Abstract
The marine pelagic archaeal community is dominated by three major groups, the marine group I (MGI) Thaumarchaeota, and the marine groups II and III (MGII and MGIII) Euryarchaeota. Studies of both MGI cultures and the environment have shown that the MGI core membrane lipids are predominantly composed of glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether (GDGT) lipids and the diether lipid archaeol. However, there are no cultured representatives of MGII and III archaea and, therefore, both their membrane lipid composition and potential contribution to the marine archaeal lipid pool remain unknown. Here, we show that GDGTs present in suspended particulate matter of the (sub)surface waters of the North Atlantic Ocean and the coastal North Sea are derived from MGI archaea, and that MGII archaea do not significantly contribute to the pool of GDGTs and archaeol. This implies, in contrast to previous suggestions, that their lipids do not affect the widely used sea surface temperature proxy TEX86. These findings also indicate that MGII archaea are not able to produce any known archaeal lipids, implying that our understanding of the evolution of membrane lipid biosynthesis in Archaea is far from complete.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The dominance of archaeal communities in the marine pelagic ocean by marine group I (MGI) Thaumarchaeota and the marine group II and III (MGII and MGIII) Euryarchaeota has been well established by numerous studies1,2,3. It is known from culture and environmental studies that the Thaumarchaeota are capable of oxidizing ammonia4,5 and that some members are able to use urea as an alternative substrate6. The metabolism of MGII and MGIII archaea is thought to be (photo)heterotrophic and these Archaea are potentially able to degrade proteins, carbohydrates, fatty acids and other lipids1,7,8,9. However, these suggestions are based solely on metagenomic data since pure cultures of MGII and MGIII archaea have as yet not been obtained.
In the marine environment, archaeal membrane lipids are used as biomarkers for the presence of Archaea in microbial ecology studies10,11 but also in the paleotemperature proxy TEX8612, commonly used in paleoclimatological studies. The membrane lipid composition of the MGI archaea has been widely studied13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 and found to include the diether lipid archaeol, glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether (GDGT) lipids with zero to 4 cyclopentane moieties, and crenarchaeol, a GDGT with four cyclopentane moieties and a cyclohexane moiety, so far exclusively found in Thaumarchaeota21. In living and intact cells, GDGTs are mostly bound to polar head groups, termed intact polar lipid GDGTs (IPL-GDGTs). These occur mostly with sugar head groups such as monohexose (MH), dihexose (DH) and hexose phosphohexose (HPH)13,16,18,19,22.
Despite their importance in the marine water column as evidenced by metagenomic surveys1,7,8,9, it is not possible to directly determine the lipid membrane composition of MGII and MGIII archaea as pure cultures are lacking. A previous study based on a combination of metagenomics, sequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons and GDGT core lipid data in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre has suggested that MGII archaea are producers of GDGTs, including crenarchaeol23. However, the low amount of extracted DNA and of archaeal gene reads together with the use of core lipid (CL)-GDGTs (which can also be attributed to cell debris) made the conclusions of this study ambiguous24,25. The absence of the gene encoding the enzyme required to synthesize the building block of archaeal GDGTs, i.e. glycerol-1-phosphate (G1P), in (meta)genomes of MGII and MGIII archaea strongly suggested that these Archaea are not able to synthesize ‘classical’ archaeal membrane lipids26. Furthermore, a recent study27 suggested that MGII archaea do not synthesize GDGTs with cyclopentane moieties. This is based on their genomes that lack the gene encoding the enzyme responsible for the internal cyclization reaction that results in the formation of cyclopentane and -hexane moieties. This would suggest that MGII archaea do not biosynthesize the GDGTs used in the TEX86 proxy. However, it is also unknown whether MGII archaea do make other typical archaeal lipids.
Here, we investigated the potential lipid composition of MGII archaea by characterizing the abundance and diversity of Archaea and composition of archaeal lipids in suspended particulate matter (SPM) of coastal North Sea water and the North Atlantic Ocean, which have previously been shown to contain high abundances of MGII and MGIII archaea28,29. We analyzed the abundance of the archaeal community by archaeal 16S rRNA gene quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), while the diversity of the archaeal community was analyzed with 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. The abundance and composition of archaeal lipids were determined by Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography coupled to High-Resolution Accurate-Mass/Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-HRAM/MS), and the results were compared in order to constrain the importance of the three main archaeal pelagic groups in their contribution to the marine archaeal lipid pool.
Results
We analyzed the ether lipid composition and archaeal diversity and abundance from suspended particulate matter (SPM) collected at depth intervals between 5–200 meters below sea level (mbsl) on glass-fiber filters with pore size 0.3 µm in the tropical North Atlantic (station 10 of Bale et al.30) and between 5–83 mbsl at four nearby stations using glass-fiber filters with pore size 0.7 µm. In addition, SPM of North Sea surface waters, collected in triplicate by sequential filtration through 0.7 µm and 0.3 µm filters, was analyzed for both lipids and DNA.
Archaeal abundance and diversity
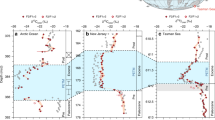
Total archaeal abundances in the tropical North Atlantic were low for the shallow waters (<50 mbsl), ranging between 0.8–8 × 107 16S rRNA gene copies L−1, compared to samples taken at greater depths (>50 mbsl), where they ranged between 0.2–5 × 108 gene copies L−1 (Fig. 1A). The only exception was station 10 at 200 mbsl (0.7 µm), which had a lower amount of 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 than at 50 mbsl (Fig. 1A).
Archaeal abundance, community composition, and lipid distributions at six stations of the tropical North Atlantic Ocean at different water depths and North Sea coastal waters. (A) Total archaeal abundance determined by quantitative PCR and given as archaeal 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 of SPM. Numbers left of the bars indicate the sampling depth in meters below sea level (mbsl). (B) The archaeal community composition based on 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. (C) The fractional abundances of IPL-GDGTs with various core lipids as specified in the legend. Abundances of IPLs containing the same core but with monohexose (MH), dihexose (DH) and hexose-phosphohexose (HPH) headgroups were summed assuming similar response factors. All stations were sampled with 0.7 µm glass-fiber filters, station 10 was also sampled with 0.3 µm glass-fiber filters. ND = not detected.
Various archaeal groups were detected in the SPM from the upper 200 m of the North Atlantic (Fig. 1B). At depths < 50 mbsl, the archaeal community consisted mainly of MGII archaea with relative abundances ranging between 65–93% of total archaeal 16S rRNA gene reads (Fig. 1B). At these depths, MGIII archaea were present in relative abundances of 6–18%, while the relative abundance of Thaumarchaeota is generally low (<4%, except for coastal station 12). At depths >50 mbsl, the relative abundance of MGI Thaumarchaeota ranged from 10–49%, while the MGII and III archaeal groups ranged from 43–84% and 5–8%, respectively.
The estimated abundances (obtained by multiplying their relative abundance given by the 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing by the total archaeal 16S rRNA gene copy abundance and assuming one 16S rRNA gene copy per MGII genome) of MGI archaea in North Atlantic SPM increased strongly at depths >50 mbsl, ranging between 1 × 105 and 1 × 108 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 (Table 1). Abundances of MGII archaea varied between 7 × 106 and 5 × 108 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 and increased with depth but not as noticeably as for the MGI archaea (Table 1). MGIII archaeal abundances were between 8 × 105 and 3 × 107 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 (Table 1).
The coastal North Sea waters contained 1 × 109 archaeal 16S rRNA gene copies L−1 when filtered on a 0.7 µm glass-fiber filter (Fig. 1A). The archaeal 16S rRNA gene copy abundance was five orders of magnitude lower when the filtrate was subsequently filtered on a 0.3 µm glass-fiber filter (7 × 103 archaeal 16S rRNA gene copies L−1; Table 1). In both cases, archaeal 16S rRNA gene reads were almost entirely (>99%) affiliated with MGII archaea (Fig. 1B; Table 1). The remaining archaeal 16S rRNA gene reads were derived of MGI archaea.
Archaeal intact polar lipid diversity and distribution
None of the numerous, ca. 650 targeted archaeal IPLs (see inclusion list in Besseling et al.31) were detected within the SPM of the shallow waters (≤50 mbsl) of the North Atlantic (except for station 12) or the summer coastal North Sea SPM (0.7 µm filter) (Fig. 1C). In North Atlantic waters >50 mbsl, archaeal IPLs were detected (Fig. 1) with a dominance of hexose-phosphohexose (HPH) crenarchaeol (0–84% of the total detected IPL-GDGTs) and dihexose (DH) crenarchaeol (0–51%), and lower relative abundances of DH-GDGT-2 (0–33%) and HPH-GDGT-0 (0–28%) (Table 2). IPLs with crenarchaeol as their CL were the most abundant IPL-GDGTs in all cases (Fig. 1C). This was especially apparent at station 12, the station closest to the coast, where IPL-crenarchaeol dominated (94–100%; Fig. 1C).
To investigate if there were IPL-GDGTs not covered by the ca. 650 targeted archaeal IPLs in our analysis, the IPLs of the North Sea SPM (0.7 µm filters), which is dominated by MGII archaea (1.4 × 109 16S rRNA gene copies L−1) and contains two orders of magnitude lower amounts of MGI archaea (6.9 × 106 16S rRNA gene copies L−1), were acid-hydrolyzed (which removes polar head groups from IPLs) to release IPL-derived GDGTs and archaeol (in triplicate). Analysis by UHPLC-MS using the selected ion monitoring mode showed that there was a small increase in the concentration after acid hydrolysis for GDGT-0 (from 4 ± 2 to 11 ± 6 ng L−1) and crenarchaeol (from 4 ± 2 to 7 ± 4 ng L−1) (Fig. 2). However, these small increases are statistically not significant (one-way ANOVA test; GDGT-0 (ρ = 0.15), crenarchaeol (ρ = 0.28)). Archaeol was barely detectable and concentrations were much lower than those of GDGTs, both before and after acid hydrolysis. This suggests that the MGII archaea, which are very abundant in these waters, do not produce IPLs with GDGTs or archaeol as core lipids and with head groups other than the targeted ones. To check whether the presence of archaeal core lipids other than GDGTs and archaeol could explain this discrepancy, we analyzed both the Bligh and Dyer total lipid extract and an acid-hydrolyzed lipid extract of the North Sea SPM with UHPLC Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (ToFMS). Additional archaeal lipids detected were hydroxylated GDGTs (OH-GDGTs), glycerol dialkanol diethers (GDDs) and butanetriol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers (BDGTs), though in very low abundance compared to the GDGTs (Fig. S5). Furthermore, no significant increase in concentration of these lipids after acid hydrolysis was observed, indicating that they do not occur in substantial amounts with an attached polar head group.
Mismatch between the cell abundance of MGII archaea and concentration of GDGT lipids in SPM of the coastal North Sea. SPM obtained with 0.7 um glass-fiber filters. The concentration of crenarchaeol, GDGT-0, the two most abundant GDGTs present in the form of core lipids (CL; blue bars) and present as CLs and IPLs (i.e. after acid hydrolysis of the Bligh Dyer extract; red bars) are shown. The indicated errors reflect the standard deviation of triplicate measurements. The estimated abundance of IPL-GDGTs based on the cell numbers derived from the measured gene copy numbers of MGI (orange bar) and MGII (green bar) archaea are shown for comparison. These estimations are based on the presence of 1 fg of IPL-GDGTs cell−1, an estimated abundance of 1.4 × 109 MGII euryarchaeotal cells L−1 and 6.9 × 106 MGI thaumarchaeotal cells L−1 (see text for details). Note the log-scale on the y-axis. The abundance of MGII archaea is at least two orders of magnitude too high to account for the GDGT concentration, whereas that of the MGI archaea is well in that range.
Discussion
The archaeal community composition at station 10 at 200 mbsl in the North Atlantic and in the coastal North Sea was independent of the pore size of the filter used for filtration (Fig. 1B). Hence, the filter pore-size does not affect the archaeal community composition but only the amount of captured archaeal cells. MGII archaea were detected in high relative abundances in the shallow waters (0–50 mbsl) of the tropical North Atlantic Ocean (Fig. 1B). This is similar to other studies in which members of the MGII archaea were relatively more abundant near the surface compared to deeper waters29,32,33. Furthermore, the estimated MGII archaeal abundance in the North Atlantic ranged between 7 × 106 and 5 × 108 cells L−1, which is similar to previously reported values of the abundance of MGII archaea in the shallow waters of the North Atlantic Ocean (i.e. 3 × 107 cells L−1)29. The MGII archaeal abundance in summer coastal North Sea was much higher, i.e. 1 × 109 cells L−1, which is similar to previously reported MGII archaeal abundances and coincided within the known MGII archaea summer bloom at the same location5. Both the relative (Fig. 1) and absolute (Table 1) abundance of Thaumarchaeota MGI increased with depth in the tropical North Atlantic Ocean. This is in line with the reported niche preference of MGI archaea for subsurface waters (approximately 50–500 m depth)10,23,32,34,35. The MGI archaeal abundance in summer coastal North Sea was 7 × 106 cells L−1, similar to earlier studies19,28 reporting MGI archaeal abundances of < 1 × 107 cells L−1 in summer coastal North Sea SPM. Hence, the archaeal community composition and abundances in the SPM studied here compare well to those of previous studies and indicates an archaeal community composition in both surface waters (<50 mbsl) of the tropical North Atlantic and North Sea waters that almost entirely consists of MGII archaea.
IPL-GDGTs were only detected in SPM of the North Atlantic in which MGI archaea were present in substantial abundances (i.e. >9 × 106 cells L−1; Fig. 3; Fig. S4). In contrast, in the shallow waters of the tropical North Atlantic and in the coastal water of the North Sea, the low abundances of MGI archaea (between 7 × 104 and 7 × 106 cells L−1; Fig. 1A) coincided with the lack of detection of IPL-GDGTs (Fig. 3; Fig. S4) and IPL-archaeol. Apparently below a certain MGI archaeal abundance (<~9 × 106 cells L−1), the IPL-GDGTs and IPL-archaeol are below the detection limit of our IPL analysis method. These observations support previous reports that Thaumarchaeota are the dominant source of IPL-GDGTs in the ocean (cf. review by Schouten et al.36).
Estimates of abundances of Marine Thaumarchaeota (MGI) and Marine Euryarchaeota group II (MGII) (as cells L−1, based on archaeal 16S rRNA gene copies per liter) (median, first and third quartiles, whiskers depicting minimum and maximum values). Abundances in SPM from the tropical North Atlantic Ocean and North Sea coastal waters with detected intact polar lipid (IPL-) GDGTs (MH, DH, and HPH as headgroup) and in those in which IPL-GDGT were not detected.
A different picture emerges for MGII archaea. At all stations in the North Atlantic and North Sea where the MGII archaeal abundance was >7 × 106 cells L−1, i.e. the minimal abundance of MGI archaea at which their IPL-GDGTs can be detected, but when the MGI archaeal abundance was low (<7 × 106), no IPL-GDGTs could be detected, nor any IPLs with an archaeol CL (Fig. 3; Table 1). Since the cell sizes and, therefore, the amount of IPLs per cell, are similar for MGI and MGII archaea, this strongly suggests that IPLs of MGII archaea are either not the same as commonly known archaeal IPLs or not detectable in our analytical window. To rule out the latter, acid hydrolysis was performed on SPM collected from the coastal North Sea (0.7 µm pore size). This only resulted in a minor and statistically insignificant increase of crenarchaeol and GDGT-0 compared to the CL-GDGTs already present (Fig. 2), which indicates the presence of only very low, if any, amounts of unaccounted IPL-GDGTs.
Further support for a predominant MGI archaeal source of GDGTs in the marine environment comes from an estimation of the IPL-GDGT concentration of MGI and MGII archaea, based on the amount of GDGTs expected to be present in MGI and MGII archaeal cells. MGI archaeal cells contain approximately 1 fg cell−1 of GDGTs based on culture and environmental studies (ranged from 1 fg cellular lipids cell−1, Sinninghe Damsté et al.37; 1.4 fg IPL-GDGTs cell−1 Lipp et al.38; 0.1–8.5 fg IPL-GDGTs cell−1, Huguet et al.39; 0.8–1.8 fg IPL-GDGTs cell−1 according to Elling et al.13). Thus, we would predict the presence of approximately 7 ng GDGTs per liter in coastal North Sea water derived from MGI archaea, in good agreement with the small and statistically insignificant, increase in concentration of crenarchaeol and GDGT-0 after acid hydrolysis (Fig. 2), which converts IPL-GDGTs into CL-GDGTs. The size of MGII archaeal cells is similar to that of MGI archaea9 and, therefore, they would be expected to contain approximately the same amount of IPL-GDGTs as estimated for MGI archaeal cells (i.e. 1 fg cell−1). Because of the orders of magnitude higher abundance of MGII archaeal cells in coastal North Sea SPM compared to MGI archaea, the expected concentration of IPL-GDGTs (or other archaeal lipids) attributed to MGII archaeal cells would be ca. 1,400 ng L−1. This is 2–3 orders-of-magnitudes higher than what is released after acid hydrolysis (Fig. 2). This mismatch indicates that if MGII archaea would produce IPL-GDGTs, acid hydrolysis would have indicated much higher concentrations of IPL-GDGTs than observed (Fig. 2).
Our data strongly suggests that MGII archaea do not produce known archaeal lipids such as GDGTs (or analogues thereof such as OH-GDGTs, BDGTs and GDD) or archaeol (diether lipids). Our results strongly contrast those of Lincoln et al.23, who stated that MGII archaea are able to synthesize archaeal GDGTs and, therefore, contribute substantially to the total archaeal GDGT pool, potentially affecting the paleotemperature proxy TEX86. Our results are in agreement with the recent study of Zeng et al.27 who suggested that MGII archaea might not synthesize GDGTs with cyclopentane and –hexane moieties based on the lack of cyclase coding genes in their genomes. Our study goes a step further as our results not only indicate the MGII archaea do not contribute to the GDGTs involved in the TEX86 proxy, but also do not seem to synthesize any other known archaeal membrane lipids.
Consequently, the question arises which lipids MGII archaea do produce. Phylogenomic analyses by Villanueva et al.26 of MGII archaeal genomes and metagenomes7 revealed that MGII archaea lack the gene coding for glycerol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase (G1PDH), the enzyme responsible for the formation of G1P in Archaea. This implies that they are not able to synthesize the G1P backbone found in archaeal membrane lipids, at least not by the classical biosynthetic pathway. However, MGII archaea still harbor other archaeal membrane lipid biosynthetic pathway genes such as geranylgeranylglyceryl phosphate synthase (GGGP) and digeranylgeranylglyceryl phosphate synthase (DGGGP), among others26. Therefore, they could potentially be capable of synthesizing isoprenoid-based ether lipids, but not with G1P as the glycerol building block, in contrast with other archaeal groups40. However, our current UHPLC-MS method would not be able to distinguish GDGTs of different glycerol stereochemistries.
Interestingly, MGII archaea also possess a putative fatty-acid biosynthetic pathway and putative homologs of the bacterial 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase (PlsC; Villanueva et al.26) involved in esterifying fatty acids to glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) in bacterial membrane lipids. MGII archaea could potentially produce a bacterial-like or a ‘chimeric’ lipid membrane, i.e. with a G3P backbone linked to di- or tetraether-linked isoprenoidal lipids, or lipids with one ether-linked isoprenoidal chain at position sn−1 and one ester-bound fatty acid at position sn-2 of the G3P backbone26. In fact, a mixed bacterial/archaeal lipid membrane could potentially favor the MGII archaea in variable environments. Caforio et al.41 recently demonstrated that the bacterium E. coli, when modified with archaeal/ether lipid biosynthetic genes, is able to synthesize a mixed lipid membrane, comprised of archaetidylglycerol (with a G1P backbone) alongside the bacterial lipids phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylethanolamine (both with a G3P backbone). The engineered E. coli with mixed membranes was more resistant to several chemical/physical stresses compared to the wild type E. coli41. However, careful inspection of the IPL composition as revealed by UHPLC-HRAM/MS did not reveal any unusual IPLs in high abundances or those which could be tentatively related to the hypothetical mixed lipids discussed above. A variety of other IPLs were detected in the North Atlantic (cf. Bale et al.30) and the coastal North Sea SPM. These are comprised of diacyl glycerides and common headgroups such as phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylcholine (PC) and diacylglyceryl-carboxyhydroxymethylcholine (DGCC), among others (Fig. S2) and most likely have a bacterial or eukaryotic origin. This suggest that they either synthesize other non-archaeal IPLs commonly found in marine environments or more unusual IPLs which escape our analytical window. Clearly, the nature of the lipid membrane of MGII archaea will need to ultimately be confirmed by analyzing the membrane lipid composition of MGII archaea isolates.
Conclusion
Analysis of North Atlantic Ocean and summer coastal North Sea SPM showed a dominance of MGII archaea with lower amounts of MGI and MGIII archaea. Only in SPM with a sufficient abundance of MGI archaea, we were able to detect known archaeal IPLs, but not in those with a dominance of MGII archaea such as summer coastal North Sea SPM containing abundant archaeal 16S rRNA gene reads attributed to MGII archaea. Acid hydrolysis followed by core lipid analysis ruled out the presence of intact polar archaeal lipids with unknown headgroup(s) in samples with dominant MGII archaeal populations. Based on our results, we conclude that it is unlikely that “planktonic Euryarchaeota are a significant source of archaeal tetraether lipids in the ocean”, as previously proposed by others23, or other known archaeal lipids. Therefore, the question remains as to which lipids MGII archaeal membranes do comprise. Further research focusing on the cultivation of the elusive MGII archaea and analysis of their membrane lipids are required to resolve this enigma.
Methods
Sampling and physicochemical analyses
Suspended particulate matter (SPM) was collected from the North Atlantic during the HCC cruise in September 2014 with R/V Pelagia30. SPM samples were taken with three McLane WTS-LV in-situ pumps (McLane Laboratories Inc., Falmouth, MA, USA). The pumps were deployed at various depths and locations (station numbers are according to Bale et al.30), i.e. between 5–200 meters below sea level (mbsl) at station 10 (6°41.04′N; 47°29.25′W), as well as from 5–83 mbsl at four nearby stations (station 12; 6°4.04′N; 52°27.69′W, station 8; 6°29.24′N; 45°26.98′W, station 5; 10°49.74′N; 40°28.20′W and station 4; 12°24.42′N; 38°30.12′W) (Fig. S1). SPM was filtered onto pre-ashed glass-fiber filters (0.7 µm nominal pore sizes, GF/F, 142 mm in diameter, Pall Corporation, Port Washington, NY) at all stations. Station 10 was also filtered on pre-ashed glass-fiber filters with 0.3 µm nominal pore sizes (GF75; 142 mm in diameter, Avantec, Japan). Between 89 and 399 liters of seawater were filtered (Table 1). Physical data and dissolved inorganic nutrients are reported in Bale et al.30). Coastal North Sea SPM was collected in July 2015 at high tide from the NIOZ jetty (53°0.1′N; 4°47.2′E). Coastal North Sea water (ranging around 7.5–10 liters) was filtered in triplicate through 0.7 µm and the filtrate subsequently on 0.3 µm pore size glass-fiber filters (Whatman, 142 mm in diameter). For all sampling locations, the filters were both used for lipid and nucleic acid analyses and were immediately stored at −80 °C after sampling.
IPL extraction and analysis
Total lipids were extracted from freeze-dried glass-fiber filters using a modified Bligh and Dyer method42 as previously described earlier43. C16-PAF (1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) was added to the extracts as an internal standard. The extracts including the internal standard were dried under a stream of nitrogen, re-dissolved in known quantities of injection solvent (hexane:isopropanol:H2O 718:271:10 v/v/v) and filtered through a 0.45 µm, 4 mm-diameter True Regenerated Cellulose syringe filter (Grace Davison, Columbia, MD, USA).
IPLs were analyzed using UHPLC-HRAM/MS, designed for the analysis of a wide range of intact polar lipids. An Ultimate 3000 RS UHPLC, equipped with thermostated auto-injector and column oven, coupled to a Q Exactive Orbitrap MS with Ion Max source with heated electrospray ionization (HESI) probe (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), was used. Separation was achieved on a YMC-Triart Diol-HILIC column (150 × 2.0 mm, 1.9 µm particles, pore size 12 nm; YMC Co., Ltd, Kyoto, Japan) with a guard column of the same material (10 × 2.1 mm) maintained at 30 °C. The following elution program was used with a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1: 100% A for 5 min, followed by a linear gradient to 66% A: 34% B in 20 min, maintained for 15 min, followed by a linear gradient to 40% A: 60% B in 15 min, followed by a linear gradient to 30% A: 70% B in 10 min, where A = hexane/2-propanol/formic acid/14.8 M NH3aq (79:20:0.12:0.04 [v/v/v/v]) and B = 2-propanol/water/formic acid/14.8 M NH3aq (88:10:0.12:0.04 [v/v/v/v]). The samples from the North Atlantic (0.7 µm pore-size glass-fiber filters) were run with heptane instead of hexane in the mobile phase. Total run time was 70 min with a re-equilibration period of 20 min in between runs. HESI settings were as follows: sheath gas (N2) pressure 35 (arbitrary units), auxiliary gas (N2) pressure 10 (arbitrary units), auxiliary gas (N2) T 50 °C, sweep gas (N2) pressure 10 (arbitrary units), spray voltage 4.0 kV (positive ion ESI), capillary temperature 275 °C, S-Lens 70 V. IPLs were analyzed with a mass range of m/z 375 to 2000 (resolving power 70,000 at m/z 200), followed by data dependent MS2 (resolving power 17,500 ppm at m/z 200), in which the ten most abundant masses in the mass spectrum (with the exclusion of isotope peaks) were fragmented (stepped normalized collision energy 15, 22.5, 30; isolation window 1.0 m/z). A dynamic exclusion window of 6 s was used as well as an inclusion list with a mass tolerance of 3 ppm to target specific compounds (see Besseling et al.31 for the list of targeted compounds). The Q Exactive Orbitrap MS was calibrated within a mass accuracy range of 1 using the Thermo Scientific Pierce LTQ Velos ESI Positive Ion Calibration Solution (containing a mixture of caffeine, MRFA, Ultramark 1621, and N-butylamine in an acetonitrile-methanol-acetic acid solution).
Peak areas for each individual IPL were determined by integrating the combined mass chromatogram (within 3 ppm) of the monoisotopic and first isotope peak of all relevant adducts formed (protonated, ammoniated and/or sodiated adducts may be formed in different proportions depending on the type of IPL). C16-PAF was used as internal standard to continuously monitor MS performance and to assess matrix effects. Reported peak areas were corrected for these effects. Absolute quantification of IPL GDGTs was not possible due to a lack of authentic standards. Peak areas were not corrected for possible differences in response factors between the various classes of IPL-crenarchaeol. IPLs with crenarchaeol or its isomer(s) as its core lipid, but with the same headgroup, co-elute with the chromatographic system used here and any peak area reported for a crenarchaeol IPL thus represents the sum of both crenarchaeol and its isomer(s).
Analysis of GDGTs and IPL-derived GDGTs
The Bligh and Dyer extracts from three separate 0.7 µm pore-size glass-fiber filters obtained from coastal North Sea water were analyzed for their CL-GDGTs and IPL-derived GDGTs. The extracts from the North Sea were dried under nitrogen and hydrolyzed separately with 1.5 M HCl in methanol by reflux at 130 °C for 2 h to remove the headgroups from the IPL-GDGTs and release the CL-GDGTs. The pH was adjusted to 7 by adding 2 M KOH/MeOH (1:1 v/v) and, after addition of water to a final 1:1 (v/v) ratio of H2O-MeOH, extracted three times with dichloromethane (DCM). The DCM fractions were collected and dried over sodium sulfate. The extracts containing IPL-derived CL-GDGTs and CL-GDGTs in case of the acid-hydrolyzed extracts or only CL-GDGTs in case of the not hydrolyzed extracts, were dried under N2 and dissolved in hexane–2-propanol (99:1, vol/vol) and filtered over a 0.45-µm polytetrafluoroethylene filter. Extracts were analyzed by UHPLC–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) MS for archaeol and GDGTs, according to Hopmans et al.44, with some modifications. Briefly, analysis was performed on an Agilent 1260 UHPLC coupled to a 6130 quadrupole MSD in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. This allowed the detection of GDGTs with 0 to 4 cyclopentane moieties, crenarchaeol and is isomer as well as archaeol. Separation was achieved on two UHPLC silica columns (BEH HILIC columns, 2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 µm; Waters) in series, fitted with a 2.1 × 5 mm pre-column of the same material (Waters) and maintained at 30 °C. Archaeol and GDGTs were eluted isocratically for 10 min with 10% B, followed by a linear gradient to 18% B in 20 min, then a linear gradient to 100% B in 20 min, where A is hexane and B is hexane: isopropanol (9:1). Flow rate was 0.2 ml/min. Total run time is 61 min with a 20 min re-equilibration. Source settings were identical to Schouten et al.45. Typical injection volume was 10 µl of a 1 mg/ml solution (weighted dried Bligh and Dyer extract dissolved in hexane:isopropanol (99:1, v/v ratio). The m/z values of the protonated molecules of archaeol and isoprenoid GDGTs were monitored. GDGTs were quantified by adding a C46 GTGT internal standard46. A response factor derived from an archaeol:GDGT-0 standard (1:1, wt:wt) was used to correct for the difference in ionization between archaeol and GDGTs.
The Bligh and Dyer extract and the acid hydrolyzed Bligh and Dyer extract were also analyzed using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to positive ion atmospheric pressure chemical ionization/Time-of-Flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-APCI/ToFMS) on an Agilent 1290 Infinity II UHPLC, equipped with automatic injector, coupled to a 6230 Agilent TOF MS and Mass Hunter software. This additional analysis was performed to detect other ether lipids that were not included in our SIM method on the 6130 quadrupole MSD. Separation of the ether lipids was achieved according to Hopmans et al.44 with some modifications using two silica BEH HILIC columns in series (2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 µm; Waters) at a temperature of 25 °C. The injection volume was 10 µL. Compounds were isocratically eluted with 90% A and 10% B for the first 10 min, followed by a gradient to 18% B in 15 min, a gradient to 30% B in 25 min and a linear gradient to 100% B in 30 min. A = hexane and B = hexane/isopropanol (9:1, v/v) and the flow rate was 0.2 mL/min. The conditions for the APCI source were identical to Schouten et al.45 and Hopmans et al.44. In addition, the fragmentor was set at 300 V. The ToFMS was operated in extended dynamic range mode (2 GHz) with a scan rate of 2 Hz. We assessed archaeal lipid distributions by monitoring m/z 600 to 1400. Ether lipids were identified by searching within 10 ppm mass accuracy for relevant [M + H]+ signals.
Nucleic acids extraction and quantitative PCR (qPCR) analyses
DNA was extracted from the glass-fiber filters with the RNA PowerSoil® Total Isolation Kit plus the DNA elution accessory (Mo Bio Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA). 1/16th of the filter was used of the 0.7 µm filters (North Atlantic Ocean and coastal North Sea samples) and 1/8th of the filter of the 0.3 µm filters (North Atlantic Ocean, station 10). Concentration of DNA was quantified by Qubit fluorometric quantitation (ThermoFisher Scientific). Quantification of archaeal 16S rRNA gene copies were estimated by qPCR by using the primers Parch519F and ARC915R (archaeal 16S rRNA gene) as previously described by Pitcher et al.10. For details on the qPCR conditions, efficiency and R2 of the qPCR assays see Table S1.
16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, analysis, and phylogeny
PCR reactions were performed with the universal, Bacteria and Archaea, primers 515F-Y (5′-GTG YCA GCM GCC GCG GTA A-3′)47 and 806RB (5′-GGA CTA CNV GGG TWT CTA AT-3′)48 amplifying the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Sequencing was done by the Utrecht Sequencing Facility (www.useq.nl) on a MiSeq platform (Illumina, CA, USA) 2 × 250 bp, using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (Illumina). The 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences were analyzed by Cascabel49, an amplicon sequence data analysis pipeline based on Snakemake50. Briefly, quality-filtered paired-end reads were assembled using PEAR (v0.9.8)51. Quality-filtered with a minimum quality score of 20 (Phred quality score), length between 250–350 bp, and allowing maximum two errors in the barcode sequence. The operational taxonomic units were picked based on a 97% similarity using UCLUST52 with pick_otus.py using QIIME53. Taxonomy was assigned with assign_taxonomy.py within QIIME, using UCLUST and based on the SILVA database version 12852,53. The phylogenetic affiliation of the partial archaeal 16S rRNA gene sequences was compared to release 123 of the SILVA NR SSU Ref database (http://www.arb-silva.de/; Quast et al.40) using the ARB software package54. Sequences were added to the reference tree supplied by the Silva database using the ARB Parsimony tool. Affiliation of any 16S rRNA gene sequences to a given subgroup was done assuming a similarity cutoff of ≥85%.
16S rRNA gene amplicon reads counts per sample are listed in Table S1. Rarefaction curves, indicating the OTU richness per sample (based on the 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequences, both bacterial and archaeal OTUs), are shown in Fig. S3.
Abundances of the three archaeal marine groups were estimated by multiplying archaeal copy number (16S rRNA gene copies L−1) by the relative abundance of the marine group (in % of all archaeal reads), assuming one copy of 16S rRNA gene per genome55.
References
Li, M. et al. Genomic and transcriptomic evidence for scavenging of diverse organic compounds by widespread deep-sea archaea. Nat. Commun. 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9933 (2015).
DeLong, E. F. Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5685–5689 (1992).
Fuhrman, J. A., McCallum, K. & Davis, A. A. Novel major archaebacterial group from marine plankton. Nature 356, 148–9 (1992).
Könneke, M. et al. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437, 543–546 (2005).
Wuchter, C. et al. Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12317–12322 (2006).
Bayer, B. et al. Physiological and genomic characterization of two novel marine thaumarchaeal strains indicates niche differentiation. ISME J. 10, 1051–1063 (2016).
Iverson, V. et al. Untangling genomes from metagenomes: revealing an uncultured class of marine Euryarchaeota. Science. 335, 587–590 (2012).
Martin-Cuadrado, A.-B. et al. A new class of marine Euryarchaeota group II from the Mediterranean deep chlorophyll maximum. ISME J. 9, 1–16 (2014).
Orsi, W. D. et al. Ecophysiology of uncultivated marine euryarchaea is linked to particulate organic matter. ISME J. 9, 1747–1763 (2015).
Pitcher, A. et al. Niche segregation of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and anammox bacteria in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone. ISME J. 5, 1896–904 (2011).
Biddle, J. F. et al. Heterotrophic Archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 3846–3851 (2006).
Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., Schefuβ, E. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. Distributional variations in marine crenarchaeotal membrane lipids: A new tool for reconstructing ancient sea water temperatures? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 204, 265–274 (2002).
Elling, F. J. et al. Effects of growth phase on the membrane lipid composition of the thaumarchaeon Nitrosopumilus maritimus and their implications for archaeal lipid distributions in the marine environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 141, 579–597 (2014).
Elling, F. J. et al. Chemotaxonomic characterisation of the thaumarchaeal lipidome. Environ. Microbiol. 19, 2681–2700 (2017).
Sinninghe Damsté, J. S., Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., van Duin, A. C. T. & Geenevasen, J. A. J. Crenarchaeol: The characteristic core glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether membrane lipid of cosmopolitan pelagic crenarchaeota. J. Lipid Res. 43, 1641–1651 (2002).
Schouten, S. et al. Intact membrane lipids of “Candidatus Nitrosopumilus maritimus,” a cultivated representative of the cosmopolitan mesophilic group I crenarchaeota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 2433–2440 (2008).
Wuchter, C., Schouten, S., Coolen, M. J. L. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. Temperature-dependent variation in the distribution of tetraether membrane lipids of marine Crenarchaeota: Implications for TEX86 paleothermometry. Paleoceanography 19, 1–10 (2004).
Pitcher, A. et al. Crenarchaeol dominates the membrane lipids of Candidatus Nitrososphaera gargensis, a thermophilic group I.1b Archaeon. ISME J. 4, 542–552 (2010).
Pitcher, A. et al. Core and intact polar glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether lipids of ammonia-oxidizing archaea enriched from marine and estuarine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 3468–3477 (2011).
Bale, N. J. et al. Membrane lipid composition of the moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing archaeon “Candidatus Nitrosotenuis uzonensis” at different growth temperatures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85, 1–17 (2019).
Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. et al. The enigmatic structure of the crenarchaeol isomer. Org. Geochem. 124, 22–28 (2018).
Elling, F. J., Könneke, M., Mußmann, M., Greve, A. & Hinrichs, K.-U. Influence of temperature, pH, and salinity on membrane lipid composition and TEX86 of marine planktonic thaumarchaeal isolates. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 171, 238–255 (2015).
Lincoln, S. A. et al. Planktonic Euryarchaeota are a significant source of archaeal tetraether lipids in the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 9858–63 (2014).
Lincoln, S. A. et al. Reply to Schouten et al.: Marine Group II planktonic Euryarchaeota are significant contributors to tetraether lipids in the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 4286 (2014).
Schouten, S., Villanueva, L., Hopmans, E. C., van der Meer, M. T. J. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. Are Marine Group II Euryarchaeota significant contributors to tetraether lipids in the ocean? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, E4285 (2014).
Villanueva, L., Schouten, S. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. Phylogenomic analysis of lipid biosynthetic genes of Archaea shed light on the ‘lipid divide’. Environ. Microbiol. 19, 54–69 (2017).
Zeng, Z. et al. GDGT cyclization proteins identify the dominant archaeal sources of tetraether lipids in the ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1909306116 (2019).
Wuchter, C. Ecology and membrane lipid distribution of marine Crenarchaeota: Implications for TEX86 paleothermometry (2006).
Herndl, G. J. et al. Contribution of Archaea to total prokaryotic production in the deep Atlantic Ocean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 2303–2309 (2005).
Bale, N. J. et al. C5 glycolipids of heterocystous cyanobacteria track symbiont abundance in the diatom Hemiaulus hauckii across the tropical North Atlantic. Biogeosciences 15, 1229–1241 (2018).
Besseling, M. A., Hopmans, E. C., Boschman, R. C., Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. & Villanueva, L. Benthic archaea as potential sources of tetraether membrane lipids in sediments across an oxygen minimum zone. Biogeosciences 15, 4047–4064 (2018).
Massana, R., Delong, E. F. & Pedrós-Alió, C. A few cosmopolitan phylotypes dominate planktonic archaeal assemblages in widely different oceanic provinces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 1777–1787 (2000).
Delong, E. F. et al. Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean’s interior. Science (80-.). 311, 496–503 (2006).
Beman, J. M., Popp, B. N. & Alford, S. E. Quantification of ammonia oxidation rates and ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria at high resolution in the Gulf of California and eastern tropical North Pacific Ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 57, 711–726 (2012).
Liu, H. et al. Marine group II dominates planktonic Archaea in water column of the northeastern South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1–11 (2017).
Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. The organic geochemistry of glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids: A review. Org. Geochem. 54, 19–61 (2013).
Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. et al. Distribution of membrane lipids of planktonic crenarchaeota in the Arabian Sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 2997–3002 (2002).
Lipp, J. S., Morono, Y., Inagaki, F. & Hinrichs, K.-U. Significant contribution of Archaea to extant biomass in marine subsurface sediments. Nature 454, 991–994 (2008).
Huguet, C. et al. Changes in intact membrane lipid content of archaeal cells as an indication of metabolic status. Org. Geochem. 41, 930–934 (2010).
Quast, C. et al. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D590–596 (2013).
Caforio, A. et al. Converting Escherichia coli into an archaebacterium with a hybrid heterochiral membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 115, 3704–3709 (2018).
Bligh, E. G. & Dyer, W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917 (1959).
Lengger, S. K. et al. Intact polar and core glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether lipids in the Arabian Sea oxygen minimum zone. Part II: Selective preservation and degradation in sediments and consequences for the TEX86. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 98, 244–258 (2012).
Hopmans, E. C., Schouten, S. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. The effect of improved chromatography on GDGT-based palaeoproxies. Org. Geochem. 93, 1–6 (2016).
Schouten, S., Huguet, C., Hopmans, E. C., Kienhuis, M. V. M. & Sinninghe Damsté, J. S. Analytical methodology for TEX86 paleothermometry by high-performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 2940–2944 (2007).
Huguet, C. et al. An improved method to determine the absolute abundance of glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether lipids. Org. Geochem. 37, 1036–1041 (2006).
Parada, A. E., Needham, D. M. & Fuhrman, J. A. Every base matters: assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 18, 1403–1414 (2016).
Apprill, A., Mcnally, S., Parsons, R. & Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 75, 129–137 (2015).
Alejandro, A. A. et al. Cascabel: a flexible, scalable and easy-to-use amplicon sequence data analysis pipeline. bioRxiv 1–8 (2019).
Köster, J. & Rahmann, S. Snakemake—a scalable bioinformatics workflow engine. Bioinformatics 28, 2520–2522 (2012).
Zhang, J., Kobert, K., Tomas, F. & Stamatakis, A. PEAR: a fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 30, 614–620 (2014).
Edgar, R. C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460–2461 (2010).
Caporaso, J. G. et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336 (2010).
Ludwig, W. et al. ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1363–71 (2004).
Stoddard, S. F., Smith, B. J., Hein, R., Roller, B. R. K. & Schmidt, T. M. rrnDB: Improved tools for interpreting rRNA gene abundance in bacteria and archaea and a new foundation for future development. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D593–D598 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank the referees for insightful comments. The HCC cruise was funded by the NIOZ and the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) through grant 822.01.017 to SS. Thanks are due to the captain and crew of the R/V Pelagia for assistance and technical support, Denise Dorhout and Marijke de Bar are thanked for sampling during the HCC cruise. Michel Koenen and Marianne Baas provided help with the acid hydrolyses of lipids. Elda Panoto and Sanne Vreugdenhil are thanked for assistance with molecular analyses. NIOZ is thanked for providing a PhD studentship to M.A.B. This research was supported by the NESSC and SIAM Gravitation Grants (024.002.001 and 024.002.002) to J.S.S.D., S.S., and L.V. from the Dutch Ministry of Education, Culture and Science (OCW) and by the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (grant agreement no. 694569 – MICROLIPIDS) to J.S.S.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.A.B., J.S.S.D. and L.V. designed the study; M.A.B. wrote the paper; M.A.B., E.C.H., S.S., J.S.S.D. and L.V. analyzed the data; M.A.B., N.J.B. and E.C.H. performed experiments. All authors participated in data interpretation and provided editorial comments on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Besseling, M.A., Hopmans, E.C., Bale, N.J. et al. The absence of intact polar lipid-derived GDGTs in marine waters dominated by Marine Group II: Implications for lipid biosynthesis in Archaea. Sci Rep 10, 294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57035-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57035-0
This article is cited by
-
Lipid biomarkers: molecular tools for illuminating the history of microbial life
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.