Abstract
Long-term implantable neural interfacing devices are able to diagnose, monitor, and treat many cardiac, neurological, retinal and hearing disorders through nerve stimulation, as well as sensing and recording electrical signals to and from neural tissue. To improve specificity, functionality, and performance of these devices, the electrodes and microelectrode arrays—that are the basis of most emerging devices—must be further miniaturized and must possess exceptional electrochemical performance and charge exchange characteristics with neural tissue. In this report, we show for the first time that the electrochemical performance of femtosecond-laser hierarchically-restructured electrodes can be tuned to yield unprecedented performance values that significantly exceed those reported in the literature, e.g. charge storage capacity and specific capacitance were shown to have improved by two orders of magnitude and over 700-fold, respectively, compared to un-restructured electrodes. Additionally, correlation amongst laser parameters, electrochemical performance and surface parameters of the electrodes was established, and while performance metrics exhibit a relatively consistent increasing behavior with laser parameters, surface parameters tend to follow a less predictable trend negating a direct relationship between these surface parameters and performance. To answer the question of what drives such performance and tunability, and whether the widely adopted reasoning of increased surface area and roughening of the electrodes are the key contributors to the observed increase in performance, cross-sectional analysis of the electrodes using focused ion beam shows, for the first time, the existence of subsurface features that may have contributed to the observed electrochemical performance enhancements. This report is the first time that such performance enhancement and tunability are reported for femtosecond-laser hierarchically-restructured electrodes for neural interfacing applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Ageing population and existence of a multitude of cardiac1,2, neurological3,4,5,6, retinal7,8 and hearing disorders,9,10 that cannot be cured solely by medication, have resulted in a significant growth in the number of patients who require long-term implantable devices. These devices and their wide range of applications are summarized in Table 1. Implantable devices function via artificial stimulation of the living tissue through transfer of an external electrical signal from a neurostimulator or an implantable pulse generator (IPG) to an implantable electrode or microelectrode array and then across the membrane of the neural cells or tissue11. The nervous system is responsible for transportation of the electrical signals that travel from brain to muscles for eliciting muscle motion, and vice versa from the sensory organs to the brain (e.g., sensing, hearing, and vision). If a nerve is injured and the communication between the brain and the periphery is disrupted, as in the case of spinal cord injury for example12,13,14,15, it is possible to use a device to either restore the function that the brain cannot control4 or record this information from the nervous system. Over the past several decades, many patients across the globe have been reliant on implantable devices for life-critical and life-sustaining functions16,17,18, which has resulted in massive transformations in these devices. Particularly, there has been a strong trend towards device miniaturization since smaller implantable devices are desired to make them compatible with normal human activities and enhance the comfort of the host19,20. Therefore, all components of such devices need to be optimized for weight, size, and patients’ comfort. The majority of these devices consist of three major components: (1) neurostimulator or IPG, which contains a battery and electronics; (2) electrodes or microelectrode arrays, responsible for sensing and recording intrinsic neurological or cardiac activity and also delivering pulses for pacing and stimulating purposes; and (3) leads, which bridge between the IPG and the electrodes or (micro)electrode arrays1,3,6,8,20,21. Figure 1 shows an example of a neurostimulation device and all three major components outline above.
An example of a responsive neurostimulation device (RNS® System, NeuroPace, Inc.; photo used with permission and courtesy of NeuroPace, Inc.); The neurostimulator is implanted in the skull, replacing a similarly shaped section of bone. The cortical strip or depth electrodes (Pt-10Ir alloy) are implanted in or on the epileptic seizure focus.
Electrodes and microelectrode arrays are the basis of many emerging devices. They are fabricated to have very specific sizes, geometries, profiles, as well as electrical, electrochemical, and mechanical properties to match the biological requirements of their intended applications. Electrodes are vastly diverse because different applications demand different electrode types in terms of their size, invasiveness, selectivity, material composition and performance3,4,9,32,81,82. A microelectrode array is a very thin piece of plastic carrying embedded metallic structures, which is implanted into the human body to interact with the nervous system3,4,9,32,81,82,83,84. A higher density array of electrodes allows a greater number of discrete neurons or groups of neurons to be activated which results in increased localization and control of the desired biological response11,62,85. However, manufacturing limitations have hindered progress in the development of high-density microelectrode arrays86,87. In most implantable devices, high-performing electrodes or microelectrode arrays are characterized by low impedance (for sensing and recording purposes), high charge injection capacity (for safe and reversible stimulation purposes), and high capacitance for cardiac pacing applications42,88,89. We will use these parameters as performance metrics throughout this report. Figure 2 shows some examples of state-of-the-art electrodes and electrode arrays currently in practice.
(a) Typical two-column spinal cord stimulation paddle electrode arrays with 8 and 16 electrodes (photo reproduced with permission from Bradley, K. Pain Medicine 7, 20061); (b) a leadless pacemaker that is implanted directly into the heart where the anode is a circumferential ring located in the proximal portion of the device and responsible for cardiac pacing (photo with permission and courtesy of Medtronic); (c) a cochlear implant electrode array with 22 electrodes (photo with permission and courtesy of Cochlear Limited, Sydney, Australia).
Considering the overall dimensions of the implant, fabrication of electrodes that are small enough for communication with neurons is technologically feasible81. However, a size reduction of the actual conducting site is inevitably accompanied by an increase in the impedance of the electrode, and consequently a decrease in signal to noise ratios. Therefore, the size of an electrode for clinical use is determined by a trade-off between high selectivity (obtained by small size) and optimized electrochemical characteristics81. Larger electrodes have greater Geometric Surface Area (GSA), and thus can inject more charge before exceeding the electrochemically safe limits42. However, their large size limits the spatial selectivity and resolution of the device90. To increase the charge injection capacity, for delivering a higher resolution signal and improving performance86,90, one can increase GSA by increasing the number of electrodes. Nevertheless, considering the space limitations within organs such as brain, spinal cord, cochlea, and eye, such increase in number of electrodes must be accompanied by a reduction in electrode size, which significantly reduces the amount of charge that can be delivered. This adversely impacts the device performance and defeats the purpose of increasing the number of electrodes. To overcome the aforementioned tradeoff, an alternative approach is to increase the number of electrodes to achieve high selectivity, where each electrode has a small GSA, but an enhanced Electrochemical Surface Area (ESA)42,86,90, to achieve high charge transfer capability and low impedance. By maximizing ESA, while minimizing GSA, a large number of electrodes can be accommodated in the device, promoting enhanced performance, selectivity, fidelity, and lower power consumption. Increasing ESA has been achieved through two classes of techniques: (1) surface technologies through which a different material (e.g., coatings, thin films, and nanomaterials with greater electrochemical performance than the electrode itself) is added or deposited onto the electrode surface; (2) physical and electrochemical techniques to enhance/alter surface roughness of the electrode. Typical electrode coatings include but are not limited to iridium oxide thin films (IrO2)39,42,44,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105, titanium nitride coatings (TiN)38,96,106,107, black or porous platinum (Pt) coatings81,108,109,110, conductive polymers83,86,111,112,113,114,115,116, two-dimensional materials117,118, carbon nanotubes119,120,121,122, and nanostructured scaffolds123. Despite their ability to enhance electrochemical performance of electrodes, some of these coating material platforms: (1) pose technological challenges in the manufacturing environment, such as not lending themselves to serial or in-line processing, the need for costly time-consuming vacuum and batch processes, and the need for use of masks to selectively coat areas of interest on the electrode surface; (2) have some unfavorable properties, such as poor adhesion of the coatings and additive layers to the underlying electrode surface and shortcomings associated with long-term durability. Examples of such challenges are provided in Table 2.
In light of the described shortcomings of coating and thin film approaches, commercially viable technologies that can increase the electrochemical performance of electrodes and microelectrode arrays, while negating the need for coating or depositing a new material onto the surface, are deemed valuable. Such aim can be achieved using surface treatment techniques, which include: (1) electrochemical roughening132,133; (2) physical methods that use a laser to alter surface morphology via etching, melting, or roughening of the electrode surface28,134. Laser restructuring of neural interfacing electrodes and microelectrode arrays to improve their electrochemical performance has been studied in the literature in an ad hoc fashion28,85,134,135. Table 3 summarizes these studies.
The concept of hierarchical surfaces and structures have been vastly studied in the literature. Many natural and man-made materials exhibit bulk or surface structures on more than one length scale, meaning that the structural or surface elements themselves have a structure within. In neural interfacing applications, thin films of iridium oxide (IrO2), palladium oxide (PdO), ruthenium oxide (RuO2), rhodium oxide (Rh2O3), and their binary solid solution thin films103,104,105, for example, exhibit a hierarchical (also known as fractal, in this context) surface structure when synthesized under specific processing parameters. This hierarchy plays a large part in achieving an ultra-high ESA that renders them ideal thin film materials for neural interfacing applications. It is hypothesized here that formation of hierarchical surface structures on electrodes and microelectrode arrays, i.e. electrodes with topographic surface features comprised of varying length scales as illustrated in the schematic of Fig. 3 can give rise to electrochemical performance because the surface properties shall be governed by both the chemical composition of the electrode surface and the morphological effect of nanostructures within the micrometer-scale areas of the hierarchical surface140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148.
Several methods have been reported in the literature for the fabrication of hierarchical surface structures on different materials146 such as spin-coating149, polymer imprinting150,151,152, self-assembly153, replica casting of natural surfaces143, nanolithography141,144,154,155, chemical etching148, and nanoparticle deposition142,156. The possibility of material nano-processing, using femtosecond laser pulse ablation, was first reported by Pronko et al.157 in 1995 and others158,159,160,161,162,163,164,165 thereafter. Because of its ultrashort pulse duration and the large laser peak fluence, this method allows restructuring of almost all classes of materials with the desired precision and without the occurrence of noticeable heat affected zones166. Several studies specifically have reported on the use of femtosecond lasers for hierarchical and surface nanostructuring of various materials146,158,166,167,168,169,170,171,172,173. The developed techniques for surface nanostructuring using femtosecond laser include mask projection174, near-field ablation175, laser-assisted chemical etching176, nanotexturing by deposition from a femtosecond laser ablation plume177, nanostructuring of thin metal films by femtosecond laser induced melt178, plasmonic nanoablation179, and interferometric femtosecond laser ablation180,181. Importantly, use of femtosecond lasers for fabrication of biomimetic surfaces has gained significant attention in recent decades166,182.
Objectives
In this report, we have investigated the applicability and performance benefits of femtosecond laser hierarchical surface restructuring. We then explored the tunability of performance as a function of two of the most important and readily accessible laser parameters, i.e., fluence and average power. In addition to establishing the correlation between laser parameters and performance, we sought to understand what contributed to such unprecedented performance in these hierarchically restructured electrodes. The widely adopted reasoning in the literature has been the increased surface area and/or surface roughening. Using correlative confocal microscopy (CM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), the restructured electrodes were fully characterized in all three dimensions, i.e., 2D lateral texture and morphology with SEM and height information with CM with nanometer resolution. While there exists some loose correlation between surface parameters and performance, we show that surface parameters alone fail to fully explain the trend and the extent of enhanced electrochemical performance. Further cross-sectional analysis using high resolution focused ion beam (FIB) cross-sectioning and subsequent SEM imaging show, for the first time, the existence of subsurface features that may have contributed to the observed electrochemical performance and calls for further studies that investigate both surface and subsurface features.
Materials and methods
Femtosecond laser hierarchical surface restructuring
Electrodes or microelectrode arrays have specific electrochemical performance requirements for their intended applications. Therefore, the ability to selectively tune their performance metrics by tweaking tunable laser parameters is of great interest for both researchers and medical device manufacturers. Of the several laser processing parameters that enable surface tunability, Average Power and Fluence are the focus of this study as they can be readily tuned in almost all commercial lasers. A series of flat 0.3 mm thick Pt-10Ir electrodes were hierarchically restructured in two experiments. In experiment 1, Average Power was varied from 0.6 to 3.35 W, while all the other known/controllable lasering parameters were kept constant. In experiment 2, Fluence was varied from 12.3 to 2 J/cm2, while Average Power was kept constant at about 17 W. Table 4 outlines the Average Power and Fluence values that were used in these two experiments. Additionally, and to demonstrate feasibility and practicality of hierarchical surface restructuring in real world applications, a series of Pt-10Ir electrodes with flat and 3D/complex geometries were restructured.
The laser system used was a diode pumped Yb:YAG solid state laser (Coherent StarFemto, Santa Clara, CA) that generates 300 fs pulses with a central wavelength of 1030 nm. The rationale behind using a femtosecond laser in this work was that literature clearly shows femtosecond lasers can be utilized for material processing with minimal to zero undesired collateral damage (e.g., due to dissipation of generated heat)183,184. Such ability is key for achieving a surface restructuring process that is controllable and repeatable, with no undesired artifacts. The experiments were performed in air, under ambient conditions. Surface patterns were created via a graphical editor (Visual Laser Marker provided by Coherent), tied into the axis controls, and the beam path was directed using a deflection head. Electrodes were mounted onto a vacuum plate mounted on a tip-tilt stage (Edmunds Optics, Barrington, NJ) on an XYZ-translation stage. The electrodes were leveled to within 5 µm delta across the surface using an optical non-contact displacement transducer (Micro Epsilon, Ortenburg, Germany). Electrodes were brought directly under the deflection head to minimize incident angle.
Confocal and scanning electron microscopy and FIB cross-sectioning
Restructured electrodes underwent correlative confocal microscopy (CM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging. CM was performed in a ZEISS Smart proof 5 (ZEISS, Jena, Germany) and Keyence VK 3000 (Keyence, Osaka, Japan). The SEM and FIB/SEM imaging were performed using a ZEISS Crossbeam 340 (ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany). SEM Imaging was conducted with a secondary electron detector at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV under various magnifications. Magnifications of 50k, 20k, 10k, 5k, 2k, 1k, and 500 corresponding to pixel sizes of 2.23, 5.58, 11.16, 22.33, 55.82, 111.6, and 223.3 nm were used, which enabled the investigation of the hierarchal structures at various length scales. Further, micrographs were taken at 0° and 45° tilt angles, enabling better visualization of the overall topology of the surface and correlation with the 3D confocal data. In order to reveal subsurface features induced by restructuring, FIB cross-sectioning was performed using a gallium FIB at a current of 100 nA and an accelerating voltage of 30 kV to create a trench with dimensions of 50 µm width and 100 µm length and 80 µm depth. Polishing of the cross-section was done in multiple steps, using lower currents down to 1 nA to ensure best cross-sectional wall surface quality. The confocal data provides nanometer height resolution (the exact resolution depends on the selected objective) while SEM provides similar resolution in lateral directions. The correlation between the two, enabled by Mountain Software (Digital Surf, Besancon, France), allows for full characterization of surfaces in all three dimensions. The objective lens and acquisition modes were chosen such that the surface roughness of the restructured electrodes could be fully captured with the highest resolution possible. Due to the difficulty associated with aligning features such as peaks and valleys from one image to another, 180 µm × 180 µm areas that contain 25 full peaks, 20 half peaks and four quarter peaks were extracted from every image that was acquired. The following image processing steps were applied to obtain various surface parameters: (1) Filling non-measured points (i.e. filling points on the surface where no confocal information was present using interpolation; the total number of non-measured points for our images were less than 5%); (2) Removing outliers; (3) Leveling; (4) Filling non-measured points (only if the previous process yielded any additional non-measured points (which is always less than 1%); (5) Thresholding to remove foreign objects; (6) Extracting surface parameters. Surface parameters established by the ISO 25178 standard were calculated. Root mean square (RMS) height of the surface (Sq), and the surface area ratio (Sdr) were selected as two parameters that reflect “surface roughness” and “added surface area” also reported by Taylor et al. for similar neural interfacing applications104. Their mathematical formulation is provided in Eqs. (1) and (2):
RMS roughness (Sq)
Surface area ratio (Sdr)
where Z denotes the height of each point on the surface and A is the area of the sample. RMS roughness corresponds to the standard deviation of the height distribution and is a widely used parameter due to its robustness being less sensitive to measurement noise. The surface point cloud can be triangulated for surface area measurements. In particular, Sdr calculates the area of each individual triangular and sums them up to define the curvilinear area that follows each asperity and texture element of the surface. This area is then divided by the horizontal area in order to determine how much the surface differs from a horizontal plane. Throughout this report, we use Sdr to quantitatively characterize added surface area.
Electrochemical measurements
Charge storage capacity (CSC) is an important property to consider when determining the usefulness of an electrode or a microelectrode array42,90 and can be measured via cyclic voltammetry (CV). The voltage in a CV test is restricted to a range where no detrimental electrochemical reactions occur to the biological tissue or nerves. Since tissue reactions are application specific, in practice, these voltage limits are commonly determined by the so called “water window”, representing the potential-range where oxidation or reduction currents will not lead to formation of hydrogen or oxygen at the electrode/tissue interface (e.g. −0.6 V to 0.8 V vs. a Ag/AgCl reference electrode)42. In this work, CV was used to measure CSC and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used to measure impedance and specific capacitance. Both CV and EIS tests were performed in a three-electrode Teflon® plate cell (Fig. 4), comprising an Ag/AgCl reference electrode (ALS-Co Ltd., RE-1B, Tokyo, Japan), a coiled Pt counter-electrode, and hierarchically restructured electrodes as the working electrodes. The geometric surface area (GSA) of the working electrodes in the cell was 0.09 cm2. The electrolyte used was a commercially available phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution (Blood Bank Saline, Azer Scientific, Morgantown, PA). All potentials were recorded with respect to the Ag/AgCl reference electrode. All CV tests were performed at room temperature and at a 50 mV/s voltage sweep rate (ν) between potential limits of −0.6 V and 0.8 V, beginning at open-circuit potential (OCP) and sweeping in the positive direction first. As outlined earlier, potential windows were selected to ensure water electrolysis did not occur. EIS measurements were performed at OCP and measured over a frequency range of 0.1–105 Hz using a 10 mV root-mean-square (Vrms) sinusoidal excitation voltage amplitude about a fixed potential between −0.6 V and 0.8 V. All CV and EIS measurements were performed using a Gamry potentiostat (5000E interface, Warminster, PA) and the vendor supplied software. All data reported for CV and EIS are an average of three electrodes per condition, tested three times, i.e., a total of 9 measurements. Specific capacitance was calculated using EIS data and common Randles model.
Results and discussion
Hierarchical surface structures
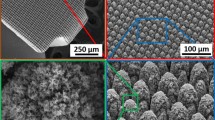
As shown in the optical and SEM micrographs of Fig. 5, hierarchical surface restructuring was employed successfully as a robust surface modification technology on a diverse range of electrode shapes and geometries for various neural interfacing applications, e.g. cylindrical (Fig. 5a) and helical (Fig. 5b) Pt-10Ir electrodes for cardiac rhythm applications, rivet-style Pt-10Ir electrodes for ultrahigh density mapping electrophysiology catheters (Fig. 5c) and a cylindrical (Fig. 5d) Pt-10Ir electrode for use in percutaneous spinal cord stimulation electrode arrays. The hierarchical surface structure created as a result of restructuring can be observed in the SEM micrographs of a flat Pt-10Ir electrode targeted for use in a paddle-lead spinal cord stimulation electrode array (Fig. 6). The micrographs reveal that the surface hierarchy is notable by a periodic topography comprised of coarse-scale mound-like features that are several microns wide and ~ 10 to 20 µm high and a finer structure subset on top of the mound-like structures in the range of about a few nanometers to a few hundred nanometers in size. The observed pattern in Fig. 6 has been maintained throughout this study for preserving the larger scale structures. This allows for the investigation of tunability independent of the pattern focusing on the most commonly accessible laser parameters of fluence and average power. The authors acknowledge the need for exploring pattern (i.e., the geometric path of laser spot on the surface) as a tunable parameter in future studies but believe lessons learned from the current work provides valuable insights toward such studies and can confine an otherwise prohibitively broad experimental field.
SEM micrographs of hierarchically restructured electrodes for various neural interfacing applications: (a) a cylindrical, and, (b) a helix Pt-10Ir electrode for cardiac rhythm management applications; (c) a rivet-style Pt-10Ir electrode for an electrophysiology mapping catheter and, (d) a cylindrical Pt-10Ir electrode for use in a percutaneous spinal cord stimulation electrode array.
Figure 7 shows representative SEM micrographs of the electrodes from experiment 1 restructured at 0.61, 1.98, and 3.35 Watts (top row) and electrodes from experiment 2 restructured at 12.3, 4.1, and 2.46 J/cm2 of fluence (bottom row). All SEM micrographs were taken at 45° tilt angles, enabling better visualization of the overall topology of the surface, while the insets were captured at 0° tilt angles. These SEM micrographs qualitatively show that the prevalence of smaller-length-scale features on the electrode surface is higher at higher average power. This observation is quantitatively confirmed by correlated confocal images provided in Fig. 8, showing representative 2D heat-map view (top row) and 3D view (bottom row) confocal maps of hierarchically restructured Pt-10Ir electrodes at 0.61, 1.98, and 3.35 W average power. Representative confocal images for 12.30, 4.10, and 2.46 J/cm2 fluence are provided in Fig. 9. Similarly, increase in roughness and texture as a function of average power is observed in SEM and confocal images. The 2D heat map view confocal images and SEM micrographs show that the increased roughness presents itself as increased undulations. In images with variable average power the increased roughness is accompanied with increased depth of structures while varying fluence does not present a similar trend. The deviation from circular shape is also more pronounced in Fig. 9 (fluence) than Fig. 8 (average power), significantly reducing the gaps between peaks. Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) was performed at 0° tilt angles for both an un-restructured and hierarchically restructured Pt-10Ir electrodes. Figure 10 shows the compositional EDS maps of both electrode surfaces. Table 5 summarizes the elemental composition of both electrode surfaces. Note that oxygen concentration increased by ~ 5% after hierarchical surface restructuring at 12.30 J/cm2 fluence.
Representative 2D (top row), 1D (middle row), and 3D (bottom row) confocal maps of hierarchically restructured surfaces of Pt-10Ir electrodes at 0.61, 1.98, and 3.35 W Average Power. Note that the cross-sectional profile (1D confocal map) is obtained at the center of the map along the horizontal direction.
Representative 2D (top row), 1D (middle row), and 3D (bottom row) confocal maps of hierarchically restructured surfaces of Pt-10Ir electrodes at 12.30, 4.10, and 2.46 J/cm2 Fluence. Note that the cross-sectional profile (1D confocal map) is obtained at the center of the map along horizontal direction.
Correlation of laser parameters and electrochemical performance and the role of surface properties
In order to investigate the performance behavior of the observed surfaces, cyclic voltammograms of all electrodes from experiment 1 restructured while varying average power and a pristine un-restructured Pt-10Ir electrode (inset) are shown in Fig. 11a. Total Charge Storage Capacity (CSCtotal) was calculated according to Eq. (3) by integrating the area under the cyclic voltammograms:
Cyclic voltammograms of, a) a series of electrodes restructured under varying restructuring conditions (0.61 to 3.35 W) and a pristine un-restructured Pt-10Ir electrode (inset), and, b) a 4 µm thick TiN coating for comparison with an electrode restructured at 3.35 W, and a pristine Pt-10Ir electrode; noteworthy is the two orders of magnitude increase in CSCtotal for the electrode restructured at 3.35 W average power compared to its un-restructured counterpart.
Here, it is clearly observed that tunability can be achieved by varying average power. Increase in average power is shown to continuously enhance CSCtotal (Fig. 11a). To provide a better context and for the sake of comparison, cyclic voltammograms of a 4 µm thick TiN coating, an electrode restructured at 3.35 W, and a pristine Pt-10Ir electrode are shown in Fig. 11b. Electrodes restructured at 3.35 W not only show over two orders of magnitude increase in their CSCtotal compared to their un-restructured Pt-10Ir counterparts, but also their CSCtotal exceeds that of the 4 µm thick TiN coating routinely used in cardiac rhythm management applications. This is the first time that such performance enhancement and tunability are reported for laser restructured electrodes. The pristine Pt10Ir electrode exhibits distinct oxidation and reduction peaks similar to Pt electrodes42. The laser restructured Pt10Ir electrodes, on the other hand, exhibit substantially larger voltammograms that are both semi-rectangular, indicating double-layer capacitance similar to TiN, and also contain an oxidation peak at 0.8 V and a small reduction peak near 0.1 V inherent to Pt-10Ir, as shown in the inset CV voltammogram of the pristine Pt-10Ir electrode.
Impedance magnitude as a function of frequency (plotted in the 0.1–105 Hz frequency range) for select electrodes from experiment 1, the pristine Pt-10Ir electrode and the TiN coating are shown in Fig. 12. Most notably, at frequencies below 1000 Hz, EIS tests and impedance measurements (Fig. 12) exhibit approximately up to two orders of magnitude reduction in impedance for hierarchically restructured electrodes (at 3.35 W) compared to the pristine Pt-10Ir counterparts. At higher frequencies, all electrodes exhibit resistive behavior dominated by electrolyte conductivity. Most notably, as illustrated in Fig. 12c, the impedance behavior of the electrode restructured at 3.35 W is nominally identical to that of the TiN coated electrode. More notably, the EIS measurements and capacitance calculations demonstrate over 700-fold increase in specific capacitance (Fig. 13) after hierarchical surface restructuring (at 3.35 W). Additionally, hierarchical surface restructuring has the unique advantage and possibility of engineering the electrodes’ ESA through variation and tunability of laser parameters. Here, such tunability is conveniently achieved by simply dialing a different average power value for the laser. Similar trends are observed for fluence. However, there still remains the question of what drives such performance and tunability and whether the widely adopted reasoning of increased surface area and roughening of the electrodes are the key contributors to the observed increase in performance.
(a) Impedance magnitude as a function of frequency (plotted in the 0.1–105 Hz frequency range) for a pristine unrestructured Pt-10Ir electrode, and select hierarchically restructured electrodes as a function of average power (only those electrodes restructured at 0.61, 1.52 and 3.35 W are shown for simplicity), (b) impedance magnitude as a function of frequency (plotted in the 0.1–10 Hz frequency range) for a 4 µm thick TiN coated Pt-10Ir electrode and a pristine Pt-10Ir electrode for comparison with the restructured electrode at 0.61 W, and, (c) impedance magnitude as a function of frequency (plotted in the 0.1–10 Hz frequency range) for the 4 µm thick TiN coated Pt-10Ir electrode and the Pt-10Ir electrode restructured at 3.35 W.
Plots of surface area ratio (Sdr) as well as total charge storage capacity (a) and specific capacitance (b) as a function of laser average power; Also, plots of mean surface roughness (Sq) as well as total charge storage capacity (c) and specific capacitance (d) as a function of laser average power.
The relationship between laser parameters, surface structure and performance
Figures 13 and 14 show the relationship between the variations of laser processing parameters (average power and fluence), surface parameters and performance. In Fig. 13, performance metrics (CSCtotal and specific capacitance) and surface parameters (Sdr and Sq) have been correlated with average power while Fig. 14 demonstrates that correlation with fluence. While both performance metrics of CSCtotal and specific capacitance exhibit a relatively consistent increasing behavior with average power and fluence, surface parameters tend to follow a less predictable behavior negating a direct relationship between these surface parameters and performance. It is evident from Fig. 13 that an increase in performance—when average power is increased—does not necessarily guarantee a consistently increasing trend in either of the surface parameters. Additionally, Fig. 14 shows that despite the relatively consistent increasing trend in performance—when fluence increases—both surface parameters exhibit a decreasing trend.
These observations and trends can be attributed to several potential contributors. Firstly, looking at Figs. 8 and 9, one can clearly see that the prevalence of finer nanoscale features with higher frequencies is more pronounced on electrodes with improved performance. The lower performance surfaces have almost ideal circular shape while surfaces with higher performance deviate from circularity and the vicinity of peaks exhibit high frequency undulations. However, when measured quantitatively, other features of surfaces might have dominated the calculations. In our opinion, this calls for devising new functional surface parameters different from conventional surface metrics that can better correlate the surfaces to the performance metrics observed. Another key neglected factor is the existence of any subsurface structures that might be invisible to surface sensitive imaging techniques such as the ones used in this study, i.e. SEM and CM. The subsurface features herein refer to the structural changes that are made to the electrodes below the visible surface. These include voids, cracks, fissures, and the like features. It is hypothesized that these subsurface features—not visible using the presented surface characterization techniques but whose structure is connected to the surface terrains—can contribute to the overall performance metrics of the sample and play an important role in increasing the accessible electrochemical surface area of the electrodes. To explore this further, FIB cross-sections of several electrodes restructured in this study were obtained to investigate whether features invisible to imaging techniques utilized herein exist, or not. Figure 15 shows representative FIB cross-sections of two electrodes hierarchically restructured at 4.10 J/cm2 fluence (Fig. 15a,b) and 1.98 W average power (Fig. 15c). Subsurface features (shown by red dashed arrows in Fig. 15) that are consistently occurring close to the valleys are evident in both FIB cross sections of Fig. 15. The existence of such features can likely be attributed to laser shock waves that induce void further away from the spot location of lasers. Although femtosecond lasers are perceived to have significantly less heat and induced shock waves than their counterparts, they still do exist and can create subsurface features as evidenced here.
Conclusions
In this work, a novel method was introduced for hierarchical surface restructuring of electrode surfaces, using femtosecond laser technology, to promote tunability and controllability of their electrochemical performance for a wide range of neural interfacing applications. The performance of a series of hierarchically restructured electrodes was evaluated and compared with those of un-restructured electrodes as well as TiN coated electrodes and the advantages of laser restructured electrodes over the other two were discussed. Further, tunability of performance metrics, via variation of lasering parameters, was shown and the role of surface and subsurface parameters was investigated. It was demonstrated that surface RMS and added surface area are not able to fully describe the trends observed in performance metrics; thus, further studies are required to correlate surface parameters with performance metrics more confidently. Finally, we have shown that even in the presence of femtosecond pulses, there are potential shock wave induced structures below the surface and away from the interaction spot between the laser and the electrodes. Subsurface features can also contribute to performance. Future studies that include both surface and cross-sectional characterization can better correlate the effect of subsurface features and performance. Lastly, we acknowledge the need for exploring laser patterning as a tunable parameter in future studies but believe lessons learned from the current work provides valuable insights toward such studies and can confine an otherwise prohibitively broad experimental field.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Mulpuru, S. K., Madhavan, M., McLeod, C. J., Cha, Y. M. & Friedman, P. A. Cardiac pacemakers: Function, troubleshooting, and management: Part 1 of a 2-part series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 69, 189–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.061 (2017).
Stevenson, I. & Voskoboinik, A. Cardiac rhythm manegement devices. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. (AJGP) 47, 264–271. https://doi.org/10.31128/AJGP-12-17-4439 (2018).
Epstein, L. J. & Palmieri, M. Managing chronic pain with spinal cord stimulation. Mt. Sinai J. Med. J. Transl. Pers. Med. 79, 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.21289 (2012).
Ordonez, J., Schuettler, M., Boehler, C., Boretius, T. & Stieglitz, T. Thin films and microelectrode arrays for neuroprosthetics. MRS Bull. 37, 590–598. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2012.117 (2012).
Stenehjem, E. & Armstrong, W. S. Central nervous system device infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 26, 89–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2011.09.006 (2012).
Schalk, G. & Leuthardt, E. C. Brain-computer interfaces using electrocorticographic signals. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 4, 140–154. https://doi.org/10.1109/RBME.2011.2172408 (2011).
Kelly, S. K. et al. A hermetic wireless subretinal neurostimulator for vision prostheses. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58, 3197–3205. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2011.2165713 (2011).
Theogarajan, L. Strategies for restoring vision to the blind: Current and emerging technologies. Neurosci. Lett. 519, 129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.001 (2012).
Carlson, M. L., Driscoll, C. L., Gifford, R. H. & McMenomey, S. O. Cochlear implantation: Current and future device options. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 45, 221–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2011.09.002 (2012).
Wilson, B. S. et al. Better speech recognition with cochlear implants. Nature 352, 236–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/352236a0 (1991).
Eljamel, S. & Slavin, K. Neurostimulation : Principles and Practice (Wiley, 2013).
Compton, A. K., Shah, B. & Hayek, S. M. Spinal cord stimulation: A review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 16, 35–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-011-0238-7 (2012).
Jackson, A. & Zimmermann, J. B. Neural interfaces for the brain and spinal cord–restoring motor function. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 8, 690–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.219 (2012).
Mailis-Gagnon, A., Furlan, A. D., Sandoval, J. A. & Taylor, R. Spinal cord stimulation for chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003783.pub2 (2004).
Wolter, T. Spinal cord stimulation for neuropathic pain: Current perspectives. J. Pain Res. 7, 651–663. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.S37589 (2014).
Stellbrink, C. & Trappe, H.-J. The follow-up of cardiac devices: what to expect for the future?. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 9, I113–I115. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/sum071 (2007).
Halperin, D., Heydt-Benjamin, T. S., Fu, K., Kohno, T. & Maisel, W. H. Security and privacy for implantable medical devices. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 7, 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1109/MPRV.2008.16 (2008).
Maisel, W. H. Safety issues involving medical devices implications of recent implantable cardioverter-defibrillator malfunctions. JAMA 294, 955–958. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.294.8.955 (2005).
Ko, W. H. Early history and challenges of implantable electronics. ACM J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. 8, 8. https://doi.org/10.1145/2180878.2180880 (2012).
Bazaka, K. & Jacob, M. Implantable devices: Issues and challenges. Electronics 2, 1–34. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics2010001 (2012).
Madhavan, M., Mulpuru, S. K., McLeod, C. J., Cha, Y. M. & Friedman, P. A. Advances and future directions in cardiac pacemakers: Part 2 of a 2-part series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 69, 211–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.064 (2017).
Witherell, C. L. Cardiac rhythm control devices. Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 6, 85–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-5885(18)30510-0 (1994).
Halbfass, P., Sonne, K., Nentwich, K., Ene, E. & Deneke, T. Current developments in cardiac rhythm management devices. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 107, 100–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1313-4 (2018).
Lau, C. P., Siu, C. W. & Tse, H. F. Future of implantable devices for cardiac rhythm management. Circulation 129, 811–822. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.000312 (2014).
Kirwin, S. H. Cochlear Implants : Technological Advances, Psychological/social Impacts and Long-term Effectiveness (Nova Science Publishers Inc, 2014).
Fitzpatrick, D. A. Implantable Electronic Medical Devices.
Sennaroglu, L. Cochlear implantation in inner ear malformations—A review article. Cochlear Implants Int. 11, 4–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/cii.416 (2010).
Dodds, C.W.D., Byrnes-Preston, P.J., Rendl, M., Lovell, N.H. & Suaning, G.J. in Proceedings of the 4th International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering. 88–91.
Dowling, J. Current and future prospects for optoelectronic retinal prostheses. Eye 23, 1999–2005. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2008.385 (2009).
Suaning, G. J., Lovell, N. H., Schindhelm, K. & Coroneo, M. T. The bionic eye (electronic visual prosthesis): A review. Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthalmol. 26, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.1998.tb01310.x (1998).
Shepherd, R. K., Shivdasani, M. N., Nayagam, D. A., Williams, C. E. & Blamey, P. J. Visual prostheses for the blind. Trends Biotechnol 31, 562–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.07.001 (2013).
Guenther, T., Lovell, N. H. & Suaning, G. J. Bionic vision: System architectures—A review. Expert Rev. Med. Dev. 9, 33–48. https://doi.org/10.1586/erd.11.58 (2012).
Maynard, E. M. Visual prostheses. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 3, 145–168. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.3.1.145 (2001).
Weiland, J. D. & Humayun, M. S. Intraocular retinal prosthesis. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 25, 60–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/MEMB.2006.1705748 (2006).
Chan, D. T. M. et al. Complications of deep brain stimulation: A collective review. Asian J. Surg. 32, 258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1015-9584(09)60404-8 (2009).
Navarro, X. et al. A critical review of interfaces with the peripheral nervous system for the control of neuroprostheses and hybrid bionic systems. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 10, 229–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1085-9489.2005.10303.x (2005).
Obeso, J. A. O., Rodriguez-Oroz, M. C., Krack, P., Kumar, R. & Lang, A. E. Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 956–963. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa000827 (2001).
Aryan, N. P. et al. 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 2866–2869 (2011).
Ullah, N. & Omanovic, S. Large charge-storage-capacity iridium/ruthenium oxide coatings as promising material for neural stimulating electrodes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 159, 119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.03.061 (2015).
Cogan, S. F. Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No .03CH37439). Vol. 3794. 3798–3801.
Prochazka, A., Mushahwar, V. K. & McCreery, D. B. Neural prostheses. J. Physiol. 533, 99–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0099b.x (2001).
Cogan, S. F. Neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 10, 275–309. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160518 (2008).
Merrill, D. R. Review of electrical stimulation in cerebral palsy and recommendations for future directions. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 51(Suppl 4), 154–165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8749.2009.03420.x (2009).
Wessling, B., Mokwa, W. & Schnakenberg, U. RF-sputtering of iridium oxide to be used as stimulation material in functional medical implants. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, S142–S148. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/16/6/s21 (2006).
Robblee, L. S., McHardy, J., Marston, J. M. & Brummer, S. B. Electrical stimulation with Pt electrodes. V. The effect of protein on Pt dissolution. Biomaterials 1, 135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(80)90035-6 (1980).
Taylor, R. S. et al. The cost effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation in the treatment of pain: A systematic review of the literature. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 27, 370–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2003.09.009 (2004).
Grider, J. S. et al. Effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation in chronic spinal pain: A systematic review. Pain Phys. 19, E33-54 (2016).
Linderoth, B. & Foreman, R. D. Physiology of spinal cord stimulation: Review and update. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural Interface 2, 150–164. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1403.1999.00150.x (1999).
Frey, M. E. et al. Spinal cord stimulation for patients with failed back surgery syndrome: A systematic review. Pain Phys. 12, 379–397 (2009).
Siddiqui, N. Y., Wu, J. M. & Amundsen, C. L. Efficacy and adverse events of sacral nerve stimulation for overactive bladder: A systematic review. Neurourol. Urodyn. 29, S18–S23. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.20786 (2010).
Leng, W. W. & Chancellor, M. B. How sacral nerve stimulation neuromodulation works. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 32, 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ucl.2004.09.004 (2005).
Malouf, A. J., Vaizey, C. J., Nicholls, R. J. & Kamm, M. A. Permanent sacral nerve stimulation for fecal incontinence. Ann. Surg. 232, 143–148. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200007000-00020 (2000).
Kamm, M. A. et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for intractable constipation. Gut 59, 333. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2009.187989 (2010).
Schmidt Richard, A. et al. Sacral nerve stimulation for treatment of refractory urinary urge incontinence. J. Urol. 162, 352–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(05)68558-8 (1999).
Jarrett, M. E. D. et al. Systematic review of sacral nerve stimulation for faecal incontinence and constipation. BJS (Br. J. Surg.) 91, 1559–1569. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4796 (2004).
Handforth, A. et al. Vagus nerve stimulation therapy for partial-onset seizures. Neurology 51, 48. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.51.1.48 (1998).
Schachter, S. C. & Saper, C. B. Vagus nerve stimulation. Epilepsia 39, 677–686. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1157.1998.tb01151.x (1998).
Howland, R. H. Vagus nerve stimulation. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 1, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40473-014-0010-5 (2014).
Plachta, D. T. et al. Blood pressure control with selective vagal nerve stimulation and minimal side effects. J. Neural Eng. 11, 036011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/11/3/036011 (2014).
Albert, G. C., Cook, C. M., Prato, F. S. & Thomas, A. W. Deep brain stimulation, vagal nerve stimulation and transcranial stimulation: An overview of stimulation parameters and neurotransmitter release. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 33, 1042–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.04.006 (2009).
Amar, A. P. Vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of intractable epilepsy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 7, 1763–1773. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.7.12.1763 (2007).
Cagnan, H., Denison, T., McIntyre, C. & Brown, P. Emerging technologies for improved deep brain stimulation. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0244-6 (2019).
Bergey, G. K. Neurostimulation in the treatment of epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 244, 87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.04.004 (2013).
Shealy, C., Mortimer, J. & Reswick, J. Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns: Preliminary clinical report. Anesth. Analg. 46, 489–491 (1967).
Aló, K. M. & Holsheimer, J. New trends in neuromodulation for the management of neuropathic pain. Neurosurgery 50, 690–704. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200204000-00003 (2002).
Melzack, R. & Wall, P. D. Pain Mechanisms: A New Theory. Science 150, 971–979 (1965).
Thompson, D. M., Koppes, A. N., Hardy, J. G. & Schmidt, C. E. Electrical stimuli in the central nervous system microenvironment. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 16, 397–430. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-121813-120655 (2014).
Holtzheimer, P. E. & Mayberg, H. S. Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disorders. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 34, 289–307. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113638 (2011).
Gardner, J. A history of deep brain stimulation: Technological innovation and the role of clinical assessment tools. Soc. Stud. Sci. 43, 707–728. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306312713483678 (2013).
Williams, N. R. & Okun, M. S. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) at the interface of neurology and psychiatry. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 4546–4556. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci68341 (2013).
Bronstein, J. M. et al. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: An expert consensus and review of key issues. Arch. Neurol. 68, 165. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2010.260 (2011).
Deuschl, G. et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 355, 896–908. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa060281 (2006).
Henle, C. et al. First long term in vivo study on subdurally implanted micro-ECoG electrodes, manufactured with a novel laser technology. Biomed. Microdev. 13, 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9471-9 (2011).
Pistohl, T., Ball, T., Schulze-Bonhage, A., Aertsen, A. & Mehring, C. Prediction of arm movement trajectories from ECoG-recordings in humans. J. Neurosci. Methods 167, 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.10.001 (2008).
Schuettler, M. et al. 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 1612–1615.
Raspopovic, S. et al. Restoring natural sensory feedback in real-time bidirectional hand prostheses. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 222219. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006820 (2014).
Donoghue, J. P., Nurmikko, A., Black, M. & Hochberg, L. R. Assistive technology and robotic control using motor cortex ensemble-based neural interface systems in humans with tetraplegia. J. Physiol. 579, 603–611. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.127209 (2007).
Hochberg, L. R. et al. Reach and grasp by people with tetraplegia using a neurally controlled robotic arm. Nature 485, 372–375. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11076 (2012).
Stieglitz, T. et al. Neurotherapy: Progress in Restorative Neuroscience and Neurology Progress in Brain Research. 297–315 (2009).
Homer, M. L., Nurmikko, A. V., Donoghue, J. P. & Hochberg, L. R. Sensors and decoding for intracortical brain computer interfaces. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 15, 383–405. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071910-124640 (2013).
Boehler, C., Stieglitz, T. & Asplund, M. Nanostructured platinum grass enables superior impedance reduction for neural microelectrodes. Biomaterials 67, 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.036 (2015).
Bradley, K. The technology: The anatomy of a spinal cord and nerve root stimulator: The lead and the power source. Pain Med. 7, S27–S34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4637.2006.00120.x (2006).
Normann, R. A. & Fernandez, E. Clinical applications of penetrating neural interfaces and Utah electrode array technologies. J. Neural Eng. 13, 061003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/13/6/061003 (2016).
Hayden, C. J. & Dalton, C. Direct patterning of microelectrode arrays using femtosecond laser micromachining. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 3761–3766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.01.022 (2010).
Green, R. A. et al. Cytotoxicity of implantable microelectrode arrays produced by laser micromachining. Biomaterials 31, 886–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.09.099 (2010).
Green, R. A., Lovell, N. H., Wallace, G. G. & Poole-Warren, L. A. Conducting polymers for neural interfaces: Challenges in developing an effective long-term implant. Biomaterials 29, 3393–3399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.04.047 (2008).
Hoh, G., Tamm, A., Schier, M. & Schaldach, M. A comparative study of the sensing behavior of electroactive coated catheter electrodes versus conventional electrodes. Prog. Biomed. Res. 98, 18–21 (1998).
Daubinger, P., Kieninger, J., Unmussig, T. & Urban, G. A. Electrochemical characteristics of nanostructured platinum electrodes—A cyclic voltammetry study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 8392–8399. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp00342j (2014).
Norlin, A., Pan, J. & Leygraf, C. Investigation of electrochemical behavior of stimulation/sensing materials for pacemaker electrode applications II. Conducting oxide electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1933372 (2005).
Green, R. A. et al. Laser patterning of platinum electrodes for safe neurostimulation. J. Neural Eng. 11, 056017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/11/5/056017 (2014).
Beebe, X. & Rose, T. L. Charge injection limits of activated iridium oxide electrodes with 0.2 ms pulses in bicarbonate buffered saline (neurological stimulation application). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 35, 494–495. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.2122 (1988).
Harris, A. R., Paolini, A. G. & Wallace, G. G. Effective area and charge density of iridium oxide neural electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 230, 285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.02.002 (2017).
Zeng, Q. et al. Electrodeposited iridium oxide on platinum nanocones for improving neural stimulation microelectrodes. Electrochim. Acta 237, 152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.213 (2017).
Negi, S., Bhandari, R., Rieth, L. & Solzbacher, F. In vitro comparison of sputtered iridium oxide and platinum-coated neural implantable microelectrode arrays. Biomed. Mater. 5, 15007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/5/1/015007 (2010).
Cogan, S. F., Troyk, P. R., Ehrlich, J. & Plante, T. D. In vitro comparison of the charge-injection limits of activated iridium oxide (AIROF) and platinum-iridium microelectrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52, 1612–1614. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2005.851503 (2005).
Weiland, J. D., Anderson, D. J. & Humayun, M. S. In vitro electrical properties for iridium oxide versus titanium nitride stimulating electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49, 1574–1579. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2002.805487 (2002).
Wessling, B. R., Besmehn, A., Mokwa, W. & Schnakenberg, U. Reactively sputtered iridium oxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2713691 (2007).
Nguyen, C. M. et al. Sol-gel deposition of iridium oxide for biomedical micro-devices. Sensors (Basel) 15, 4212–4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150204212 (2015).
Cogan, S. F., Plante, T. D. & Ehrlich, J. The 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 4153–4156.
Slavcheva, E., Vitushinsky, R., Mokwa, W. & Schnakenberg, U. Sputtered iridium oxide films as charge injection material for functional electrostimulation. J. Electrochem. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1747881 (2004).
Cogan, S. F. et al. Sputtered iridium oxide films for neural stimulation electrodes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 89, 353–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31223 (2009).
Cogan, S. F., Ludwig, K. A., Welle, C. G. & Takmakov, P. Tissue damage thresholds during therapeutic electrical stimulation. J. Neural Eng. 13, 021001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/13/2/021001 (2016).
Taylor, G. et al. Investigation of iridium, ruthenium, rhodium, and palladium binary metal oxide solid solution thin films for implantable neural interfacing applications. Surface and Coatings Technology 426, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127803 (2021).
Taylor, G. et al. Electrochemical enhancement of reactively sputtered rhodium, ruthenium, and iridium oxide thin films for neural modulation, sensing, and recording applications. Electrochim. Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.139118 (2021).
Page, N. et al. The effect of deposition parameters on microstructure and electrochemical performance of reactively sputtered iridium oxide coatings. Mater. Today Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102967 (2021).
Outten, C. A., Konopka, D. W. & Fennessey, T. F. Society of Vacuum Coaters, 57th Annual Technical Conference Proceedings, Chicago.
Meijs, S. et al. Electrochemical properties of titanium nitride nerve stimulation electrodes: An in vitro and in vivo study. Front. Neurosci. 9, 268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00268 (2015).
Li, M., Zhou, Q. & Duan, Y. Y. Nanostructured porous platinum electrodes for the development of low-cost fully implantable cortical electrical stimulator. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.053 (2015).
Boretius, T. et al. 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 5404–5407 (2011).
Xia, K., Sun, B., Zeng, Q., Wu, T. & Humayun, M. S. 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS). 291–294 (2017).
Green, R. A. et al. Performance of conducting polymer electrodes for stimulating neuroprosthetics. J. Neural Eng. 10, 016009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/10/1/016009 (2013).
Green, R. A. et al. Substrate dependent stability of conducting polymer coatings on medical electrodes. Biomaterials 33, 5875–5886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.05.017 (2012).
Latif, T., McKnight, M., Dickey, M. D. & Bozkurt, A. In vitro electrochemical assessment of electrodes for neurostimulation in roach biobots. PLoS ONE 13, e0203880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203880 (2018).
Du, Z. J., Luo, X., Weaver, C. & Cui, X. T. Poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-ionic liquid coating improves neural recording and stimulation functionality of MEAs. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 3, 6515–6524. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TC00145E (2015).
Xiao, Y. et al. Electrochemical polymerization of poly(hydroxymethylated-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT-MeOH) on multichannel neural probes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 99, 437–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2003.12.067 (2004).
Green, R. & Abidian, M. R. Conducting polymers for neural prosthetic and neural interface applications. Adv. Mater. 27, 7620–7637. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501810 (2015).
Driscoll, N. et al. Fabrication of Ti3C2 MXene microelectrode arrays for in vivo neural recording. J. Vis. Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/60741 (2020).
Driscoll, N. et al. Two-dimensional Ti3C2 MXene for high-resolution neural interfaces. ACS Nano 12, 10419–10429. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b06014 (2018).
Wang, K., Fishman, H. A., Dai, H. & Harris, J. S. Neural stimulation with a carbon nanotube microelectrode array. Nano Lett. 6, 2043–2048. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl061241t (2006).
Voge, C. M. & Stegemann, J. P. Carbon nanotubes in neural interfacing applications. J. Neural Eng. 8, 011001. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/8/1/011001 (2011).
Ben-Jacob, E. & Hanein, Y. Carbon nanotube micro-electrodes for neuronal interfacing. J. Mater. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/b805878b (2008).
Keefer, E. W., Botterman, B. R., Romero, M. I., Rossi, A. F. & Gross, G. W. Carbon nanotube coating improves neuronal recordings. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 434–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.174 (2008).
Seidlits, S. K., Lee, J. Y. & Schmidt, C. E. Nanostructured scaffolds for neural applications. Nanomedicine 3, 183–199. https://doi.org/10.2217/17435889.3.2.183 (2008).
Park, S., Song, Y. J., Boo, H. & Chung, T. D. Nanoporous Pt microelectrode for neural stimulation and recording: In vitro characterization. J. Phys. Chem. 114, 8721–8726. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp911256h (2010).
Maher, M., Pine, J., Wright, J. & Tai, Y.-C. The neurochip: A new multielectrode device for stimulating and recording from cultured neurons. J. Neurosci. Methods 87, 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0270(98)00156-3 (1999).
Cogan, S. F., Guzelian, A. A., Agnew, W. F., Yuen, T. G. & McCreery, D. B. Over-pulsing degrades activated iridium oxide films used for intracortical neural stimulation. J. Neurosci. Methods 137, 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.02.019 (2004).
Mailley, S. C., Hyland, M., Mailley, P., McLaughlin, J. M. & McAdams, E. T. Electrochemical and structural characterizations of electrodeposited iridium oxide thin-film electrodes applied to neurostimulating electrical signal. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 21, 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-4931(02)00098-X (2002).
Schuettler, M., Stiess, S., King, B. V. & Suaning, G. J. Fabrication of implantable microelectrode arrays by laser cutting of silicone rubber and platinum foil. J. Neural Eng. 2, S121-128. https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2560/2/1/013 (2005).
Cui, X. T. & Zhou, D. D. Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for chronic neural stimulation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 15, 502–508. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2007.909811 (2007).
Jan, E. et al. Layered carbon nanotube-polyelectrolyte electrodes outperform traditional neural interface materials. Nano Lett. 9, 4012–4018. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl902187z (2009).
Aregueta-Robles, U. A., Woolley, A. J., Poole-Warren, L. A., Lovell, N. H. & Green, R. A. Organic electrode coatings for next-generation neural interfaces. Front. Neuroeng. 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneng.2014.00015 (2014).
Weremfo, A., Carter, P., Hibbert, D. B. & Zhao, C. Investigating the interfacial properties of electrochemically roughened platinum electrodes for neural stimulation. Langmuir 31, 2593–2599. https://doi.org/10.1021/la504876n (2015).
Tykocinski, M., Duan, Y., Tabor, B. & Cowan, R. S. Chronic electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve using high surface area (HiQ) platinum electrodes. Hear. Res. 159, 53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5955(01)00320-3 (2001).
Schuettler, M. Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS. 186–189.
Fisk, A. E. Biocompatible Implantable Electrode. U.S.A. Patent (2013).
Christian Henle, S., Member, Juan S. Ordonez, Thomas Stieglitz. 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference. 4208–4211.
Green, R. A. H. T., Dodds, C. & Lovell, N. H. Variation in performance of platinum electrodes with size and surface roughness. Sens. Mater. 24, 165–180 (2012).
Stover, T. et al. Development of a drug delivery device: Using the femtosecond laser to modify cochlear implant electrodes. Cochlear Implants Int. 8, 38–52. https://doi.org/10.1179/cim.2007.8.1.38 (2007).
Zhang, J. A Comparison of the Effects of Surface Topography on Electrode Performance in an Artificial Suprachoroidal Interstitial Fluid (University of New South Wales, 2016).
Rohrig, M., Thiel, M., Worgull, M. & Holscher, H. 3D direct laser writing of nano- and microstructured hierarchical gecko-mimicking surfaces. Small 8, 3009–3015. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200308 (2012).
Zhang, F. & Low, H. Y. Anisotropic wettability on imprinted hierarchical structures. Langmuir 23, 7793–7798. https://doi.org/10.1021/la700293y (2007).
Xiu, Y., Zhu, L., Hess, D. W. & Wong, C. P. Biomimetic creation of hierarchical surface structures by combining colloidal self-assembly and Au sputter deposition. Langmuir 22, 9676–9681. https://doi.org/10.1021/la061698i (2006).
Koch, K., Bhushan, B., Jung, Y. C. & Barthlott, W. Fabrication of artificial Lotus leaves and significance of hierarchical structure for superhydrophobicity and low adhesion. Soft Matter https://doi.org/10.1039/b818940d (2009).
Lee, Y., Park, S. H., Kim, K. B. & Lee, J. K. Fabrication of hierarchical structures on a polymer surface to mimic natural superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Mater. 19, 2330–2335. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200700820 (2007).
Greiner, C., Arzt, E. & del Campo, A. Hierarchical Gecko-like adhesives. Adv. Mater. 21, 479–482. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801548 (2009).
Kunz, C., Muller, F. A. & Graf, S. Multifunctional hierarchical surface structures by femtosecond laser processing. Materials (Basel) https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050789 (2018).
Papadopoulou, E. L. et al. Reversible photoinduced wettability transition of hierarchical ZnO structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 2891–2895. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8085057 (2009).
Cortese, B. et al. Superhydrophobicity due to the hierarchical scale roughness of PDMS surfaces. Langmuir 24, 2712–2718. https://doi.org/10.1021/la702764x (2008).
Erbil, H. Y., Demirel, A. L., Avci, Y. & Mert, O. Transformation of a simple plastic into a superhydrophobic surface. Science 299, 1377–1380 (2003).
Lee, W., Jin, M.-K., Yoo, W.-C. & Lee, J.-K. Nanostructuring of a polymeric substrate with well-defined nanometer-scale topography and tailored surface wettability. Langmuir 20, 7665–7669. https://doi.org/10.1021/la049411+ (2004).
Guo, C. et al. Large-area fabrication of a nanostructure-induced hydrophobic surface from a hydrophilic polymer. ChemPhysChem 5, 750–753. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200400013 (2004).
Feng, X. J. & Jiang, L. Design and creation of superwetting/antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 18, 3063–3078. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200501961 (2006).
Zhai, L., Cebeci, F. Ç., Cohen, R. E. & Rubner, M. F. Stable superhydrophobic coatings from polyelectrolyte multilayers. Nano Lett. 4, 1349–1353. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl049463j (2004).
Yu, E., Kim, S. C., Lee, H. J., Oh, K. H. & Moon, M. W. Extreme wettability of nanostructured glass fabricated by non-lithographic, anisotropic etching. Sci. Rep. 5, 9362. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09362 (2015).
Liu, M., Wang, S., Wei, Z., Song, Y. & Jiang, L. Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv. Mater. 21, 665–669. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200801782 (2009).
Ming, W., Wu, D., van Benthem, R. & de With, G. Superhydrophobic films from raspberry-like particles. Nano Lett. 5, 2298–2301. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl0517363 (2005).
Pronko, P. P. et al. Machining of sub-micron holes using a femtosecond laser at 800 nm. Opt. Commun. 114, 106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(94)00585-I (1995).
Korte, F. et al. Towards nanostructuring with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. A 77, 229–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-003-2110-z (2003).
Chichkov, B. N., Momma, C., Nolte, S., von Alvensleben, F. & Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 63, 109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567637 (1996).
Nedialkov, N. N., Imamova, S. E. & Atanasov, P. A. Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37, 638–643. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/37/4/016 (2004).
Momma, C. et al. Short-pulse laser ablation of solid targets. Opt. Commun. 129, 134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(96)00250-7 (1996).
Yin, K. et al. Femtosecond laser thermal accumulation-triggered micro-/nanostructures with patternable and controllable wettability towards liquid manipulating. Nano-Micro Lett. 14, 97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00840-6 (2022).
Wu, T. et al. Femtosecond laser textured porous nanowire structured glass for enhanced thermal imaging. Chin. Opt. Lett. 20, 033801 (2022).
Yin, K. et al. Femtosecond laser induced robust periodic nanoripple structured mesh for highly efficient oil–water separation. Nanoscale 9, 14229–14235. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR04582D (2017).
Wu, Z. et al. Recent advances in femtosecond laser-structured Janus membranes with asymmetric surface wettability. Nanoscale 13, 2209–2226. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR06639G (2021).
Vorobyev, A. Y. & Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photon. Rev. 7, 385–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.201200017 (2013).
Ashitkov, S. I. et al. Ablation and nanostructuring of metals by femtosecond laser pulses. Quantum Electron. 44, 535–539. https://doi.org/10.1070/QE2014v044n06ABEH015448 (2014).
Vorobyev, A. Y. & Guo, C. Femtosecond laser nanostructuring of metals. Opt. Exp. 14, 2164–2169. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.14.002164 (2006).
Ling, E. J. Y. et al. Investigating and understanding the effects of multiple femtosecond laser scans on the surface topography of stainless steel 304 and titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 353, 512–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.137 (2015).
Oliveira, V., Polushkin, N. I., Conde, O. & Vilar, R. Laser surface patterning using a Michelson interferometer and femtosecond laser radiation. Opt. Laser Technol. 44, 2072–2075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.03.024 (2012).
Vorobyev, A. Y. & Guo, C. Multifunctional surfaces produced by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4905616 (2015).
Vorobyev, A. Y., Makin, V. S. & Guo, C. Periodic ordering of random surface nanostructures induced by femtosecond laser pulses on metals. J. Appl. Phys. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2432288 (2007).
Tommaso Baldacchini, J. E. C., Zhou, M. & Mazur, E. Superhydrophobic surfaces prepared by microstructuring of silicon using a femtosecond laser. Langmuir 22, 4917–4919 (2006).
Simon, P. & Ihlemann, J. Ablation of submicron structures on metals and semiconductors by femtosecond UV-laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 109–110, 25–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(96)00615-0 (1997).
Chimmalgi, A., Choi, T. Y., Grigoropoulos, C. P. & Komvopoulos, K. Femtosecond laser aperturless near-field nanomachining of metals assisted by scanning probe microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1146–1148. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1555693 (2003).
Wu, C. et al. Near-unity below-band-gap absorption by microstructured silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1850–1852. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1358846 (2001).
Pereira, A. et al. Surface nanostructuring of metals by laser irradiation: Effects of pulse duration, wavelength and gas atmosphere. Appl. Phys. A 79, 1433–1437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2804-x (2004).
Koch, J. et al. Nanotexturing of gold films by femtosecond laser-induced melt dynamics. Appl. Phys. A 81, 325–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3212-6 (2005).
Eversole, D., Luk’yanchuk, B. & Ben-Yakar, A. Plasmonic laser nanoablation of silicon by the scattering of femtosecond pulses near gold nanospheres. Appl. Phys. A 89, 283–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-4166-7 (2007).
Nakata, Y., Okada, T. & Maeda, M. Lithographical laser ablation using femtosecond laser. Appl. Phys. A 79, 1481–1483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2825-5 (2004).
Békési, J., Klein-Wiele, J. H. & Simon, P. Efficient submicron processing of metals with femtosecond UV pulses. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 76, 355–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-002-1820-y (2003).
Bonse, J., Hohm, S., Kirner, S. V., Rosenfeld, A. & Kruger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures—A scientific evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstqe.2016.2614183 (2017).
Phoulady, A. et al. Rapid high-resolution volumetric imaging via laser ablation delayering and confocal imaging. Scientific Reports 12(1), 12277. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16519-2 (2022).
May, N., Choi, H., Phoulady, A., Tavousi, P. & Shahbazmohamadi, S. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Printed Circuit Boards: Comparative Study between 3D Femtosecond Laser Serial Sectioning and Optical Imaging versus 3D X-Ray Computed Tomography. Microsc. Microanal. 28(S1), 284–286. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1431927622001945 (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to conducting experiments, data analysis and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Amini, S., Seche, W., May, N. et al. Femtosecond laser hierarchical surface restructuring for next generation neural interfacing electrodes and microelectrode arrays. Sci Rep 12, 13966 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18161-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18161-4
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.