Abstract
Size shifts may be a by-product of alterations in life history traits driven by natural selection. Although this approach has been proposed for islands, it has not yet been explored in continental faunas. The trends towards size decrease experienced by some hipparionins constitute a good case study for the application of a life history framework to understand the size shifts on the continent. Here, we analysed bone microstructure to reconstruct the growth of some different-sized hipparionins from Greece and Spain. The two dwarfed lineages studied show different growth strategies. The Greek hipparions ceased growth early at a small size thus advancing maturity, whilst the slower-growing Spanish hipparion matured later at a small size. Based on predictive life history models, we suggest that high adult mortality was the likely selective force behind early maturity and associated size decrease in the Greek lineage. Conversely, we infer that resource limitation accompanied by high juvenile mortality triggered decrease in growth rate and a relative late maturity in the Spanish lineage. Our results provide evidence that different selective pressures can precipitate different changes in life history that lead to similar size shifts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Body size is a key aspect of organisms’ biology as it is tightly correlated with many aspects of their physiology, ecology and life history1,2,3; body size, hence, is a fitness component4. Based on the coupling between life history traits and body mass, some authors5,6,7,8 have addressed size shifts in insular environments within the framework of life history theory.
Life history theory is built around the idea that selection acts on the life history characteristics of an organism to maximise its reproductive success or fitness9,10. To explain the range of life history strategies observed in nature, evolutionary biologists have traditionally used the approach of life history optimization11. Different optimality studies have provided a broad range of predictive models for the evolution of life cycle traits under different ecological constraints9,12,13. These models provide an explanatory framework for understanding how selective pressures can shape the life history of an organism.
Based on this scheme, Palkovacs7 proposed that body size shifts on islands can indirectly result from variation in life history traits instead of direct selection acting on size, as previously suggested by other authors14,15,16. He pointed out that two factors, extrinsic mortality and resource availability, influence life history traits to which adult size is sensitive, especially individual growth rate and age at maturity7. Although this approach has been theoretically proposed7 and tested17,18,19,20 in insular environments, it has not yet been explored in continental settings, where predictive life history models should also be applicable to explain body size evolution.
On continents, trends in size reduction have been identified in various taxonomic groups from different stratigraphic ages21,22,23. For instance, contrary to the notion of size increase over geological time within the horse lineage (Copes’ Rule)24, some equid clades experienced dwarfing21,25,26. This is the case of the Arenahippus lineage during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum27, of some hipparionins during the European late Miocene28,29,30, and of the Equus lineage during the Pleistocene25,31,32.
The first hipparionins that dispersed throughout the Old World in the Vallesian were large sized hipparions33 that likely evolved from a large ancestor34. Late Miocene hipparionins from the Eastern and Western Mediterranean basins exemplify an interesting case of continental trends in size decrease. The Western Mediterranean late Turolian (MN13) dwarf hipparions from the Teruel Basin (Spain) have been interpreted to represent an evolutionary gradation towards reduced body size, simplified enamel abrasive figures, increasing hypsodonty and gracility29,30. This size reduction led to some of the smallest Hipparion sensu lato forms of the Old World, Hipparion gromovae and Hipparion periafricanum, with estimated mean body masses of 59 kg and 23 kg respectively29. These two taxa coexisted sympatrically with the larger 138 kg Hipparion truyolsi29. In the Eastern Mediterranean basins, the existence of the small macedonicum morphotype is already reported in the early Vallesian (MN9), and its temporal range extends up to the middle Turolian (MN12), and possibly to the late Turolian (MN13)28,35. Similar to the Spanish small hipparionins, the Greek Hipparion macedonicum underwent a body mass decrease coupled with a simplification of the enamel plication and an increased gracility of the metapodials28. The body mass estimations for this taxon range from 72.3–121 kg during the Vallesian (MN9-MN10) to 49.5–94.7 kg during the early-middle Turolian (MN11-12)28. This small morphotype coexisted with larger species that pertain to the primigenium, the dietrichi and the proboscideum morphotypes, which almost double the body mass of the small forms35.
The occurrence of these dwarfed hipparionins in the European late Miocene represents a good opportunity to test for the coupling of life history changes and size shifts. In the present study, we aim to unravel the possible mechanisms and causes underlying trends in size reduction of these hipparions from a life history approach. For this purpose, we reconstruct the bone growth pattern of different-sized hipparionins through bone histology. Due to the fact that tissue type and bone growth marks reflect tempo and rate of bone growth36,37, bone histology is a valuable tool for reconstructions of life histories38,39 and growth patterns40,41,42.
Results
Bone histology
Bone microstructure is generally better preserved in the Spanish specimens (Supplementary Fig. S1a), while some Greek metapodials have suffered different taphonomical alterations. In most cases this does not erase histological details such as vascularization or bone growth marks (Supplementary Fig. S1b). The sample from the Nikiti-2 (NIK) fossil site, however, is especially damaged diagenetically or through microbiological attack (Supplementary Fig. S1c), and it has therefore not been used for our growth curves reconstruction.
Both metacarpals and metatarsals of all the groups studied present a similar tissue and vascular arrangement. Their primary bone consists of a fibrolamellar complex (FLC) with longitudinal primary osteons oriented in circular rows (Fig. 1a). A similar histological pattern has been observed in previous studies in the metapodials of extant43 and fossil equids44,45. The amount of parallel fibered bone (PFB) within the FLC46 is higher in the innermost cortex of the metapodials than in the outer cortical area, coinciding with a smaller diameter of the primary osteons in the inner cortex (Fig. 1a). This observation is in agreement with the tissue pattern observed in extant equid bones43,47.
Hipparionin metapodial histology observed under polarised light using a 1/4λ filter. Scale: 0.5 mm. (a) Primary bone tissue formed by fibrolamellar complex (FLC) in the innermost cortex of the Hipparion truyolsi metatarsal IPS-28842. The arrow points out the transition between a FLC with higher parallel fibered bone component (PFB) to a FLC with higher fibrous component and larger osteons. (b) Laminar bone tissue in the inner cortex of the Hipparion cf. sebastopolitanum (primigenium morphotype) PNT-22. (c) Radial vascular canals present in the first growth cycle of the Hipparion philippus (dietrichi morphotype) metatarsal PER-342. (d) Secondary bone tissue in the lateral posterior area of the Hipparion gromovae metacarpal IPS-101807. Dense Haversian systems (HS) are concentrated in the contact zone with the lateral metapodials, and lamellar tissue is filling the resorption cavities near the medullary area (arrow indicating resorption line).
We also have identified the following primary tissues and vascular orientations within the histological samples: Laminar bone is present in the posterior inner cortical zone (Fig. 1b) in some metapodials. Half of the Spanish H. gromovae specimens exhibit this tissue in the innermost cortex, while it is present in only some metapodials from Greek Vallesian sites. Radial canals are also identified within the first growth cycle of metatarsals of the large dietrichi morphotype (Fig. 1c) and one primigenium metatarsal (PNT-4). Radial canals are also sparsely situated in some regions of one dietrichi metacarpal (DTK-58) and in metapodials of the macedonicum morphotype (PER-23 and PER-425). The different vascular arrangements exhibit modest differences in growth rate compared to the bone matrix typology48. Nevertheless, tissues with radial osteons present higher growth rates compared to those with predominant circular osteons, as laminar tissues, when observed within the same bone49,50. Accordingly, the radial canals mainly observed in some dietrichi and primigenium metatarsals can be related to higher growth rates, while the laminar bone tissue present in four of the eight H. gromovae specimens can be an indicator of slower growth rates. These extrapolations from bone vascularization patterns must be done carefully in fossil taxa because of the high range of variability48,49.
We identified large resorption cavities (RC) distributed near the medullary cavity within the posterior area of almost all metapodials. These RC appear early in ontogeny and, in some cases, lamellar bone is deposited at their margins, resulting in a high concentration of secondary tissue in the inner posterior zone of the metapodials (Fig. 1d). Besides, dense Haversian tissue is identified in our samples (Fig. 1d). The Haversian tissue is mainly concentrated within the lateral posterior and medial posterior areas, where the lateral metapodials (II and IV) contact the central one. The major secondary remodelling of these areas is related to higher biomechanical loadings43,44. Two metapodials show an extensive distribution of Haversian systems (PER-X and IPS-28842), though the growth marks are still identifiable (Supplementary Fig. S2). Superimposition of different ontogenetic stages shows that neither medullary expansion nor Haversian canals completely eroded the cyclical growth marks (CGMs). Lamellar bone is present in the outermost cortex of some metapodials, forming the external fundamental system (EFS, see Material and Methods) in adult individuals that have attained their final size (Figs 2 and 3).
Bone growth marks in the periosteum of adult metacarpals. Growth marks are indicated by white arrows, small black arrows mark the growth lines present within the EFS, which is identified by a white line. The images were obtained under polarised light using a 1/4λ filter. Scale: 0.5 mm. (a) Hipparion aff. giganteum (primigenium morphotype) metacarpal NKT-22. (b) H. philippus (dietrichi morphotype) metacarpal PER-X. (c) Hipparion macedonicum (macedonicum morphotype) metacarpal PER-23. (d) H. gromovae metacarpal IPS-96274.
Bone growth marks in the periosteum of adult metatarsals. Growth marks are indicated by white arrows, small black arrows mark the growth lines present within the EFS, and EFS is identified by a white line. The images were obtained under polarised light using a 1/4λ filter. Scale: 0.5 mm. (a) H. cf. sebastopolitanum (primigenium morphotype) metatarsal PNT-4. (b) Hipparion aff. platygenys (dietrichi morphotype) metatarsal DTK-106. (c) H. philippus (dietrichi morphotype) metatarsal PER-1211. (d) H. gromovae metatarsal IPS-101809. (e) H. macedonicum (macedonicum morphotype) metatarsal PER-485. (f) H. truyolsi metatarsal IPS-28842.
Skeletocronology
We have used the specimens that approached their final size for skeletocronological analysis and growth reconstruction. In most cases, the three Greek morphotypes present two CGMs embedded in the FLC matrix, both in the metacarpals (Fig. 2a,b) and the metatarsals (Fig. 3a,b,e). However, one of the three metatarsals of the dietrichi morphotype (DTK-106) exhibits three CGMs in the FLC prior to deposition of the EFS in the lateral and medial areas, while two of the five specimens of the macedonicum morphotype (PER-23 and VAT-112) have only one CGM each. This can suggest an advanced maturity in the small Greek representatives though there appears to be some variability. The main difference between the Greek forms, however, lies in the spacing between the last growth mark of the FLC and the EFS. Generally, when analogous regions are compared, the large primigenium and dietrichi metacarpals (Fig. 2a,b) continue to grow after the second CGM compared to the macedonicum morphotype (Fig. 2c). Similarly, a higher amount of tissue is deposited during the third growth cycle of the larger metatarsals of primigenium and dietrichi morphs (Fig. 3a–c), while the small macedonicum metatarsals deposits fewer tissue in this zone (Fig. 3e). This early narrowing of the growth zones51 lends support to the idea of an earlier attainment of maturity in the smaller Greek form compared to the larger ones. Within the Spanish hipparionins, the H. gromovae metapodials show three CGMs in the bone cortex prior to the EFS (Figs 2d and 3d), while the larger H. truyolsi metatarsal has only two CGMs embedded in the FLC (Fig. 3f). Although it has not reached maturity, the H. gromovae metacarpal IPS-96275 (Supplementary Fig. S1a) also points towards extended growth period as it exhibits open vascular canals in the periosteum after the deposition of the second CGM. Consequently, the metapodials of the small H. gromovae present three or more cycles of active growth, contrary to the small Greek morphotype and the larger Spanish taxon. These differences in growth cessation can also be identified by the overall growth trajectory reconstruction.
Growth Curves Reconstruction
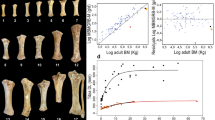
The curve fitting allowed us to obtain characteristic growth parameters and to estimate growth variables (Table 1, see Material and Methods). At birth, metapodial size shows an almost isometric relationship (0.834-slope) with the asymptotic maximum size obtained for each specimen (parameter A) (R2 = 0.908; p-value (Pearson) < 0.001) (Fig. 4a). Therefore, metapodial postnatal growth starts at analogous sizes in each hipparionin group, depending on their adult final circumference. If we consider bone perimeter as a proxy of body mass50,52, these values correspond to those predicted from isometric scaling of eutherian neonatal mass with adult body mass1. This contrasts with insular dwarf lineages where neonate size is smaller than predicted from allometry18. After birth, the growth rate during the first growth cycle (age = 0.5 years, Table 1) also scales positively with adult bone size (Fig. 4b, R2 = 0.543; p-value (Pearson) < 0.001). However, when the same relationship is established but considering the relative growth rate at that point (size factor extracted), the correlation is not significant (R2 = 0.160; p-value (Pearson) > 0.05). During the first stages of growth, hence, metapodials grow at analogous velocities relative to their size, and the allometrical relationship with a 1.46 slope results in slightly higher growth rates in the metapodials of large forms compared to the small ones. For comparison, we have also related the growth rate and the femoral lateromedial diameter, a good proxy of body size in equids53, on a sample of different-sized extant equid femurs (see Material and Methods). Although the points of the obtained regression are scattered (R2 = 0.387) (Supplementary Fig. S3) and the correlation is not statistically significant (p-value (Pearson) = 0.099), we can identify a trend indicating higher growth rates in larger taxa and lower growth rates in the smaller species or breeds. Similar to what we observe in hipparionins, hence, extant smaller equid species and horse breeds, such as Equus hemionus and the Shetland pony, tend to grow at absolute slower rates than larger representatives of the genus Equus.
(a) Linear regression between the neonatal metapodial size and the adult final size (A) of mature metapodials. (b) Allometric regression relating the growth rate during the first growth cycle (t = 0.5 years) and the adult final body size (A) of mature metapodials. All variables were log-transformed to linearise the relationship. See main text for statistics information.
The overall growth patterns in hipparionins are graphically visualised in the curves from discrete measurements of the CGMs (Fig. 5, dashed lines). From the obtained logistic parameters (Table 1), we reconstructed the mean growth trajectory for each group (Table 1 and Fig. 5, solid lines). In the mean and individual growth curves, we identified the point where the growth rate is reduced as the change in the slope of the trajectory43 (Fig. 5, arrow), which coincides with the lower bone deposition observed histologically. This signal has been related to epiphyseal fusion and reflects the end of longitudinal bone growth43. The growth rate of the larger Greek metapodials substantially declines by around ~2.5 years after birth, and generally at sizes above 75 mm of perimeter (Fig. 5). Growth deceleration starts earlier in the small Greek macedonicum morphotype, about the first year in the metatarsals and within the second year in the metacarpals, both at perimeter sizes around ~65 mm. The Spanish dwarf form, on the contrary, grows at sustained rates over a longer period until the age of approximately ~2.5 years (Fig. 5), comparable to the large Greek morphs. Indeed, the growth in H. gromovae metapodials and the larger Greek morphs declines later compared to the small Greek morphotype and to the larger Spanish H. truyolsi (Fig. 5), in which the absolute (GR) and relative (RGR) growth rates are considerably low at the second and third year of growth (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. S4).
Growth curves of mature metapodials. Dashed lines represent each metapodial growth trajectory while solid lines indicate the mean fitted logistic growth curves for the different groups. Arrows pointed out the change of slope of the growth curves that characterises metapodial maturity43. (a) Metacarpal growth curves. (b) Metatarsal growth curves. The unusual size of the H. gromovae metatarsal IPS-101809 is due to a more proximal cut of the specimen, however, the growth trajectory is still identifiable.
The logistic growth parameters (Table 1) also show the aforementioned growth differences. Accordingly, the growth parameter k, that represents the relative growth velocity (see Material and Methods), tends to be higher in the metapodials of the macedonicum morphotype (kMCmc = 1 in metacarpals and kMTmc = 1.6 in metatarsals, Table 1) than in the specimens of the other groups (e.g. dietrichi morphotype metacarpals kMCdt = 0.84 and metatarsals kMTdt = 1, Table 1), when metacarpals and metatarsals are compared separately. This indicates an initially faster growth relative to size, and an earlier attainment of maturity in this Greek dwarf form. In contrast, the small metapodials from H. gromovae and the larger from the large Greek morphotypes (primigenium and dietrichi) exhibit lower k values (e.g. kMCgr = 0.78 and kMTgr = 0.98, Table 1), which indicates a longer growth period and a later onset of maturity. Conversely, the large Spanish H. truyolsi has one of the highest k value (kMTty = 1.3, Table 1) as it grows fast and decreases the deposition rate before the second year of life (Fig. 5). The growth period, or the time required to attain the 95% of its final size (t95A), illustrates the same fast development in the macedonicum morphotype compared to the Spanish small species and the larger Greek morphs (Table 1). For instance, while the metatarsals of the macedonicum morphotype complete the 95% of growth by the age of 1 year (t95AMTmc = 1.01, Table 1), the small metatarsals of H. gromovae and the larger ones from dietrichi and primigenium morphotypes double this time (t95AMTgr = 2.04, t95AMTdt = 2.04, t95AMTpg = 2, Table 1). The single metatarsal of the larger H. truyolsi (t95AMTty = 1.39, Table 1) ceases growth earlier than the metatarsals of the other taxa except for the macedonicum morphotype. This earlier maturity in H. truyolsi, however, should be taken with caution since there is only one remodelled metatarsal available and there is no other metatarsal of this species to compare with. In all groups analysed, the metacarpals attain their final size later than metatarsals, as shown both by the parameter k and by the time required to complete growth (Table 1). This finding can be related to the variability reported between other limb bones of equids43 and the ontogenetic differences between bones54. Distinct loading charges and biomechanics between hipparion metapodials may be the reason underlying this difference55.
Discussion
Body size variations in continental settings, and concretely in equid lineages, have been hypothesised to represent direct adaptations to habitat change25,29, resources shifts27,30,31,34 or to climate change25,27. These hypotheses are closely linked because of the strong relationship between climate, habitat and resources. Alternatively, life history theory provides a theoretical background to explain size shifts as a by-product of life history adaptations to environmental conditions. This approach has been proposed for islands7; however, it has not been explored in mainland size trends. Our analysis of the growth strategies of different-sized hipparionins provides a first attempt to understanding the possible causes behind continental trends in size decrease within a life history framework.
In the present study, we inferred the growth trajectories of small and large hipparionin groups from two continental bioprovinces using metapodial bone histology. Although the bone microstructure of metapodials does not provide the absolute age of physiological maturity43, it informs about the relative maturity that, within the context of body mass, indicates whether these size reductions were coupled with shifts towards either slower or faster life histories. Future histological analysis on adult femurs could provide an absolute estimation of the age at sexual maturity and, thus, help to support our inferences.
We found that the metapodials of the larger hipparionins grow at higher rates than the metapodials of the smaller forms during the first growth stages (Fig. 4b and Table 1). We can infer, hence, lower growth rates for the small taxa and higher rates for the larger forms as predicted from allometry1 and observed in dinosaurs36,56 and in extant and fossil artiodactyls6,18,39,57. Moreover, we identified a similar trend in extant equids, since femora of larger wild equids and of larger domestic breeds tend to grow at higher rates than the smaller-sized species or breeds (Supplementary Fig. S3). In hipparionins, although the differences in development have principally been identified from growth curve reconstructions, bone tissue microstructure also indicates distinct growth velocities. Thus, we principally found radial vascularity in the large dietrichi and primigenium metatarsals, and laminar bone in the small H. gromovae. In fact, growth rate is particularly low in H. gromovae, where besides the growth rate scaling (Fig. 4b), the relative growth rate expressed by the logistic growth parameter k is also lower (Table 1). On the other hand, the small macedonicum morphotype metapodials exhibit in some cases disperse radial canals, indicating a probable higher growth rate for its size, which is supported by the greater k values. Regarding the attainment of relative maturity, the small macedonicum morphotype and the large H. truyolsi considerably decrease their growth rate between the first and the second year, while the two large Greek morphotypes and the small Spanish H. gromovae decrease growth rate after the second year. The large Greek forms, hence, grew at high rates and attained their maturity later than the small Greek macedonicum morphotype that advance the growth rate decline. The small Greek macedonicum morphotype, thus, shifted towards a faster life history. The small Spanish H. gromovae, on the contrary, matured relatively late, similar to the large Greek representatives. However, it does it at much lower growth rates. H. truyolsi, on the other hand, grew at high rates and decreased growth early (based on a single specimen). Martinez-Maza et al.44 observed two CGMs within the cortex of the metapodials of the larger (160–186 kg58) Hipparion concudense from a Vallesian and a middle Turolian Spanish locality. These growth marks are situated close to the periosteal surface44, suggesting an early decrease in growth rate. Moreover, in half of the metapodials of their middle Turolian sample, only one CGM is situated within the bone cortex44. From allometric scaling1, the smaller H. gromovae should be expected to show less CGMs within the cortex than H. truyolsi or H. concudense; however, it exhibits more growth marks indicating a delayed maturity in relation to these larger Spanish species. Besides, our results have also shown that in some cases metacarpals tend to decrease their growth later than metatarsals. This difference is beyond the scope of the present study, but may indicate different timings in the growth cessation between these bones.
In summary, we did not only find differences in the growth patterns between the small and the large Greek morphotypes as predicted from scaling, but also between the small Greek macedonicum morphotype and the small Spanish H. gromovae, since the Spanish species matured later than expected from size. The two dwarf lineages, hence, followed different growth strategies that led to a similar reduction in adult size. Our results, thus, are congruent with two different evolutionary scenarios where dwarfing is caused by distinct selective pressures. Following life history theory, attainment of sexual maturity and growth rate are the two main characteristics that determine the final size of an organism7,9. These factors, in turn, are modulated by environmental changes in mortality regimes and resource availability respectively7,9,12,59,60,61. Palkovacs7, in his life history based model for size evolution on islands, considered the changes in resource levels and mortality rates (caused by low predation) between mainland and islands as the principal selective pressures involved in size shifts. However, variations in ecological factors over time and space can be far more complex on the continent where, for example, predation pressure can either increase or decrease, and can affect specific ontogenetic stages differently. As age-specific survival and fecundity indexes are the basis of life history and demographic studies9,10,60, it is important to determine which is the life cycle stage affected by a shift in the selective agent. Organisms that suffer from high extrinsic mortality regimes acting on adult stages will maximise their fitness following a different life history strategy compared to those exposed to high juvenile mortality61,62. Concretely, when the adult stage is affected by high predation pressure, animals maximise their fitness by reproducing earlier62. By this, organisms are able to increase their reproductive output before they fall prey to carnivores, hence accelerating their life history. Both theoretical60,62 and comparative surveys59,61,63 provide evidence for advancement of reproductive maturity in populations facing high adult mortality regimes. This suggests that increased predation pressure upon adult individuals selected for advanced maturity through earlier growth cessation, leading to dwarfing in the macedonicum lineage. On the other hand, under high juvenile mortality, organisms maximise fitness by reproducing later in time12,13,60,61. A delay in maturity is predicted if the benefits outweigh the disadvantages of a late reproduction12,64. These advantages are based on two key assumptions; fecundity increases with size, and juvenile mortality decreases with increasing age and size at maturity of the progenitor12. Because equids are monotocous65, a significant increase in fecundity related to larger size is not expected; however, a delay in maturity can compensate high juvenile mortality by increasing juvenile survival rates due to more experienced progenitors59. Age-specific juvenile mortality increases during periods of low resource availability59,66,67,68,69,70, which are common in arid and semi-arid environments71. Seasonal or unpredictable fluctuations in food quantity and quality have a high influence on juvenile mortality72, since at this ontogenetic stage young mammals are more sensitive to environmental stresses due to their smaller size, lower fat reserves, immature immunological system and inexperience61. Furthermore, resource availability affects individual growth, with low resource levels constraining growth rates7,9. Under this scenario, individuals are forced to grow over an extended period to attain a size large enough for successful reproduction12,13, which leads to a delay in maturity7. This suggests that low resource availability played an important role in the dwarfing process of H. gromovae, triggering a decrease in growth rate and an associated delay in maturity. Hence, we interpret the small size of the later maturing H. gromovae as a consequence of low growth rates and a high juvenile mortality regime due to low resource availability. The analysis of the growth strategies indicates that dwarfing in the two small hipparionins resulted from different adaptive shifts in their life histories under distinct selective pressures.
Extant equids are less diverse in size, form and ecology than they used to be in the past73. Nowadays, only domestic horse breeds show a large size range, while size differences in wild taxa are much less pronounced (e.g. Equus hemionus weighting 230 kg74 and Equus grevyi 384 kg74). Despite the size disparity, different-sized horse breeds have comparable growth patterns75. Gestation lengths also show little variation between breeds76, and the time of growth plates closure is similar between small and large horses77. Considering this, the size difference in domestic horses is not caused by variations in the duration of growth, but by the higher or lower prenatal76 and postnatal77 growth rates. Accordingly, we identified a trend indicating higher growth rates in femora of larger extant equids compared to smaller representatives of Equus. Hence, differences in growth rates lead to size diversity in extant equids. Similar to the case of H. gromovae, epiphyseal closure in the small Iceland horse is delayed, and even later compared to that in Thoroughbreds77,78. The lower growth rates and delayed growth plate closure in the small Iceland horse have been related to the original harsher living conditions in which this breed evolved78. Likewise, one of the smallest extant wild equid, Equus hemionus, dwells in resource-poor environments as the arid and semi-arid steppes and deserts from Asia79. In this case, resource limitation led to reduced growth rates and, thus, to a smaller size at maturity. The body size differences between extant taxa, hence, are likely the result of differences in somatic growth rates triggered by differential selective pressures (e.g. resource availability).
Our different life history deductions for the small hipparionins are supported by the different ecological settings inferred for the two bioprovinces. Small ungulates suffer stronger predation pressure than larger ones80. They therefore prefer habitats with dense canopy cover (forested areas) that provide shelter and that are more secure than open areas80,81,82,83,84, albeit the poor forage supply80,81,82,83. From Vallesian through Turolian, the Eastern Mediterranean bioprovince was characterised by open dry bushlands and grasslands with low tree cover85,86,87, a risky habitat for small ungulates80. The presence of diverse carnivore associations dominated by hyaenids and felids85, provides support to our inference from life history models that early maturity and a corollary size decrease in the macedonicum morphotype was triggered by high predation pressure. In contrast, the Western Mediterranean biomes during the late Turolian were composed of deciduous forests and xeric woodlands with shrublands and grasslands88,89,90. At the H. gromovae site – Rambla de Valdecebro II (=El Arquillo) –, the climate was characterised by a high aridity regime91. There was a high carnivore diversity in this area at that time92,93, but within a patchy landscape there were forest and xeric woodland areas available for cover. These more forested areas could have provided site humidity and increased protection against predation82,83, habitat parameters preferred by extant small ungulates80. This suggests that H. gromovae, and possibly also the sympatric smaller Hipparion periafricanum, likely dwelled in such forested and more secure habitats. Although conferring the advantage of protection, closed areas support fewer grasses and forbs compared to open habitats because of the shading effect of the canopy83. The quantity of available forage, hence, is lower under denser tree cover82,83,94. Additionally, these small hipparions must have faced longer periods of resource stress because of the high aridity of El Arquillo site91, which most likely affected the quality and quantity of available resources71. Such adverse climatic conditions must have been an additional problem for equids because their digestive strategy of hindgut fermentation makes them dependent on continuous resource supply95. The environmental scenario of low and fluctuating resource levels provides support to our inference from life history models that H. gromovae grew at low rates and delayed maturity, which led to a reduction of adult body size. It is conceivable that these resource conditions might have also affected juvenile mortality as observed in extant ungulate populations59,66,67,68,69,70.
The causes and mechanisms behind size decrease trends on continents are not completely understood. In this survey focused on the bone histology of different-sized hipparionins, we tested if changes in life history traits are related to size decrease in continental settings. We recognised opposed growth strategies in the two dwarfed lineages, a faster life history characterised by an early maturity in the Greek small hipparion vs. a slower strategy with slow growth and later maturity in the Spanish one; otherwise leading to parallel size shrinking under different ecological scenarios. Based on Palkovacs7 life history model, we consider the size decrease as a by-product of life adaptations to differential ecological constraints. Specifically, we interpret the shift of the Spanish small H. gromovae towards a slow life history as a response to limited and unpredictable resource supply and an associated increase in juvenile mortality, and the shift of the Greek small macedonicum morphotype towards a fast life history as an adaptation to cope with increased adult mortality regimes. Our results show that there is more than one possible life history strategy behind evolutionary dwarfing, and that bone histology is a powerful tool to unravel the mechanisms involved.
Material and Methods
Previous studies of the characterization and variability of equid bone tissue43,44 have provided evidences of the usefulness of metapodial bone microstructure for life history reconstruction in this group. Moreover, we used metapodials due to their higher abundance in fossil assemblages and the possibility to assign them to a specific morphotype. We sectioned 31 hipparionin metapodials from the late Miocene of Greece and Spain for histological analysis. The Greek sample comprises metacarpals and metatarsals of one small (macedonicum morphotype) and two large (primigenium and dietrichi morphotypes sensu Vlachou35) hipparionin morphotypes from seven fossil sites ranging from early Vallesian to late Turolian (Table 2). Large-sized hipparions are used for comparative purposes. The Spanish sample includes metapodials from one small species (Hipparion gromovae) and one specimen of the large H. truyolsi, both from a late Turolian fossil site of the Teruel Basin (Table 2). Metapodial histology of other large-to-medium sized hipparionins from early Vallesian and middle Turolian of Spain have already been studied in an exhaustive survey by Martinez-Maza et al.44.
To support our interpretations of the growth rates in hipparionins, we also analysed bone appositional rates in extant equids of different body sizes. Because the femur develops over a longer time period96, its use in Equus bone histology is preferred if possible43. Hence, we calculated the appositional growth in femora to estimate the growth rates of different-sized extant equids. The entire extant sample was composed by eight femora of wild and domestic equids; two belonging to Equus grevyi, two to Equus hemionus, and four to different-sized horse breeds (Iceland, Welsh, Hackney and Shetland) (Supplementary Table S1).
Adult body mass estimations of the fossil Greek morphotypes were calculated from the material published in Vlachou35 and were kindly provided by the author. Body mass estimations of the Spanish sample were calculated (Supplementary Table S2) following the same measurements and regressions used for the Greek metapodials (Table 2). These estimations were obtained for each morphotype from measurements on metapodials (Mc10, Mt10, Mc13, Mt13, following Eisenmann et al.97) and using the equations provided by Eisenmann and Sondaar98 and Scott53.
Preparation of histological slides
Histological slides were produced following the standard protocol of our laboratory43,99. Mid-shaft blocks of each metapodial were embedded in epoxy resin (Araldite 2020) and sectioned using an IsoMet low-speed saw (Buehler). The exposed surfaces were polished using a grinder polisher (Buehler, MetaServ 250) and glued to a glass slide using the same epoxy resin. The mounted samples were cut using a diamond saw (Buehler, Petrothin) up to a thickness of 300 μm and grounded to 150–100 μm, using the grinder polisher. Finally, the slides were dehydrated in alcohol gradients and immersed in a histological clearing agent (Histo-Clear II) prior to cover them with a DPX medium.
The histological samples were studied under polarised light using a Zeiss Scope.A1 microscope with an attached digital camera (AxioCam ICc5). The slides were examined using a retardation filter of ¼ λ to improve the observation of the bone tissues and growth marks100. The micrographs of the cortex were merged using Adobe Photoshop® and analysed with Image J software.
Bone histology
We analysed bone tissues and bone growth marks to reconstruct metapodial growth. Description of bone tissues types follows the classification of Francillon-Viellot et al.101 and de Margerie et al.48. The analysis of cyclical growth marks (CGM) of annual periodicity99 provide the temporal basis for the reconstruction of metapodial growth and the assessment of certain life history traits6,37,38. Where the growth marks were faint due to poor tissue preservation or partially eroded by secondary osteons, we retrocalculated their track by superimposition102. The identification of a non-cyclical growth mark, the neonatal line47, in the innermost cortical area of almost all metapodials allowed the estimation of bone size at birth.
The significant decrease in bone growth rate marks the attainment of bone maturity. This event is identified by the periosteal deposition of slow-growing lamellar bone after fast-growing fibrous tissue37 and by the narrowing of consecutive growth zones51. By counting the CGM that precede the deposition of the avascular lamellar bone found in the outermost cortex of bone (external fundamental system (EFS) sensu Woodward et al.102), some authors have inferred the organism’s age at sexual maturity38,103 or skeletal maturity44,57 from mainly tibia and femora tissues. Nacarino-Meneses et al.43, however, provided evidence that the decrease in periosteal growth rate in equids metapodials – represented by the inflection point of the growth curves – is an indicator of their epiphyseal fusion and the end of longitudinal growth. As metapodials fuse their epiphyses earlier than other long bones96, the identification of the moment of metapodial growth decrease only provides a relative age at skeletal maturity. Thus, we obtain a proxy of maturity attainment, instead of an absolute age at which the animal should end its growth. We used this ‘relative maturity’ to compare between taxa and to identify which species tends to delay or to advance it.
In the extant femur sample used for comparative purpose, we estimated the growth rate between the first and the second year of growth. We identified these two CGM and measured their perimeter. The estimation of the growth rate was calculated as the perimeter difference between the second and the first CGM.
Growth curves
Growth data in metapodials were obtained by counting the bone growth marks and by calculating their perimeters. Contrary to studies on dinosaurs41,104 that use body mass estimations for each growth cycle, our growth curves are based on direct measures. We did not estimate body mass at each growth cycle because the correlation between equid metapodial mid-shaft dimensions and body mass is not significant25, and the regressions are based adult individuals. Instead, we took the direct skeletal measurement of the mid-shaft circumference as a proxy of body size, a more conservative alternative to an estimate of body mass52. In those cases where exact mid-shaft cuts were not possible due to the fragmentary nature of the specimen (IPS-101809, H. gromovae metatarsal), the bone circumference is slightly overestimated. This is particularly true in metatarsals which are anteroposteriorly wider in more proximal planes; however, the growth trajectory can be equally reconstructed. From the available sample, we used only those specimens for the growth curve reconstructions where the radial growth was finished (18 metapodials). The other specimens have been analysed for bone tissue characterization, growth mark superimposition, and the study of the ontogenetic development.
Similar to other biological processes, growth is generally modelled using nonlinear sigmoidal equations105,106. Among several models, and considering the nature of our data, we used the logistic equation (1) 1,107 to describe the pattern of metapodial radial growth because it presents good fitting values (Akaike Information Criterion) (Supplementary Table S3) and provides the most realistic asymptotic size values. A similar logistic model has been used to describe the circumferential growth of dinosaurian femora and tibiae40,108, as well as dinosaur body mass growth104. We used the nonlinear least squares fitting of the PAST software to fit the curves equations to our data109.
In sigmoidal equations, the parameter A represents the final asymptotic value to which the response variable approaches in an exponentially decreasing rate after reaching the growth inflection point50. In our case, the A parameter shows the final adult metapodial circumferential size. The mean relative growth rate, or the relative velocity at which the response variable is approaching to this final size, is characterised by the exponent k108, while the parameter b represents the quotient between the initial and final size110. Hence, the parameter k expresses the ratio of the maximum growth rate in relation to the adult size, indicating delayed maturity when k is low and advanced maturity when k is high111. These growth curve parameters were calculated for each specimen and the results were also averaged to obtain a mean growth curve for the metacarpals and metatarsals of each group42. The rate at which bone grows was calculated from the derivative (2) of this logistic equation (1), representing the instantaneous growth rate at a concrete time. It should be considered that the calculated growth rate values expressed as mm/year do not represent a real approximation of the rate at which those bones were growing, because bone growth rate varies with the season of the year99. However, these values represent useful estimates for comparison42. In order to compare the growth rates between species, we estimated the relative growth rate (RGR) extracting the effect of size (3), because growth rates tightly scale with size1. The relative growth rate is defined as the increase per unit of time relative to the size at a concrete point112.
Additionally, we calculated the time required to attain the 95% of the final size (4) as an indicator of the growth duration time108.
Statistics
Statistical analyses and graphs were performed using Past 3.14109 and Microsoft Office Excel. Pearson’s correlation was used for the linear correlation analysis. A significance level of 0.05 was used for all tests.
Data Availability
The data sets generated and/or analysed during the current study are included on this published article. Raw data not included is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
11 July 2019
A correction to this article has been published and is linked from the HTML and PDF versions of this paper. The error has been fixed in the paper.
References
Calder, W. A. Size, Function, and Life History. (Harvard University Press, 1984).
Peters, R. H. The Ecological Implications of Body Size. Cambridge Studies inEcology, https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511608551 (Cambridge University Press, 1983).
Damuth, J. D. & MacFadden, B. J. Body Size in Mammalian Paleobiology: Estimation and Biological Implications. (Cambridge University Press, 1990).
Barbault, R. In Evolutionary Biology 261–286, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-0931-4_6 (Springer US, 1988).
Raia, P. & Meiri, S. The island rule in large mammals: paleontology meets ecology. Evolution 60, 1731–1742 (2006).
Köhler, M. & Moyà-Solà, S. Physiological and life history strategies of a fossil large mammal in a resource-limited environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 20354–8 (2009).
Palkovacs, E. P. Explaining adaptive shifts in body size on islands: a life history approach. Oikos 103, 37–44 (2003).
Bromage, T. G. et al. A life history and climate change solution to the evolution and extinction of insular dwarfs: a Cypriot experience. In Waldren, W. H., Ensenyat, J. A. (Eds) World Islands in Prehistory. International Insular Investigations, V Deià Conference of Prehistory. 420–427 (Archaeopress, 2002).
Stearns, S. C. The Evolution of Life Histories. (Oxford University Press, 1992).
Roff, D. A. The Evolution of Life Histories: Theory and Analysis. (Chapman & Hall, 1992).
Stearns, S. C. Life history evolution: Successes, limitations, and prospects. Naturwissenschaften 87, 476–486 (2000).
Stearns, S. C. & Koella, J. C. The evolution of phenotypic plasticity in life-History traits: predictions of reaction norms for age and size at maturity. Evolution (N. Y). 40, 893 (1986).
Berrigan, D. & Koella, J. C. The evolution of reaction norms: simple models for age and size at maturity. J. Evol. Biol. 7, 549–566 (1994).
Lomolino, M. V. Body size of mammals on islands: the Island Rule reexamined. Am. Nat. 125, 310–316 (1985).
Case, T. J. A general explanation for insular body size trends in terrestrial vertebrates. Ecology 59, 1–18 (1978).
Foster, J. B. Evolution of mammals on islands. Nature 202, 234–235 (1964).
Jordana, X. & Köhler, M. Enamel microstructure in the fossil bovid Myotragus balearicus (Majorca, Spain): Implications for life-history evolution of dwarf mammals in insular ecosystems. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 300, 59–66 (2011).
Köhler, M. Fast or slow? The evolution of life history traits associated with insular dwarfing. In Pérez-Mellado, V. & Ramon, Ma. M. (Eds), Islands and Evolution 19, 261–280 (Institut Menorquí d’Estudis, Recerca, 2010).
Orlandi-Oliveras, G., Jordana, X., Moncunill-Solé, B. & Köhler, M. Bone histology of the giant fossil dormouse Hypnomys onicensis (Gliridae, Rodentia) from Balearic Islands. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 15, 247–253 (2016).
Moncunill-Solé, B., Orlandi-Oliveras, G., Jordana, X., Rook, L. & Köhler, M. First approach of the life history of Prolagus apricenicus (Ochotonidae, Lagomorpha) from Terre Rosse sites (Gargano, Italy) using body mass estimation and paleohistological analysis. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 15, 235–245 (2016).
Gould, G. C. & MacFadden, B. J. Gigantism, dwarfism, and Cope’s Rule: “nothing in evolution makes sense without a phylogeny”. Bull. Am. Museum Nat. Hist. 285, 219–237 (2004).
Kurtén, B. Pleistocene Mammals of Europe. (Aldine Transaction, 2009).
Prothero, D. R. & Sereno, P. C. Allometry and paleoecology of medial Miocene dwarf rhinoceroses from the Texas Gulf Coastal Plain. Paleobiology 8, 16–30 (1982).
Stanley, S. An explanation for Cope’s Rule. Evolution (N. Y). 27, 1–26 (1973).
Alberdi, M. T., Prado, J. L. & Ortiz-Jaureguizar, E. Patterns of body size changes in fossil and living Equini (Perissodactyla). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 54, 349–370 (1995).
MacFadden, B. J. Evolution. Fossil horses–evidence for evolution. Science 307, 1728–1730 (2005).
D’Ambrosia, A. R. D., Clyde, W. C., Fricke, H. C., Gingerich, P. D. & Abels, H. A. Repetitive mammalian dwarfing during ancient greenhouse warming events. Sci. Adv. 1–19 (2017).
Koufos, G. D. Hipparion macedonicum revisited: New data on evolution of hipparionine horses from the Late Miocene of Greece. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. 61, 519–536 (2016).
Ortiz-Jaureguizar, E. & Alberdi, M. T. El patrón de cambios en la masa corporal de los Hipparionini (Perissodactyla, Equidae) de la península ibérica durante el Mioceno Superior-Plioceno Superior. Coloquios Paleontol. 1, 499–509 (2003).
Pesquero, M. D. Hipparion del Turoliense superior de Las Casiones (Fosa de Teruel). Coloquios Paleontol. Volumen Ex, 511–548 (2003).
Guthrie, R. D. Rapid body size decline in Alaskan Pleistocene horses before extinction. Nature 426, 169–171 (2003).
Forstén, A. Size decrease in pleistocene-holocene true or caballoid horses of europe. Mammalia 55, 407–420 (1991).
Bernor, R. L. et al. Systematic, stratigraphic, and paleoenvironmental contexts of first-appearing Hipparion in the Vienna Basin, Austria. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 8, 427–452 (1988).
Cantalapiedra, J. L., Prado, J. L., Hernández Fernández, M. & Alberdi, M. T. Decoupled ecomorphological evolution and diversification in Neogene-Quaternary horses. Science (80-.). 355, 627–630 (2017).
Vlachou, T. D. Palaeontological, Biostratigraphical and Palaeoecological Study of the Greek Hipparions. (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 2013).
Chinsamy-Turan, A. The Microstructure of Dinosaur Bone. (The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2005).
Padian, K. & Lamm, E.-T. Bone Histology of Fossil Tetrapods: Advancing Methods, Analysis, and Interpretation. (University of California Press, 2013).
Marín-Moratalla, N., Jordana, X. & Köhler, M. Bone histology as an approach to providing data on certain key life history traits in mammals: Implications for conservation biology. Mamm. Biol. 78, 422–429 (2013).
Amson, E., Kolb, C., Scheyer, T. M. & Sánchez-Villagra, M. R. Growth and life history of Middle Miocene deer (Mammalia, Cervidae) based on bone histology. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 14, 637–645 (2015).
Bybee, P. J., Lee, A. H. & Lamm, E.-T. Sizing the Jurassic Theropod Dinosaur Allosaurus: Assessing Growth Strategy and Evolution of Ontogenetic Scaling of Limbs. J. Morphol. 267, 347–359 (2006).
Lehman, T. M. & Woodward, H. N. Modeling growth rates for sauropod dinosaurs. Paleobiology 34, 264–281 (2008).
Woodward, H. N., Freedman Fowler, E. A., Farlow, J. O. & Horner, J. R. Maiasaura, a model organism for extinct vertebrate population biology: a large sample statistical assessment of growth dynamics and survivorship. Paleobiology 41, 1–25 (2015).
Nacarino-Meneses, C., Jordana, X. & Köhler, M. Histological variability in the limb bones of the Asiatic wild ass and its significance for life history inferences. PeerJ 4, e2580 (2016).
Martinez-Maza, C., Alberdi, M. T., Nieto-Diaz, M. & Prado, J. L. Life-history traits of the miocene Hipparion concudense (Spain) inferred from bone histological structure. PLoS One 9, e103708 (2014).
Sander, P. M. & Andrássy, P. Lines of arrested growth and long bone histology in Pleistocene large mammals from Germany: what do they tell us about dinosaur physiology? Palaeontogr. A 277, 143–159 (2006).
Prondvai, E., Stein, K. H. W., de Ricqlès, A. J. & Cubo, J. Development-based revision of bone tissue classification: the importance of semantics for science. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 112, 799–816 (2014).
Nacarino-Meneses, C. & Köhler, M. Limb bone histology records birth in mammals. PLoS One 13, e0198511 (2018).
de Margerie, E., Cubo, J. & Castanet, J. Bone typology and growth rate: Testing and quantifying ‘Amprino’s rule’ in the mallard (Anas platyrhynchos). Comptes Rendus - Biol. 325, 221–230 (2002).
de Margerie, E. et al. Assessing a relationship between bone microstructure and growth rate: a fluorescent labelling study in the king penguin chick (Aptenodytes patagonicus). J. Exp. Biol. 207, 869–79 (2004).
Lee, A. H., Huttenlocker, A. K., Padian, K. & Woodward, H. N. In Bone Histology of Fossil Tetrapods - Advancing Methods, Analysis, and Interpretation 086, 217–251 (2013).
Chinsamy, A. & Valenzuela, N. Skeletochronology of the endangered Side-Neck Turtles Podocnemis expansa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 104, 311–314 (2008).
Campione, N. E. & Evans, D. C. A universal scaling relationship between body mass and proximal limb bone dimensions in quadrupedal terrestrial tetrapods. BMC Biol. 10, 60 (2012).
Scott, K. M. In Body Size in Mammalian Paleobiology: Estimation and Biological Implications (eds Damuth, J. & Macfadden, B. J.) 301–335 (Cambridge University Press, 1990).
Horner, J. R., Ricqlès, Ade & Padian, K. Variation in Dinosaur Skeletochronology Indicators: Implications for Age Assessment and Physiology. Paleobiology 25, 295–304 (1999).
Castanet, J., Rogers, K. C., Cubo, J. & Boisard, J.-J. Periosteal bone growth rates in extant ratites (ostriche and emu). Implications for assessing growth in dinosaurs. C. R. Acad. Sci. III. 323, 543–550 (2000).
Martin Sander, P., Mateus, O., Laven, T. & Knötschke, N. Bone histology indicates insular dwarfism in a new Late Jurassic sauropod dinosaur. Nature 441, 739–741 (2006).
Kolb, C. et al. Growth in fossil and extant deer and implications for body size and life history evolution. BMC Evol. Biol. 15, 19 (2015).
Pesquero, M. D. & Alberdi, M. T. New evidence of conspecificity between Hipparion primigenium melendezi Alberdi, 1974 from Los Valles de Fuentidueña (Segovia) and Hipparion concudense concudense Pirlot, 1956 from Concud (Teruel) Spain. Estud. Geológicos 68, 247–260 (2012).
Gaillard, J.-M., Festa-Bianchet, M., Yoccoz, N. G., Loison, A. & Toïgo, C. Temporal Variation in Fitness Components and Population Dynamics of Large Herbivores. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 31, 367–393 (2000).
Law, R. Optimal life histories under age-specific predation. Am. Nat. 114, 399–417 (1979).
Promislow, D. E. L. & Harvey, P. H. Living fast and dying young: A comparative analysis of life-history variation among mammals. J. Zool. 220, 417–437 (1990).
Gadgil, M. & Bossert, W. H. Life historical consequences of natural selection. American Naturalist 104, 1–24 (1970).
Skogland, T. Natural selection of wild reindeer life history traits by food limitation and predation. Oikos 55, 101 (1989).
Koons, D. N., Metcalf, C. J. E. & Tuljapurkar, S. Evolution of delayed reproduction in uncertain environments: a life-history perspective. Am. Nat. 172, 797–805 (2008).
Moehlman, P. D. Equids: Zebras, Asses, and Horses: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. (IUCN/SSC Equid Specialist Group, 2002).
Georgiadis, N., Hack, M. & Turpin, K. The influence of rainfall on zebra population dynamics: Implications for management. J. Appl. Ecol. 40, 125–136 (2003).
Bartmann, R. M., White, G. C. & Carpenter, L. H. Compensatory Mortality in a Colorado Mule Deer Population. Wildl. Monogr. 121, 1–39 (1992).
Grange, S. et al. What limits the Serengeti zebra population? Oecologia 140, 523–532 (2004).
Choquenot, D. Density-dependent growth, body condition, and demography in feral donkeys: testing the food hypothesis. Ecology 72, 805–813 (1991).
Sand, H. Life history patterns in female moose (Alces alces): the relationship between age, body size, fecundity and environmental conditions. Oecologia 106, 212–220 (1996).
Illius, A. W. & O’Connor, T. G. Resource heterogeneity and ungulate population dynamics. Oikos 89, 283–294 (2000).
Rubenstein, D. I. Life history and social organization in arid adaptated ungulates. J. Arid Environ. 17, 145–156 (1989).
MacFadden, B. J. Fossil Horses–Evidence for Evolution. Science (80-.). 307, 1728–730 (2005).
Tacutu, R. et al. Human Ageing Genomic Resources: Integrated databases and tools for the biology and genetics of ageing. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D1027–D1033 (2013).
Green, D. A. A review of studies on the growth rate of the horse. Br. Vet. J. 117, 181–191 (1961).
Heck, L., Clauss, M. & Sánchez-Villagra, M. R. Gestation length variation in domesticated horses and its relation to breed and body size diversity. Mamm. Biol. 84, 44–51 (2017).
Strand, E., Braathen, L. C., Hellsten, M. C., Huse-Olsen, L. & Bjornsdottir, S. Radiographic closure time of appendicular growth plates in the Icelandic horse. Acta Vet. Scand. 49, 19 (2007).
Łuszczyński, J., Pieszka, M. & Kosiniak-Kamysz, K. Effect of horse breed and sex on growth rate and radiographic closure time of distal radial metaphyseal growth plate. Livest. Sci. 141, 252–258 (2011).
Kaczensky, P., Lkhagvasuren, B., Pereladova, O., Hemami, M. & Bouskila, A. Equus hemionus. IUCN Red List Threat. Species 2015 (2015).
Djagoun, C. A. M. S. et al. Hunting affects dry season habitat selection by several bovid species in northern Benin. Wildlife Biol. 20, 83–90 (2014).
Fischhoff, I. R., Sundaresan, S. R., Cordingley, J. & Rubenstein, D. I. Habitat use and movements of plains zebra (Equus burchelli) in response to predation danger from lions. Behav. Ecol. 18, 725–729 (2007).
Godvik, I. M. R. et al. Temporal scales, trade-offs, and functional responses in red deer habitat selection. Ecology 90, 699–710 (2009).
Mysterud, A. & Ostbye, E. Cover as a habitat element for temperate ungulates: effects on habitat selection and demography. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 27, 385–394 (1999).
Wiens, J. A. In The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics (eds Pickett, S. & White, P.) 169–193, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-050495-7.50015-6 (Academic Press, 1985).
Koufos, G. D. & Konidaris, G. E. Late Miocene carnivores of the Greco-Iranian Province: Composition, guild structure and palaeoecology. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 305, 215–226 (2011).
Merceron, G. et al. Stable isotope ecology of Miocene bovids from Northern Greece and the ape/monkey turnover in the Balkans. J. Hum. Evol. 65, 185–198 (2013).
Merceron, G., Blondel, C., Viriot, L., Koufos, G. D. & De Bonis, L. Dental microwear analysis of bovids from the Vallesian (late Miocene) of Axios Valley in Greece: Reconstruction of the habitat of Ouranopithecus macedoniensis (Primates, Hominoidea). Geodiversitas 29, 421–433 (2007).
García-Alix, A. A multiproxy approach for the reconstruction of ancient continental environments. The case of the Mio-Pliocene deposits of the Granada Basin (southern Iberian Peninsula). Glob. Planet. Change 131, 1–10 (2015).
Domingo, L. et al. Late Neogene and Early Quaternary paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic conditions in southwestern Europe: isotopic analyses on mammalian taxa. PLoS One 8, e63739 (2013).
Hernández Fernández, M. et al. Identification problems of arid environments in the Neogene-Quaternary mammal record of Spain. J. Arid Environ. 66, 585–608 (2006).
Matson, S. D. & Fox, D. L. Stable isotopic evidence for terrestrial latitudinal climate gradients in the Late Miocene of the Iberian Peninsula. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 287, 28–44 (2010).
Salesa, M. J. et al. A rich community of Felidae (Mammalia, Carnivora) from the late Miocene (Turolian, MN 13) site of Las Casiones (Villalba Baja, Teruel, Spain). J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 32, 658–676 (2012).
Alcalá, L. Macromamiferos Neogenos de la Fosa de Alfambra-Teruel. (Instituto de Estudios Turolenses, 1994).
Mysterud, A. & Ims, R. Functional Responses in Habitat Use: Availability Influences Relative Use in Trade-Off Situations. Ecology 79, 1435–1441 (1998).
Janis, C. M. The evolutionary strategy of the equidae and the origins of rumen and cecal digestion. Evolution (N. Y). 30, 757 (1976).
Silver, I. A. In Science in Archaeology (eds Brothweel, D. & Higgs, E.) 250–268 (1969).
Eisenmann, V., Alberdi, M. T., De Giuli, C. & Staesche, U. Studying fossil horses. Collected papers after the “New York International Hipparion Conference, 1981” 1, 1–72 (1988).
Eisenmann, V. & Sondaar, P. Y. Pliocene vertebrate locality of Çalta, Ankara, Turkey. 7. Hipparion. Geodiversitas 20, 409–439 (1998).
Köhler, M., Marín-Moratalla, N., Jordana, X. & Aanes, R. Seasonal bone growth and physiology in endotherms shed light on dinosaur physiology. Nature 487, 358–361 (2012).
Turner-Walker, G. & Mays, S. In Advances in Human Palaeopathology 121–146, https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470724187.ch7 (John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2008).
Francillon-Vieillot, H. et al. In Skeletal Biomineralization: Patterns, Processes and Evolutionary Trends (ed. Carter, J. C.) l, 471–530 (Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1990).
Woodward, H. N., Padian, K. & Lee, A. H. In Bone Histology of Fossil Tetrapods - Advancing Methods, Analysis, and Interpretation (eds Padian, K. & Lamm, E.-T.) 195–216 (2013).
Jordana, X., Marín-Moratalla, N., Moncunill-Solé, B., Nacarino-Meneses, C. & Köhler, M. Ontogenetic changes in the histological features of zonal bone tissue of ruminants: A quantitative approach. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 15, 265–276 (2016).
Erickson, G. M., Curry, K. A. & Yerby, S. A. Dinosaurian growth patterns and rapid avian growth rates. Nature 412, 429–433 (2001).
Ricklefs, R. E. The Economy of Nature. (Macmillan, 2008).
Zullinger, E. M., Ricklefs, R. E., Redford, K. H. & Mace, G. M. Fitting sigmoidal equations to mammalian growth curves. J. Mammal. 65, 607–636 (1984).
Ricklefs, R. E. Adaptation, constraint, and compromise in avian postnatal development. Biol. Rev. 54, 269–290 (1979).
Lee, A. H. & O’connor, P. M. Bone histology confirms determinate growth and small body size in the noasaurid theropod Masiakasaurus knopfleri. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 33, 865–876 (2013).
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. Ta. T. & Ryan, P. D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 4(1), 1–9 (2001).
Brody, S. Bioenergetics and Growth. (Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, 1945).
Lupi, T. M., Nogales, S., Leon, J. M., Barba, C. & Delgado, J. V. Characterization of commercial and biological growth curves in the Segurena sheep breed. Animal 9, 1341–1348 (2015).
von Bertalanffy, L. A quantitative theory of organic growth (inquiries on growth laws. II). Hum. Biol. 10, 181–213 (1938).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank M. Soteras for access to the museum collections at the Institut Català de Paleontologia Miquel Crusafont (ICP). G.O.-O. would also like to thank D. Kostopoulos (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, AUT) for the help during his visit to the Laboratory of Geology and Palaeontology at the University of Thessaloniki collections, and to T. Vlachou (AUT) for the help on the taxonomic identification and the body mass estimations of the Greek material. We are grateful to M. Fernández, G. Prats-Muñoz and L. Gordón for preparation of the thin slices, and to the ICP preparators for moulding the specimens. B. Lamglait (currently at Université de Montréal) together with the Réserve Africaine de Sigean are acknowledged for the donation extant equid specimens to the ICP collections. Thanks go further to T. Kaiser and R. Schafberg for loans and permission to cut bones of extant Equus from the collections of the Zoologisches Museum of Universität Hamburg, and the Museum für Haustierkunde of the Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, respectively, and also to the Zoologisches Institut und Museum, Christian-Albrechts-Universität Kiel. A. García-Alix (Universidad de Granada) is acknowledged for valuable discussion and two anonymous referees for their helpful comments on the manuscript. Finally, G.O.-O. thanks the assistance of A. Capalvo in the growth curves modelling. Funding for this study was provided by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) (PI: M.K., CGL2015-63777) and the CERCA Programme (Generalitat de Catalunya). The research group formed by M.K., C.N.-M. and G.O.-O. is recognised without funding by AGAUR (Generalitat de Catalunya) (2017 SGR 960). G.O.-O. is supported by a FI-DGR 2016 grant (2016FI_B00202) awarded by AGAUR (Generalitat de Catalunya) and C.N.-M. held FPI grant 2013 from the MINECO (BES-2013-066335).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.O.-O. and M.K. conceived and designed the experiments. C.N.-M. provided helpful advice during interpretation of the histological part and contributed with the analysis of the extant equids’ material. G.O.-O. wrote the manuscript and prepared the figures and tables. M.K. supervised the histological study, the interpretation and discussion of the results, and the preparation of the manuscript. G.D.K. provided the Greek material for analysis. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Orlandi-Oliveras, G., Nacarino-Meneses, C., Koufos, G.D. et al. Bone histology provides insights into the life history mechanisms underlying dwarfing in hipparionins. Sci Rep 8, 17203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35347-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35347-x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Rib remodelling changes with body size in fossil hippopotamuses from Cyprus and Greece
Journal of Mammalian Evolution (2023)
-
Palaeohistology reveals a slow pace of life for the dwarfed Sicilian elephant
Scientific Reports (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.