Abstract
Using high throughput Illumina sequencing technology, we determined complete sequences for the mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) and nuclear ribosomal DNA (rDNA) complex for three African freshwater snail taxa within the genus Biomphalaria, B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala, and for two laboratory strains of B. glabrata originating from the Neotropics. Biomphalaria snails are obligate vectors of the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni, a major etiologic agent of human intestinal schistosomiasis. Our data show that mitogenomes from African and Neotropical Biomphalaria are highly conserved. With respect to rDNA, the two internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and 2) were found to be highly variable whereas the three ribosomal RNA genes (28S, 5.8S and 18S rRNA) exhibited no or very limited variation. Our analyses reveal that the two taxa inhabiting Lake Victoria, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala, are very similar to one another relative to the similarity either shows to B. pfeifferi or B. glabrata. This new sequence information may prove useful for developing new markers for snail identification, environmental detection/monitoring purposes or for tracking epidemiology and snail dependencies of S. mansoni in endemic areas. It also provides new information pertinent to still unresolved questions in Biomphalaria systematics and nomenclature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Freshwater snails of the genus Biomphalaria (Gastropoda, Planorbidae) are obligate intermediate hosts of the digenetic trematode Schistosoma mansoni, the causative agent of intestinal schistosomiasis that afflicts over 83 million people across Africa, the Middle East, and South America1. In sub-Saharan Africa, where >90% of all cases of S. mansoni now occur, the Lake Victoria basin remains a hyperendemic region of transmission. A recent large-scale survey of children in schools around Lake Victoria revealed that prevalence of S. mansoni infection in some schools reached up to 90%2. Three Biomphalaria taxa, B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala, vectors of S. mansoni in and around the lake, have been found to play a vital role in transmission of schistosomiasis in the region. Although the status of the nomenclature for B. sudanica and B. choanomphala remains contentious, a point we will return to later in the paper, for the sake of convenience, we use throughout the paper the species names traditionally applied to these taxa3,4.
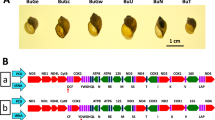
Biomphalaria pfeifferi (Krauss, 1848) is characteristically associated with streams, ponds, reservoirs and irrigation ditches4,5,6,7,8. Many streams in which B. pfeifferi resides directly connect to Lake Victoria. B. sudanica and B. choanomphala are lacustrine and generally considered to be responsible for the majority of transmission of S. mansoni in Lake Victoria4. B. sudanica is found in swampy areas along the shoreline of the lake whereas B. choanomphala is usually found in deeper water (down to 40 m, occurring hundreds of meters from shore), though it can also be collected from the shoreline in some locations4,9,10,11,12. Although anatomical details of the soft parts of B. sudanica and B. choanomphala are similar, the two taxa differ in shell size and shape. B. sudanica has a relatively flat shell 1.0–1.8 cm in diameter characterized by a flat apical surface and broad and shallow umbilical region. In contrast, the shell of B. choanomphala is smaller in diameter (0.5–0.8 cm) and relatively deeper, and shows angulations on the whorls of both upper and lower surfaces (Fig. 1A). Both taxa are susceptible to experimental infections12,13 (Mutuku, personal communication) and are found naturally infected with S. mansoni9,14,15. The question of whether the two taxa should be considered as separate species, subspecies or merely eco-phenotypes has been, and is still, actively discussed9,15,16. Standley et al.10 analyzed mitochondrial CoxI (mtCoxI) and mt16S sequences from Biomphalaria collected from Lake Victoria and proposed that B. sudanica and B. choanomphala should be considered as two subspecies, B. choanomphala sudanica and B. choanomphala choanomphala, respectively (see Discussion for further consideration).
(A) Showing the relative size of the five snail specimens. BP: B. pfeifferi; BS: B. sudanica; BC: B. choanomphala; G72M: G72 M line B. glabrata; G16B: G16 BS90 B. glabrata. ND: NADH dehydrogenase subunit; CytB: cytochrome b; Cox: cytochrome c oxidase subunit. ATP: ATP synthase F0 subunit: 12S: small subunit ribosomal RNA; 16S: large subunit ribosomal RNA; Please note that the abbreviations are applied throughout the paper. (B) Showing locations of all genes in the mitogenomes. The detailed information for each gene is presented in Supplementary Dataset Table 1.
Molecular analyses based on mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) and nuclear ribosomal DNA (rDNA) have been widely used for identification of species and populations, and for studies of population genetics, evolutionary biology and phylogenetics17,18,19. There are 34 described species of genus Biomphalaria, 12 from Africa and 22 from the Americas4,20,21,22. Of the 34 species, eighteen species are known or suspected intermediate hosts for S. mansoni22. Mitogenomes have been reported only for two South American Biomphalaria species, B. glabrata and B. tenagophila23,24, but none from African species.
We used the Illumina platform to sequence complete mitogenomes and rDNA gene complexes for three African taxa, B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala. In addition, we also sequenced the mitogenomes of two highly inbred lines of B. glabrata Say, 1818, the G72 M line and G16 BS90 lines, which were recently developed in our laboratory. G72 M line and G16 BS90 were derived from two B. glabrata strains commonly known M line and BS90 snails, respectively25,26. B. glabrata, the most important species for transmission of schistosomiasis in the New World, was widely adopted over half a century ago as a model snail host for schistosome parasites. Several laboratory strains of B. glabrata have since been developed25,26,27,28,29. The genome sequence30, a linkage map31, and complete mitogenome24 have been documented for B. glabrata. In this study, our goal is to examine the two inbred strains of B. glabrata and the three African Biomphalaria taxa to assess the extent to which the mitogenomes of Old and New World representatives differ, and how this compares to the extent of differences noted between the taxa B. sudanica and B. choanomphala from the Lake Victoria region.
Results
Mitogenomes
Complete mitogenomes for B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica, B. choanomphala, and G72M and G16BS90 lines of B. glabrata were determined and submitted to GenBank under access numbers MG431962, MG431963, MG431964, MG431965, and MG431966, respectively. All mitogenomes possessed the 37 genes typical of animal mitogenomes, comprising 13 protein-coding genes (PCG), two ribosomal RNA genes (12S rRNA and 16S rRNA), and 22 tRNA genes. The order and orientation of all genes were identical for the five mitogenomes. Differences were found in the length of some genes (Fig. 1B, Supplementary Dataset 1).
Nucleotide composition analysis indicated the mitogenomes were biased towards high A + T content, ranging from 74.68% (G72M) to 76.64% (B. pfeifferi). Base composition, measured by the AT-skew and GC-skew, i.e., asymmetry in nucleotide composition, showed AT and GC skews are at the range of −0.11 to −012 and 0.11 to 0.12, respectively, suggesting the preference for A and G nucleotides, a widespread characteristic of animal mtDNAs32. Detailed information for nucleotide composition and AT and GC skews in individual genes is provided in the Supplementary Dataset 2.
Genetic analyses
The percent identity matrix was generated at the nucleotide (nt) level for the entire mitogenome and at the amino acid (aa) level for gene products of all 13 PCG combined (Fig. 2). It is remarkable that identity between B. sudanica and B. choanomphala at the nt and aa level is 98.31% and 98.82%, respectively, much higher than that between two strains of B. glabrata (94.95% for nt and 97.27% for aa). After including the reported mitogenome of B. tenagophila (accession no: EF433576) for comparative analysis, it was found that B. tenagophila has the lowest identity with the Biomphalaria species included in this study, 85.31–86.06% at the nt level, and 87.39–88.10% at the aa level. Further analyses of individual PCG revealed relatively high variation in ATP8 and ND3, whereas CoxI showed very little variation (Fig. 3A,B). To provide a view of the evolutionary forces acting on mitogenomes of Biomphalaria, Ka/Ks ratios generated from individual PCG are provided in Fig. 4. All ratios were found to be less than 1, suggestive of purifying selection acting on all protein coding genes.
Percent identity matrix of mitogenomes. Blue and red colors show percent identity at nt and aa levels, respectively. At the nt level, whole mitogenome sequences were used. At the aa level, gene products for a given PCG were aligned and trimmed, then all 13 PCGs from a given mitogenome were combined.
Nuclear rDNA
GenBank accession numbers of rDNA sequences for B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica, B. choanomphala, G72 M line and G16BS90 B. glabrata are MG461588, MG461589, MG461590, MG461591, and MG461592, respectively. The sequences of 18S and 5.8S were found to be identical for all five specimens. Minor variation was noted in the 28S region that exhibited overall nt identity at a range of 99.76–100.00%. Differences in 28S sequence were not found between B. sudanica and B. choanomphala (Supplementary Figure 1). By contrast and not surprisingly, the internal transcribed spacer region 1 (ITS1) and 2 regions exhibited more variation. Figure 5 shows the sequence variations and percent identity of ITS1 and 2 among the five rDNA sequences.
Phylogenetic analyses
Using complete mitogenome nt, and aa sequences of all 13 PCG combined, three phylogenetic methods, Maximum Likelihood (ML), Neighbor-Joining (NJ) and Minimum Evolution (ME), were applied. The topology and bootstrap values of all trees based on nt sequence were essentially the same (Fig. 6). For trees based on aa sequences, topology of the three trees was identical to that obtained using the nt sequences, and only slight differences of bootstrap value were found among the three trees. From the trees, it can be seen that the three African species form a clade that is separated from B. glabrata. Among the two American species, B. glabrata is more closely related to African species than B. tenagophila.
A consensus phylogenetic tree was constructed using whole mtDNA nucleotide sequence and aa sequences of all 13 PCG combined. Three methods, ML, NJ and ME, were used to build the tree. For the whole mtDNA sequences, the three trees are identical in terms of topology and bootstrap values (all with 100). For aa sequences, the topology is exactly the same as that was built by nt sequences. The bootstrap values are almost the same except for one node that is highlighted in the box. GenBank accession numbers for B. tenagophila (BT) and Radix auricularia are EF433576 and NC_026538, respectively. Please note that due to gene re-arrangement, the gene order of Physella acuta (Physidae) is different from that of Biomphalaria. So mitogenome of Radix auricularia (Lymnaeidae) was used as outgroup.
In addition, we also used the three phylogenetic methods to examine relationships using ITS1, ITS2 and the two ITS combined (Supplementary Figure 2) but as expected, because of the variability of these sequences, they are not as useful for discriminating among species as whole mitogenome sequences.
Discussion
This study presents complete mitogenome and rDNA sequence for Biomphalaria species that play a key role in vectoring S. mansoni. B. pfeifferi and B. glabrata are the two most important intermediate host species for S. mansoni, in the Afrotropical and Neotropical regions, respectively. B. sudanica and B. choanomphala are responsible for transmission of schistosomiasis in Lake Victoria, one of the world’s great hyperendemic schistosomiasis regions. The study provides useful genetic markers for snail diagnostics and systematics, and for schistosome epidemiology.
Gene arrangements reported here are identical to those found in three Biomphalaria mitogenomes previously reported, for two strains of B. glabrata24 and for B. tenagophila23. This suggests that gene order in mitogenomes of Biomphalaria from the Old World (B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala) and New World (B. glabrata and B. tenagophila) are highly conserved.
There are five families proposed for the gastropod Order Hygrophila: Acroloxidae, Chilinoidae, Planorbidae, Lymnaeidae and Physidae33. So far complete mitogenomes are documented only for representatives of the Planorbidae23,24, Lymnaeidae34, and Physidae35. The order of mitochondrial genes in the Planorbidae to which Biomphalaria belongs is similar to the Lymnaeidae except for differences in location of a few tRNAs23,34, whereas gene order is quite different in the Physidae35 (for more information about the comparative mitogenome gene orders of the gastropod, please see articles)35,36. It has been noted that gastropods display an unusually large variety of gene orders among their mitogenomes36. Further studies are needed to characterize more complete gastropod mitogenomes, which will shed light on their evolution and diversification, and at the same time, provide more genetic markers for population genetics, evolutionary and phylogenetic studies. Our study also provides additional rDNA sequence data, thereby adding further genetic characterization of more snail species involved in transmission of human schistosomiasis.
Our analyses based on the mitochondrial DNA and nuclear rDNA sequences lead to the following conclusions: (1) Diversity within the species B. glabrata is relatively high; (2) Variation between the two Neotropical species is higher than among the Afrotropical species we examined; and (3) Data are consistent with B. sudanica and B. choanomphala being eco-phenotypes of the same species. Further explanations are provided below.
For B. glabrata, four mitogenomes from different strains are now available, two (M line and 1742) reported a decade ago24 and two (G72M and G16BS) presented in this study. The 1742 strain was from the Natural History Museum, London, UK37, and the M line strain was maintained at University of New Mexico (UNM), USA24. Both were originally derived from early crosses between albino Brazilian strain, resistant to Puerto Rican S. mansoni, and pigmented Puerto Rican snails, susceptible to the same parasite25. The G72 M line was derived from the UNM M line colony by continually selecting snails derived from self-fertilization. Not surprisingly, M line (accession no: AY380567), 1742 (AY380531) and G72M line share high genetic similarity (99.87–99.93% nt identity). The pigmented BS90 strain, a schistosome-resistant strain, also referred to frequently as the Salvador strain, was isolated in Salvador, Brazil26. G16BS90 was derived from the BS90 strain by repeatedly selecting snails by self-fertilization. It is notable that the divergence between G16BS90 and the other three strains of B. glabrata is high (94.95%). This supports earlier observations of high genetic variation within B. glabrata22,38.
Because Biomphalaria are vectors for S. mansoni, the origin and diversification of the genus has attracted much attention. An early hypothesis suggested that the origin of Biomphalaria was in Gondwanaland as much as 100 million years ago (MYA), and as a consequence, Biomphalaria snails were already present on what became Africa and South America as they rafted apart39,40. A number of molecular investigations using allozymes, PCR-based fragments of mtDNA or partial rDNA sequences, have since suggested that Biomphalaria snails originated in South America, and later dispersed to Africa less than 3 MYA and gave rise to the African species21,22,37,38,41,42,43. Our phylogenetic analyses based on whole mitogenome sequences demonstrated that B. glabrata, not B. tenagophila, is closely related to the group of African species, adding additional evidence suggesting that African Biomphalaria came from the New World’s species, likely from a B. glabrata-like ancestor22,37,38.
Identification of Biomphalaria species is challenging because shell features are often highly variable and can even be confused with shells of other genera like Helisoma44. Anatomical characteristics, often revealed only by painstaking dissections of specially prepared materials, require experience, patience and practice to discern13,45,46. Nonetheless, reference to both shell and anatomical features in conjunction with provision of an ever-increasing array of molecular data has provided an improved and workable overall systematic framework for Biomphalaria. However, significant conundrums remain, among them the relationships between, and naming considerations for B. sudanica and B. choanomphala from Lake Victoria. This issue is of interest because, as previously noted, the shells of the two taxa are quite distinct, and because both play key roles in transmission of S. mansoni in the lake. Our phylogenetic analyses indicated the two taxa are closely related, consistent with representing the same species, as evidenced by the high sequence identity in their mitogenomes (98.31% nt identity), higher than that observed among different strains of B. glabrata (94.95% nt identity). An allozyme-based study also supported a close relationship between the two taxa but also showed some evidence of separate gene pools between them42. DeJong et al.22 using mt16S and ITS1 and 2 sequences regarded B. choanomphala as a lacustrine form of B. sudanica. Based on restriction enzyme digestion of ITS1 and mtCoxI sequence, Standley et al.10,11 noted that specimens with both classic B. choanomphala and B. sudanica shell forms occurred among various clades in a CoxI tree. They noted that habitat predicted shell morphology and suggested snails exemplifying the two shell forms were ecophenotypes of the same species. They did not differentiate between the two ecophenotypes in their study of the population genetics of Biomphalaria in Lake Victoria11.
With respect to what to formally call the Biomphalaria snails inhabiting Lake Victoria, Standley et al.10 reasonably proposed that the name B. choanomphala should take priority based on the description of this species from the lake by Martens47. They proposed the two taxa should then be considered as B. c. choanomphala and B. c. sudanica. They argued that B. sudanica from other localities in Africa is likely a separate species, based on the genetic distance observed between the Lake Victoria samples and those from Genbank, whereas B. choanomphala is considered endemic to Lake Victoria10.
Martens first described B. sudanica in 1870 with the type locality given as the Bahr el Ghazal at Meshra el Req, in what is now South Sudan. Nine years later (1879), he described B. choanomphala based on specimens collected from the southwest shore of Lake Victoria in Tanzania4,48. In 1890, he re-described B. sudanica and B. choanomphala both collected from an area called Nyansa (present day West Kenya) of Lake Victoria, implying that B. sudanica in Lake Victoria should be considered as the same species he first described from the South Sudan type locality. Key to the decision as to what name to apply to the Lake Victoria specimens is whether B. sudanica, given the temporal priority of the name, from elsewhere in Africa but most especially from the original type locality, is genetically distinct from Biomphalaria specimens from Lake Victoria. A phylogenetic analysis based on sequence data currently available in GenBank does not provide bootstrap support for differentiating B. sudanica from Lake Victoria from B. sudanica from other locations (Supplementary Figure 3), but more morphological and molecular data, particularly for B. sudanica from South Sudan or Sudan, are needed. If B. sudanica from the type locality is found to be genetically similar to those from the lake, then this name would have precedence and Biomphalaria from Lake Victoria might best be called B. sudanica sudanica and B. sudanica choanomphala or B. sudanica (one species with two ecophenotypes). Also, although our data support the finding by Standley et al.10 that B. sudanica and B. choanomphala from the lake are genetically very similar, it is not clear how commonly gene flow may occur within and between the two ecophenotypes, and whether this could ever significantly influence their respective levels of susceptibility to S. mansoni. Here it should be noted that Biomphalaria in the lake must respond to selective pressures imposed by many different trematode species, along with other biotic and physical factors, and these factors are bound to differ between the shoreline habitats frequented by B. sudanica and the deeper waters usually occupied by B. choanomphala.
Finally, we note that mtDNA and rDNA from both snails and schistosomes have proven to have considerable utility as source material for the development of marker sequences of potential use in various kinds of diagnostic or identification assays49. We note that as schistosomiasis control efforts enter phases where surveillance and monitoring efforts of snail populations become more critical, having reliable tools for proper identification of the snail species present and defining their role in transmission will be critical. Provision of additional sequence data to aid this effort is another potential benefit of this work.
Materials and Methods
Specimens
All snail specimens sequenced were laboratory-reared at the Center for Evolutionary and Theoretical Immunology, Department of Biology, at the University of New Mexico (UNM). Founding stocks of B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala were originally collected in western Kenya, and have been maintained for 5, 4, and 0.5 years, respectively. This project was undertaken with approval of Kenya’s National Commission for Science, Technology, and Innovation (permit number NACOSTI/P/15/9609/4270), National Environment Management Authority (NEMA/AGR/46/2014) and the Kenya Wildlife Service (permit #0004754). B. pfeifferi was collected from Asao stream (00°19′5.50′′S, 35°0′24.99′′E). B. sudanica and B. choanomphala were collected from Lake Victoria: B. sudanica from the car-wash site in Kisumu, Kenya (00°05′45.00′′S, 34°44′57.69′′E) and B. choanomphala from Usenge Beach (00°3′42.00′′S, 34°2′37.00′′E). The M line G72 line and the BS-90 G16 lines of B. glabrata snails have been generated through 72 and 16 generations of selfing, respectively, the highly inbred lines that are used for genetic studies of snail resistance to schistosomes. The founding M line B. glabrata snails that are susceptible to S. mansoni were originally acquired from Dr. C. S. Richards and have been maintained in the lab for at least 40 years. The BS-90 snails, resistant to S. mansoni, were acquired from Dr. Lobato Paraense in the late 1980’s and were originally obtained from him from natural habitats in Salvador, Brazil26.
Extraction of DNA
The shell of each snail was removed and the intact whole body was rinsed and then ground to a fine powder using mortar and pestle in liquid nitrogen. The powder was transferred to 1.5 ml tubes for subsequent DNA extraction.
Two methods were used for DNA extraction, depending on the use to which the samples were being put. For B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica and B. choanomphala, we applied a mtDNA enrichment method typically used for mammalian cells50. This method was originally developed based on the notion that mtDNA in a eukaryotic cell is comparable to plasmids in a bacterium in terms of size and form. Therefore, a Miniprep kit (Qiagen) normally used for extraction of plasmid DNAs from bacteria was used to extract mtDNA from snail cells.
For G72 M line and G16 BS90 B. glabrata, we used the CTAB method51 rather than the mtDNA enrichment method as described above. The CTAB method can extract all cellular DNAs (nuclear DNA and mtDNA), which can be subsequently sequenced by next generation sequencing. In this study, our main interest is in the mitogenomes. So we conducted bioinformatics analyses to separate mtDNA reads from nuclear DNA reads for assembly and annotation of mitogenomes (see below).
After extraction, all DNA samples were treated with RNase A (Invitrogen) at 37 °C for 30 min and then 70 °C for 10 min. DNA samples were further purified using SPRselect Beads (Beckman Coulter). Quality and quantity of DNA were measured using a Nanodrop and a Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen).
Preparation, amplification and sequencing of Illumina libraries
A 150 nucleotide (nt) × 2 paired-end library for each sample was prepared (KAPA Hyper Prep Kit, KAPA Biosystems, www.kapabiosystems.com). Each DNA sample was barcoded by an adaptor. Sequencing the libraries was performed on the Illumina NextSeq500 platform at the UNM Biology Department’s Molecular Biology Facility (http://ceti.unm.edu/core-facilities/molecular-biology.html).
Assembly and annotation of mitogenomes
Two methods were used to assemble mitochondrial genomes, the semi-reference based assembly using MITOBIM and de novo assembly using SPAdes52. MITOBIM is a tool developed to recursively find reads mapped to related reference mitogenomes and uses these reads to build the targeted mitogenome. The published mitogenome of M line B. glabrata was used as a reference24. In addition, de novo assembly using SPAdes was also conducted. The longest contig with BLASTN e-value < 10−5 against the reference mitogenome was selected to assemble the new mitogenome. Mitogenomes based on the two methods were aligned and manually checked for consistency. To check read support consistency, reads were mapped to final assembled mitogenomes and visualized using Integrated Genome Viewer53.
Mitogenome annotation was done using MITOS2 that includes the latest protein identification model54,55. We used two references in MITOS2, RefSeq63 Metazoa and RefSeq81 Metazoa, to annotate the mitogenomes for verification and confirmation, especially if one version did not predict all genes. For other criteria, default settings were applied (E-value exponent: 2; final maximum overlap: 50; fragment quality factor: 100). Moreover, we have re-checked mitogenome sequences manually using the ExPASY translation tool (http://web.expasy.org/translate/), which enabled us to see the correct reading frames of protein coding genes and to identify potential start and stop codons in the flanking regions of predicted genes. Based on annotation features, multiple circular mitogenome maps were drawn using the R package Circlize56,57.
Assembly and annotation of nuclear rDNA
Two methods, de novo assembly and mapping reads to reference B. glabrata BBO2 rDNA, were used for assembly. Annotation of gene segment of nuclear rDNA that consists of 18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2, and 28S was determined based on BBO2 rDNA sequence (http://biology.unm.edu/Biomphalaria-Genome/rDNABg.html).
Genetic and phylogenetic analyses
Sequence alignments and percent identity of nucleotides (nt) and amino acids (aa) were determined using Clustal Omega58 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). Heat-maps of pair-wise sequence identities were generated using the R package ggplot259. Evolutionary rate including synonymous, non-synonymous substitution rates and their ratio were calculated using KaKsCalculator60. The line plot chart for mitochondrial genes Ka/Ks comparisons among species was drawn using R package ggplot259. All the intermediate data organization and filtering were done with in-house bash and Perl scripts and Microsoft Excel.
Phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA761. Alignments were conducted using ClustalW integrated in MEGA7. Three methods were used for construction of trees, Maximum Likelihood (ML), Neighbor-Joining (NJ) and Minimum Evolution (ME). To evaluate the reliability of phylogenetic relationships, 1,000 bootstrap replications were applied in the three methods.
Accession Codes
GenBank accession numbers of the mitogenomes for B. pfeifferi, B. sudanica, B. choanomphala, and G72M and G16BS90 lines of B. glabrata, are MG431962, MG431963, MG431964, MG431965, and MG431966, respectively. The Genbank accession numbers of rDNA for the five specimens (in the same order) are MG461588, MG461589, MG461590, MG461591, and MG461592, respectively.
References
Crompton, D. W. How much human helminthiasis is there in the world? J. Parasitol. 85, 397–403 (1999).
Woodhall, D. M. et al. Use of geospatial modeling to predict Schistosoma mansoni orevalence in Nyanza province, Kenya. PLoS One. 8, e71635 (2013).
Mandahl-Barth, G. Intermediate host of Schostosoma. World Heal. Organ. Geneva. Monogr. Ser. No 37 (1958).
Brown, D. S. Freshwater snails of Africa and their medical importance. Taylor & Francis (1994).
Loker, E. S. et al. Distributions of freshwater snails in southern Kenya with implications for the biological control of schistosomiasis and other snail-mediated parasites. J. Med. Appl. Malacol. 5, 1–20 (1993).
Mutuku, M. W. et al. Field-derived Schistosoma mansoni and Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Kenya: a compatible association characterized by lack of strong local adaptation, and presence of some snails able to persistently produce cercariae for over a year. Parasit. Vectors 7, 533 (2014).
Mutuku, M. W. et al. A comparison of Kenyan Biomphalaria pfeifferi and B. sudanica as vectors for Schistosoma mansoni, including a discussion of the need to better understand the effects of snail breeding systems on transmission. J Parasitol. 103, 669–676 (2017).
Buddenborg, S. K. et al. Transcriptomic responses of Biomphalaria pfeifferi to Schistosoma mansoni: Investigation of a neglected African snail that supports more S. mansoni transmission than any other snail species. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 11, e0005984 (2017).
Magendantz, M. The biology of Biomphalaria choanomphala and B. sudanica in relation to their role in the transmission of Schistosoma mansoni in Lake Victoria at Mwanza, Tanzania. Bull. World Health Organ. 47, 331–342 (1972).
Standley, C. J., Wade, C. M. & Stothard, J. R. A fresh insight into transmission of schistosomiasis: A misleading tale of biomphalaria in lake victoria. PLoS One 6, e26563 (2011).
Standley, C. J., Goodacre, S. L., Wade, C. M. & Stothard, J. R. The population genetic structure of Biomphalaria choanomphala in Lake Victoria, EastAfrica: implications for schistosomiasis transmission. Parasit. Vectors 7, 524 (2014).
Lu, L., Zhang, S.-M., Mutuku, M. W., Mkoji, G. M. & Loker, E. S. Relative compatibility of Schistosoma mansoni with Biomphalaria sudanica and B. pfeifferi from Kenya as assessed by PCR amplification of the S. mansoni ND5 gene in conjunction with traditional methods. Parasit. Vectors 9, 166 (2016).
Adriko, M. et al. Compatibility of Ugandan Schistosoma mansoni isolates with Biomphalaria snail species from Lake Albert and Lake Victoria. Acta Trop. 128, 303–308 (2013).
Rowel, C. et al. Environmental epidemiology of intestinal Schistosomiasis in Uganda: Population dynamics of Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Albert and Lake Victoria with observations on natural infections with digenetic trematodes. Biomed Res Intl. 2015, 717261 (2015).
Gouvras, A. N. et al. Longitudinal survey on the distribution of Biomphalaria sudanica and B. choanomophala in Mwanza region, on the shores of Lake Victoria, Tanzania: implications for schistosomiasis transmission and control. Parasit. Vectors 10, 316 (2017).
Goodman, J. D. & Panesar, T. S. Parasymphylodora manterin. sp., an adult trematode from a fresh-water pulmonate snail, Biomphalaria choanomphala choanomphala, from Lake Victoria, Uganda. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 95, 204–209 (1976).
Harrison, R. G. Animal mitochondrial DNA as a genetic marker in population and evolutionary biology. Trends Ecol Evol. 4, 6–11 (1989).
Crawford, A. R., Bassam, B. J., Drenth, A., Maclean, D. J. & Irwin, J. A. G. Evolutionary relationships among Phytophthora species deduced from rDNA sequence analysis. Mycol. Res. 100, 437–443 (1996).
Bernt, M., Braband, A., Schierwater, B. & Stadler, P. F. Genetic aspects of mitochondrial genome evolution. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 69, 328–338 (2013).
Malek E. A. Snail hosts of schistosomiasis and other snail-transmitted diseases in tropical America: A manual. World Heal. Organ. Sci. Publ. No: 478, (1985).
JØrgensen, A., Kristensen, T. K. & Stothard, J. R. Phylogeny and biogeography of African Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae), with emphasis on endemic species of the great East African lakes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 151, 337–349 (2007).
DeJong, R. J. et al. Evolutionary relationships and biogeography of Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) with implications regarding its role as host of the human bloodfluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Mol. Biol. Evol. 18, 2225–2239 (2001).
Jannotti-Passos, L. K. et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Biomphalaria tenagophila (Orbigny, 1835) (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 105, 504–511 (2010).
DeJong, R. J., Emery, A. M. & Adema, C. M. The mitochondrial genome of Biomphalaria glabrata (Gastropoda: Basommatophora), intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni. J. Parasitol. 90, 991–7 (2004).
Newton, W. L. The establishment of a strain of Australorbis glabratus which combines albinism and high susceptibility to infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J. Parasitol 41, 526–528 (1955).
Paraense, W. L. & Correa, L. R. Variation in susceptibility of populations of Australorbis glabratus to a strain of Schistosoma mansoni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 5, 15–22 (1963).
Richards, C. S. Variations in infectivity for Biomphalaria glabrata in strains of Schistosoma mansoni from the same geographical area. Bull World Heal. Organ. 54, 706–7 (1976).
Theron, A., Coustau, C., Rognon, A., Gourbière, S. & Blouin, M. S. Effects of laboratory culture on compatibility between snails and schistosomes. Parasitology 135, 1179–1188 (2008).
Richards, C. S., Knight, M. & Lewis, F. A. Genetics of Biomphalaria glabrata and its effect on the outcome of Schistosoma mansoni infection. Parasitol. Today 8, 171–174 (1992).
Adema, C. M. et al. Whole genome analysis of a schistosomiasis-transmitting freshwater snail. Nat. Commun. 8, 15451 (2017).
Tennessen, J. A., Bollmann, S. R. & Blouin, M. S. A targeted capture linkage map anchors the genome of the schistosomiasis vector snail, Biomphalaria glabrata. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 7, 2353–2361 (2017).
Saccone, C., De Giorgi, C., Gissi, C., Pesole, G. & Reyes, A. Evolutionary genomics in Metazoa: The mitochondrial DNA as a model system. Gene 238, 195–209 (1999).
Dayrat, B. et al. Phylogenetic relationships and evolution of pulmonate gastropods (Mollusca): new insights from increased taxa sampling. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 59, 425–437 (2011).
Feldmeyer, B., Greshake, B., Funke, E., Ebersberger, I. & Pfenninger, M. Positive selection in development and growth rate regulation genes involved in species divergence of the genus Radix. BMC Evol. Biol. 15, 164 (2015).
Nolan, J. R., Bergthorsson, U. & Adema, C. M. Physella acuta: Atypical mitochondrial gene order among panpulmonates (Gastropoda). J. Molluscan Stud. 80, 388–399 (2014).
Grande, C., Templado, J. & Zardoya, R. Evolution of gastropod mitochondrial genome arrangements. BMC Evol. Biol. 8, 61 (2008).
Campbell, G. et al. Molecular evidence supports an African affinity of the Neotropical freshwater gastropod, Biomphalaria glabrata, Say 1818, an intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 267, 2351–2358 (2000).
Woodruff, D. & Mulvey, M. Neotropical schistosomiasis: African affinities of the host snail Biomphalaria glabrata (Gastropoda: Planorbidae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 60, 505–516 (1997).
Davis, G. M. Snail hosts of Asian Schistosoma infecting man: evolution and coevolution. Malacol Rev. Suppl. 2, 195–238 (1980).
Davis, G. M. Evolution of prosobranch snails transmitting Asian Schistosoma; coevolution with Schistosoma: a review. Prog. Clin. Parasitol. 3, 145–204 (1993).
Bandoni, S. M., Mulvey, M. & Loker, E. S. Phylogenetic analysis of eleven species of Biomphalaria Preston, 1910 (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) based on comparisons of allozymes. Bio J Linn Soc. 54, 1–27 (1995).
Bandoni, S. M., Mulvey, M. & Loker, E. S. Population structure and taxonomic discrimination among three species of Biomphalaria Preston, 1910 (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) from Kenya. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 129, 387–401 (2000).
Morgan, J. A. et al. A phylogeny of planorbid snails, with implications for the evolution of Schistosoma parasites. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 25, 477–88 (2002).
Pointier J. P. Guide to the freshwater molluscs of the lesser antilles. ConchBooks, (2008).
Plam, M., Jørgensen, A., Kristensen, T. K. & Madsen, H. Sympatric Biomphalaria species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Albert, Uganda, show homoplasies in shell morphology. African Zool. 43, 34–44 (2008).
Palasio, R. G. S., Guimarães, M. C. A., Ohlweiler, F. P. & Tuan, R. Molecular and morphological identification of Biomphalaria species from the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Zookeys 2017, 11–32 (2017).
Martens, E. van. Beschalte Weichthiere Deutsch-Ost-Afrikas. 7 pls. Möbius, K. (Ed.) Berlin, Diterich reamer (Ernst Volsen). In Deutsch-Ost-Afrika 4, 308 pp (1879).
Brown, D. S., Fison, T., Southgate, V. R. & Wright, C. A. Aquatic snails of the Jonglei region, southern Sudan, and transmission of trematode parasites. Hydrobiologia 110, 247–271 (1984).
Tchuem Tchuenté, L.-A., Rollinson, D., Stothard, J. R. & Molyneux, D. Moving from control to elimination of schistosomiasis in sub-Saharan Africa: time to change and adapt strategies. Infect. Dis. Poverty 6, 42 (2017).
Quispe-Tintaya, W., White, R. R., Popov, V. N., Vijg, J. & Maslov, A. Y. Fast mitochondrial DNA isolation from mammalian cells for next-generation sequencing. Biotechniques 55, 133–136 (2013).
Winnepenninckx, B., Backeljau, T. & Wachter, R. Extraction of high molecular DNA from molluscs. Trends Genet. 9, 407 (1993).
Bankevich, A. et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and Its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19, 455–477 (2012).
Thorvaldsdóttir, H., Robinson, J. T. & Mesirov, J. P. Integrative genomics viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 14, 178–192 (2013).
Bernt, M. et al. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 69, 313–319 (2013).
Al Arab, M. et al. Accurate annotation of protein-coding genes in mitochondrial genomes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 106, 209–216 (2017).
Ihaka, R. & Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5, 299–314 (1996).
Gu, Z., Gu, L., Eils, R., Schlesner, M. & Brors, B. Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 30, 2811–2812 (2014).
Sievers, F. et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7 (2011).
Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J Royal Statist Soci: Series A, 174, 245–246 (2011).
Wang, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhu, J. & Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics, Proteomics Bioinformatics. 8, 77–80 (2010).
Kumar, S., Stecher, G. & Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 33, 1870–1874 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Coen Adema for advising on annotation of mitogenomes and translating German literature, Dr. Sara Brant for discussing construction of phylogenetic trees, and Mr. George Rosenberg for assistance in performing Illumina sequencing. This work was supported by NIH grants R37AI101438 and NIH P30 GM110907. This paper is published with the approval of the Director of KEMRI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.M.Z. and E.S.L. conceived the project; S.M.Z. conducted the experiment; S.M.Z. and L.B. analyzed the data; M.R.L., L.L., and M.W.M. collected samples and maintained snail colony; S.M.Z., G.M.M., and E.S.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, SM., Bu, L., Laidemitt, M.R. et al. Complete mitochondrial and rDNA complex sequences of important vector species of Biomphalaria, obligatory hosts of the human-infecting blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni. Sci Rep 8, 7341 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25463-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25463-z
This article is cited by
-
Comparative mitogenomics of freshwater snails of the genus Bulinus, obligatory vectors of Schistosoma haematobium, causative agent of human urogenital schistosomiasis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Assessing the diversity and distribution of potential intermediate hosts snails for urogenital schistosomiasis: Bulinus spp. (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) of Lake Victoria
Parasites & Vectors (2020)
-
Genetic diversity of Biomphalaria pfeifferi, the intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni in Shamva district, Zimbabwe: role on intestinal schistosomiasis transmission
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.