Abstract
Long-distance terrestrial migrations are imperiled globally. We determined both round-trip migration distances (straight-line measurements between migratory end points) and total annual movement (sum of the distances between successive relocations over a year) for a suite of large mammals that had potential for long-distance movements to test which species displayed the longest of both. We found that caribou likely do exhibit the longest terrestrial migrations on the planet, but, over the course of a year, gray wolves move the most. Our results were consistent with the trophic-level based hypothesis that predators would move more than their prey. Herbivores in low productivity environments moved more than herbivores in more productive habitats. We also found that larger members of the same guild moved less than smaller members, supporting the ‘gastro-centric’ hypothesis. A better understanding of migration and movements of large mammals should aid in their conservation by helping delineate conservation area boundaries and determine priority corridors for protection to preserve connectivity. The magnitude of the migrations and movements we documented should also provide guidance on the scale of conservation efforts required and assist conservation planning across agency and even national boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Long-distance animal migrations (repeated seasonal movement from 1 discrete area to another) are a widespread and highly conspicuous phenomenon in the natural world1. The evolutionary mechanisms behind migratory behavior are ecological and biogeographic, and reflect the fitness advantage of seasonally tracking habitats that vary in their distribution of resources, environmental conditions, intra- and inter-specific competition, predation, gene flow, and parasites2,3,4,5. Resources include high quality forage or surface water, with greater seasonality and variability in vegetative productivity providing impetus for herbivore migration and concomitant benefits of reduced exposure to predation2,6,7.
Long-distance, terrestrial migrations are globally imperiled, especially for large mammals, and many have already been extinguished or are under threat6,8,9. Loss of migration is cited as a threat to declines of large herbivores worldwide10 and once migratory patterns are lost, they may never resume or take decades for populations to relearn11. Habitat loss, fences, roads, and other types of human infrastructure and disturbance can act as semi-permeable or impermeable barriers to migration6,8,12. Major losses of roadless areas continue13 and there are only about 42,000 patches of roadless areas > 100 km2 globally14. Further, climate change could alter species distributions and migration patterns15. Migratory herbivores affect forage biomass, patterns of nutrient diffusion across regions, ecosystem functioning, and predators, which in turn influence decomposers and primary producers16,17,18. Impairment of large herbivore migration can also reduce population sizes19, with economic and societal impacts on the people and businesses that benefit from their persistence through harvest or tourism6,20.
Two of the most well-known terrestrial migrations are undertaken by caribou (Rangifer tarandus) traveling between their winter ranges and calving grounds in the Arctic21 and blue wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus) moving between wet and dry seasonal ranges in the Serengeti ecosystem22. Caribou are often credited with exhibiting the longest terrestrial migrations on the planet without documentation, or by referencing Fancy et al.’s21 5055 km figure (e.g.8,23). However, this value was not a migration distance per se, but rather the total cumulative distance traveled in a year. Moreover, it was based on currently outdated technology with high positional error, making direct comparisons to current (e.g. GPS) technology problematic. This begs the interesting conservation and management questions: how is migration best measured and which migrations are the longest?
Net squared displacement (NSD) could be used to determine migration distance (e.g.24), although it was designed to be a tool to parse behavioral states and the location of greatest displacement may not be a migratory end point (i.e., calving ground or winter range). For example, some Porcupine Herd caribou migrate along non-linear routes that wrap around the east edge of the Brooks Range mountains before turning northwest during their north-bound, spring migration21. Thus, maximum NSD does not necessarily occur at the calving grounds. Selection of the start (and end) location(s) have also been shown to greatly impact the results of the NSD-based method (e.g.25,26,27).
A different metric, total cumulative annual distance (TCAD) traveled, which we define as the sum of the distances between successive positional locations over the course of a year, could also be used to assess total migration. Many have misinterpreted Fancy et al.’s21 results in this manner. While TCAD is a simple, repeatable metric, it is an estimate of movement distance: all movements, not just migratory ones. Thus, it is meaningful and computable for any mobile animal - whether migratory or not. In fact, the TCAD of migratory and non-migratory individuals within the same population can be similar (e.g.28).
We suggest that the straight-line, round-trip distance (RTD) between migratory end points is perhaps the most repeatable, versatile, and straight-forward means to measure migration distance. Furthermore, RTD can also be directly compared with historic studies that identify, for example, wintering and calving grounds without recourse to collar-based data. Much like TCAD, RTD varies among individuals within years, among years for the same individual, with changes in population size and density, with differences in seasonal range fidelity, and with new barriers to migration over time21,29,30. Reported and historical migration distances are, however, typically reported as a static measurement at the population level. The utility of RTD is constrained to species that display clear migratory patterns but is not applicable to nomadic and resident species31.
Obviously, the importance of movement is not just limited to migration. Animals move to acquire food, resources and mates, mark and defend territories, evade predation and parasites, disperse to avoid strife or competition, or increase mating potential32. All of these behaviors lie largely outside the migration rubric1. How much a particular animal moves depends on its size, trophic level, forage/prey availability, own population density and that of its competition, and on the amount of variability in seasonality, among other factors. We hypothesize that TCAD will be greater for cursorial predators than their prey, as only a limited amount of energy is transferred between trophic levels33 and thus these predators must range more widely to track and successfully secure their prey.
In areas with greater seasonal variability, as once-abundant resources become scarce in 1 area, animals must move to another area3. Similarly, areas with low primary productivity and/or unpredictable resource availability may force animals to roam more or become nomadic34. Thus, we posit that TCAD for larger animals will be less than it will be for smaller animals of the same guild (e.g., grazers), as they can use more ubiquitous, lower-quality forage35,36,37 and may be more resilient to environmental stochasticity due to larger body stores. However, like migration, movement in general has also been adversely affected by human activity and development. For example, Tucker et al.38 documented that, in large animals, movements were reduced by 50–67% in areas of high human activity. Thus, we predict that TCAD will be greater in more remote, less impacted regions. However, in some cases anthropogenic barriers could force wide-ranging species to move further to find suitable crossing opportunities even in remote areas39,40.
Our goals for this paper were to: 1) provide methods to consistently measure migration and movements so that direct comparisons can be made, 2) document the length of RTD migrations for a wide array of species that encompass different regions and ecosystems so that we could determine which species exhibit the longest terrestrial migrations, and 3) determine the TCAD traveled in a year for a suite of animals that varied in movement patterns (migratory, territorial, and nomadic), trophic level, and body size which also had potential to be among the most cursorial large mammals in the world. Lastly, we discuss our results in relation to our hypotheses about trophic levels, vegetative productivity, body size, and human population density in order to explore some of the underlying factors that influence migration and movements.
Material and Methods
Study area and literature review
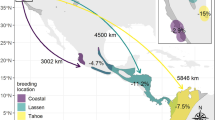
The study area included terrestrial ecosystems worldwide (Fig. 1). We focused our efforts on areas with known long-distance (~300 km) large mammal migrations, a high degree of seasonality, low primary productivity, and/or little human footprint (e.g., the Arctic, central Asia, central and southern Africa, and the inter-mountain and northern great plains regions of North America). We began with existing studies (e.g.6,8,34) and then conducted Google Scholar searches using different species name and the term ‘migration’ or ‘movement’. The remaining datasets we collected ourselves.
Locations of the study areas of some of the longest, terrestrial migrations and movements in the world. Migration distances are shown as lines of a length equaling half the round-trip distance (RTD), roughly oriented in the direction of the migration for that species. Total annual movement distances (TCAD) are depicted as circles with circumferences equaling how far that species moves in a year. Both RTDs and TCADs are color-coded to match species icons and are scaled to be directly comparable to each other and to all species. They may not match the world backdrop in some locations due to projection issues. Areas with greater human density are shaded darker.
Determining migration distances
We used the Euclidean (straight-line), round-trip distance (RTD) between end points to determine length (km) of migrations. The 2 most common sets of migratory end points were winter range and calving area (e.g., caribou) and wet and dry seasonal ranges (e.g., wildebeest). We used information found in studies identified during our literature review and with our own datasets. Mostly, the distances were taken exactly as reported in the literature or as double the estimated distances from the far extent of 1 end point (e.g., winter range) to the center of the other end point (e.g., calving area) based on provided range maps. For studies at the population rather than individual level, we measured from the distal portion of the winter (or dry season) range to the center of the calving (or wet season) range.
Determining total cumulative annual distances
We used GPS datasets that we collected, colleagues made available, or were generally available (e.g., publicly housed in Movebank; www.movebank.org) to estimate total annual distance moved (not as a precise measurement of absolute distance traveled). We defined this distance as the cumulative distance between successive GPS locations over the span of 365 days. Movement rate estimates, like TCAD, are strongly correlated with sample interval7,41. Therefore, where possible, we used relocations that were on 8-hour intervals to standardize according to this bias. For datasets collected at shorter intervals (e.g., 1, 2 or 4 hours), we subsampled the data to achieve an 8-hour interval when possible. When we could not obtain an 8-hour interval (e.g., 5- or 12-hour intervals), we determined the total annual distance moved and adjusted it by the negative relationship between movement rates and sampling interval determined for caribou by Joly41 (see that study’s Fig. 3). For example, if a wildebeest collar collected data every 12 hours, its calculated total annual movement would be increased by 10%, whereas if it collected data every 5 hours, it would be decreased by 6% (instances noted in the tables). While the relationship between movement rate and sample interval likely varied by species and study area, our method provided an approximate method to standardize movements for direct comparisons. We also assess correlation between TCAD and primary productivity (http://silvis.forest.wisc.edu/data/dhis/)42 and human population density (http://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/data/collection/gpw-v4/sets/browse) at the center of the range of each species.
Compliance with guidelines and regulations
All capture, handling, and collaring of study species was in accordance with applicable guidelines and regulations. This includes permitting and institutional animal care and use committee review and approvals from: Alberta Sustainable Resource Development, Fish and Wildlife Research 11861, 16707, 20394, 059-08MHECS-120908, 059-09MHWB-12209; Mongolian Ministry of Nature, Environment and Tourism 5/4275, 5/5656, 6/4136, 6/5621; Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks 11-2007; National Park Service 2010-1, AKR_GAAR_Gustine_GrizzlyBear_2014, AKR_DENA_Borg_GrayWolf_2016.A3, AKR_YUCH_Sorum_GrayWolf_2016.A3; Saskatchewan Ministry of Environment 09FW040; State of Alaska 07-11, 253217-3, 2012-031R; University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna ETK-15/03/2016; U. S. Geological Survey 2014-01.
Results
Migration distances
Caribou and reindeer (also Rangifer tarandus) dominated terrestrial migrations in terms of longest RTD (Table 1). They were the only species exceeding 1000 km, with the exception of a population of gray wolves (Canis lupus; 1016 km) in the Northwest Territories, Canada that were thought to track caribou and be migratory rather than territorial43. There were some outliers of note. First, Alerstam et al.44 reported a 1200 km, one-way migration for Canadian caribou based on a personal communication. Based on our findings of the same species in the same region and geography of the area, we believe this is probably the round-trip distance. Second, Bekenov et al.45 reported a 2400 km round-trip migration for 1 population of saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica) and 600–1200 km for 2 others.
Total annual movement distances
The animal that had the greatest TCAD (7247 km) was a male gray wolf from southwest Mongolia (Table 2). A territorial female wolf with pups from the same area traveled 5429 km in a year. An adult female gray wolf (without pups) from central Alaska moved 5630 km in a year and hunted caribou. An adult male whose pack hunted moose (Alces alces) moved 5554 km in a year. Gray wolves from east-central Alaska traveled similar, yet slightly less, distances: a young female gray wolf (without pups) traveled 5116 km in a year, was territorial, and hunted caribou during the winter months. A wolf from this same area dispersed shortly after capture and ended up in the Yukon Territory, Canada. Including the long-distance dispersal, this wolf moved 4686 km in a year. Wolves that primarily hunted moose from this region moved less (maximum = 3131 km/year) than wolves that primarily hunted caribou.
Aside from gray wolves, nomadic khulan (Equus hemionus; also known as the Mongolian wild ass) exhibited greater TCAD than any other species we analyzed (Table 2). In southeast Mongolia, khulan moved as much as 6145 km/year and as much as 5067 km/year in southwest Mongolia. Caribou in northern North America moved as much as 4868 km/year. No other species besides wolves, khulan, arctic fox (Vulpes lagopus) and caribou had total annual movements >3500 km (Table 2). Mongolian gazelle (Procapra gutturosa) and Burchell’s zebra (Equus quagga) were just below this threshold. Some barren-ground caribou traveled more than 4 times the distance boreal caribou (e.g., Little Smoky Herd) did in a year (1131 km; Table 2).
In southwest Mongolia, gray wolves moved more than khulan or wild Bactrian camels (Camelus bactrianus; Table 2; Fig. 2), which are among their prey species. In Alaska, gray wolves moved more than their primary prey of caribou or moose. Similarly, in Alberta, gray wolves moved more than elk (Cervus canadensis) or boreal caribou. In north-central Alaska, brown bear (Ursus arctos) also moved more than moose from the same region. Khulan moved more than camels in southwest Mongolia. This was true for sympatric (unfortunately these data had too many missed GPS fixes for us to report TCAD) and allopatric populations (Table 2, Fig. 3a). In Alberta, pronghorn (Antilocapra americana) moved more than elk and caribou, and, in Alaska, caribou moved more than moose. Caribou in northern Canada moved more than those in southern Canada, and pronghorn in Alberta/Saskatchewan moved more than those in Montana/Saskatchewan 400 km to the south. However, moose in northern Alaska had similar annual movement distances as those in southern Canada. TCAD of herbivores was significantly and negatively correlated with primary productivity (Fig. 3b; P < 0.01, F = 10.35, df = 17, R2 = 0.393). TCAD was not significantly correlated with human population density.
Discussion
Caribou have long been thought to exhibit the longest, terrestrial migrations on the planet, albeit often without robust validation. Our study of comparable migratory distances provides substantially more robust support for this claim. With multiple populations with > 1200 km straight-line, round-trip migration distance, caribou are indeed world-class migrators. While we believe caribou likely exhibit the longest extant terrestrial migrations, it is possible that another species may claim that recognition.
In particular, the 2400 km RTD migration reported for saiga antelope in Kazakhstan is by far the longest to our knowledge. However, this distance was estimated without the assistance of tracking technology that allowed known individuals to be relocated45 and thus there remains the possibility that Saiga antelope seen on 1 winter range were from different sub-populations than others found on the calving grounds used to determine this distance. Moreover, there have been dramatic declines in saiga antelope populations46,47 and populations are currently becoming increasingly constrained by human developments48. Thus, saiga antelope migrations have likely been diminished and the species may not exhibit the longest, extant, terrestrial migrations (E.J. Milner-Gulland, pers. comm.6). We encourage the support and publication of GPS-collar research to help identify, quantify and conserve long-distance migrations in this species. Future work quantifying migration distances should focus on movements at the scale of the individual rather than populations for repeatability and comparability.
Migration distance is thought to be positively correlated with population size and density21,29,30. We offer 2 more examples that support this hypothesis. First, the Bathurst Caribou Herd, in central Canada, used to migrate up to 1500 km (see49), but as the herd has declined, it now migrates about 1350 km50. Second, the round-trip migration distance covered by Western Arctic Herd caribou was about 1500 km at its peak population of nearly 500,000 animals (circa 2003), but is now about 1250 km with a population of about half of its peak (this study). Recently, however, the Porcupine Herd has shown the opposite trend.
While RTD is a recognizable and valuable metric, it has numerous limitations. Start and end points can be difficult to objectively and quantifiably define and population-level analyses might over-estimated migration distances. Greater standardization and explicit definitions would aid in future comparisons. Additionally, facultative winter migrations, nomadism, dispersal events, territorial and other movements fall outside the domain of RTD. TCAD provides a much more straight-forward, repeatable and quantifiable method to directly compare movements across individuals, populations and species.
Our TCAD results are intriguing, yet preliminary. Predator species consistently moved more than their prey, in line with our hypothesis (Fig. 2). We could not rigorously test our hypotheses due to small samples sizes and biased geography, however, gray wolves from southwest Mongolia moved more than sympatric khulan or wild camels from near the same region. In Alaska, the gray wolf moved more than its primary prey species, caribou or moose, and similarly, in Alberta, the gray wolf moved more than elk or boreal caribou. Also, brown bears moved more than moose in north-central Alaska. While brown bears are omnivores, they prey upon moose and their calves in this region. We suspect this pattern of predators moving more than their prey may be widespread among cursorial predators. We also hypothesize that the TCAD of cursorial predators will increase with more vagile prey or with prey at lower densities and be greater than those for ambush predators. Our findings also suggest that complex social structure, territoriality, and extended periods of relative immobility of young, rather than metabolic and/or anatomical inefficiencies, could prevent wolves and similar cursorial predators from tracking their prey year-round (see2,5): not only can they keep up, they can go farther.
In agreement with another of our hypotheses, but also hampered by small sample sizes, smaller members of the same guild appeared to move more than larger members found in the same region (Fig. 3a). For example, in southwest Mongolia, khulan (~230 kg) moved more than wild camels (~690 kg), in Alaska, barren-ground caribou (~90 kg) moved more than moose (~480 kg), in the Serengeti, wildebeest (~140 kg) moved more than zebras (~320 kg), and in Alberta, pronghorn (~55 kg) moved more than elk (~235 kg) and boreal caribou (~180 kg). Again, we suspect this pattern is widespread and related to allometry and the ability of larger species to use lower quality forage than smaller species35,36,37. Our results did, however, document elk moving more than boreal caribou in Alberta. These 2 studies did not overlap spatially and primary productivity was lower in the region where the elk occurred.
We confirmed our prediction that species dwelling in areas with dramatic seasonal variability or low primary productivity (e.g., the Arctic and central Asia) would have greater TCAD (Fig. 3). We expect that low vegetative productivity and high degree of seasonality in southern Mongolia contributed to this region having the greatest TCAD we found34. Khulan in southeast Mongolia, where resource availability is more variable, moved more than khulan in southwest Mongolia51,52. Zebra in Botswana, where primary productivity is lower, moved more than zebra in the Serengeti. Furthermore, we found wolves in Alaska moved more than wolves found 3000 km south in Alberta, caribou in northern Canada moved more than those in southern Canada, and pronghorn in Alberta/Saskatchewan moved more than those 400 km to the south in Montana/Saskatchewan. We did not find a significant correlation between human population density and TCAD, but that may be related to our focus on species with high TCAD. Indeed, all TCADs > 3500 km were found in areas with densities of < 0.2 people/km2. Large patch sizes, associated with low human population density, may also facilitate greater movements.
In our study, gray wolves were the most cursorial species, with individuals from southwest Mongolia exhibiting the longest annual movements. However, like other species (e.g., caribou), wolves displayed a high degree of plasticity. Territorial wolves had greater total annual movements than even long-distance (>450 km) dispersing conspecifics. This may be due to territory maintenance53 or hunting behavior. Wolves in packs that hunted caribou moved more than packs that focused on less cursorial moose. Frame et al.54 reported 1 denning female wolf traveled 341 km in 14 days, to a maximum distance of 103 km from her active den, in pursuit of caribou. Wolves from central Alaska, where caribou density was lower, moved more than wolves from east-central Alaska, where caribou density was greater. While wolves were the most mobile species that we studied, they modulate movements in relation to their primary prey55. Meso-carnivores inhabiting low productivity regions, such as the arctic fox, warrant more attention as they can travel very long distances (>4400 km) in 4 or 5 months56,57 as well as annually (>4900 km based on daily or every other day PTT relocations56, also see Table 2).
While caribou exhibited the longest migration distances, these did not translate into the greatest annual distances traveled. Caribou were outpaced annually by nomadic khulan, but also by their primary predator, the gray wolf and the arctic fox. Caribou, from various study areas, were the next most cursorial species. We posit that extreme movements, in caribou and other species that travel great distances, are driven by extreme seasonal variability, patchy distribution of key resources, low primary productivity, predator avoidance, territoriality of conspecifics, and/or access to parturition location.
Conclusion
Our work documents and compares some of the longest, extant terrestrial migrations and movements in the world in a standardized way. Such long-distance movements are increasingly challenged by infrastructure development that hinders mobility38, thus data on long-distance migrations will help future efforts to identify key areas and species of conservation concern, as well as a better understanding of the mechanisms that structure overall movement of large terrestrial mammals. Furthermore, the spatial and temporal scale of these movements should be accounted for when conservation, corridor, and mitigation planning is undertaken. Territorial, migratory, and nomadic species populations may require different conservation planning strategies58. Conservation of long-distance terrestrial movements should also have ancillary benefits to a wide array of other species and ecosystem services.
Data availability
Data generated during this study are included in this published article (see Tables 1 and 2). Underlying GPS data used to generate these results may made available from the corresponding author on a case by case basis, in conjunction with the researcher(s) managing those datasets, and in accordance with respective legal constraints.
Change history
15 January 2020
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via a link at the top of the paper.
References
Dingle, H. Migration: the biology of life on the move (Oxford University Press, 2014).
Fryxell, J. M. & Sinclair, A. R. E. Causes and consequences of migration by large herbivores. Trends Ecol. Evol. 3, 237–241 (1988).
Fryxell, J. M. & Sinclair, A. R. E. Seasonal migration by white-eared kob in relation to resources. Afr. J. Ecol. 26, 17–31 (1988).
Dingle, H. & Drake, A. What is migration? BioScience 57, 113–121 (2007).
Avgar, T., Street, G. & Fryxell, J. M. On the adaptive benefits of mammal migration. Can. J. Zool. 92, 481–490 (2014).
Harris, G., Thirgood, S., Hopcraft, J. G. C., Cromsigt, J. P. G. M. & Berger, J. Global decline in aggregated migrations of large terrestrial mammals. Endanger. Species Res. 7, 55–76 (2009).
Mueller, T. et al. How landscape dynamics link individual to population-level movement patterns: a multispecies comparison of ungulate relocation data. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 20, 683–694 (2011).
Berger, J. The last mile: how to sustain long-distance migration in mammals. Conserv. Biol. 18, 320–331 (2004).
Wilcove, D. S. & Wikelski, M. Going, going, gone: is animal migration disappearing? PLoS Biol. 6, 1361–1364 (2008).
Ripple, W. J. et al. Collapse of the world’s largest herbivores. Science Advances 1, e14000103 (2015).
Jesmer, B. R. et al. Is ungulate migration culturally transmitted? Evidence of social learning from translocated animals. Science 361, 1023–1025 (2018).
Seidler, R. G., Long, R. A., Berger, J., Bergen, S. & Beckmann, J. P. Identifying impediments to long-distance mammal migrations. Conserv. Biol. 29, 99–109 (2015).
Watson, J. E. M. et al. Catastrophic declines in wilderness areas undermine global environment targets. Curr. Biol. 26, 29292–2934 (2016).
Ibisch, P. L. et al. A global map of roadless areas and their conservation status. Science 354, 1423–1427 (2016).
Walther, G.-R. et al. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 416, 389–395 (2002).
McNaughton, S. J., Ruess, R. W. & Seagle, S. W. Large mammals and process dynamics in African ecosystems. BioScience 38, 794–800 (1988).
Hobbs, N. T. Modification of ecosystems by ungulates. J. Wildlife Manage. 60, 695–713 (1996).
Fortin, D. et al. Wolves influence elk movements: behavior shapes a trophic cascade in Yellowstone National Park. Ecology 86, 1320–1330 (2005).
Bolger, D. T., Newmark, W. D., Morrison, T. A. & Doak, D. F. The need for integrative approaches to understand and conserve migratory ungulates. Ecol. Lett. 11, 63–77 (2008).
Gordon, I. J., Hester, A. J. & Festa-Bianchet, M. The management of wild large herbivores to meet economic, conservation and environmental objectives. J. Appl. Ecol. 41, 1021–1031 (2004).
Fancy, S. G., Pank, L. F., Whitten, K. R. & Regelin, W. L. Seasonal movements of caribou in arctic Alaska as determined by satellite. Can. J. Zool. 67, 644–650 (1989).
Thirgood, S. et al. Can parks protect migratory ungulates? The case of the Serengeti wildebeest. Anim. Conserv. 7, 113–120 (2004).
Schaefer, J. A. & Mahoney, S. P. Spatial dynamics of the rise and fall of caribou (Rangifer tarandus) in Newfoundland. Can. J. Zool. 91, 767–774 (2013).
Bunnefeld, N. et al. A model driven approach to quantify migration patterns: individual, regional and yearly differences. J. Anim. Ecol. 80, 466–476 (2011).
Gurarie, E. et al. A framework for modelling range shifts and migrations: asking when, whither, whether and will it return. J. Anim. Ecol. 86, 943–959 (2017).
Spitz, D. B., Hebblewhite, M. & Stephenson, T. R. ‘MigrateR’: extending model-driven methods for classifying and quantifying animal movement behavior. Ecography 40, 788–799 (2017).
Jakes, A. F. et al. Classifying the migration behaviors of pronghorn on their northern range. J. Wildlife Manage. 82, 1229–1242 (2018).
Joly, K., Craig, T., Sorum, M. S., McMillan, J. S. & Spindler, M. A. Moose (Alces alces) movement patterns in the upper Koyukuk river drainage, northcentral Alaska. Alces 51, 87–96 (2015).
Couturier, S., Otto, R. D., Cote, S. D., Luther, G. & Mahoney, S. P. Body size variations in caribou ecotypes and relationships with demography. J. Wildlife Manage. 74, 395–404 (2010).
Peters, W. et al. Migration in geographic and ecological space by a large herbivore. Ecol. Monogr. 87, 297–320 (2017).
Mueller, T. & Fagan, W. F. Search and navigation in dynamic environments – from individual behaviors to population distributions. Oikos 117, 654–664 (2008).
Nathan, R. An emerging movement ecology paradigm. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 19050–19051 (2008).
Elton, C. Animal Ecology (McMillan, 1927).
Teitelbaum, C. S. et al. How far to go? Determinants of migration distance in land mammals. Ecol. Lett. 18, 545–552 (2015).
Jarman, P. J. The social organization of antelope in relation to their ecology. Behaviour 48, 215–266 (1974).
Senft, R. et al. Large herbivore foraging and ecological hierarchies. BioScience 37, 789–799 (1987).
Barboza, P. S. & Bowyer, R. T. Sexual segregation in dimorphic deer: a new gastrocentric hypothesis. J. Mammal. 81, 473–489 (2000).
Tucker, M. E. et al. Moving in the Anthropocene: global reductions in terrestrial mammalian movements. Science 359, 466–469 (2018).
Jakes, A., Jones, P. F., Paige, C. L., Seidler, R. G. & Huijser, M. P. A fence runs through it: a call for greater attention to the influence of fences on wildlife and ecosystems. Biol. Conserv. 227, 310–318 (2018).
Xu, W., Huang, Q., Stabach, J., Buho, H. & Leimgruber, P. Railway underpass location affects migration distance in Tibetan antelope (Pantholops hodgsonii). PLoS ONE 14, e0211798 (2019).
Joly, K. The effects of sampling regime on the analysis of movements of overwintering female caribou in east-central Alaska. Rangifer 25, 67–74 (2005).
Hobi, M. L. et al. A comparison of Dynamic Habitat Indices derived from different MODIS products as predictors of avian species richness. Remote Sens. Environ. 195, 142–152 (2017).
Walton, L. R., Cluff, H. D., Paquet, P. C. & Ramsay, M. A. Movement patterns of barren-ground wolves in the central Canadian Arctic. J. Mammal. 82, 867–876 (2001).
Alerstam, T., Hedenstrom, A. & Akesson, S. Long-distance migration: evolution and determinants. Oikos 103, 247–260 (2003).
Bekenov, A. B., Grachev, I. A. & Milner-Gulland, E. J. The ecology and management of the Saiga antelope in Kazakhstan. Mammal Rev. 28, 1–52 (1998).
Milner-Gulland, E. J. et al. Reproductive collapse in saiga antelope harems. Nature 422, 135 (2003).
Kock, R. A. et al. Saigas on the brink: multidisciplinary analysis of the factors influencing mass mortality events. Science Advances 4, eaao2314 (2018).
Linnell, J. D. C. et al. Border security fencing and wildlife: the end of the transboundary paradigm in Eurasia? PLoS Biol. 14, e1002483 (2016).
Chen, W. et al. Assessing the Impacts of Summer Range on Bathurst Caribou’s Productivity and Abundance since 1985. Nat. Res. 5, 130–145 (2014).
BQCMB (Beverly and Qamanirjuaq Caribou Management Board). 2015-2016 Annual Report, http://arctic-caribou.com/pdf/annual-reports/2015_2016_annual_report.pdf (2016).
Buuveibaatar, B. et al. Human activities negatively impact distribution of ungulates in the Mongolian Gobi. Biol. Conserv. 203, 168–175 (2016).
Nandintsetseg, D., Kaczensky, P., Ganbaatar, O., Leimgruber, P. & Mueller, T. Spatiotemporal habitat dynamics of ungulates in unpredictable environments: the khulan (Equus hemionus) in the Mongolian Gobi desert as a case study. Biol. Conserv. 204, 313–321 (2016).
Lewis, M. A. & Murray, J. D. Modelling territoriality of deer-wolf interactions. Nature 366, 738–740 (1993).
Frame, P. F., Hik, D. S., Cluff, D. & Paquet, P. C. Long foraging movement of a denning tundra wolf. Arctic 57, 196–203 (2004).
Furey, N. B., Armstrong, J. B., Beauchamp, D. A. & Hinch, S. G. Migratory coupling between predators and prey. Nature Ecol. Evol. 2, 1846–1853 (2018).
Tarroux, A., Berteaux, D. & Bety, J. Northern nomads: ability for extensive movements in adult arctic foxes. Polar Biol. 33, 1021–1026 (2010).
Fuglei, E. & Tarroux, A. Arctic fox dispersal from Svalbard to Canada: one female’s long run across sea ice. Polar Res. 38, https://doi.org/10.33265/polar.v38.3512 (2019).
Nandintsetseg, D. et al. Challenges in the conservation of wide-ranging nomadic species. J. Appl. Ecol. 56, 1916–1926 (2019).
Taillon, J., Festa-Bianchet, M. & Cote, S. D. Shifting targets in the tundra: protection of migratory caribou calving grounds must account for spatial changes over time. Biol. Conserv. 147, 163–173 (2012).
Baskin, L. & Danell, K. Ecology of ungulates: a handbook of species in eastern Europe and northern and central Asia (Springer, 2003).
Ferguson, M. A. D. & Messier, F. Mass emigration of arctic tundra caribou from a traditional winter range: population dynamics and physical condition. J. Wildlife Manage. 64, 168–178 (2000).
Peterson, C. Epic Wyoming mule deer migration documented again, confirming the longest path in the world, https://trib.com/lifestyles/recreation/epic-wyoming-mule-deer-migration-documented-again-confirming-the-longest/article_b8ea34e0-fe07-5305-998c-2720103944d8.html. Accessed August 29, 2018 (Casper Star Tribune, August 16, 2018).
Joly, K., Dale, B. W., Collins, W. B. & Adams, L. G. Winter habitat use by female caribou in relation to wildland fires in interior Alaska. Can. J. Zool. 81, 1192–1201 (2003).
Schaller, G. B., Kang, A., Cai, X. & Liu, Y. Migratory and calving behavior of Tibetan antelope population. Acta Theriologica Sinica 26, 105–113 (2006).
Torney, C. J., Hopcraft, J. G. C., Morrison, T. A., Couzin, I. D. & Levin, S. A. From single steps to mass migration: the problem of scale in the movement ecology of the Serengeti wildebeest. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 373, 20170012 (2018).
Miura, N. et al. Analysis of the seasonal migrations of Mongolian gazelle, using MODIS data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inform. Sci. 35, 418–422 (2004).
Bartlam-Brooks, H. L. A., Bonyongo, M. C. & Harris, S. Will reconnecting ecosystems allow long-distance mammal migrations to resume? A case study of a zebra Equus burchelli migration in Botswana. Oryx 45, 210–216 (2011).
Naidoo, R. et al. A newly discovered wildlife migration in Namibia and Botswana is the longest in Africa. Oryx 50, 138–146 (2016).
Soper, J. D. History, range and home life of the northern bison. Ecol. Monogr. 11, 347–412 (1941).
Mauer, F. J. Moose migration: northeastern Alaska to northwestern Yukon Territory, Canada. Alces 34, 75–81 (1998).
Berger, J., Cain, S. L. & Berger, K. M. Connecting the dots: an invariant migration corridor links the Holocene to the present. Biol. Lett. 2, 528–531 (2006).
Kaczensky, P., Enkhsaikhan, N., Ganbaatar, O. & Walzer, C. The Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area in Mongolia - refuge or sink for wolves Canis lupus in the Gobi? Wildlife Biol. 14, 444–456 (2008).
Bartlam-Brooks, H. L. A., Beck, P. S. A., Bohrer, G. & Harris, S. In search of greener pastures – using satellite images to predict the effects of environmental change on zebra migration. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 188(1), 11 (2013).
Bartlam-Brooks, H. L. A. & Harris, S. Data from: In search of greener pastures – using satellite images to predict the effects of environmental change on zebra migration. Movebank Data Repository, https://doi.org/10.5441/001/1.f355b4f (2013).
Kaczensky, P. et al. Space and habitat use by wild Bactrian camels in the Transaltai Gobi of southern Mongolia. Biol. Conserv. 169, 311–318 (2014).
Hopcraft, J. G. C. et al. Competition, predation, and migration: individual choice patterns of Serengeti migrants captured by hierarchical models. Ecol. Monogr. 84, 355–372 (2104).
Hebblewhite, M. & Merrill, E. H. Multiscale wolf predation risk for elk: does migration reduce risk? Oecologia 152, 377–387 (2007).
Hebblewhite, M., Merrill, E. H. & McDermid, G. A multi-scale test of the forage maturation hypothesis in a partially migratory ungulate population. Ecol. Monogr. 78, 141–166 (2008).
DeCesare, N. J. et al. Transcending scale dependence in identifying habitat with resource selection functions. Ecol. Appl. 22, 1068–1083 (2012).
Peters, W., Hebblewhite, M., DeCesare, N., Cagnacci, F. & Musiani, M. Resource separation analysis with moose indicates threats to caribou in human altered landscapes. Ecography 36, 487–498 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We thank the following for graciously providing GPS caribou data used in our analyses: Jan Adamczewski, Bruno Croft, and Bonnie Fournier. Funding for KJ, MSS and MDC was provided by the National Park Service. Various Alaska collaring projects were funded the National Park Service, Alaska Department of Fish and Game, US Fish and Wildlife Service and Bureau of Land Management. Funding for MH and EG was provided by NASA’s Arctic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (Grant # NNX15AW71A), and NSF LTREB to MH (1556248). PK was supported by the Austrian Science Foundation (FWF projects P14992 and P18634) and by the Great Gobi B Strictly Protected Area staff and administration. JGCH was supported by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement 641918 (AfricanBioServices). Funding for Serengeti wildebeest and zebra collaring supported by the Frankfurt Zoological Society, Lord Kelvin Adam Smith Fellowship and the British Ecological Society. Capture and collaring of khulan occurred within the framework of the Core Biodiversity Monitoring by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), administered through a cooperative agreement with Sustainability East Asia LLC (SEA) originating from Oyu Tolgoi (OT) gold and copper mining company. Maxwell Newton assisted with our literature search. We thank anonymous reviewers for constructive critiques that improved our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.J. conceived of the project. K.J., E.G. and B.L.B. conducted analyses. E.G. developed the figures. K.J., E.G., M.S.S., P.K., M.D.C., A.J., B.L.B., D.N., G.H., B.B., P.J., T.M., C.W., K.O., J.P., A.Y. & M.H. provided data and contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Joly, K., Gurarie, E., Sorum, M.S. et al. Longest terrestrial migrations and movements around the world. Sci Rep 9, 15333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51884-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51884-5
This article is cited by
-
A century of exercise physiology: concepts that ignited the study of human thermoregulation. Part 4: evolution, thermal adaptation and unsupported theories of thermoregulation
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2024)
-
To move or not to move—factors influencing small-scale herder and livestock movements in the Dzungarian Gobi, Mongolia
Regional Environmental Change (2023)
-
Wild Mountain reindeer Rangifer tarandus tarandus winter foraging: snow-free areas a key resource for feeding
Polar Biology (2023)
-
Death comes for us all: relating movement-integrated habitat selection and social behavior to human-associated and disease-related mortality among gray wolves
Oecologia (2023)
-
Ungulates on the move
Nature Ecology & Evolution (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.