-1α and mitochondria by Ca2+ and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature 464, 1313–1319 (2010).
Cantó, C. et al. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 458, 1056–1060 (2009).
Awazawa, M. et al. Adiponectin suppresses hepatic SREBP1c expression in an AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK dependent pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 382, 51–56 (2009).
Shibata, R. et al. Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through AMPK- and COX-2-dependent mechanisms. Nat. Med. 11, 1096–1103 (2005).
Acknowledgements
The authors were supported by US National Institutes of Health grants R01-DK55758, R01-DK099110, P01-DK088761 and P01-AG051459 as well as by an unrestricted Novo Nordisk Foundation grant (to P.E.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Straub, L.G., Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: adiponectin. Nat Metab 1, 334–339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0041-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0041-z
This article is cited by
-
Reevaluating Adiponectin’s impact on obesity hypertension: a Chinese case-control study
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2024)
-
Inter-organ crosstalk during development and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2024)
-
Adipose tissue macrophages secrete small extracellular vesicles that mediate rosiglitazone-induced insulin sensitization
Nature Metabolism (2024)
-
The causal impact of gut microbiota on circulating adipokine concentrations: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Hormones (2024)
-
Adiponectin receptor 1-mediated stimulation of Cav3.2 channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons induces nociceptive behaviors in mice
The Journal of Headache and Pain (2023)