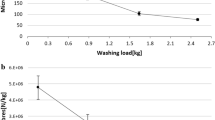
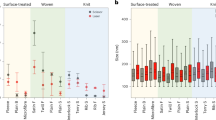
Abstract
Microplastic fibres (MPFs) released during the laundering of synthetic textiles are one of the largest sources of microplastic pollution in oceanic environments, forming a barrier to a sustainable textile industry. Here we report a robust fabric finish for nylon, taking advantage of environmentally friendly polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) brushes, which lessens the release of MPFs by lowering friction. Tribological evaluation reveals a substantially reduced coefficient of friction for PDMS-coated nylon in both dry and wet conditions. A molecular primer based on sulfonated mercaptosilane creates strong ionic bonding between the PDMS coating and the nylon fabric to enhance wash durability. Accordingly, MPF formation can be reduced by 93 ± 2% for coated fabrics after repeated laundering. Importantly, none of the essential properties, such as hydrophobicity, surface structure and comfort of the fabrics, are compromised after washing. Low-friction fabric finishes provide a green route for the design of synthetic fabrics and could help the textile industry transition away from its current, unsustainable practices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the public repository: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.21828543.
References
Guha Roy, A. Detailing plastic pollution. Nat. Sustain. 2, 654 (2019).
Lau, W. W. Y. et al. Evaluating scenarios toward zero plastic pollution. Science 369, 1455–1461 (2020).
Koelmans, A. A. et al. Risk assessment of microplastic particles. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 138–152 (2022).
Rochman, C. M. Microplastics research—from sink to source. Science 360, 28–29 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Atmospheric microplastics: a review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci. Rev. 203, 103118 (2020).
Nowack, B., Cai, Y., Mitrano, D. M. & Hufenus, R. Formation of fiber fragments during abrasion of polyester textiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 8001–8009 (2021).
Henry, B., Laitala, K. & Klepp, I. G. Microfibres from apparel and home textiles: prospects for including microplastics in environmental sustainability assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 652, 483–494 (2019).
Boucher, J. & Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources (IUCN, 2017).
Evangeliou, N. et al. Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions. Nat. Commun. 11, 3381 (2020).
Bergmann, M. et al. White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci. Adv. 5, 1157 (2019).
Brahney, J., Hallerud, M., Heim, E., Hahnenberger, M. & Sukumaran, S. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States. Science 368, 1257–1260 (2020).
Jenner, L. C. et al. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 831, 154907 (2022).
Leslie, H. A. et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 163, 107199 (2022).
Zabala, A. Ocean microfibre contamination. Nat. Sustain. 1, 213 (2018).
De Falco, F. et al. Evaluation of microplastic release caused by textile washing processes of synthetic fabrics. Environ. Pollut. 236, 916–925 (2018).
De Falco, F. et al. Novel finishing treatments of polyamide fabrics by electrofluidodynamic process to reduce microplastic release during washings. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 165, 110–116 (2019).
Suaria, G. et al. Microfibers in oceanic surface waters: a global characterization. Sci. Adv. 6, 8493 (2020).
Woodward, J., Li, J., Rothwell, J. & Hurley, R. Acute riverine microplastic contamination due to avoidable releases of untreated wastewater. Nat. Sustain. 4, 793–802 (2021).
De Falco, F. et al. Pectin based finishing to mitigate the impact of microplastics released by polyamide fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 198, 175–180 (2018).
Zhao, X. et al. Macroscopic evidence of the liquidlike nature of nanoscale polydimethylsiloxane brushes. ACS Nano 15, 13559–13567 (2021).
Shabanian, S., Khatir, B., Nisar, A. & Golovin, K. Rational design of perfluorocarbon-free oleophobic textiles. Nat. Sustain. 3, 1059–1066 (2020).
Khatir, B., Shabanian, S. & Golovin, K. Design and high-resolution characterization of silicon wafer-like omniphobic liquid layers applicable to any substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 31933–31939 (2020).
Soltani, M. & Golovin, K. Lossless, passive transportation of low surface tension liquids induced by patterned omniphobic liquidlike polymer brushes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2107465 (2022).
Wang, L. & McCarthy, T. J. Covalently attached liquids: instant omniphobic surfaces with unprecedented repellency. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 244–248 (2016).
Liu, J. et al. One-step synthesis of a durable and liquid-repellent poly(dimethylsiloxane) coating. Adv. Mater. 33, 2100237 (2021).
Özek, H. Z. Silicone-based water repellents. in Waterproof and Water Repellent Textiles and Clothing (ed. Williams, J. T.) 153–189 (Woodhead Publishing, 2018).
Cao, C. et al. Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic PDMS-ormosil@fabrics for highly effective self-cleaning and efficient oil-water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 12179–12187 (2016).
Dong, K. et al. Shape adaptable and highly resilient 3D braided triboelectric nanogenerators as e-textiles for power and sensing. Nat. Commun. 11, 2868 (2020).
Jiang, L., Cheng, Y., Wang, S., Xu, Z. & Zhao, Y. Non-fluorine oil repellency: how low the intrinsic wetting threshold can be for roughness-induced contact angle amplification? Langmuir 38, 5857–5864 (2022).
Ge, M. et al. A ‘PDMS-in-water’ emulsion enables mechanochemically robust superhydrophobic surfaces with self-healing nature. Nanoscale Horiz. 5, 65–73 (2020).
Chauvin, J. P. R. & Pratt, D. A. On the reactions of thiols, sulfenic acids, and sulfinic acids with hydrogen peroxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 6255–6259 (2017).
Gunji, T., Shigematsu, Y., Kajiwara, T. & Abe, Y. Preparation of free-standing films with sulfonyl group from 3-mercaptopropyl(trimethoxy)silane/1,2-bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane copolymer. Polym. J. 42, 684–688 (2010).
Remington, W. R. & Gladding, E. K. Equilibria in the dyeing of nylon with acid dyes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72, 2553–2559 (1950).
Herzberg, W. J. & Erwin, W. R. Gas-chromatographic study of the reaction of glass surfaces with dichlorodimethylsilane and chlorotrimethylsilane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 33, 172–177 (1970).
Bielecki, R. M., Crobu, M. & Spencer, N. D. Polymer-brush lubrication in oil: sliding beyond the Stribeck curve. Tribol. Lett. 49, 263–272 (2013).
Zhou, S. M., Tashiro, K. & Ii, T. Moisture effect on structure and mechanical property of nylon 6 as studied by the time-resolved and simultaneous measurements of FT-IR and dynamic viscoelasticity under the controlled humidity at constant scanning rate. Polym. J. 33, 344–355 (2001).
Venoor, V., Park, J. H., Kazmer, D. O. & Sobkowicz, M. J. Understanding the effect of water in polyamides: a review. Polym. Rev. 61, 598–645 (2021).
Napper, I. E. & Thompson, R. C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 112, 39–45 (2016).
Napper, I. E., Barrett, A. C. & Thompson, R. C. The efficiency of devices intended to reduce microfibre release during clothes washing. Sci. Total Environ. 738, 140412 (2020).
Chiong, J. A., Tran, H., Lin, Y., Zheng, Y. & Bao, Z. Integrating emerging polymer chemistries for the advancement of recyclable, biodegradable, and biocompatible electronics. Adv. Sci. 8, 2101233 (2021).
Ceseracciu, L., Heredia-Guerrero, J. A., Dante, S., Athanassiou, A. & Bayer, I. S. Robust and biodegradable elastomers based on corn starch and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 3742–3753 (2015).
De Falco, F., Gentile, G., Di Pace, E., Avella, M. & Cocca, M. Quantification of microfibres released during washing of synthetic clothes in real conditions and at lab scale. Eur. Phys. J. 133, 257 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge that this work was conducted at the University of Toronto, on the traditional land of the Huron-Wendat, the Seneca and the Mississauga of the Credit. This project was supported by the Canada Foundation for Innovation, through grant no. 41543, and by the University of Toronto through the WaterSeed programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.G. conceived and directed the project. S.K.L. and Z.A.D. performed the experimental work and wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to manuscript writing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Sustainability thanks Jintu Fan and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Text, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figs. 1 – 15 and Supplementary references.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lahiri, S.K., Azimi Dijvejin, Z. & Golovin, K. Polydimethylsiloxane-coated textiles with minimized microplastic pollution. Nat Sustain 6, 559–567 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-022-01059-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-022-01059-4
This article is cited by
-
Microplastic Abundance and Sources in Surface Water Samples of the Vaal River, South Africa
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2024)
-
Morphological and Chemical Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Water of the Vaal River, South Africa
Environmental Processes (2024)
-
Sustainable electronic textiles towards scalable commercialization
Nature Materials (2023)
-
How to stop fleece clothes from fouling the sea: bring in the tiny brushes
Nature (2023)
-
Microplastics that don’t come out in the wash
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2023)