Abstract
Mass-wasting of ocean island volcanoes is a well-documented phenomenon. Massive flank collapses may imply tens to hundreds of km3 and generate mega-tsunamis. However, the causal links between this large-scale, low-frequency instability, and the time–space evolution of magma storage, crystal fractionation/accumulation, lithospheric assimilation, and partial melting remains unclear. This paper aims at tracking time variations and links between lithospheric, crustal and surface processes before and after a major flank collapse (Monte Amarelo collapse ca. 70 ka) of Fogo volcano, Cape Verde Islands, by analysing the chemical composition (major, trace elements, and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopes) and age-controlled stratigraphy (K–Ar and Ar–Ar dating) of lavas along vertical sections (Bordeira caldera walls). The high-resolution sampling allows detecting original variations of composition at different time-scales: (1) a 60 kyrs-long period of increase of magma differentiation before the collapse; (2) a 10 kyrs-long episode of reorganization of magma storage and evacuation of residual magmas (enriched in incompatible elements) after the collapse; and (3) a delayed impact at the lithospheric scale ~ 50 kyrs after the collapse (increasing EM1-like materiel assimilation).
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Among the largest landslides on Earth (tens to hundreds of km3) occur on the flanks of ocean island volcanoes such as Hawaii, La Réunion, the Canary or the Cape Verde Islands1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9. The influence of external parameters such as climate and sea-level variations has been debated6,10,11,12, but large-scale flank instability of ocean island volcanoes seems closely linked to their volcanic and intrusive history. Indeed, mechanisms of feedback between gravitational instability, structural discontinuities and the intrusive system have been appraised13,14,15,16,17,18,19. Most of these studies focused on edifice-scale processes, without considering deeper (lithospheric) processes. Numerical simulations20 indicate that a massive flank collapse may induce pressure changes at depth down to magma storages in the uppermost mantle (~ 20–40 km), thus accounting for observed variations in magma composition after the collapse21,22,23,24,25,26.
This paper aims at tracking potential variations of magma source, partial melting conditions, lithospheric assimilation, levels of storage, crystal accumulation, and fractional crystallisation of lavas emitted at Fogo Island volcano, Cape Verde, before and after a massive flank collapse. The classic top-down approach of the problem (i.e. what are the consequences of the collapse on magma plumbing system and eventually on mantle melting?) is combined with an innovative bottom-up approach (i.e. does the collapse reflect a particular evolution at the source of the magmas, variations of the levels of storage?). We focus on the last 160 kyrs, with a major flank collapse (130–160 km3) at ~ 60–70 ka27,28,29,30,31,32. The walls of the horseshoe-shaped collapse caldera (Bordeira on Fig. 1) provides the opportunity for a complete sampling (Table S1) of (a) pre-collapse lavas of the caldera walls, (b) wall-top early post-collapse lavas cut by erosion, (c) post-collapse lavas cascading down wall, and (e) caldera floor lavas (Fig. 1).
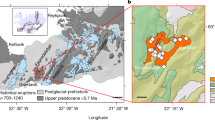
Location map of sampling sites on Fogo Island (Cape Verde archipelago). (1) Western caldera wall; (2) northern caldera wall; (3) southern caldera wall; (4) south-eastern coast; (5) north-eastern coast. Two types of samples are distinguished: samples pre-dating the Monte Amarelo flank collapse (68 ka), and post-collapse samples found on (1) top of the caldera rim, (2) cascading on the wall, or (3) on the caldera floor. Blue and red squares correspond respectively to pre-collapse and post-collapse samples. Shaded relief view derived from the DEMFI (2010) 5 m digital elevation model. Maps realised using QGIS 3.14 (https://www.qgis.org).
New insights on the volcanic history of Fogo Island
The Cape Verde Islands are considered as the surface expression of a mantle plume at 500–800 km west of the African continental margin33,34,35. The spatial and chronological evolution of volcanic activity, from East to West, is consistent with the slow progression of the African plate over the hotspot since at least the Oligocene, with a decoupling between two distinct branches at ca. 5 Ma36. All islands exhibit Quaternary volcanism except Boa Vista and Maio, but Fogo was the only active volcano of the archipelago for the last five centuries37,38,39.
Fogo Island has the morphology of a shield volcano overtopped by a steeper stratovolcano that is truncated by an 8 km-wide horseshoe-shaped caldera opened to the east (Fig. 1: Bordeira). The caldera is bounded on its northern, western and southern sides by steep walls up to 1000 m high offering an open book on the eruptive and intrusive evolution of the volcanic edifice. The origin of the caldera is still debated: a pure gravitational model implying at least one massive flank collapse of the eastern flank of the volcano27,31,32, and a hybrid model combining central subsidence (caldera collapse s.s.) and flank collapse30,40,41. The caldera floor is filled by post-caldera volcanism, including the growth of the Pico do Fogo central cone and historical lavas. The volcanic history of Fogo Island is poorly documented, although different stages of growth separated by major unconformities were distinguished27,32,38. Uplifted lavas of the seamount stage are exposed in valleys of the western part of the island together with carbonatite dated 5.1 to 3.2 Ma42,43. The early subaerial stage (lower shield), exposed in the northern valleys and in the lower part of the caldera walls, is not chronologically well constrained, with only one lava flow dated 212 ± 20 ka (K–Ar) at the base of the caldera wall31. The lavas produced during this stage range from nephelinite and melilitite, to phonolite. Eroded remnants of the lower shield are overlapped by an upper shield, the Monte Amarelo edifice32, thus forming a major erosional unconformity that is clearly visible on the walls of the caldera (Fig. S1). The Monte Amarelo stage is characterised by the growth of a ~ 3000 m high central edifice with poorly-defined peripheral rift-zones32. The central part of this edifice is densely intruded by dykes and sills, as observed all along the western caldera wall.
Our new K–Ar and 40Ar/39Ar ages of lava flows (Tables S2 & S3) allow the dating of the early activity of the Amarelo shield at 160 ± 4 ka on the northern caldera wall (Fig. S1), and 135 ± 4 ka on the western wall (Fig. S2). The northern rift-zone was particularly active between 160 and 122 ka. Waning of activity to the north at ~ 120 ka coincides with enhanced activity of the central edifice, including explosive activity. Indeed, thick units of ignimbrites represent half of the material accumulated along the western wall, which contrasts with the absence of explosive products on the northern wall (Fig. S2). Interestingly, it is possible to correlate the ignimbrite units with tephra layers observed in deep-sea cores44. A major tephra layer dated 145 ka44 might in fact correspond to the ignimbrite observed at the base of the western caldera wall (sample Fo-22 > 135 ka on Fig. S2). Other marine tephra layers at 117 and 88 ka are also concordant with the stratigraphic position of the main ignimbrites found on the western caldera wall. The latest ignimbrite is found on the caldera rim or intercalated with the uppermost pre-collapse lava flows (Figs. S2 & S3). The recurrence of eruptions producing ignimbrites at Fogo, as reported here for the first time, corroborates the existence of caldera collapse structures in the central part of the volcanic edifice30,40,41.
New constraints on the age of the Monte Amarelo collapse
The eastern flank of the Monte Amarelo edifice was destroyed by a massive flank failure leading to the formation of the horseshoe-shaped caldera5,28,30,32. Multibeam bathymetry of the eastern flanks of Fogo Island5,45 confirmed the existence of a large debris avalanche deposit covering 6820 km2 with a volume > 160 km3 and a thickness of 100–400 m. The age of the Monte Amarelo collapse was previously inferred from (a) 3He exposure ages of pre-collapse (~ 123 ka) and early post-collapse (~ 62 ka) lava flows on Fogo27; (b) 3He exposure ages of megaclasts transported by the collapse-generated tsunami on Santiago Island (65–84 ka29), (c) and K–Ar ages of pre-collapse (~ 60 ka) and post-collapse (43 ka) lava flows of the caldera walls31.
Our K–Ar and 40Ar/39Ar ages give a more precise age of ~ 68 ka for the Monte Amarelo collapse (Fig. 1). Indeed, the uppermost pre-collapse lava flow of the southern caldera wall, which is K–Ar dated 69 ± 2 ka (Fig. S3 & Table S2), is overlain by a post-collapse lava flow which is 40Ar/39Ar dated 66.9 ± 8.3 ka (Table S3). A post-collapse lava flow overlapping the northern caldera rim has an age of 59 ± 10 ka (Fig. S1), that is concordant with the ages previously obtained on similar wall top lavas31. Two post-collapse lava flows cascading from the steep slopes of the caldera wall are dated at 21 ± 2 ka (southern wall), and 20 ± 2 ka (western wall, above a lava previously dated 43 ka31). The oldest post-collapse lava flow exposed along the eastern coast is 35 ± 4 ka old (Table S2). Using a first-order reconstruction of the Monte Amarelo edifice before and after its collapse, we estimate a pre-collapse growth rate of 2.2 km3/ka (~ 200 km3 of lavas produced between 160 and 68 ka), which is relatively high compared to growth rates calculated for the Canary Islands46,47,48. Post-collapse volcanism represents a volume of 74 km3 filling the collapse scar at a lower rate of 1.1 km3/ka (< 68 ka).
Sources and processes controlling the composition of the magmas
Silicate lavas of the Cape Verde Islands are ranging from foidites and basanites, to phonolites and trachytes33,34,49. Lavas of the southern islands are slightly more alkaline than those of the northern islands34. Intrusive and extrusive carbonatites found on São Vicente, Maio, Santiago, Fogo and Brava are interpreted as resulting or deriving from the partial melting of a carbonated oceanic crust50,51,52,53. Mixing models accounting for the spatial variability of the isotopic signature (Sr–Nd–Pb–He–Os) of the Cape Verde Islands have been proposed33,34,54,55,56,57,58,59. Isotopic and trace element compositions of the lavas of the southern islands suggest a mixture between a moderate HIMU-like (High µ = high 238U/204Pb) end-member and an EM1-like (Enriched Mantle 1) end-member during magma differentiation at shallow depth34,56. The HIMU component is commonly explained by the recycling of a Proterozoic oceanic crust by the mantle plume, while the origin of the enriched component has been debated (lithospheric56,57 or asthenospheric58). The existence of a third component similar in composition to the Depleted MORB Mantle (DMM) was proposed57, but in a very small proportion in the southern islands. Some Cape Verde basalts have also experienced shallow-level contamination by oceanic crustal material (i.e., Jurassic MORB basement)34, especially in São Nicolau Island, but this interaction is negligible (possibly non-existent) for Fogo lavas57. The overall isotopic (Sr–Nd–Pb) composition of the 48 lava samples collected in Fogo (Fig. S4) is concordant with the model of two main components, with an EM1 component reflecting the assimilation of fragments of continental lithosphere incorporated in the oceanic lithosphere during the opening of the Atlantic Ocean57. Interestingly, 206Pb/204Pb vs. 208Pb/204Pb and 87Sr/86Sr vs. 143Nd/144Nd plots of lavas preceding the Monte Amarelo collapse (160–68 ka) do not fully overlap with post-collapse lavas (Fig. S4).
Fogo lavas range from foidites and tephriphonolites (Fig. S5). The ignimbrites observed along the caldera walls have a phonotephritic-to-tephriphonolitic composition, which is concordant with the composition of offshore tephra units44. Major-element compositions are controlled by (a) minor variations in the primitive melt composition, and (b) fractionation/accumulation of crystals, mainly pyroxene and olivine. This was previously demonstrated24,60,61, and it is also confirmed by the negative correlation between incompatible elements and MgO (Fig. S6), in agreement with highly variable phenocryst content inferred from petrographic observations. Megacrystals are most often not in equilibrium with the melt, and they can be classified as antecrysts from a former magmatic stage. Mass balance calculations (Fig. S7) indicate that the whole rock composition of the lavas implies a crystal fractionation of up to 50% (mostly involving clinopyroxene and amphibole, with lesser proportions of Fe–Ti oxides, apatite, and olivine), and an accumulation of up to 40% (mostly clinopyroxene, olivine ± Fe–Ti oxides). This is in good agreement with the modal compositions of the most commonly observed lavas, where clinopyroxene is often the most abundant megacrysts phase, and with values reported for fractional crystallization of lavas produced by the 1995 eruption60. Magma storage and differentiation occurs in the uppermost mantle at depths between 18 and 28 km60,61, with short-term secondary storages in the crust24,60,61.
Pre-collapse lavas (160–68 ka)
Detailed logging, sampling and dating along the Bordeira caldera walls provide a unique opportunity to address the evolution of magma composition through time, and its possible links with the Monte Amarelo flank collapse (68 ka). Because the major element composition of the primary magmas is almost independent of the source mantle components24,60,61, trends of major element composition of the lavas through time indicate a progressive increase of magma differentiation during the 60 kyrs (~ 130–68 ka) preceding the Monte Amarelo collapse (Fig. 2). Lavas become slightly more alkaline with time, as observed on the SiO2/(Na2O + K2O) trend (Fig. 2A). This temporal evolution of magma composition is likely due to increasing pyroxene (± amphibole) fractionation rather than crystal accumulation, as suggested by the Na2O/MgO and CaO/Al2O3 trends (Fig. 2B,C). Variation of K2O/TiO2 with time displays distinct patterns (Fig. 2D) with high (> 2%) K2O lavas on western caldera wall, and low (< 1.5%) K2O lavas on the southern flanks. Major element composition somehow varies geographically, with lavas being more differentiated near the paleo-centre of the Monte Amarelo edifice (Fig. S9).
The distinct components in the source of the Fogo magmas can be distinguished based on their Pb–Sr isotope compositions34,56. The HIMU component is characterised by a relatively high 206Pb/204Pb but low 87Sr/86Sr, and the EM1 component has low 206Pb/204Pb and high 87Sr/86Sr. The Pb–Sr–Nd isotopic composition of the lavas displays a significant temporal evolution during the last 160 kyrs (Fig. 3), but unlike the major and trace element trends, these variations are not clearly linked to the Monte Amarelo collapse (Fig. 3). The 87Sr/86Sr ratio decreases from 160 to 35 ka, whereas the 143Nd/144Nd ratio shows a slight increase during the same period. The 206Pb/204Pb is characterised by a progressive increase from 160 to 20 ka, with possibly a more pronounced one after the Monte Amarelo flank collapse (68 ka). Near-collapse lavas are characterised by higher 143Nd/144Nd and low 87Sr/86Sr ratios compared to other pre-collapse lavas (Fig. 3). There is thus a long-term increase of the proportion of HIMU component or decline of the EM1 component in the magma source during the pre-collapse period, and this trend persists during 40–50 kyrs after the collapse.
Post-collapse lavas (< 68 ka)
Lavas produced soon after the collapse (68–59 ka) share some similarities with the latest pre-collapse lavas in terms of differentiation (Fig. 2A) and isotopic composition (Fig. 3). However, most of these early post-collapse lavas are considerably enriched in incompatible elements (Fig. 4). All these observations converge to a short-term (~ 10 kyrs after the collapse) evacuation of residual magmas characterized by a low degree of partial melting, as observed on a La/Sm vs La plot (Fig. S8). The eruptive vents of these lavas are all located on the rim of the caldera and their products (lava flows) are found in discontinuity on the pre-collapse lavas, although both pre- and post-collapse lavas are cut by retrogressive erosion of the caldera walls.
Late post-collapse lavas (< 59 ka) are characterized by a degree of differentiation that is similar to early (> 100 ka) pre-collapse lavas, i.e. significantly less differentiated than near-collapse lavas (Fig. 2A). This is not directly linked to crystal fractionation, as indicated by similar Na2O/MgO for late pre-collapse (< 100 ka) and late post-collapse lavas (Fig. 2B). Peripheral post-collapse lavas filling the collapse embayment on the eastern coast are characterized by olivine rather than pyroxene fractionation (e.g. high MgO and CaO/Al2O3, but low Na2O lavas at 30–40 ka on Fig. 2B,C, see also Fig. S8).
Since 20–30 ka, the 87Sr/86Sr ratio increased slightly faster than it was decreasing before the collapse (Fig. 3). The 206Pb/204Pb ratio shows a very fast decline from 19.4 at 20 ka (Table S2: sample Fo-60 dated 20 ka) to < 19.0 for historical lavas, although Mata et al. (2017) reported smaller and shorter-term variations between historical lavas, interpreted as small-scale mantle heterogeneities. After at least 140 kyrs of constant augmentation, the proportion of HIMU component compared to EM1 thus abruptly decreases since 20–30 ka. Although it cannot be definitively proved that the Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic variations illustrated here are connected to the collapse, they most likely correspond to the response to pressure changes at lithospheric depth20 favouring EM1-like materiel assimilation that becomes then a dominant process at the magma source.
Discussion and conclusions
Timescales of astenospheric, lithospheric, and volcanic processes are different, but their respective histories are not disconnected, and the Fogo example provides an original example of interactions between the source and storage of the magmas, and a major volcano flank collapse. In the case of Fogo volcano, major element composition of lavas evidence a progressive magma differentiation due to increasing crystal fractionation during the 60 kyrs preceding the Monte Amarelo flank collapse. This temporal evolution of magma storage in the lithospheric mantle is coeval with the development of shallower reservoirs, including a plutonic complex inside the volcanic edifice itself, and recurrent explosive activity forming ignimbrites. The increasing load of the growing volcano may have promoted magma stagnation, as previously proposed for Teno volcano, Canary Islands23. A similar pre-collapse evolution towards more differentiated products was observed on Taburiente volcano, La Palma, Canary Islands62, but this trend persisted during the early post-collapse stage (Bejenado lavas) until volcanic activity moved to the South, thus building a new shield (Cumbre Vieja). The central edifice of Tenerife provides another example of such correlation between volcano growth, storage conditions, eruptive processes shifting from effusive to explosive, and flank instability of an ocean island48,63,64,65.
However, the unique dataset presented here for Fogo volcano highlights two different scales of consequences of the flank collapse on lava composition. The delayed response to the unloading effect of the collapse takes ~ 50 kyrs at the lithospheric scale (i.e., the depth at which the EM1-like component is incorporated into the moderate-HIMU-like plume magmas), compared to ~ 10 kyrs at the depth of the main magma storage and crystal fractionation. The shallow and short-term impact (~ 10 kyrs) is evidenced by the composition of early post-collapse lavas (68–59 ka) that are incompatible element-rich. The collapse-induced unloading upset magma storage conditions in the lithospheric mantle (~ 20–30 km) and favoured the release of highly fractionated magma. Major and trace element composition of lavas generated during the last 60 kyrs indicates a degree of differentiation that is similar to that of early (> 100 ka) pre-collapse lavas.
The temporal and spatial distribution of post-collapse volcanism supports and refines the model of eastward vent shifting19, with early post-collapse lavas (68–59 ka) being located along the head of a large failure plane corresponding to the present-day caldera rim (Fig. 5), lavas cascading on the caldera walls between 43 and 20 ka, and later lavas (< 20 ka) on the caldera floor (Fig. 1). This eastward migration may also reflect the retrogressive dynamics of the eastward collapse28,31,45. The main collapse is now accurately dated at 68 ka, but secondary collapses may have occurred between 59 and 43 ka. The multistage nature of Fogo flank instability is confirmed by offshore data showing two successive debris avalanche deposits45 and it is concordant with what is observed on many other ocean islands9,65.
The model proposed here for Fogo should now be compared with other studies using a similar approach, i.e. combining structural, chronological and compositional data26. The analytical cost of such studies is high but it is the only way to understand the causal links between volcano growth, instability, and magma storage down to the lithospheric mantle.
Methods
Sampling strategy and description of the lavas
A total of 48 lava flows, 11 intrusions (dykes, sills, and intrusive complex of Monte Amarelo), and 2 ignimbrite samples were collected along the caldera walls and coastal cliffs (Table S1, Figs. 1, S1, S2 and S3). The majority of the samples (75%) predate the Monte Amarelo collapse, but almost all the accessible post-collapse lavas were sampled. The geographic distribution of the sampling allows the volcano-stratigraphic units to be dated directly (K–Ar and Ar–Ar ages from this work, and published K–Ar ages31) or indirectly (considering their stratigraphic position compared to the dated samples). Six stratigraphic sections were extensively sampled: (1) the northern caldera wall and the Montinho post-collapse lava flow on the caldera rim (Fig. S1); (2) the intrusive complex (dykes and plutonic bodies) of the Monte Amarelo (Fig. S1); (3) the western caldera wall along a 500 m-high via ferrata (Fig. S2); (4) the southeastern caldera wall (Fig. S3); (5) the paleocliff forming the southeastern tip of the collapse scar (Fig. 1); (6) and the cliff of Corvo on the eastern coast (Fig. 1). Four types of lavas were distinguished: aphyric lavas (< 5% of phenocrysts), porphyric lavas (5–40% of phenocrysts, clinopyroxene ± olivine ± amphibole), ankaramites (> 40% of pyroxene and olivine phenocrysts), and intrusive lavas (basanite dykes, nepheline syenites). The mesostatis is micro-crystallised in oxides, pyroxene, olivine, plagioclase and rare felspathoïdes (nepheline, leucite, haüyne). The syenites of the Monte Amarelo intrusive complex are composed of clinopyroxenes, alkali feldspars, nepheline, oxides, and rare biotite. The pyroxene phenocrysts are typically euhedral but often fragmented, and their rims are not in equilibrium with the melt. They display a weak normal zonation (although inverse zonation is also present), with textures of dissolution and recrystallization. Thus, these pyroxenes were most probably captured from a crystal mush during magma storage and ascent.
Geochronology: unspiked K–Ar technique
Splits of purified groundmass separates from 4 pre-collapse (Fo-36, Fo-43, Fo-31, and Fo-48) and 6 post-collapse samples (Fo-28, Fo-73, Fo-44, Fo-60, Fo-54, and Fo-70) were prepared following the procedure described by66. Alteration may cause gain and/or loss of K and Ar and as a consequence may lead to under or overestimated K–Ar ages67. To decide if a sample should be used for dating, it is crucial to estimate its degree of alteration. Indeed, after macroscopic and microscopic observations many pre-collapse samples collected along the walls of the caldera were discarded due to their high degree of alteration. The loss-on-ignition values (L.O.I.) range from 0 to 0.4% (Table S1). They are indicative of unaltered samples. The absence of alteration phases in the samples was also verified by observations with a binocular microscope. Isotopic compositions of Ar were determined via the unspiked method68 and achieved using the new argon extraction, purification and transfer line recently developed at the LSCE (Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement69). Groundmass splits (1.0–2.5 g) of samples were wrapped into 99.5% copper foil packets, loaded in the sample holder, which had been turbo-molecular pumped for about 20 h. During the last two hours of that stage, the molybdemium (Mo) crucible was degassed at about 1500 °C until the pressure decreased to 10–9 Torr. The sample was then dropped into the Mo crucible and molten at full power of the induction furnace. During the melting stage (i.e. 20 min), the extracted gas was adsorbed by an active charcoal finger at liquid nitrogen temperature. Next to the melting, the gas was released by heating the charcoal at 110 °C and purified via the mutual action of a titanium sublimation pump and a SAES 10 GP-MK3 Zr–Al getter operated at 400 °C. This first step of gas clean-up generally lasted 40 min and was followed by three consecutive exposures of five minutes each of the gas to SAES 10 GP-MK3 Zr–Al getters also operated at 400 °C. The gas was then adsorbed 5 min by a second active charcoal maintained at liquid nitrogen temperature. After adsorption, this sector is isolated. The gas, released at room temperature, was finally cleaned up by a SAES APGP-10 Zr–Al getter operated at 400 °C during another 5 min and introduced into a 180°, 6 cm radius mass spectrometer, equipped with a double Faraday collector. Isotopic analysis was performed on total 40Ar contents ranging between 0.5 and 2.5 × 10–11 mol. One or multiple manometrically-calibrated doses of atmospheric argon were used to convert beam intensities into atomic abundances and to monitor the atmospheric correction. The manometric calibration is based on periodic, replicate determinations of the international dating standard HD-B1 (24.21 ± 0.32 Ma70,71). Uncertainties for the K and Ar data reported in Table S2 are 1σ (analytical only), and consist of propagated and quadratically averaged experimental uncertainties arising from the K, 40Ar (total), and 40Ar* determinations. All uncertainties on the ages are given at 2σ.
Geochronology: 40Ar/39Ar method
In addition to K–Ar dating and to better constrain the age of the collapse, we have achieved a 40Ar/39Ar age determination on sample Fo-01 (Table S3), previously K–Ar dated at 86 ± 3 ka28. Indeed, the K–Ar age of this post-collapse sample was questioned29. 40Ar/39Ar measurements on similar groundmass samples of FO-01 may allow verifying if the K–Ar age was in error by excess. Irradiation, extraction, gas clean-up procedures, mass spectrometric measurements and blank corrections, are detailed in 66. The total decay constants given by 72 and the 40Ar/36Ar atmospheric ratio at 298.5673 were used for age calculations. The precision of the mass discrimination correction was monitored by daily measurements of air argon and is about 0.15% (2σ standard deviation for multiples of experiments). Neutron fluence (J) was monitored by co-irradiation of Acs crystals74 placed in three pits encircling each sample. The J value for each sample was determined from 6 single crystal laser fusion analyses of Acs. Corresponding J values were calculated using an age of 1.1840 ± 0.0007 Ma75.
Major and trace elements chemistry
Major element compositions (Table S1) were analysed by ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometry) at LMV (Clermont-Ferrand, France) after alkaline melting with lithium borate and nitric acid dissolution (100 mg of sample)76. BHVO-1 standard was also analysed during the analytical session. For trace elements analysis (Table S1), samples were dissolved in a HNO3–HF mixture, heated for 24 h and then evaporated. After dissolution, fluoride precipitates were dissolved with several cycles of additions of 7 N HNO3 and 6 N HCl and evaporations. Additionally, major element composition of ignimbrite and pumice samples (Table S1) was determined using an electronic microprobe (SX100 CAMECA) at LMV. An accelerating voltage of 15 kV was combined with a beam current of 10 nA for a beam diameter of 1 μm.
Whole-rock trace elements were obtained by solution Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass-Spectrometry (ICP-MS, Agilent 7500) at LMV. The BHVO-2 standard was measured every five samples, and the reproducibility was determined with BCR-2 and CMS standards77.
Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic composition
One hundred milligrams of bulk-rock powder were leached with hot 6 M-HCl (75 °C) during 3 h following the protocol described in 57, acid-digested with HF-HNO3, and passed through the chromatography procedure of 78. Strontium, Nd and Pb analytical blanks were all negligible with respect to sample contents. Strontium isotopic measurements were performed on a Finnigan Triton thermo-ionization mass spectrometer (TIMS), Pb measurements on a Thermo Fisher Neptune Plus Multiple Collector—Inductively Coupled Plasma—Mass Spectrometer (MC–ICP–MS), and Nd measurements used both instrumentations (Table S1). Strontium isotope ratios were mass-fractionation-corrected to 86Sr/88Sr = 0.1194 and normalized to 87Sr/86Sr = 0.71025 for the NIST SRM987 standard. Neodymium isotope ratios were mass-fractionation-corrected to 146Nd/144Nd = 0.7219 and normalized to 143Nd/144Nd = 0.512100 for the JnDi-1 standard. Repeated TIMS analyses of the two standards during the course of the study gave 87Sr/86Sr = 0.710242 ± 18 (2sd, n = 33) and 143Nd/144Nd = 0.512104 ± 6 (2sd, n = 17). Lead mass discrimination was corrected by standard bracketing of samples with NBS-981 standard using values of 79 recalculated to 208Pb/206Pb = 2.167780. Average NBS-981 deviations from drifts observed during the different day-sessions of analysis were in the ranges 35–120, 45–190 and 65–255 ppm for 206Pb/204Pb, 206Pb/204Pb and 206Pb/204Pb ratios. This corresponds to maximum errors of ± 0.002, 0.003 and 0.010, respectively.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information files).
References
Holcomb, R. T. & Searle, R. C. Large landslides from oceanic volcanoes. Mar. Geotechnol. 10, 19–32 (1991).
Moore, J. G. et al. Prodigious submarine landslides on the Hawaiian Ridge. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 17465–17484 (1989).
Carracedo, J. C., Day, S. J., Guillou, H. & Pérez Torrado, F. J. Giant Quaternary landslides in the evolution of La Palma and El Hierro, Canary Islands. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 94, 169–190 (1999).
Masson, D. G. et al. Slope failures on the flanks of the western Canary Islands. Earth Sci. Rev. 57, 1–35 (2002).
Masson, D. G., Le Bas, T. P., Grevemeyer, I. & Weinrebe, W. Flank collapse and large-scale landsliding in the Cape Verde Islands, off West Africa: Large-scale landsliding, Cape Verde Islands. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, Q07015 (2008).
McMurtry, G. M., Watts, P., Fryer, G., Smith, J. R. & Imamura, F. Giant landslides, mega-tsunamis, and paleo-sea level in the Hawaiian Islands. Mar. Geol. 203, 219–233 (2004).
Oehler, J.-F., Labazuy, P. & Lénat, J. F. Recurrence of major flank landslides during the last 2−Ma−history of Réunion Island. Bull. Volcanol. 66, 585–598 (2004).
Perinotto, H. et al. The extreme mobility of debris avalanches: A new model of transport mechanism. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 120, 011994 (2015).
Hunt, J. E., Wynn, R. B., Talling, P. J. & Masson, D. G. Turbidite record of frequency and source of large volume (>100 km 3) Canary Island landslides in the last 1.5 Ma: Implications for landslide triggers and geohazards: Record of Canary Island Landslides. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 14, 2100–2123 (2013).
Quidelleur, X., Hildenbrand, A. & Samper, A. Causal link between Quaternary paleoclimatic changes and volcanic islands evolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, 02303 (2008).
Hunt, J. E., Talling, P. J., Clare, M. A., Jarvis, I. & Wynn, R. B. Long-term (17 Ma) turbidite record of the timing and frequency of large flank collapses of the Canary Islands. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 15, 3322–3345 (2014).
Paris, R. et al. Mega-tsunami conglomerates and flank collapses of ocean island volcanoes. Mar. Geol. 395, 168–187 (2018).
Walter, T. R. et al. Rift zone reorganization through flank instability in ocean island volcanoes: An example from Tenerife, Canary Islands. Bull. Volcanol. 67, 281–291 (2005).
Famin, V. & Michon, L. Volcano destabilization by magma injections in a detachment. Geology 38, 219–222 (2010).
Delcamp, A., Vries, B., James, M. R. & Lebas, E. Relationships between volcano gravitational spreading and magma intrusion. Bull. Volcanol. 74, 743–765 (2011).
Le Friant, A. et al. A new model for the evolution of La Réunion volcanic complex from complete marine geophysical surveys. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, 11 (2011).
Cayol, V. et al. Sheared sheet intrusions as mechanism for lateral flank displacement on basaltic volcanoes: Applications to Réunion Island volcanoes. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119, 7607–7635 (2014).
Klügel, A., Longpré, M. A., García-Cañada, L. & Stix, J. Deep intrusions, lateral magma transport and related uplift at ocean island volcanoes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 431, 140–149 (2015).
Maccaferri, F., Richter, N. & Walter, T. R. The effect of giant lateral collapses on magma pathways and the location of volcanism. Nat. Commun. 8, 1097 (2017).
Manconi, A., Longpré, M. A., Walter, T. R., Troll, V. R. & Hansteen, T. H. The effects of flank collapses on volcano plumbing systems. Geology 37(12), 1099–1102 (2009).
Presley, T. K., Sinton, J. M. & Pringle, M. Postshield volcanism and catastrophic mass wasting of the Waianae volcano, Oahu, Hawaii. Bull. Volcanol. 58, 597–616 (1997).
Hildenbrand, A., Gillot, P. Y. & Le Roy, I. Volcano-tectonic and geochemical evolution of an oceanic intra-plate volcano: Tahiti-Nui (French Polynesia). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 217, 349–365 (2004).
Longpré, M. A., Troll, V. R., Walter, T. R. & Hansteen, T. H. Volcanic and geochemical evolution of the Teno massif, Tenerife, Canary Islands: Some repercussions of giant landslides on ocean island magmatism. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, 12017 (2009).
Hildner, E., Klügel, A. & Hansteen, T. H. Barometry of lavas from the 1951 eruption of Fogo, Cape Verde Islands: Implications for historic and prehistoric magma plumbing systems. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 217–218, 73–90 (2012).
Boudon, G., Villemant, B., Le Friant, A., Paterne, M. & Cortijo, E. Role of large flank-collapse events on magma evolution of volcanoes. Insights from the Lesser Antilles Arc. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 263, 224–237 (2013).
Watt, S. F. L. et al. From catastrophic collapse to multi-phase deposition: Flow transformation, seafloor interaction and triggered eruption following a volcanic-island landslide. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 517, 135–147 (2019).
Foeken, J. P. T., Day, S. & Stuart, F. M. Cosmogenic 3He exposure dating of the Quaternary basalts from Fogo, Cape Verdes: Implications for rift zone and magmatic reorganisation. Quat. Geochronol. 4, 37–49 (2009).
Paris, R., Giachetti, T., Chevalier, J., Guillou, H. & Frank, N. Tsunami deposits in Santiago Island (Cape Verde archipelago) as possible evidence of a massive flank failure of Fogos volcano. Sed. Geol. 239, 129–145 (2011).
Ramalho, R. S. et al. Hazard potential of volcanic flank collapses raised by new megatsunami evidence. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500456 (2015).
Martínez-Moreno, F. J. et al. Investigating collapse structures in oceanic islands using magnetotelluric surveys: The case of Fogo Island in Cape Verde. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 357, 152–162 (2018).
Marques, F. O., Hildenbrand, A., Victória, S. S., Cunha, C. & Dias, P. Caldera or flank collapse in the Fogo volcano? What age? Consequences for risk assessment in volcanic islands. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 388, 106686 (2019).
Day, S. J., Heleno da Silva, S. I. N. & Fonseca, J. F. B. D. A past giant lateral collapse and present-day flank instability of Fogo, Cape Verde Islands. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 94, 191–218 (1999).
Gerlach, D. C., Cliff, R. A., Davies, G. R., Norry, M. & Hodgson, N. Magma sources of the Cape Verdes archipelago: Isotopic and trace element constraints. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 2979–2992 (1988).
Doucelance, R., Escrig, S., Moreira, M., Gariépy, C. & Kurz, M. D. Pb-Sr-He isotope and trace element geochemistry of the Cape Verde Archipelago. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 67, 3717–3733 (2003).
Pim, J., Peirce, C., Watts, A. B., Grevemeyer, I. & Krabbenhoeft, A. Crustal structure and origin of the Cape Verde rise. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 272, 422–428 (2008).
Holm, P. M. et al. An 40Ar-39Ar study of the Cape Verde hot spot: Temporal evolution in a semistationary plate environment. J. Geophys. Res. 113, 08201 (2008).
Ribeiro, O. A Ilha do Fogo e as suas erupcoes. in Junto de Investigacoes do Ultramar (eds. Memorias, E. & Publ, I.) (1960).
Machado, F. Vulcanismo das islas de Cabo Verde e das outras ilhas atlantidas. In Publ. Junto de Investigacoes do Ultramar, Lisboa, Portugal. Estudos, Ensaios e Documentos. Vol. 117, 83 (1965).
Torres, P. C. et al. Carta geologica das erupcoes historicas da Ilha do Fogo : Revisao e actualizacao In A erupcao vulcanica de 1995 na Ilha do Fogo, Cabo Verde. Publ. IICT, 119–132 (1997).
Brum da Silveira, A., Madeira, J. & Serralheiro, A. A estrutura da Ilha do Fogo, Cabo Verde. In A Erupção Vulcânica de 1995 na Ilha do Fogo, Cabo Verde. Publ. IICT, 63–78 (1997).
Madeira, J., Brum da Silveira, A., Mata, J., Mourão, C. & Martins, S. The role of mass movements on the geomorphologic evolution of island volcanoes: Examples from Fogo and Brava in the Cape Verde archipelago. Comun. Geol. 93–106 (2008).
Foeken, J., Stuart, F., Day, S. & Wall, F. Carbonatite Seamount Formation and First Subaerial Exposure of Fogo. Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 9, 09688 (2007).
Madeira, J. et al. K/Ar ages of carbonatites from the Island of Fogo (Cape Verde). in Proceedings of the XIV Semana de Geoquímica/VIII Congresso de Geoquímica dos Países de Lingua Portuguesa 475–478 (2005).
Eisele, S. et al. Pleistocene to Holocene offshore tephrostratigraphy of highly explosive eruptions from the southwestern Cape Verde Archipelago. Mar. Geol. 369, 233–250 (2015).
Barrett, R. et al. Revisiting the tsunamigenic volcanic flank collapse of Fogo Island in the Cape Verdes, offshore West Africa. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 500, 13–26 (2020).
Paris, R., Guillou, H., Carracedo, J. C. & Pérez Torrado, F. J. Volcanic and morphological evolution of La Gomera, based on new K/Ar ages and magnetic stratigraphy: implications for oceanic islands evolution. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 162, 501–512 (2005).
Carracedo, J. C., Day, S., Guillou, H. & Gravestock, P. The later stages of the volcanic and structural evolution of La Palma, Canary Islands: The Cumbre Nueva giant collapse and the Cumbre Vieja volcano. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 111–5, 755–768 (1999).
Carracedo, J. C. et al. Evolution of ocean island rifts: The northeast rift-zone of Tenerife, Canary Islands. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 123, 562–584 (2011).
Kogarko, L. N. Characteristics of alkali magma differentiation at the Cape Verde Islands. Geochem. Int. 46, 1071–1080 (2008).
Hoernle, K., Tilton, G., Le Bas, M. J., Duggen, S. & Garbe-Schonberg, D. Geochemistry of oceanic carbonatites: mantle recycling of crustal carbonate. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 142, 520–542 (2002).
Doucelance, R., Hammouda, T., Moreira, M. & Martins, J. C. Geochemical constraints on depth of origin of oceanic carbonatites: The Cape Verde case. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 74, 7261–7282 (2010).
Doucelance, R., Bellot, N., Boyet, M., Hammouda, T. & Bosq, C. What coupled cerium and neodymium isotopes tell us about the deep source of oceanic carbonatites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 407, 175–186 (2014).
Amsellem, E. et al. Calcium isotopic evidence for the mantle sources of carbonatites. Sci. Adv. 6, 13 (2020).
Davies, G. R., Cliff, R. A., Norry, M. J. & Gerlach, D. C. A combined chemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotope study of the Azores and Cape Verde hot-spots: the geodynamic implications. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 42, 231–255 (1989).
Christensen, B. P., Holm, P. M., Jambon, A. & Wilson, J. R. Helium, argon and lead isotopic composition of volcanics from Santo Antao and Fogo, Cape Verde Islands. Chem. Geol. 178, 127–142 (2001).
Escrig, S., Doucelance, R., Moreira, M. & Allègre, C. J. Os isotope systematics in Fogo Island: Evidence for lower continental crust fragments under the Cape Verde Southern Islands. Chem. Geol. 219, 93–113 (2005).
Millet, M.-A., Doucelance, R., Schiano, P., David, K. & Bosq, C. Mantle plume heterogeneity versus shallow-level interactions: A case study, the São Nicolau Island, Cape Verde archipelago. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 176, 265–276 (2008).
Barker, A. K., Holm, P. M., Peate, D. W. & Baker, J. A. A 5 million year record of compositional variations in mantle sources to magmatism on Santiago, southern Cape Verde archipelago. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 160, 133–154 (2010).
Barker, A. K. et al. Magmatic evolution of the Cadamosto Seamount, Cape Verde: Beyond the spatial extent of EM1. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 163, 949–965 (2012).
Hildner, E., Klügel, A. & Hauff, F. Magma storage and ascent during the 1995 eruption of Fogo, Cape Verde Archipelago. Contrib. Miner. Petrol. 162, 751 (2011).
Mata, J. et al. The 2014–15 eruption and the short-term geochemical evolution of the Fogo volcano (Cape Verde): Evidence for small-scale mantle heterogeneity. Lithos 288–289, 91–107 (2017).
Carracedo, J. C., Badiola, E. R., Guillou, H., de la Nuez, J. & Pérez Torrado, F. J. Geology and volcanology of La Palma and El Hierro, Western Canary Islands. Estud. Geol. 57, 175–273 (2001).
Bryan, S. E., Martí, J. & Cas, R. A. F. Stratigraphy of the Bandas del Sur Formation: An extracaldera record of Quaternary phonolitic explosive eruptions from the Las Cañadas edifice, Tenerife (Canary Islands. Geol. Mag. 135, 605–636 (1998).
Deegan, F. M. et al. Crustal versus source processes recorded in dykes from the Northeast volcanic rift zone of Tenerife, Canary Islands. Chem. Geol. 334, 324–344 (2012).
Paris, R., Coello Bravo, J. J., Kelfoun, K. & Nauret, F. Explosive eruption, flank collapse and megatsunami at Tenerife ca. 170 ka. Nat. Commun. 8, 15246 (2017).
Guillou, H. et al. Effectiveness of combined unspiked K-Ar and 40Ar/39Ar dating methods in the 14C age range. Quat. Geochronol. 6, 530–538 (2011).
Guillou, H., Hémond, C., Singer, B. S. & Dyment, J. Dating young MORB of the Central Indian Ridge (19°S): Unspiked K–Ar technique limitations versus 40Ar/39Ar incremental heating method. Quat. Geochronol. 37, 42–54 (2017).
Charbit, S., Guillou, H. & Turpin, L. Cross calibration of K-Ar standard minerals using an unspiked Ar measurement technique. Chem. Geol. 150, 147–159 (1998).
Guillou, H., Scao, V. & Nomade, S. 40Ar/39Ar age of Cryptochron C2r.2r-1 as recorded in a lava sequence within the Kóolau Volcano (Hawaii, USA). Quat. Geochronol. 43, 91–101 (2018).
Hess, J. C. & Lippolt, H. J. Compilation of K-Ar measurements on HD-B1 standard biotite. Liais. Inform. I.U.G.S., Subcom. Geochronol. 12, 19–23 (1994).
Schwarz, W. H. & Trieloff, M. Intercalibration of 40Ar-39Ar age standards NL25, HB3gr hornblendes, GA-1550, SB-3, HD-B1 biotite and BMus/2 muscovite. Chem. Geol. 241, 218–231 (2007).
Min, K. W., Mundil, R., Renne, P. R. & Ludwig, K. R. A test for systematic errors in 40Ar/39Ar geochronology through comparison with U-Pb analysis of a 1.1 Ga rhyolite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 64, 73–98 (2000).
Lee, J. Y. et al. A redetermination of the isotopic abundances of atmospheric Ar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 70, 4507–4512 (2006).
Nomade, S. et al. Alder creek sanidine (ACs-2): A quaternary 40Ar/39Ar dating standard tied to the Cobb mountain geomagnetic event. Chem. Geol. 218, 315–338 (2005).
Phillips, D., Matchan, E. L., Honda, M. & Kuiper, K. F. Astronomical calibration of 40Ar/39Ar reference minerals using high-precision, multi-collector (ARGUS VI) mass spectrometry. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 196, 351–369 (2017).
Elahpour, E. et al. The petrogenesis and geochemistry of Tabas Black Land volcanic field: Implications for volcanic activity along the Nayband fault, East Iran. Volcanica 2, 105–127 (2019).
Vlastélic, I. et al. Magma degassing during the April 2007 collapse of Piton de la Fournaise: The record of semi-volatile trace elements (Li, B, Cu, In, Sn, Cd, Re, Tl, Bi). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 254, 94–107 (2013).
Pin, C., Gannoun, A. & Dupont, A. Rapid, simultaneous separation of Sr, Pb, and Nd by extraction chromatography prior to isotope ratios determination by TIMS and MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 29, 1858–1870 (2014).
Doucelance, R. & Manhès, G. Reevaluation of precise lead isotope measurements by thermal ionization mass spectrometry: Comparison with determinations by plasma source mass spectrometry. Chem. Geol. 176, 361–377 (2001).
Thirlwall, M. F. Multicollector ICP-MS analysis of Pb isotopes using a 207pb–204pb double spike demonstrates up to 400 ppm/amu systematic errors in Tl-normalization. Chem. Geol. 184, 255–279 (2002).
Acknowledgements
This research was financed by the French Government Laboratory of Excellence initiative No. ANR-10-LABX-0006, the Region Auvergne and the European Regional Development Fund. We thank Claire Fonquernie, Jean-Luc Devidal, and Christophe Constantin (LMV Clermont-Ferrand), and the members of the PhD jury of M.N. Cornu for helpful discussion (Meritxell Aulinas Junca, Maud Boyet, José Madeira and Georges Boudon). This work also benefited from a wise review of our regretted colleague Hervé Martin, to whom we wish to dedicate this contribution. We are also grateful to Takeshi Kuritani, Ricardo Ramalho and an anonymous reviewer for their relevant comments. This is Laboratory of Excellence ClerVolc contribution No. 500.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.N.C., R.P. and P.B. collected the samples. M.N.C., C.B., D.A., M.B., and H.G. prepared and analysed the samples. All authors contributed to data interpretation and preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Cornu, MN., Paris, R., Doucelance, R. et al. Exploring the links between volcano flank collapse and the magmatic evolution of an ocean island volcano: Fogo, Cape Verde. Sci Rep 11, 17478 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96897-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96897-1
This article is cited by
-
The Challenging Nature of Volcanic Heritage: The Fogo Island (Cabo Verde, W Africa)
Geoheritage (2024)
-
Long-term volcano evolution controlled by lateral collapse at Antuco volcano, southern Andes, Chile
Communications Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Internal igneous growth, doming and rapid erosion of a mature ocean island: the Miocene evolution of Maio (Cabo Verde)
International Journal of Earth Sciences (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.