Abstract
Lignin is a complex phenylpropanoid polymer deposited in plant cell walls. Lignin has long been recognized as an important limiting factor for the polysaccharide-oriented biomass utilizations. To mitigate lignin-associated biomass recalcitrance, numerous mutants and transgenic plants that produce lignocellulose with reduced lignin contents and/or lignins with altered chemical structures have been produced and characterised. However, it is not fully understood how altered lignin chemistry affects the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose, and consequently, its utilization properties. Herein, we conducted comprehensive chemical and supramolecular structural analyses of lignocellulose produced by a rice cad2 mutant deficient in CINNAMYL ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE (CAD), which encodes a key enzyme in lignin biosynthesis. By using a solution-state two-dimensional NMR approach and complementary chemical methods, we elucidated the structural details of the altered lignins enriched with unusual hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived substructures produced by the cad2 mutant. In parallel, polysaccharide assembly and the molecular mobility of lignocellulose were investigated by solid-state 13C MAS NMR, nuclear magnetic relaxation, X-ray diffraction, and Simon’s staining analyses. Possible links between CAD-associated lignin modifications (in terms of total content and chemical structures) and changes to the lignocellulose supramolecular structure are discussed in the context of the improved biomass saccharification efficiency of the cad2 rice mutant.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the secondary cell walls of vascular plants, lignin and structural polysaccharides, i.e., cellulose and hemicelluloses, are intricately interwoven through both covalent and non-covalent linkages, making up a complex lignocellulose biocomposite1. Lignin, a phenylpropanoid polymer accounting for 15%–30% of lignocellulose, has long been recognized as a key recalcitrant factor limiting the efficiency of lignocellulose deconstruction and downstream processing in polysaccharide-oriented biomass utilization processes, for example, those used in the production of pulp and paper and the generation of fermentable sugars for biofuels and biomaterials2. To mitigate lignin-associated biomass recalcitrance, numerous transgenic plants that produce lignocellulose with lower lignin contents and/or lignins with altered chemical structures have been generated via up- and/or down-regulation of genes in lignin biosynthesis. Indeed, some lignin-modified mutant and transgenic plants have improved biomass characteristics. For example, reducing the lignin content is a common strategy to improve the extractability and the subsequent enzymatic saccharification of cell wall polysaccharides into fermentable sugars3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Changing lignin structure, e.g., by altering the composition of aromatic units, distributions of inter-monomeric linkages, and end-unit types in lignin polymers, can also improve the processability of polysaccharide components6,7,8,9.
As such, there is an increasing body of evidence showing that changes in lignin contents and/or structure affect the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose, i.e., the organization, assembly, and interactions among lignin and polysaccharides in cell walls, and such changes in lignocellulose supramolecular structure ultimately affect the biomass utilization properties. However, largely because of the technical challenges in characterising the highly complex and heterogeneous structure of lignocellulose, only a few studies have attempted to analyse the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose in lignin-related mutants and transgenic plants10,11,12. Consequently, there is still much to learn about how changes in lignin chemistry affect the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose and its utilization properties.
In this study, we conducted in-depth structural analyses of the altered lignocellulose produced by a grass mutant deficient in CINNAMYL ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE (CAD), a key enzyme gene involved in lignin biosynthesis. CAD is responsible in the final stage of the biosynthesis of lignin monomers, reducing hydroxycinnamaldehyde precursors into their corresponding hydroxycinnamyl alcohols, i.e., monolignols (Fig. 1)13. The resultant monolignols are then exported to cell walls and polymerised into lignins through oxidative radical coupling mediated by wall-localized laccases and peroxidases14. In general, monolignols are the only lignin monomers in gymnosperms and eudicots, whereas, in monocotyledonous grasses (Poaceae) including rice tested in this study, a significant proportion of monolignols are γ-acylated with p-coumarate before they undergo co-polymerization with non-acylated monolignols (Fig. 1)15. In addition, grass lignins also incorporate a flavone, tricin, as a canonical lignin monomer. Tricin can be also co-polymerized with non-acylated and γ-acylated monolignols via radical coupling upon cell wall lignification in grasses (Fig. 1)16.
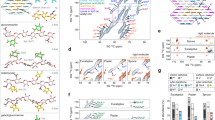
Major lignin monomers and their biosynthesis in grasses. Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) catalyses the reduction of hydroxycinnamaldehydes derived from phenylalanine and/or tyrosine into monolignols (hydroxycinnamyl alcohols). PMT, p-coumaroyl-CoA:monolignol transferase. LAC, laccase; PRX, peroxidase. H, p-hydroxyphenyl. G, guaiacyl. S, syringyl. pCA, p-coumarate. T, tricin. H′, p-coumaraldehyde-derived p-hydroxyphenyl. G′, coniferaldehyde-derived guaiacyl. S′, sinapaldehyde-derived syringyl.
Loss of function or down-regulation of CAD typically leads to unusual incorporation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes into lignins, often accompanied by reddish brown colouration of xylem tissues17,18. In grasses, such as maize19,20,21, Sorghum22,23, rice24,25,26 and Brachypodium27, mutations in CAD genes are associated with the brown midrib phenotype that often shows enhanced forage digestibility and/or biomass saccharification efficiency. Likewise, CAD-deficient transgenic plants, including non-grass species, often show improved forage digestibity28 and better properties for various biomass utilization processes such as chemical pulping29,30,31 and/or enzymatic saccharification21,24,32,33,34,35. In addition, CAD-deficient mutant and transgenic plants may display altered cell wall mechanical properties25,36,37,38,39. Thus, CAD-associated lignin modifications, e.g., reduced lignin contents and/or structural changes upon incorporation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes, may lead to substantial changes in the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose, ultimately leading to improved biomass processabity and altered cell wall mechanical properties11,12. However, our understanding of this phenomenon at the molecular level remains limited. It is therefore important to investigate the relationship between changes in chemical structure and the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose produced by CAD-deficient plants.
Herein, we conducted comprehensive chemical and supramolecular structural analyses of lignocellulose produced by a CAD-deficient mutant of rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. japonica cv. Nipponbare). Previously, we reported that the cad2 (cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 2) rice mutant, which harbours a Tos17 retrotransposon insertion in the second exon of OsCAD2 (Os02g0187800), displays a typical brown midrib phenotype and enhanced biomass saccharification efficiency along with altered lignin content and structure as determined for different rice plant tissues including internode culms examined in this study primarily by conventional wet-chemical methods (e.g., thioglycolic acid lignin assay, nitrobenzene oxidation and thioacidolysis)24. In the present study, to further dissect the altered lignin structures in the cad2 rice mutant, we used solution-state two-dimensional (2D) 1H–13C heteronuclear single-quantum coherence (HSQC) NMR and complementary chemical methods; although a number of studies applied modern HSQC approaches to analyse altered lignins produced by CAD-deficient eudicot plans34,35,40,41,42,43,44, no study to date has used such techniques for analysis of CAD-deficient grass lignins. In addition, for the first time for a lignin-associated CAD mutant, we performed an integrative analysis of lignocellulose assembly and molecular mobility in the cad2 rice cell wall using solid-state 13C magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic relaxation, wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD), and Simon’s staining analyses. The results of this study provide a molecular basis for understanding the relationships among CAD-associated lignin structural modifications, changes in the lignocellulose supramolecular structure, and biomass saccharification efficiency.
Results
The cad2 rice mutant24 was re-cultivated side-by-side with wild-type (control) rice. As previously demonstrated24, the cad2 mutant displayed typical brown midrib and gold hull and internode phenotypes, exhibiting reddish-brown colouration of the midrib, grains (hulls), and culm straws (Fig. S1). Under controlled greenhouse conditions, the cad2 mutant displayed overall similar growth performance to that of wild-type rice in terms of plant height, culm length, tillering, and biomass production (Table S1). Also, as previously reported24, the extractive-free cell wall residue (CWR) samples prepared from mature culm tissues of the cad2 mutant displayed significantly enhanced enzymatic saccharification efficiency over that of the wild type (Table S2). The enhancement of saccharification efficiency after 24 h of incubation with a cocktail of cellulolytic enzymes45 was ca. 32% when expressed as glucose yield per unit cell walls and ca. 36% when expressed as glucose yield per unit total glucan (Table S2), similar to the data reported previously24. The rice culm CWR samples were then subjected to in-depth cell wall chemical and supramolecular structure analyses.
Chemical analyses of CAD-deficient rice cell walls
Consistent with previously reported data24, the lignin content in the cad2 mutant culm cell walls was significantly reduced, by ca. 30% and 20% as determined by the Klason and thioglycolic acid lignin assays, respectively, compared with that in wild-type culm cell walls (Fig. 2a). The xylan content was significantly increased by ca. 21% in the cad2 mutant cell walls compared with that in the wild-type cell walls, whereas the contents of crystalline and amorphous glucans and arabinans in cell walls did not differ significantly between cad2 and wild type (Fig. 2a). These results suggest that the increase in xylan content at least partially compensates for the reduced lignin content in cad2 cell walls. Cell wall-bound p-coumarates (pCA) and ferulates (FA) were quantified as the corresponding free acids released by mild alkaline hydrolysis of CWRs. The cad2 mutant cell walls displayed largely reduced pCA (ca. 65% less compared to wild-type levels) and also mildly reduced FA (ca. 37% less) levels (Fig. 2b). Given that a majority of pCA is bound to lignins in typical grass cell walls15, the reduced pCA levels in the cad2 mutant cell walls were likely associated with the reduced lignin levels (Fig. 2a). Meanwhile, it is currently unclear why FA, which is mostly bound to arabinose residues in grass hemicelluloses rather than to lignins46, was reduced in the cad2 mutant cell walls even with no significant change in arabinose content (Fig. 2a).
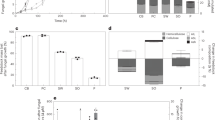
Chemical analysis data of culm cell walls from wild-type (WT) and cad2 mutant rice plants. (a) Lignin content determined by Klason and thioglycolic acid (TGA) assays and sugar content determined by neutral sugar analysis. (b) Alkaline-releasable p-coumaric acid (pCA) and ferulic acid (FA) contents. (c–e) Lignin composition analysis by thioacidolysis. Total yield (c); composition (d); and S/G molar ratio (e) of H, G, and S-type trithioethylpropane monomers released from H, G, and S-type β–O–4 lignin units. Values are means ± standard deviation (SD) from individually analysed plants (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences between WT and cad2 mutant plants (Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). CWR, cell wall residue.
Analytical thioacidolysis quantifies lignin-derived monomeric compounds released by the chemical cleavage of the major β–O–4 linkages in lignin polymers47. The cad2 mutant cell walls released considerably less monomeric compounds (ca. 73% less) upon the thioacidolysis degradation than did the cell walls of wild type (Fig. 2c). This could be attributed not only to the reduced lignin content (Fig. 2a) but also to the replacement of the normal β–O–4 linkages by unusual hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived linkages in lignin polymers. In fact, we previously demonstrated that thioacidolysis of the internode cell wall samples prepared from the cad2 mutant lines released indene derivatives24 which have been used as useful molecular markers for atypical hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived 8–O–4 linkages generated upon CAD-deficiency48. In addition, the proportion of guaiacyl (G)-type lignin monomers out of total lignin monomers [G, syringyl (S), and p-hydroxyphenyl (H)-type monomers] was considerably depleted in the cad2 mutant cell walls (Fig. 2d). Consequently, the S/G ratio in cell walls was considerably higher for the cad2 mutant than for wild type (Fig. 2e). These results suggest that the OsCAD2-knockout mutation preferentially affects G-type lignin polymer units in rice, as further examined by 2D NMR below.
2D HSQC NMR analysis of altered lignin structures in CAD-deficient rice cell walls
To further investigate changes in the chemical structure of lignin in the cad2 mutant rice, we performed 2D HSQC NMR analysis49,50 on lignin-enriched cell wall samples which were prepared via enzymatic removal of cell wall polysaccharides from CWRs50,51 and also on dioxane-soluble lignin samples which were extracted from the lignin-enriched cell walls with a dioxane-water solvent for further lignin purification51. The aromatic sub-regions of the HSQC spectra of the wild-type lignin-enriched cell wall (Fig. S2a) and dioxane-soluble lignin (Fig. 3a) samples displayed typical lignin aromatic signals from G, S and H units (G, S, and H, respectively) along with the signals from p-coumarate (pCA) and tricin (T) units (Table S3). These results are highly consistent with the fact that wild-type rice lignins are mostly derived from polymerization of γ-free and γ-p-coumaroylated monolignols and tricin52,53, as is typical for most grass lignins (Fig. 1)9.
Solution-state two-dimensional short range 1H–13C correlation (HSQC) NMR analysis of dioxane-soluble lignin samples prepared from mature culm tissues of wild-type (WT) and cad2 mutant rice plants. (a) Aromatic sub-regions showing signals from major lignin aromatic units. (b) Oxygenated aliphatic sub-regions showing signals from major lignin side-chain units. (c) Aldehyde sub-regions showing signals from aldehyde units. Contours are color-coded to match the displayed structures. Boxes labelled ×2 and ×4 represent regions with scale vertically enlarged by 2- and 4-folds, respectively. Volume integration data are listed in Table 1. For signal assignments, see Tables S3 and S4 in Supplementary Information.
The proportions of hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived G-type (G′) and S-type (S′) lignin units (Table S3)34,35,40,41,42,43,44 in wild-type lignins were estimated to be 6.3% and 3.2% per total monolignol-derived (G + S + H) and hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived (G′ + S′) aromatic units in lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin spectra, respectively, based on the volume integration analysis of the C2–H2 contour intensities (Table 1). It should be noted that the G′2 and S′2/6 signals could be overestimates of such hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived lignins, especially in lignin-enriched cell wall spectra, as these signals can overlap with those from ferulates in residual arabinoxylans52,54 and also oxidized β-aryl ether lignin units with α-carbonyl carbons44. Both the G′ and S′ signals were clearly augmented in the cad2 spectra (Figs. 3a and S2a, Table 1). The G′ signals were more prominently augmented (to ca. 19% and 16% in lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin spectra, respectively) than S′ signals (to ca. 2% and 3% in lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin spectra, respectively) in all the HSQC spectra collected for cad2 mutant samples (Table 1). Consequently, consistent with the above thioacidolysis-derived compositional data (Fig. 2e), the S/G ratio was significantly increased in cad2 (by ca. 70% and 45% in lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin spectra, respectively), whereas the overall ratio of S-type and G-type lignin aromatic signals, i.e., (S + S′)/(G + G′), was similar between cad2 and wild-type spectra (Table 1). In addition, the conjugated C7–C8 double-bond signals from hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived 8–O–4-units (I′) and cinnamaldehyde (IV′′) end-units (Table S3)34,35,40,41,42,43,44 were clearly visible in the cad2 spectra, but were practically absent in the wild-type spectra (Figs. 3a and S2a), supporting our notion that hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived lignins are considerably augmented in the cad2 mutant cell walls.
The proportions of H signals were relatively small (less than 7%) and similar between cad2 and wild-type spectra (Table 1). The abundance of pCA and T signals was also not significantly different between cad2 and wild-type spectra. Given that p-coumarates are mostly attached to S units in the cell walls of rice54,55 and other typical grasses15, that the proportions of p-coumarate units were similar in cad2 and wild-type cell walls is in line with the observation that the proportions of S units were also similar between them (Table 1). Taken together, these results show that the OsCAD2-knockout mutation promotes the incorporation of non-canonical coniferaldehyde instead of canonical coniferyl alcohol into lignin, with much less effect on the incorporation of non-canonical sinapaldehyde instead of canonical sinapyl alcohol and sinapyl p-coumarate, and no apparently significant effect on the incorporation of tricin into lignin (Fig. 1).
The oxygenated-aliphatic (Figs. 3b and S2b) and aldehyde (Figs. 3c and S2c) sub-regions of the HSQC spectra show the distributions of the various inter-monomeric and end-unit linkage types in the lignin polymers (Table S4). In line with the above aromatic compositional analysis data, the aldehyde C9–H9 signals from hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived 8–O–4-units (I′) as well as those from cinnamaldehyde (IV′′) and benzaldehyde (IV′′′) end-units34,35,40,41,42,43,44 were clearly visible in the cad2 spectra, but were much smaller or practically absent in the wild-type spectra (Figs. 3c and S2c). Collectively, the appearance of the atypical 8–O–4-units (I′) bearing 9-aldehyde and unsaturated C7–C8 double bonds provided evidence for the participation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes in oxidative radical coupling during lignification (Fig. 4)40,42. Volume integration analysis determined that I′ signals account for ca. 8% and 19% of the total of major lignin linkage signals (I + II + III + III′) in the cad2 lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin spectra, respectively (Table 1). Meanwhile, the relative signal intensities of the conventional β–O–4 (I) and β–5 (II) units were proportionally decreased and those of β–β linkages (III + III′) were increased in the cad2 spectra compared with those in the wild-type spectra (Table 1). Such decreases and increases in β–5 (II) and β–β (III + III′) units, respectively, are typical consequences of the increased S/G ratio34,55,56. The decrease in β–O–4 (I) was likely due to its partial replacement by hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived 8–O–4-units (I′)34,44.
Cross-coupling reactions of canonical non-acylated and acylated monolignols (a) and non-canonical hydroxycinnamaldehydes (b) giving rise to the β–O–4 and 8–O–4 linkage units, respectively, in lignin polymers. pCA, p-coumarate. PS, polysaccharides. QM, quinone methide intermediates. LAC, laccase; PRX, peroxidase.
Solid-state NMR and WAXD analyses of lignocellulose supramolecular structure in CAD-deficient rice cell wall samples
To investigate how the CAD-associated lignin modifications affect the supramolecular structure of lignocellulose, we performed an integrated analysis of polysaccharide molecular assembly and mobilities based on solid-state 13C MAS NMR spectra, spin-lattice relaxation times (T1), and WAXD patterns of cad2 and wild-type culm CWR powder samples. The 13C MAS NMR spectra were collected either by using typical 1H–13C cross-polarization (CP) to detect rigid cellulose components or by 13C-directed dipolar decoupling (DD or direct polarization, DP) with a fast 2-s recycling delay to emphasize more mobile components57,58,59, i.e., lignin and hemicelluloses (Fig. 5a). As expected, the CP MAS spectra of both cad2 and wild-type cell walls were dominated by signals assigned to rigid cellulose backbones with peaks at 105 ppm (C1), 89 and 84 ppm (C4), 75 and 73 ppm (C2,3,5), and 65 and 63 ppm (C6) (Fig. 5a, Table 2). The DD MAS spectra were apparently enriched with signals from mobile hemicelluloses, mainly xylans, with obvious peaks at 105 ppm (X1), 82 ppm (X4), 76 ppm (X2,3), and 64 ppm (X5), as well as signals from mobile lignin aromatic (110–180 ppm) and methoxyl (57 ppm) carbons (Fig. 5a, Table 2)58,60,61. In addition, small signals assignable to aldehyde carbonyl carbons in the hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived lignin units were present, albeit at low intensity, only in the DD spectrum of cad2 cell walls (Fig. 5a, Table 2).
Solid-state 13C MAS NMR analyses of culm cell walls from wild-type (WT) and cad2 mutant rice plants. (a) CP and DD MAS NMR spectra collected with 2-second recycling delay. (b) Expanded CP MAS spectra showing cellulose C4 and C6 signals. Inserted values are volume integrals for indicated peak areas. (c) CP 13C T1 relaxation times for slow- and fast-relaxing components in major cellulose carbon sites. (d) Fractions of slow- and fast-relaxing components in major cellulose carbon sites. For signal assignments, see Table 2.
The CP MAS spectra showed glucose C4 and C6 signals from two distinct cellulose environments, i.e., C4a (89 ppm) and C6a (65 ppm), which are often assigned to glucose residues in crystalline and/or internal cellulose, and C4b (84 ppm) and C6b (63 ppm), which are often assigned to glucose residues in amorphous and/or surface cellulose (Table 2)57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64. Interestingly, in our volume integration analysis, the relative signal intensities of the crystalline and/or internal cellulose carbons over the amorphous and/or surface cellulose carbons, i.e., C4a/C4b and C6a/C6b, were notably decreased in cad2 cell walls compared with those in wild-type cell walls (Fig. 5b), suggesting that cellulose molecular assembly is compromised in cad2 cell walls.
To quantitatively assess the defective cellulose assembly, we collected WAXD profiles of cad2 and wild-type cell walls (Fig. S3) and determined their apparent crystallinity indices as expressed by the intensity ratio of the crystalline and amorphous scatters (Fig. 6a)65. In line with our assessment by CP MAS NMR (Fig. 5b), the crystallinity index of cell walls was significantly decreased, by ca. 15%, in the cad2 mutant compared with wild type (Fig. 6a). Taken together, these data suggest that cad2 cell walls have less well-defined cellulose assembly compared with that in wild-type cell walls.
WAXD and Simon’s staining assay of culm cell walls of wild-type (WT) and cad2 mutant rice plants. WAXD-derived apparent crystallinity index (a); amounts of absorbed direct orange (DO) and direct blue (DB) dyes (b); and ratio of absorbed DO to DB dyes (c) after Simon’s staining. Values are means ± standard deviation (SD) from individually analysed plants (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences between WT and cad2 mutant plants (Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05). CWR, cell wall residue.
Next, we measured site-specific 13C spin-lattice relaxation times (T1) to investigate the mobility of cellulose in cad2 and wild-type cell walls. Because we used the common Torchia pulse sequence66, which uses CP for the initial 13C magnetization, the collected relaxation data reflect the molecular motion of mainly CP-enhanced rigid cellulose components. The relaxation data collected for major cellulose carbon sites exhibited double exponential decays with distinctively slow- (T1 > 20 s) and fast- (T1 < 5 s) relaxing components, each representing relatively rigid and mobile domains, respectively, both in the crystalline/internal and amorphous/surface cellulose backbones. This pattern was similar to the Torchia-CP relaxation profiles that have been reported for powdery biomass and cellulose samples in other studies62,63,64,67. Intriguingly, the cad2 cell wall samples tended to display higher T1 values than those of wild-type cell wall samples at most of the cellulose carbon sites, except for C1 (105 ppm) (Fig. 5c). However, most of the cellulose carbon sites, again except for C1, in cad2 cell wall samples showed higher fractional weighing for faster-relaxing components over slower-relaxing components compared with those in wild-type cell wall samples (Fig. 5d). The exceptional behaviour of T1 and the fractional weighing of faster and slower components at the C1 site might be due to the contributions of overlapping xylan X1 (Table 2) as well as syringyl (S2/6) and tricin (T2′/6′) lignin aromatic carbons (Fig. 3a; Table S3) at this particular site (δC = ca. 105 ppm). Overall, these relaxation data suggest that not only the assembly but also the molecular mobility of cellulose molecules are somehow affected in cad2 rice cell walls.
Simon’s staining assay to assess surface accessibility of cellulose in CAD-deficient rice cell wall samples
Lastly, we used Simon’s staining assay68,69 to test whether or not the enhanced saccharification performance of cad2 mutant cell walls (Table S2)24 is associated with the physical accessibility of cellulolytic enzymes to the cellulose substrate. This assay semi-quantitatively determines the amplitudes of the pore surface area and accessibility of cellulose substrates in biomass by applying two cellulose binding dyes, i.e., direct orange (DO) and direct blue (DB), with distinct colours, molecular sizes, and cellulose binding affinities; in particular, DO resembles the molecular size of typical cellulases with a high affinity for cellulose68,69. In the assay, we observed no significant differences between cad2 and wild-type control cell wall powders in terms of cellulose porosity and accessible surface area, as assessed by the amount of the adsorbed dyes (Fig. 6b) or by the ratio of the adsorbed large DO to small DB dyes (Fig. 6c)68,69. These results indicate that, at least within the limitation of the capability of Simon’s staining assay, the porosity and physical accessability of cellulose are not significantly compromised in cad2 rice cell walls.
Discussion
OsCAD2-deficient rice produces aldehyde-enriched lignins mainly from polymerization of coniferaldehyde
As envisioned, our HSQC NMR analysis revealed that cell walls produced in cad2 rice mutants are augmented in unusual aldehyde-enriched lignins. An estimation based on the HSQC contour intensities suggested that ca. 19–21% of the mutant lignins are from the polymerization of the atypical hydroxycinnamaldehydes replacing the conventional non-acylated and acylated monolignols (Table 1). The results of both the HSQC NMR and thioacidolysis analyses suggest that the OsCAD2-knockout mutation results in the replacement of mainly the G-type lignin monomer, i.e., coniferyl alcohol (and coniferyl p-coumarates, albeit with low levels), with the corresponding G-type hydroxycinnamaldehyde, i.e., coniferaldehyde, with much less impact on the replacement of the S-type lignin monomers, i.e., sinapyl alcohol and sinapyl p-coumarate (Fig. 1). The HSQC NMR analysis estimated that ca. 87–91% of the hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived lignins in cad2 rice cell walls are from polymerization of coniferaldehyde, with the rest from sinapaldehyde (Table 1). Meanwhile, it was apparent that the null mutation of OsCAD2 in our cad2 mutant24 does not completely eliminate total CAD activity for lignification, because HSQC NMR signals from the typical lignin polymer units are still prominent in the spectra of cad2 mutant cell walls (Fig. 2, Table 1); in contrast, the Arabidopsis cadc cadd double mutant34 and Medicago truncatula cad1 mutant44 produce lignins largely dominated (>95% based on 2D HSQC NMR) by unusual lignin units derived from polymerization of hydroxycinnamaldehydes, and almost completely devoid of normal lignin units derived from polymerization of canonical monolignols. Given that the rice genome encodes at least 11 CAD and CAD-like proteins besides OsCAD270,71, it is conceivable that at least some of them play a role along with OsCAD2 in rice lignification, and may particularly function in the biosynthesis of S-type lignins. Further genetic and biochemical characterizations of rice CAD and CAD-like proteins are needed to explore their specific functions.
Lignocellulose assembly is compromised in CAD-deficient rice cell walls
The results of the solid-state 13C MAS NMR, spin-lattice relaxation, and WAXD analyses of rice cell wall powder samples indicated that cellulose assembly and mobility are disrupted in the CAD-deficient rice mutant. In particular, cad2 mutant cell wall samples have less well-defined cellulose assembly compared with that in the wild type, as assessed based on the decreased peak areas of the crystalline/internal carbons over the amorphous/surface carbons of cellulose in the 13C CP MAS spectra (Fig. 5b) as well as the decreased ratio of crystalline to amorphous scatters in the WAXD profiles (Fig. 6a). Concomitantly, the site-specific spin-lattice relaxation (T1) times were increased for most of the cellulose carbons in both the crystalline/internal and the amorphous/surface cellulose backbones (Fig. 5c), whereas the fractional weighing of faster-relaxing (more mobile) components was increased over that of slower-relaxing (more rigid) components at most of the cellulose carbon sites in the cad2 mutant cell wall samples (Fig. 5d), suggesting complex changes in cellulose mobility.
Overall, our data are in line with those reported by Liu et al.12 who also detected disordered orientations of cellulose fibrils in inflorescence stems of CAD-deficient Arabidopsis cadc cadd mutant lines using high-resolution scanning X-ray microdiffraction12. A reduced lignin content (Fig. 2a) may represent the major factors causing such disintegration of lignocellulose in the cad2 mutant rice tested in this study. In fact, Ruel et al. observed altered organization of cellulose microfibrils in a lignin-reduced Arabidopsis ccr1 mutant deficient in CINNAMOYL-CoA REDUCTASE (CCR)10. Notably, however, not only reduced lignin content but also modified lignin chemical structures, i.e., incorporation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes, upon CAD-deficiency can affect cellulose molecular assembly, albeit perhaps with less impacts in our rice cad2 mutant containing lignin with ca. 20% (based on 2D HSQC NMR, Table 1) of the hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived units compared to those in the previously reported CAD-deficient mutant plants with lignins much more dominated (>95% based on 2D HSQC NMR) by the hydroxycinnamaldehyde-derived units34,44.
Our current models of lignocellulose supramolecular structure envision that, whereas direct associations between lignin and cellulose are unlikely, hemicelluloses, e.g., xylans and mannans, integrate lignin and cellulose by forming non-covalent and/or covalent linkages independently with the two, although it is yet difficult to test these models experimentally60,61,72,73,74. It is therefore plausible that the disordered cellulose assembly observed in the cell walls of CAD-deficient rice (this study) and Arabidopsis12 result from the disruption of lignin–hemicellulose associations upon lignin modifications associated with CAD-deficency. For example, the incorporation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes may increase the hydrophobicity of lignin polymers. As further demonstrated in this study, hydroxycinnamaldehydes produce the 9-aldehyde groups that replace the typical γ-alcohol or γ-p-coumarate groups, as well as the unusual 8–O–4 linkages with unsaturated C7–C8 double bonds that replace the typical β–O–4 linkages with α-hydroxyl groups in lignin polymers (Fig. 4)40,42. A previous study using molecular dynamic modelling suggested that such CAD-associated structural modifications of lignin polymers that make the polymers more hydrophobic may reduce non-covalent lignin–hemicellulose interactions in cell walls11. In addition, there may be fewer covalent linkages between lignin and hemicelluloses in CAD-deficient cell walls. In the course of typical lignin polymerization from the conventional non-acylated and acylated monolignols, the quinonemethide intermediate resulting from β–O–4 cross-coupling can be trapped for re-aromatization by a hydroxyl or a carboxyl group in hemicelluloses, resulting in lignin–carbohydrate covalent linkages (Fig. 4a)72,73,74. In contrast, the quinonemethide intermediate resulting from the analogous 8–O–4 cross-coupling of a hydroxycinnamaldehyde monomer can enter a more facile re-aromatization pathway through elimination of the 8-proton, limiting the nucleophilic attack by hemicelluloses to form lignin–carbohydrate linkages (Fig. 4b)34,44. Such reduced lignin–hemicellulose associations may eventually lead to looser lignocellulose assembly in CAD-deficient cell walls, thereby resulting in disordered cellulose assembly as observed in our cad2 rice mutant and also in Arabidopsis cadc cadd mutant12. It is also notable that our cad2 rice cell walls display a reduction in cell-wall-bound FA (Fig. 2b), which may also contribute to reducing lignin–hemicellulose associations, because FA can serve as cross-linkers between lignin and hemicelluloses (arabinoxylans) in grass cell walls9,46,74.
Altered cellulose assembly may lead to improved saccharification performance of CAD-deficient rice cell walls
Enzymatic saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass can be affected by many factors69,75. Nevertheless, the disordered cellulose assembly in our CAD-deficient rice cell walls, i.e., increased proportions of mobile amorphous/surface components over rigid crystalline/internal components in cellulose, as gauged by the solid-state NMR and WAXD data in this study (Figs. 5 and 6a), can substantially contribute to improved saccharification performance. In particular, several studies have detected negative correlations between saccharification efficiency and crystallinity indices of biomass76,77,78,79, albeit with some controversy, especially when specific chemical pretreatments have been applied prior to enzymatic hydrolysis80,81,82. The physical accessibility of cellulose is another important factor affecting biomass saccharification, because intimate contact between cellulolytic enzymes and cellulose substrates is the prerequisite step for enzymatic hydrolysis to occur69. As assessed by Simon’s staining assay (Fig. 6b,c), however, we found no significant difference in the relative porosity and accessibility of the cellulose surface between cad2 mutant and wild-type cell wall samples. Taken together, it is plausible that the improved biomass saccharification performance of our CAD-deficient rice can be mainly attributed to increased proportions of cellulose components that are more amenable for enzymatic hydrolysis, rather than changes in porosity and accessibility that affect the physical interactions between cellulose substrates and cellulolytic enzymes. Such altered cellulose assembly may possibly arise from reduced lignin content, modified lignin polymer structures, and/or disrupted lignin-hemicellulose interactions as discussed above.
In conclusion, our results provide a molecular basis for understanding the relationships between altered lignin chemistry, changes in the lignocellulose supramolecular structure, and processability of biomass in CAD-deficient mutant and transgenic plants. Future studies may extend the comparative analyses of chemical and supramolecular structures of lignocellulose to other lignin-modifed mutants and transgenic samples in which lignin content and structures are more systematically and variously altered. In particular, we envision that further understanding of the lignin–polysaccharide associations in cell walls and their relationships with lignin chemistry will greatly increase our understanding of the elusive functions of plant cell walls, as well as our ability to manipulate lignocellulose properties for better biomass utilization.
Methods
Plant materials
The cad2 (gh2; accession: NE4246) rice mutant used in this study was originally identified from the Tos17-insertional mutant population derived from O. sativa L. spp. japonica cv. Nipponbare24,83. The homozygous cad2 mutant and wild-type lines were grown side-by-side under greenhouse condition56. Mature aerial parts were harvested and dried at 27 °C for 30 days. Dried culm straws were then collected by removing the panicle, leaf blade, and leaf sheath. Culm straws were cut into ca. 5 mm pieces with scissors, homogeneously pulverized with a TissueLyser (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) (3 min at 25 Hz for each precisely weighed 400 mg culm sample), and then extracted with distilled water, methanol, and hexane84 to produce CWR samples.
Cell wall chemical analyses
The Klason lignin assay85, thioglycolic acid assay86, microscale thioacidolysis84,87, and determination of cellulosic (crystalline) and hemicellulosic (amorphous) glycan contents87 and alkaline-releasable p-hydroxycinnamic acid contents88 were conducted as previously described.
Solution-state NMR
Lignin-enriched cell wall and dioxane-soluble lignin samples for solution-state HSQC NMR were prepared according to the method described previously51. Briefly, CWRs (~300 mg) were ball milled using a Fritsch Pulverisette 7 ball-miller (Idar-Oberstein, Germany) with a 45-mL-size ZrO2 vessel containing ten ZrO2 balls (600 rpm, 12 cycles of 10 min at 5-min intervals) and then digested with crude cellulases (Cellulysin; Calbiochem, La Jolla, CA, USA) as described previously (isolation yields typically ca. 19% and ca. 13% for wild-type and cad2 mutant CWRs, respectively). Lignin-enriched cell wall samples from three biologically independent plants of wild-type and cad2 mutant lines were subjected to the NMR analysis. In parallel, dioxane-soluble lignin samples were prepared from pooled culm CWR samples (3 plants/pool). Briefly, culm CWRs (~900 mg) were ball-milled and digested with crude cellulases as described above for lignin-enriched cell wall sample preparations, and then extracted three times with dioxane-water (96:4, v/v, 50 mL) at room temperature for 3 h. The combined supernatant was concentrated to ~1 mL using a rotary evaporator and then precipitated into 200 mL of 0.01 M aqueous HCl. The precipitates were collected by centrifugation (10,000 g at room temperature for 10 min) and washed with distilled water to yield dioxane-soluble lignins (ca. 5% and ca. 2% from wild-type and cad2 mutant culm CWRs, respectively).
HSQC NMR analysis was performed on a Bruker Biospin Avance III 800US system (800 MHz for 1H; Bruker Biospin, Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with a cryogenically cooled 5-mm TCI gradient probe. The solvent was dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)-d6/pyridine-d5 (4:1, v/v)49,50. Adiabatic HSQC NMR experiments were carried out using standard Bruker implementation (“hsqcetgpsp.3”) using acquisition parameters described previously49,50. The central DMSO solvent peaks (δC/δH: 39.5/2.49 ppm) were used as an internal reference. Data processing and analysis were carried out as described previously49,50,51,52,87 using Bruker TopSpin 4.0 (Mac) software (Bruker Biospin, Billerica, MA, USA). Peak assignments were based on comparison with literature data (Tables S3 and S4)16,35,44,49,50,52,89. For volume integration of lignin aromatic signals (Table 1, Fig. 3a), we used C2–H2 correlations from G and G′, C2–H2/C6–H6 correlations from H, S, S′ and pCA, and C2ʹ–H2ʹ/C6ʹ–H6ʹ correlations from T. Signals from H, S, S′, pCA and T were logically halved. Volume integrations of lignin inter-monomeric and end-unit linkages (Table 1, Fig. 3b,c), were carried out using Cα–Hα contours from I, II, III, and III′, C9–H9 contours from I′ and IV′′, and C7–H7 contours from IV′′′. Signals from III and III′ were logically halved.
Solid-state NMR
Solid-state NMR analysis of rice CWRs was performed on a Bruker Biospin Avance III 800US system (200 MHz for 13C; Bruker Biospin, Billerica, MA, USA) with a 4-mm double resonance magic-angle-spinning (MAS) probe and a ZrO2 rotor with a KelF-made cap. The 13C MAS spectra were measured at 300 K with a MAS frequency of 12k Hz using either 1H–13C cross-polarization (CP) or 13C-directed dipolar decoupling (DD) to create the initial 13C magnetization. The CP MAS spectra were collected with a contact time of 2.5 ms and a recycling delay of 4.0 s, whereas the DD MAS spectra were collected using a short recycling delay (2.0 s) to emphasize mobile components. The 13C chemical shifts were externally referenced to the CH3 signal of silicon rubber at 1.4 ppm on the tetramethylsilane (TMS) scale. Data processing and analysis for CP and DD MAS spectra used Bruker TopSpin 4.0 (Mac) software (Bruker Biospin, Billerica, MA, USA). The 13C spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) measurements were performed using the Torchia pulse sequence63 with a CP contact time of 2.5 ms and 12 τ delay times between 0.01 and 64 s. The obtained τ-dependent signal decay I(τ) was fitted using Igor Pro 7 software (WaveMetrics, Inc., Portland, OR, USA) with the following double exponential equation:
where T1S and T1f are two independent T1 for slower- and faster-relaxing components (T1f > T1S), and I(0)s and I(0)f are their respective weighing fractions59,64,67.
X-ray diffraction analyses
The WAXD analyses were performed on rice CWR powder samples using a Rigaku Ultima-IV diffractometer (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) with nickel-filtered CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å) generated at 40 kV and 40 mA. The diffraction intensity profiles of CWR samples placed on a copper sample folder were measured at 20 °C in the 2θ range of 5 to 30° with a step size of 0.1° and a scan speed of 15 s per step. The apparent cell wall crystallinity index (CrI) was determined by the height of the 200 peak (I200, 2θ = ca. 22°) and the minimum between the 200 and 100 peaks (Iam, 2θ = ca. 18°) using the following equation:
where I200 is the height of the 200 peak (2θ = ca. 22°) and Iam is the minimum between the 200 and 100 peaks (2θ = ca. 18°)65.
Simon’s staining assay
The cellulose accessibility of CWRs was determined by the modified Simon’s staining assay using direct orange (DO) and direct blue (DB) dyes according to Chandra et al.68. Briefly, 20 mg CWR was added to a 15-mL polypropylene centrifuge tube and incubated with increasing concentrations of DO and DB dyes (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mg/mL) in phosphate buffer saline solution (pH 6.0). The mixtures were incubated at 70 °C for 6 h with shaking at 150 rpm and then centrifuged. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured using a Shimadzu UV-2600 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 455 and 624 nm, the peak absorption wavelengths of the DO and DB dyes, respectively. The amount of dye adsorbed by CWR was determined from the difference between the initial dye concentration and the final dye concentration in the supernatant. The concentrations of DB and DO were calculated based on the Lambert–Beer law for binary mixtures and the extinction coefficients for DB and DO dyes at 455 and 624 nm, which were determined by constructing standard curves for each dye68.
Enzymatic saccharification assays
Enzymatic saccharification efficiency was determined as described in Hattori et al. (2012)45. Briefly, each CWR (~15 mg) sample was placed in a polypropylene tube, destarched, and subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis with an enzyme cocktail composed of Celluclast 1.5 L (Novozymes, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) (1.1 FPU), Novozyme 188 (Novozymes) (2.5 CbU), and Ultraflo L (Novozymes) (65 μg) in sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.8). The reaction was carried out in a rotary reactor (Heatblock Rotator SN-48BN, Nissin, Saitama, Japan) at 12.5 rpm at 50 °C for 24 h. The concentration of liberated glucose was determined with a Glucose CII test kit (Wako Pure Chemicals Industries, Osaka, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Data availability
All data necessary to evaluate the conclusions in this study are included in the published paper and its Supplementary Information file. Additional data, if required, will be made available by the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Terashima, N., Yoshida, M., Hafren, J., Fukushima, K. & Westermark, U. Proposed supramolecular structure of lignin in softwood tracheid compound middle lamella regions. Holzforschung 66, 907–915 (2012).
Boerjan, W., Ralph, J. & Baucher, M. Lignin biosynthesis. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 54, 519–546, 519–546 (2003).
Chen, F. & Dixon, R. A. Lignin modification improves fermentable sugar yields for biofuel production. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 759–761 (2007).
Umezawa, T. The cinnamate/monolignol pathway. Phytochem. Rev 9, 1–17 (2010).
Fu, C. et al. Genetic manipulation of lignin reduces recalcitrance and improves ethanol production from switchgrass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 3803–3808 (2011).
Wang, P., Dudareva, N., Morgan, J. A. & Chapple, C. Genetic manipulation of lignocellulosic biomass for bioenergy. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 29, 32–39 (2015).
Mottiar, Y., Vanholme, R., Boerjan, W., Ralph, J. & Mansfield, S. D. Designer lignins: harnessing the plasticity of lignification. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 37, 190–200 (2016).
Umezawa, T. Lignin modification in planta for valorization. Phytochem. Rev. 17, 1305–1327 (2018).
Ralph, J., Lapierre, C. & Boerjan, W. Lignin structure and its engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 56, 240–249 (2019).
Ruel, K. et al. Impact of CCR1 silencing on the assembly of lignified secondary walls in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 184, 99–113 (2009).
Carmona, C., Langan, P., Smith, J. C. & Petridis, L. Why genetic modification of lignin leads to low-recalcitrance biomass. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 358–364 (2015).
Liu, J. et al. The impact of alterations in lignin deposition on cellulose organization of the plant cell wall. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9, 126, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0540-z (2016).
Mansell, R. L., Gross, G. G., Stöckigt, J., Franke, H. & Zenk, M. H. Purification and properties of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase from higher plants involved in lignin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 13, 2427–2435 (1974).
Tobimatsu, Y. & Schuetz, M. Lignin polymerization: how do plants manage the chemistry so well? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 56, 75–81 (2019).
Karlen, S. D. et al. Commelinid monocotyledon lignins are acylated by p-coumarate. Plant Physiol. 177, 513–521 (2018).
Lan, W. et al. Tricin, a flavonoid monomer in monocot lignification. Plant Physiol. 167, 1284–1295 (2015).
Higuchi, T., Ito, T., Umezawa, T., Hibino, T. & Shibata, D. Red-brown color of lignified tissues of transgenic plants with antisense CAD gene: Wine-red lignin from coniferyl aldehyde. J. Biotechnol. 37, 151–158 (1994).
Sederoff, R. R., MacKay, J. J., Ralph, J. & Hatfield, R. D. Unexpected variation in lignin. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2, 145–152 (1999).
Halpin, C. et al. Brown‐midrib maize (bm1)–a mutation affecting the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Plant J. 14, 545–553 (1998).
Guillaumie, S. et al. Differential expression of phenylpropanoid and related genes in brown-midrib bm1, bm2, bm3, and bm4 young near-isogenic maize plants. Planta 226, 235–250 (2007).
Fornalé, S. et al. Altered lignin biosynthesis improves cellulosic bioethanol production in transgenic maize plants down-regulated for cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Mol. Plant 5, 817–830 (2012).
Saballos, A., Ejeta, G., Sanchez, E., Kang, C. & Vermerris, W. A genomewide analysis of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase family in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] identifies SbCAD2 as the brown midrib6 gene. Genetics 181, 783-795 (2009).
Sattler, S. E. et al. A nonsense mutation in a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene is responsible for the Sorghum brown midrib6 phenotype. Plant Physiol. 150, 584–595 (2009).
Koshiba, T. et al. CAD2 deficiency causes both brown midrib and gold hull and internode phenotypes in Oryza sativa L. cv. Nipponbare. Plant Biotechnol. 30, 365–373 (2013).
Ookawa, T. et al. Increased lodging resistance in long-culm, low-lignin gh2 rice for improved feed and bioenergy production. Sci. Rep. 4, 6567, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06567 (2014).
Umezawa, T., Sakamoto, M. & Koshiba, T. Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase deficiency causes the brown midrib phenotype in rice in Biofuels: Greenhouse Gas Mitigation and Global Warming (ed. Kumar, A., Ogita, S. and Yau, Y.-Y.) 375–385 (Springer, 2018).
Bouvier d’Yvoire, M. et al. Disrupting the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene (BdCAD1) leads to altered lignification and improved saccharification in Brachypodium distachyon. Plant J. 73, 496–508 (2013).
Chen, L. et al. Improved forage digestibility of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) by transgenic down‐regulation of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Plant Biotechnol. J 1, 437–449 (2003).
Lapierre, C. et al. Structural alterations of lignins in transgenic poplars with depressed cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase or caffeic acid O-methyltransferase activity have an opposite impact on the efficiency of industrial kraft pulping. Plant Physiol. 119, 153–164 (1999).
O’connell, A. et al. Improved paper pulp from plants with suppressed cinnamoyl-CoA reductase or cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Transgenic Res. 11, 495–503 (2002).
Pilate, G. et al. Field and pulping performances of transgenic trees with altered lignification. Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 607 (2002).
Fu, C. et al. Downregulation of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) leads to improved saccharification efficiency in switchgrass. BioEnerg. Res. 4, 153–164 (2011).
Saathoff, A. J., Sarath, G., Chow, E. K., Dien, B. S. & Tobias, C. M. Downregulation of cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase in switchgrass by RNA silencing results in enhanced glucose release after cellulase treatment. PloS One 6, e16416, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016416 (2011).
Anderson, N. A. et al. Manipulation of guaiacyl and syringyl monomer biosynthesis in an Arabidopsis cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase mutant results in atypical lignin biosynthesis and modified cell wall structure. Plant Cell 27, 2195–2209 (2015).
Van Acker, R. et al. Different routes for conifer- and sinapaldehyde and higher saccharification upon deficiency in the dehydrogenase CAD1. Plant Physiol. 175, 1018–1039 (2017).
Hepworth, D. & Vincent, J. The mechanical properties of xylem tissue from tobacco plants (Nicotiana tabacum ‘Samsun’). Ann. Bot. 81, 751–759 (1998).
Li, X. et al. FLEXIBLE CULM 1 encoding a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase controls culm mechanical strength in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 69, 685–697 (2009).
Awad, H. et al. No trade-off between hydraulic and mechanical properties in several transgenic poplars modified for lignins metabolism. Environ. Exp. Bot. 77, 185–195 (2012).
Özparpucu, M. et al. Unravelling the impact of lignin on cell wall mechanics: a comprehensive study on young poplar trees downregulated for CINNAMYL ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE (CAD). Plant J. 91, 480–490 (2017).
Kim, H., Ralph, J., Yahiaoui, N., Pean, M. & Boudet, A. M. Cross-coupling of hydroxycinnamyl aldehydes into lignins. Org. lett. 2, 2197–2200 (2000).
Ralph, J. et al. Elucidation of new structures in lignins of CAD- and COMT-deficient plants by NMR. Phytochemistry 57, 993–1003 (2001).
Kim, H. et al. NMR analysis of lignins in CAD-deficient plants. Part 1. Incorporation of hydroxycinnamaldehydes and hydroxybenzaldehydes into lignins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 1, 268–281 (2003).
Kaur, H. et al. Environmental stresses of field growth allow cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase-deficient Nicotiana attenuata plants to compensate for their structural deficiencies. Plant Physiol. 159, 1545–1570 (2012).
Zhao, Q. et al. Loss of function of Cinnamyl Alcohol Dehydrogenase 1 causes accumulation of an unconventional lignin and a temperature-sensitive growth defect in Medicago truncatula. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 13660–13665 (2013).
Hattori, T. et al. Rapid analysis of transgenic rice straw using near-infrared spectroscopy. Plant Biotechnol. 29, 359–366 (2012).
Karlen, S. D. et al. Monolignol ferulate conjugates are naturally incorporated into plant lignins. Sci. Adv. 2, e1600393, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1600393 (2016).
Lapierre, C., Monties, B. & Rolando, C. Preparative thioacidolysis of spruce lignin: isolation and identification of main monomeric products. Holzforschung 40, 47–50 (1986).
Kim, H. et al. Identification of the structure and origin of thioacidolysis marker compounds for cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase deficiency in angiosperms. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47412–47419 (2002).
Kim, H. & Ralph, J. Solution-state 2D NMR of ball-milled plant cell wall gels in DMSO- d 6/pyridine-d 5. Org. Biomol. Chem. 8, 576–591 (2010).
Mansfield, S. D., Kim, H., Lu, F. & Ralph, J. Whole plant cell wall characterization using solution-state 2D-NMR. Nat. Protoc. 7, 1579–1589 (2012).
Tobimatsu, Y. et al. Coexistence but independent biosynthesis of catechyl and guaiacyl/syringyl lignin polymers in seed coats. Plant Cell 25, 2587–2600 (2013).
Tarmadi, D. et al. NMR studies on lignocellulose deconstructions in the digestive system of the lower termite Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki. Sci. Rep. 8, 1290, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19562-0 (2018).
Lam, P. Y. et al. OsCAldOMT1 is a bifunctional O-methyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of tricin-lignins in rice cell walls. Sci. Rep. 9, 11597, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47957-0 (2019).
Takeda, Y. et al. Downregulation of p-COUMAROYL ESTER 3-HYDROXYLASE in rice leads to altered cell wall structures and improves biomass saccharification. Plant J. 95, 796–811 (2018).
Takeda, Y. et al. Lignin characterization of rice CONIFERALDEHYDE 5‐HYDROXYLASE loss‐of‐function mutants generated with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant J. 97, 543–554 (2019).
Takeda, Y. et al. Regulation of CONIFERALDEHYDE 5-HYDROXYLASE expression to modulate cell wall lignin structure in rice. Planta 246, 337–349 (2017).
Wang, T., Salazar, A., Zabotina, O. A. & Hong, M. Structure and dynamics of Brachypodium primary cell wall polysaccharides from two-dimensional 13C solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry 53, 2840–2854 (2014).
Dupree, R. et al. Probing the molecular architecture of Arabidopsis thaliana secondary cell walls using two-and three-dimensional 13C solid state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry 54, 2335–2345 (2015).
Wang, T., Park, Y. B., Cosgrove, D. J. & Hong, M. Cellulose-pectin spatial contacts are inherent to never-dried Arabidopsis primary cell walls: evidence from solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Plant Physiol. 168, 871–884 (2015).
Simmons, T. J. et al. Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat. Commun. 7, 13902, https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13902 (2016).
Kang, X. et al. Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat. Commun. 10, 347, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08252-0 (2019).
Horii, F., Hirai, A. & Kitamaru, R. CP/MAS carbon-13 NMR study of spin relaxation phenomena of cellulose containing crystalline and noncrystalline components. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 3, 641–662 (1984).
Focher, B. et al. Structural differences between non-wood plant celluloses: evidence from solid state NMR, vibrational spectroscopy and X-ray diffractometry. Ind. Crop. Prod. 13, 193–208 (2001).
Ghosh, M., Prajapati, B. P., Suryawanshi, R. K., Dey, K. K. & Kango, N. Study of the effect of enzymatic deconstruction on natural cellulose by NMR measurements. Chem. Phys. Lett. 727, 105–115 (2019).
Segal, L., Creely, J., Martin, A. Jr & Conrad, C. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 29, 786–794 (1959).
Torchia, D. A. The measurement of proton-enhanced carbon-13 T1 values by a method which suppresses artifacts. J. Magn. Reson 30, 613–616 (1978).
Zuckerstätter, G., Terinte, N., Sixta, H. & Schuster, K. C. Novel insight into cellulose supramolecular structure through 13C CP-MAS NMR spectroscopy and paramagnetic relaxation enhancement. J. Carbohydr. Polym. 93, 122–128 (2013).
Chandra, R., Ewanick, S. & Hsieh, C. & Saddler, J. N. The characterization of pretreated lignocellulosic substrates prior to enzymatic hydrolysis, part 1: a modified Simons’ staining technique. Biotechnol. Prog. 24, 1178–1185 (2008).
Meng, X. & Ragauskas, A. J. Recent advances in understanding the role of cellulose accessibility in enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic substrates. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 27, 150–158 (2014).
Zhang, K. et al. GOLD HULL AND INTERNODE2 encodes a primarily multifunctional cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase in rice. Plant Physiol. 140, 972–983 (2006).
Hirano, K. et al. OsCAD2 is the major CAD gene responsible for monolignol biosynthesis in rice culm. Plant cell Rep. 31, 91–101 (2012).
Nishimura, H., Kamiya, A., Nagata, T., Katahira, M. & Watanabe, T. Direct evidence for α ether linkage between lignin and carbohydrates in wood cell walls. Sci. Rep. 8, 6538, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24328-9 (2018).
Giummarella, N., Pu, Y., Ragauskas, A. J. & Lawoko, M. A critical review on the analysis of lignin carbohydrate bonds. Green Chem. 21, 1573–1595 (2019).
Terrett, O. M. & Dupree, P. Covalent interactions between lignin and hemicelluloses in plant secondary cell walls. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 56, 97–104 (2019).
Li, M., Pu, Y. & Ragauskas, A. J. Current understanding of the correlation of lignin structure with biomass recalcitrance. Front. Chem. 4, 45, https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2016.00045 (2016).
Laureano-Perez, L., Teymouri, F., Alizadeh, H. & Dale, B. E. Understanding factors that limit enzymatic hydrolysis of biomass. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 124, 1081–1099 (2005).
Hall, M., Bansal, P., Lee, J. H., Realff, M. J. & Bommarius, A. S. Cellulose crystallinity–a key predictor of the enzymatic hydrolysis rate. FEBS J 277, 1571–1582 (2010).
Vandenbrink, J. P., Hilten, R. N., Das, K., Paterson, A. H. & Feltus, F. A. Analysis of crystallinity index and hydrolysis rates in the bioenergy crop Sorghum bicolor. Bioenerg. Res. 5, 387–397 (2012).
Marriott, P. E., Gómez, L. D. & McQueen‐Mason, S. J. Unlocking the potential of lignocellulosic biomass through plant science. New Phytol. 209, 1366–1381 (2016).
Foston, M. & Ragauskas, A. J. Changes in lignocellulosic supramolecular and ultrastructure during dilute acid pretreatment of Populus and switchgrass. Biomass Bioenerg. 34, 1885–1895 (2010).
Del Rio, L. F., Chandra, R. P. & Saddler, J. N. Fibre size does not appear to influence the ease of enzymatic hydrolysis of organosolv-pretreated softwoods. Bioresour. Technol. 107, 235–242 (2012).
Sun, Q. et al. Effect of lignin content on changes occurring in poplar cellulose ultrastructure during dilute acid pretreatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 7, 150, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-014-0150-6 (2014).
Miyao, A. et al. Target site specificity of the Tos17 retrotransposon shows a preference for insertion within genes and against insertion in retrotransposon-rich regions of the genome. Plant Cell 15, 1771–1780 (2003).
Yamamura, M., Hattori, T., Suzuki, S., Shibata, D. & Umezawa, T. Microscale thioacidolysis method for the rapid analysis of β-O-4 substructures in lignin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 29, 419–423 (2012).
Hatfield, R. D., Jung, H. J. G., Ralph, J., Buxton, D. R. & Weimer, P. J. A comparison of the insoluble residues produced by the Klason lignin and acid detergent lignin procedures. Plant Biotechnol. 65, 51–58 (1994).
Suzuki, S. et al. High-throughput determination of thioglycolic acid lignin from rice. Plant Biotechnol. 26, 337–340 (2009).
Lam, P. Y. et al. Disrupting Flavone Synthase II alters lignin and improves biomass digestibility. Plant Physiol. 174, 972–985 (2017).
Yamamura, M. et al. Occurrence of guaiacyl/p-hydroxyphenyl lignin in Arabidopsis thaliana T87 cell. Plant Biotechnol 28, 1–8 (2011).
Kim, H. et al. Characterization and elimination of undesirable protein residues in plant cell wall materials for enhancing lignin analysis by solution-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Plant Biotechnol. 18, 4184–4195 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Hirohiko Hirochika and Dr. Akio Miyao of the National Agriculture and Food Research Organization, Japan, for providing the cad2 mutant rice seeds, and Dr. Hironori Kaji, Ms. Ayaka Maeno and Ms. Kyoko Yamada for their assistance and helpful suggestions in NMR analysis. This work was supported in part by grants from the Japan Science and Technology Agency/Japan International Cooperation Agency (Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development, SATREPS), the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan (Genomics for Agricultural Innovation, grant no. GMA-0006), the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS, grant nos. #16K14958, #16H06198, #17F17103, and #17K05882) and RISH Kyoto University (grant no. Mission-linked Research Funding #2016-5-2-1). A.F.M. acknowledges the RISET-Pro PhD fellowship program of the Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education of Republic of Indonesia (World Bank Loan no. 8245-ID). A part of this study was conducted using the facilities in the DASH/FBAS at RISH, Kyoto University, and the NMR spectrometer in the JURC at ICR, Kyoto University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.F.M., Y.T., R.K., N.M., T.M., P.Y.L., M.Y., T.K. and M.S. performed experiments. A.F.M., Y.T., R.K. and T.U. conceived research, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript with help from all the others. A.F.M. and Y.T. contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, A.F., Tobimatsu, Y., Kusumi, R. et al. Altered lignocellulose chemical structure and molecular assembly in CINNAMYL ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE-deficient rice. Sci Rep 9, 17153 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53156-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53156-8
This article is cited by
-
The known unknowns in lignin biosynthesis and its engineering to improve lignocellulosic saccharification efficiency
Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery (2023)
-
Genome-wide analysis of the CAD gene family reveals two bona fide CAD genes in oil palm
3 Biotech (2022)
-
Initial pyrolysis mechanism and product formation of cellulose: An Experimental and Density functional theory(DFT) study
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.