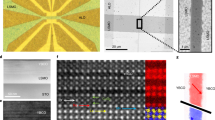
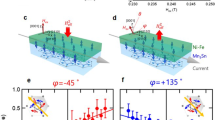
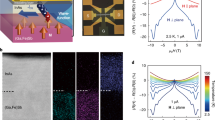
Abstract
Magnetoresistance effects are used in a variety of devices including hard disk drives and magnetic random access memories. In particular, giant magnetoresistance and tunnelling magnetoresistance can be used to create spin valves and tunnel junctions in which the resistance depends on the relative magnetization orientations of two ferromagnetic conducting layers. Here, we report a magnetoresistance effect that occurs in a platinum layer deposited on a magnon junction consisting of two insulating magnetic yttrium iron garnet (YIG) layers separated by an antiferromagnetic nickel oxide spacer layer. The resistance of the platinum layer is found to depend on the magnetization of the YIG layer in direct contact with it (an effect known as spin Hall magnetoresistance), but also the magnetization of the adjacent YIG layer in the junction. The resistance of the platinum layer is higher when the two YIG layers are aligned antiparallel than when parallel. We assign this behaviour to a magnonic nonlocal spin Hall magnetoresistance in which spin-carrying magnon propagation across the junction affects spin accumulation at the metal interface and hence modulates the spin Hall magnetoresistance. The effect could be used to develop spintronic and magnonic devices that have spin transport properties controlled by an all-insulating magnon junction and are thus free from Joule heating.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper including the main text and Supplementary Information and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Baibich, M. N. et al. Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001)Cr magnetic superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2472–2475 (1988).
Binasch, G., Grünberg, P., Saurenbach, F. & Zinn, W. Enhanced magnetoresistance in layered magnetic structures with antiferromagnetic interlayer exchange. Phys. Rev. B 39, 4828–4830 (1989).
Miyazaki, T. & Tezuka, N. Giant magnetic tunneling effect in Fe/Al2O3/Fe junction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 139, L231–L234 (1995).
Moodera, J. S., Kinder, L. R., Wong, T. M. & Meservey, R. Large magnetoresistance at room temperature in ferromagnetic thin film tunnel junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3273–3276 (1995).
Wood, R. Future hard disk drive systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 555–561 (2009).
Huai, Y., Albert, F., Nguyen, P., Pakala, M. & Valet, T. Observation of spin-transfer switching in deep submicron-sized and low-resistance magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3118–3120 (2004).
Fuchs, G. D. et al. Spin-transfer effects in nanoscale magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1205–1207 (2004).
Cornelissen, L. J. et al. Nonlocal magnon–polaron transport in yttrium iron garnet. Phys. Rev. B 96, 104441 (2017).
Nakata, K., Simon, P. & Loss, D. Spin currents and magnon dynamics in insulating magnets. J. Phys. D 50, 114004 (2017).
Cornelissen, L. J. et al. Long-distance transport of magnon spin information in a magnetic insulator at room temperature. Nat. Phys. 11, 1022–1026 (2015).
Wu, H. et al. Observation of magnon-mediated electric current drag at room temperature. Phys. Rev. B 93, 060403 (2016).
Li, J. et al. Observation of magnon-mediated current drag in Pt/yttrium iron garnet/Pt (Ta) trilayers. Nat. Commun. 7, 10858 (2016).
Lin, W. W. & Chien, C. L. Electrical detection of spin backflow from an antiferromagnetic insulator/Y3Fe5O12 interface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 067202 (2017).
Lebrun, R. et al. Tunable long-distance spin transport in a crystalline antiferromagnetic iron oxide. Nature 561, 222–225 (2018).
Qiu, Z. et al. Spin colossal magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnetic insulator. Nat. Mater. 17, 577–580 (2018).
Guo, C. Y. et al. Magnon valves based on YIG/NiO/YIG all-insulating magnon junctions. Phys. Rev. B 98, 134426 (2018).
Chumak, A. V. et al. Magnon spintronics. Nat. Phys. 11, 453–461 (2015).
Wu, H. et al. Magnon valve effect between two magnetic insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 097205 (2018).
Uchida, K. et al. Spin Seebeck insulator. Nat. Mater. 9, 894–897 (2010).
Uchida, K. et al. Observation of longitudinal spin-Seebeck effect in magnetic insulators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 172505 (2010).
Cramer, J. et al. Magnon detection using a ferroic collinear multilayer spin valve. Nat. Commun. 9, 1089 (2018).
Wright, K. Focus: a trio of magnon transistors. Physics 11, 23 (2018).
Cornelissen, L. J., Liu, J., van Wees, B. J. & Duine, R. A. Spin-current-controlled modulation of the magnon spin conductance in a three-terminal magnon transistor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 097702 (2018).
Das, K. S., Liu, J., van Wees, B. J. & Vera-Marun, I. J. Efficient injection and detection of out-of-plane spins via the anomalous spin Hall effect in permalloy nanowires. Nano Lett. 18, 5633–5639 (2018).
Das, K. S., Feringa, F., Middelkamp, M., van Wees, B. J. & Vera-Marun, I. J. Modulation of magnon spin transport in a magnetic gate transistor. Phys. Rev. B 101, 054436 (2020).
Hirsch, J. E. Spin Hall effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 1834–1837 (1999).
Zhang, S. F. Spin Hall effect in the presence of spin diffusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 393–396 (2000).
Nakayama, H. et al. Spin Hall magnetoresistance induced by a nonequilibrium proximity effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 206601 (2013).
Kim, J., Sheng, P., Takahashi, S., Mitani, S. & Hayashi, M. Spin Hall magnetoresistance in metallic bilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 097201 (2016).
Shan, J. et al. Influence of yttrium iron garnet thickness and heater opacity on the nonlocal transport of electrically and thermally excited magnons. Phys. Rev. B 94, 174437 (2016).
Avci, C. O. et al. Unidirectional spin Hall magnetoresistance in ferromagnet/normal metal bilayers. Nat. Phys. 11, 570–575 (2015).
Saglam, H. et al. Independence of spin–orbit torques from the exchange bias direction in Ni81Fe19/IrMn bilayers. Phys. Rev. B 98, 094407 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (MOST, grant nos 2017YFA0206200 and 2016YFA0300802) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, grant nos 51831012, 51620105004, 11974398, 51701203 and 11674373) and partially supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) (grant no. XDB07030200), the International Partnership Program (grant no. 112111KYSB20170090) and the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (grant no. QYZDJ-SSW-SLH016) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). C.H.W acknowledges financial support from the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS (2020008). We also thank X.-G. Zhang at the University of Florida for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.F.H. led and was involved in all aspects of the project. C.H.W. and C.Y.G. are the first authors. C.Y.G., C.H.W., W.Q.H., M.K.Z. and Y.W.X. deposited stacks and fabricated devices. C.Y.G., C.H.W. and X.W. conducted magnetic and transport property measurements. C.H.W., Z.R.Y., S.Z. and P.T. contributed to modelling and theoretical analysis. C.H.W., S.Z. and X.F.H. wrote the paper. Z.R.Y., Y.Z.L. and Y.W.L. conducted the MuMax simulation. X.F.H. and C.H.W. supervised and designed the experiments. All authors contributed to data mining and analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary Sections 1–8, Figs. 1–12 and Tables 1 and 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C.Y., Wan, C.H., He, W.Q. et al. A nonlocal spin Hall magnetoresistance in a platinum layer deposited on a magnon junction. Nat Electron 3, 304–308 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-0425-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-0425-9
This article is cited by
-
Reconfigurable spin current transmission and magnon–magnon coupling in hybrid ferrimagnetic insulators
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Coherent antiferromagnetic spintronics
Nature Materials (2023)
-
The anisotropy of spin Hall magnetoresistance in Pt/YIG structures
Applied Physics A (2021)