Abstract
The endosymbiotic bacterium Wolbachia spreads rapidly through populations of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, and strongly inhibits infection with key human pathogens including the dengue and Zika viruses. Mosquito control programs aimed at limiting transmission of these viruses are ongoing in multiple countries, yet there is a dearth of mass rearing infrastructure specific to Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes. One example is the lack of a blood meal substitute, which accounts for the Wolbachia-specific physiological changes in infected mosquitoes, that allows the bacterium to spread, and block viral infections. To that end, we have developed a blood meal substitute specifically for mosquitoes infected with the wMel Wolbachia strain. This diet, ADM, contains milk protein, and infant formula, dissolved in a mixture of bovine red blood cells and Aedes physiological saline, with ATP as a phagostimulant. Feeding with ADM leads to high levels of viable egg production, but also does not affect key Wolbachia parameters including, bacterial density, cytoplasmic incompatibility, or resistance to infection with Zika virus. ADM represents an effective substitute for human blood, which could potentially be used for the mass rearing of wMel-infected A. aegypti, and could easily be optimized in the future to improve performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Aedes aegypti mosquitoes infected with the wMel strain of the bacterium Wolbachia pipientis are currently being deployed in several countries around the world as part of an extensive program to limit the transmission of mosquito-transmitted arboviruses, which have a serious impact on human health (http://tinyurl.com/Who-report-2016). Wolbachia infections in mosquitoes naturally possess several properties that could potentially make them effective agents of disease control. Firstly, they induce the reproductive manipulation cytoplasmic incompatibility (CI) - a type of reproductive incompatibility that limits viable egg production in Wolbachia-uninfected female mosquitoes, and thus promotes the spread of the bacterium in the field1. Secondly, the bacterium is maternally transmitted at very high rates2,3. Thirdly, the wMel strain has minimal impact on host fitness3,4, which likely serves to make wMel-infected A. aegypti highly competitive with wildtype mosquitoes in the field1. Finally, wMel infection has a natural anti-pathogenic effect in mosquitoes, called pathogen interference or pathogen blocking, wherein Wolbachia limits the infection and replication of key viruses including dengue (DENV), chikungunya (CHIKV), and Zika (ZIKV) in mosquito tissues and saliva3,5,6,7,8.
The aim of the World Mosquito Program releases (www.worldmosquitoprogram.org) is to introduce Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes, which are less susceptible to arboviral infections, into areas with high levels of disease transmission. This transmission blocking approach to mosquito control does not require laborious sexing of pupae, as both males and females facilitate the spread of the bacterium. The bacterium is also naturally abundant amongst insect taxa9,10, and there is an established regulatory framework for the use of Wolbachia as a biological control agent of mosquitoes in multiple countries11,12.
Yet, as with any mosquito control program the implementation of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes on a large scale involves potential logistical issues. One of the more important of these is the need to blood feed large numbers of mosquitoes in order to generate sufficient mosquito material for the releases. In some countries, obtaining large volumes of blood could be subject to both ethical and regulatory risk, while there is also the potential that human blood stocks could be contaminated with pathogens, including arboviruses that may circulate endemically in those regions, and that could lead to the accidental infection of colony mosquitoes.
For that reason, blood meal substitutes (BMS) have long been considered as an alternative to blood feeding to facilitate the mass rearing of mosquitoes13,14. The composition of these BMS can vary from a simple protein solution to complex mixtures of compounds, including blood-derived components15,16. These diets can be considered successful as they lead mosquitoes to produce large numbers of viable eggs after feeding. However they are often also expensive to purchase, or can contain components that are laborious to prepare, which can limit their usefulness, particularly in more remote settings where sophisticated laboratory equipment may not be available.
An additional complication arises when mosquitoes are infected with Wolbachia, as the symbiont is metabolically dependent on the host17 and on nutrients imbibed by the host. Infection with wMel alters the expression of a wide range of genes involved in protein, sugar and lipid metabolism18, which suggests that infection is associated with perturbation of normal metabolic processes. Wolbachia-host metabolic interactions can affect immune response, fecundity, stress response, and metabolite levels19,20,21,22. Some Wolbachia strains also decrease host reproductive capacity, particularly when human blood is substituted for animal blood, which suggests that blood composition is critical to the fitness of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes23. Consequently, it is possible that a BMS used in the context of releases may need to be specifically tailored to Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes in order to limit potential fitness effects.
A further complication is that Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes that are fed on a BMS would need to display comparable levels of CI and pathogen interference to those that are fed on blood, as these traits are critical for effective disease control in the field, post-release. Traits like pathogen interference are strongly linked to bacterial density3, which can change depending on the protein or carbohydrate content of the host diet24,25, and thus could foreseeably be affected by feeding on a BMS.
To that end, we have developed a BMS specific to wMel-infected A. aegypti (ADM - Artificial diet for wMel-infected Aedes aegypti), which contains low-cost, widely available materials. ADM is easy and quick to prepare, and promotes high fecundity and fertility amongst fed mosquitoes. We have also compared levels of Wolbachia maternal transmission, bacterial density, longevity, CI, and inhibition of ZIKV infection for wMel-infected A. aegypti fed either human blood or ADM. We determined that ADM feeding does not significantly affect any of these key parameters, and is thus potentially suitable for use in mass rearing and mosquito control programs involving Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes.
Results
Blood fractions
We fed wMel-infected Ae. aegypti with whole human blood (WB), plasma (PLS), or red blood cells (RBC) in order to determine which blood fractions were required for mosquitoes to produce large numbers of viable eggs. Median fecundity (number of eggs laid) was significantly higher for mosquitoes fed on either WB (66 eggs) or PLS (74) than for RBC (50) (Fig. 1a, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 11.35, N = 187, P < 0.01). In contrast, median hatch rates (percentage of eggs hatched) were significantly higher for WB (81.73%) and RBC (90.12%) than for PLS (28.21%) (Fig. 1b, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 89.51, N = 187, P < 0.0001), indicating that wMel-infected mosquitoes required components from the PLS fraction to promote high fecundity, and components from the RBC fraction to promote high levels of fertility.
Fecundity and hatch rate for wMel-infected A. aegypti fed on different blood fractions. Whole human blood (WB) was separated into plasma (PLS) and red blood cells (RBC) by centrifugation, and then fed to Mel mosquitoes. Fecundity (a) and hatch rate (b) were recorded for individual mosquitoes across 2 experiments. Fecundity levels were decreased after feeding only on RBC, while hatch rate was decreased after feeding only on PLS. Data were compared using Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Different letter codes represent statistically significant differences between treatments. Box - median and interquartile range. Whiskers - minimum and maximum.
Initial development
Based on a review of the literature26 and a small pilot experiment (See Supplementary File 1 and Supplementary Fig. 1), we selected Aedes physiological saline (APS) as the most promising solution to use as a solvent for our diet. We then investigated a number of inexpensive, unflavoured, (USD $20–25 per Kg), widely available sources of plant- (pea, rice and soy) and animal-derived (albumin from eggs, concentrated milk whey, and isolated milk whey) proteins typically used as nutritional supplements for exercise and bodybuilding. We then offered these proteins to Mel mosquitoes at either 150 or 200 mg/mL in order to compare rate of feeding, and fecundity and egg hatch levels to see if any were promising candidates for inclusion in an artificial diet (Table 1). No mosquitoes fed on the soy or albumin proteins, with these proteins displaying poor solubility in APS. A small number of mosquitoes fed on the pea protein, but 80% of these died prior to laying eggs and the remainder laid no eggs. Higher feeding rates were obtained for the rice and both milk proteins. However, only the concentrated milk protein (MC) produced reasonable numbers of eggs and viable larvae.
We then performed range-finding assays, feeding MC at different concentrations (100–200 mg/mL) in order to determine the optimal feeding concentration. The fecundity resulting from MC concentrations of 150–200 mg/mL was not significantly different to fecundity of mosquitoes fed WB, and this was significantly higher than the fecundity of mosquitoes fed 100 or 125 mg/mL of MC (Fig. 2a, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 17.50, N = 495, P < 0.01). However, all MC concentrations produced a lower hatch rate than WB (Fig. 2b, Kruskal-Wallis; H = 59.27, N = 297, P < 0.0001). Comparison of median hatch rates amongst the MC diets revealed that the less concentrated diets performed better - 100 (43.74%), 125 (44.05%), 150 (16.99%), 175 (16.64%), and 200 (14.51%). This equated to between 7–8 additional larvae for the 125 diet based on treatment medians. Consequently, we selected the 125 mg/mL concentration for further testing. In further experiments we combined this concentration of protein with the blood fractions described above (See Supplementary File 1 and Supplementary Fig. 2).
Fecundity and hatch rate for wMel-infected A. aegypti fed on different concentrations of MC protein. Mel mosquitoes were fed either whole human blood (WB), or one of 5 concentrations of MC protein (100–200 mg/mL). Fecundity (a) and hatch rate (b) were recorded for individual mosquitoes. Higher MC protein concentrations (150, 175 & 200 mg/mL) produced greater levels of fecundity, but had greatly reduced hatch rates compared to WB or lower MC concentrations (100–125 mg/mL). Data were compared using Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Different letter codes represent statistically significant differences between treatments. Box - median and interquartile range. Whiskers - minimum and maximum.
Additional components
We identified powdered infant formula as a relatively inexpensive, soluble and easy-to-prepare source of carbohydrates, lipids and micronutrients. When this product was fed to mosquitoes at either 15 (Diet F1) or 25 mg/mL (Diet F2) together with MC, we observed greater fecundity than for feeding MC alone (Fig. 3). Although the effect was not statistically significant, this equated to an increase of approximately 5–7 live larvae per female, based on treatment medians. Experiments involving additional concentrations of Alfaré Infant Formula are described in Supplementary File 1 and Supplementary Fig. 3.
Fecundity and hatch rate for wMel-infected A. aegypti fed on diets incorporating infant formula and RBC. Mel mosquitoes were fed whole human blood (WB), or MC protein 125 mg/mL (MC) as control diets. These were compared against two diets that included Alfaré infant formula; FA (15 mg/mL) and FB diets (25 mg/mL), and two further diets that included formula at the same concentrations and 1 mL of Human RBC (FAR and FBR). The FA and FB diets had slightly increased fecundity (a), however hatch rates (b) were not improved over the MC diet. The FAR and FBR diets had significantly greater levels of fecundity than WB, and the FAR diet had a similar hatch rate. Data were compared using Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Different letter codes represent statistically significant differences between treatments. Box - median and interquartile range. Whiskers - minimum and maximum.
When the FA and FB diets were suspended in 1 part human RBC: 2 parts APS (Diets FAR and FBR), we observed significant increases in both fecundity (Fig. 3a, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 88.11, N = 441, P < 0.0001) and hatch rate (Fig. 3b, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 98.27, N = 399, P < 0.0001) compared to MC, and significantly higher fecundity than for WB (Dunn’s test: WB v FAR: P < 0.01, WB v FBR: P < 0.05). As the hatch rate of the FAR diet was not significantly different to that of WB (Dunn’s test: P > 0.05), we selected that diet for further testing.
One of the issues with the mass rearing of mosquitoes in disease endemic areas is the potential contamination of human bloodstocks. To that end, we tested whether the human RBC in the FAR diet could be replaced with animal RBC, in this case from bovine blood (Diet ADM). In these experiments we observed that both the FAR and ADM diets produced similar fecundity levels to WB (Fig. 4a, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 3.21 N = 336, P = 0.2011). Hatch rates for FAR and ADM were slightly lower than those for WB in these experiments (Fig. 4b, Kruskal-Wallis: H = 18.32, N = 331, P < 0.0001), although they were comparable between FAR and ADM (Dunn’s test: P > 0.05), which suggested that bovine RBCs were a suitable alternative. Over these experiments the feeding rate of ADM was 88.65%, which was comparable to feeding rates observed on whole human blood. ADM has an estimated cost of USD $0.03 per mL (See Supplementary File 1), which compares favourably with the cost of previously described BMS15. ADM can also be prepared in 10–20 minutes, and the preparation process requires only a scale balance, a centrifuge, and a freezer to store ATP stocks. Details on the composition of all diets are presented in Table 2.
Comparison of Human and Bovine RBC. Mel mosquitoes were fed whole human blood (WB), the FAR diet, or the ADM diet - where human RBC were replaced with bovine RBC. Fecundity (a) and hatch rate (b) were recorded for individual mosquitoes across 2 experiments. No significant difference in performance was observed between the F1R and ADM diets. Data were compared using Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Different letter codes represent statistically significant differences between treatments. Box - median and interquartile range. Whiskers - minimum and maximum.
Maternal transmission and Wolbachia density
We then started a series of comparative physiological experiments using the F1 generation of wMel-infected A. aegypti fed either the ADM diet or WB. The purpose of these experiments was to mimic a field release scenario, where laboratory-reared mosquitoes were fed on ADM to generate mosquito material that would be released into the field for mosquito control purposes. The comparison with WB-fed mosquitoes allowed us to examine the effects of ADM on key parameters associated with the fitness of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes. In these experiments we used the MelR line, which was being used for field releases in Brazil (www.eliminatedengue.com/br).
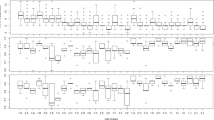
We compared the maternal transmission rate and Wolbachia density for F1 Mel_WB and Mel_ADM adult females, in a family design. 100% of the mosquitoes in the experiment tested positive for Wolbachia through qPCR (Mel_WB - 278/278, Mel_ADM - 190/190). We then compared the bacterial density across families for the two treatments (Fig. 5a) and observed that diet had a significant effect on Wolbachia density (2-way ANOVA: F = 13.17, P = 0.0003), but that this effect accounted for only 2.04% of the variation in the data set. Between-family variation was also a significant factor (2-way ANOVA: F = 6.17, P < 0.0001), accounting for 18.14% of the total variation (See Supplementary File 1). Comparison of the WB and ADM data revealed that more families with higher median Wolbachia density were associated with feeding on WB.
Characterization of the effects of ADM on key traits in wMel-infected A. aegypti. Experiments were conducted on either F1 (P generation fed either whole blood - Mel_WB (red), or ADM diet - Mel_ADM (crimson)) or F2 mosquitoes (where the P generation was fed as above, and the F1 generation fed on WB). Some experiments also involved a comparison against WT (Wolbachia-uninfected, black) mosquitoes fed on WB. Median (dot) and interquartile range (whiskers) wMel density values (relative to rps17) in F1 (a) and F2 (b) Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes. Each line represents a family of 3–15 adult female mosquitoes. Slightly higher density levels were associated with F1 Mel_WB families, and F2 Mel_ADM families. MT = Proportion of samples that tested positive for wMel. Data were compared by 2-way ANOVA. (c & d) Two independent longevity experiments conducted on F1 WT (Wolbachia-uninfected), Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes. There was no decrease in longevity associated with feeding ADM. Data were compared using Mantel-Cox test. Prevalence (proportion infected) and viral load (number of viral copies) at 7 (e) and 14 (f) days after oral infection with ZIKV for F1 WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes. The latter two treatments showed similar levels of resistance to ZIKV infection. Data were compared using Fisher’s exact test, and Mann-Whitney U test. Different letter codes represent statistically significant differences between treatments.
To determine if this effect persisted into subsequent generations, we repeated the assay with F2 Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes, after the F1 adults were fed on human blood. Again, this was modelled on a potential release scenario where released F1 generation Mel_ADM mosquitoes would feed on humans encountered in the field. Fecundity levels for the F1 generation were not significantly different between the Mel_WB and Mel_ADM lines (See Supplementary Fig. 4, Mann-Whitney U test: U = 664, P = 0.8277). Maternal transmission was measured for a total of 223 Mel_WB females and 220 Mel_ADM females, across 15 families per treatment. All of these mosquitoes tested positive for the presence of wMel, again indicating 100% maternal transmission. Bacterial density was compared for these families (Fig. 5b), and we observed that both diet and between-family variation were significant factors, with the latter accounting for 33.00% of the total variation. However in this experiment, higher Wolbachia density was observed for Mel_ADM families than for Mel_WB families.
Cytoplasmic Incompatibility
Fecundity and fertility data were compared for 9 reciprocal crosses involving F1 WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM adult mosquitoes (Table 3). In both predicted incompatible crosses (WT female vs Mel_WB male, and WT female vs Mel_ADM male) we observed an average in excess of 62 eggs laid per female, however all of these eggs failed to hatch. There was a statistically significant difference in hatch rate across the 9 crosses (Kruskal-Wallis; H = 148.2, N = 311, P < 0.0001), however this difference was solely due to the two incompatible crosses, with no difference in hatch rate observed between the other 7 crosses according to Dunn’s multiple comparisons tests (See Supplementary File 1).
Longevity
We performed two longevity experiments involving WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes, and mortality was monitored daily. In the first replicate (Fig. 5c), WT mosquitoes (N = 135) lived an average (±s.e.m.) of 30.69 ± 0.71 days, Mel_WB mosquitoes (N = 141) an average of 33.38 ± 0.61 days, and Mel_ADM mosquitoes (N = 129) an average of 34.39 ± 0.66 days. Statistical comparison of these groups revealed a significant difference in survival times only between the WT and Mel_ADM groups (Mantel-Cox; X 2 − 8.788, P = 0.003). In the second replicate (Fig. 5d), WT mosquitoes (N = 109) lived an average (±s.e.m.) of 31.20 ± 0.80 days, Mel_WB mosquitoes (N = 138) an average of 29.23 ± 0.64 days, and Mel_ADM mosquitoes (N = 139) an average of 30.93 ± 0.65 days. Statistical comparison of these groups revealed a significant difference in survival times only between the WT and Mel_WB groups (Mantel-Cox; X 2 − 4.097, P = 0.043).
ZIKV infection
We orally infected WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes with ZIKV, and then compared the prevalence of infection (proportion of individuals infected), and viral load (number of viral copies in infected individuals) at 7 (Fig. 5e) and 14 days post-infection (dpi) (Fig. 5f). We observed no significant difference in either prevalence of infection (Fisher’s exact test; 7dpi - P = 1.000; 14dpi - P = 0.4391) or viral load (Mann Whitney U test; 7dpi - U = 35, P = 0.595; 14dpi - U = 39, P = 0.5208) between the two wMel-infected lines. A comparison of the WT and Mel_WB lines revealed a decrease in prevalence of infection (Fisher’s exact test; 7dpi - P < 0.0001; 14dpi - P < 0.0001) and viral load (Mann Whitney U test; 7dpi - U = 30, P < 0.0001; 14dpi - U = 7, P < 0.0001) associated with wMel infection. Comparable decreases in prevalence (Fisher’s exact test; 7dpi - P < 0.0001; 14dpi - P < 0.0001) and viral load (Mann Whitney U test; 7dpi - U = 95, P = 0.0042; 14dpi - U = 3, P < 0.0001) were observed between the WT and Mel_ADM lines.
Discussion
We have developed a BMS, ADM, which has been designed specifically for use for the mass rearing of Wolbachia-infected A. aegypti prior to field releases. ADM consists of protein and infant formula, suspended in a mixture of APS and bovine RBC, with ATP used as a phagostimulant. These components are cheap, with the diet costing an estimated USD $0.03/mL of diet. The components are also widely available for commercial purchase from supermarkets and pharmacies in Brazil, with similar products likely to be available in other countries. ADM has an average preparation time of 10–20 minutes, and the preparation process is not particularly arduous, involving no long, complicated experimental procedures, or expensive equipment. Most critically, feeding with ADM leads to the production of large numbers of viable eggs, which suggests that it is a suitable tool for the mass rearing of mosquitoes. Our results suggest that ADM performs comparably with whole human blood, and that it should function as an adequate substitute in situations where large-scale blood feeding is either impossible or impractical.
One of the key aims in the development of this diet was that it be completely free of blood in order to eliminate the need to screen the BMS for human pathogens such as DENV and ZIKV, which could foreseeably be present in blood obtained from disease endemic areas, such as many of the release sites of the EDP. During development of ADM, we saw that feeding a blood-free diet, or an RBC-free diet was severely detrimental to egg production and hatching in Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes. While ADM is not completely free of blood, it is free of human blood, which should substantially decrease the risk of viral contamination. Our data showed similar levels of fecundity and egg hatch rate were achieved when either human or bovine RBC were used in the BMS. We hypothesize that the source of RBC could be changed without a great effect on the diet, in the case that a specific type of animal blood could not be sourced, or could not be used for religious or ethical reasons in different regions. However, it should be noted that the use of rodent or avian blood has been shown to have a significant negative impact on the fecundity and fertility of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes23, and we do not recommend this for incorporation into a similar BMS.
In our data, we saw that both the PLS and RBC fractions of the blood meal were important to viable egg production in wMel-infected A. aegypti. This stands in contrast to the results of similar experiments with uninfected where no eggs were laid after feeding on RBC, and PLS was not associated with a significant decline in hatch rate26. While neither assay made a direct comparison of these traits between Wolbachia-infected and -uninfected A. aegypti, the difference in results could suggest that egg production in Wolbachia-infected A. aegypti differs from in uninfected mosquitoes. Wolbachia-iron interactions appear to be a key component of the Wolbachia-host relationship, with Wolbachia exhibiting a requirement for iron, altering oxidative stress response in mosquitoes, and increasing host tolerance to iron toxicity19,27,28,29. Our results here could be a further example of this metabolic relationship.
A BMS used with Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes must not affect the ability of released mosquitoes to spread into wild mosquito populations, with this ability dependent on high levels of maternal transmission and CI, and high competitiveness with uninfected mosquitoes in the release area. We observed complete (100%) maternal transmission in the F1 and F2 progeny of wMel-infected females fed on ADM, with in excess of 400 mosquitoes examined. We also observed complete CI when ADM males mated with WT females, and no cost to longevity, fecundity or hatch rate associated with ADM feeding. Together, these data offer no indications that the release of ADM-derived mosquito material would negatively affect the ability of the Wolbachia to invade wild mosquito populations.
Another potential consequence of feeding with a BMS was a decrease in bacterial density, which could detrimentally affect the stability of Wolbachia infection in a mosquito population, or even lead to less effective interference against key pathogens. To that end, we examined the density of wMel in F1 and F2 Mel_WB and Mel_ADM adults. Our data highlight the high degree of variability inherent within this trait, with between-family variation in density a significant factor in both experiments. Our statistical models could not explain large proportions of the variation in density, and we hypothesize that this component was likely within-family variation. In both experiments, diet (WB vs ADM feeding) was a significant predictor. However, not only did this variable account for only a small proportion of the total variance in density (F1–2.04%, F2–3.75%), the effect was not consistent between the F1 and F2 generations. What these data suggest is that there is unlikely to be a consistent, detrimental effect of ADM on wMel density. However, this would be an important effect to test further in the event this BMS were adopted for mass rearing purposes. Similarly, we saw no evidence that feeding on ADM was associated with a change in the ability of wMel to interfere with ZIKV infection, a critical finding given that the Wolbachia transmission blocking strategy is reliant on this phenotype.
It is currently unclear whether ADM is suitable for use with other Wolbachia-mosquito host combinations. There could feasibly be difficulties in the application of the diet to other mosquito populations, particularly in those cases where the infecting Wolbachia strain has a greater fitness cost. It is also possible that the diet could have utility for mosquitoes that are not infected by Wolbachia. However, we recommend that a similar process of characterization be performed before the diet is used with other mosquito populations, including other populations of wMel-infected A. aegypti.
The ADM diet appears to have two key shortcomings. The first is the need to include ATP as a phagostimulant, with this component making up approximately 80% of the overall cost. The second is the use of RBC, which will likely limit the storage time of the diet, and could be difficult to source in some locations. However, our results do suggest that RBC or a RBC-derived component is a necessity for a BMS aimed at Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes. The identification of a substitute for either of these compounds could greatly improve the diet. Comparative compositional analysis of eggs produced from blood- or ADM-fed wMel-infected A. aegypti could further understanding of the effects of Wolbachia infection on mosquito egg production. A further avenue of future investigation is to determine whether multigenerational use of ADM is appropriate for Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes, or the associated process of adaptation would have negative consequences. The next phase of experiments involving ADM should primarily be focused on applying the diet to a mass rearing setting, and the key issue of diet preservation and storage should also be considered in more depth. Additionally, there is also further scope to investigate the physiological effects of the diet on A. aegypti including whether it influences mating competitiveness, and whether egg production in ADM-fed mosquitoes is still comparable to those fed on human blood through multiple gonotrophic cycles. However, in its current state, ADM still represents a critical step forward in the mass rearing of Wolbachia-infected A. aegypti for disease control purposes.
Methods
Mosquito lines and rearing
Mosquito lines used in this project were reared in a climate-controlled insectary (temperature 27 °C ± 1 °C, RH - 70 ± 10%, photoperiod - 12 hours light: dark). Mosquito eggs were hatched in 3 L of RO water containing ½ a tetramin tropical tablet ground into powder (Tetramin). The next day larvae were moved to a fresh tray with the density reduced to 200 in 4 L. Pupae were collected in cups containing no more than 70, and these were transferred to bug dorms (dimensions: 30 × 30 × 30 cm), and allowed to eclose. At 4 days post-eclosion, groups of 50–70 females were transferred to smaller cages (height: 16.5 cm, diameter: 17.5 cm), and starved overnight prior to feeding experiments.
Experiments linked to the development of artificial diets were performed only on a line of wMel-infected Ae. aegypti (Mel). This line was derived from the original wMel-infected line developed in Australia3, and was then backcrossed into a Brazilian generic background, as previously described2. Experiments involving this line took place between G37 and G41 after the backcrossing was completed. Mel colony mosquitoes were fed on human blood drawn from a willing volunteer, after written consent was obtained. Regular outcrossing of colony material was performed as previously described22.
Physiological characterization experiments utilized several mosquito lines. Wolbachia-uninfected, insecticide-resistant Ae. aegypti (WT) were collected from neighborhoods surrounding Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil starting in late 2015. Each generation 50 F1 or F2 males were introduced into Mel cages to produce a completely outcrossed Wolbachia-infected line (MelR), which has been used for release experiments associated with the World Mosquito Program (www.worldmosquitoprogram.org). MelR and WT adults were fed either whole human blood (WB) or diet ADM (see below) in order to produce eggs. The F1 progeny of these lines, named WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM were used in experiments described below. Eggs involved in these experiments were stored when nearly dry and used in experiments within a month of being laid.
Feeding protocol and fecundity and fertility experiments
During the diet development process, Mel mosquitoes were fed using glass feeders, pig intestine and a waterbath. During the physiological characterization experiments, large cages of MelR and WT mosquitoes were fed either blood or the ADM diet using a hemotek system (Hemotek). In all cases, mosquitoes were allowed to feed for 1 to 1.5 hours under low light levels. After the feed, mosquitoes were immediately screened on ice, and non-fed females were removed from cages.
Two days after feeding, Mel mosquitoes were moved to individual opaque plastic cups (height: 5 cm, diameter: 7 cm), containing a piece of damp filter paper on the bottom as an oviposition medium. These cups were placed in closed plastic trays, containing a cup of wet cotton wool in order to maintain high humidity levels. Mosquitoes were provided with 10% sucrose solution ad libitum. Females were removed from cups after 4 days. Eggs were then counted and dried slowly over 3 days before being hatched in hatching water (containing ½ of a ground tetramin tropical tablet in 3L). Larvae were counted and removed from cups after 4 days, with this process repeated after a further 3 days. Experiments involving each group of components were repeated 2–4 times.
Diet components and preparation
We performed a series of fecundity and fertility experiments in order to examine the suitability of different components for use in the development of a BMS. Solid components of these different diets included several types of animal- or plant-derived proteins: Milk C (WPC 80% Nutrifont – Lactallys) or Milk I (Probiotica), Albumin, Pea, Rice, or Soy (Growth Supplements), and Alfaré Infant Formula (Nestlé). The nutritional composition of these ingredients is provided in Supplementary File 2. Solid components were weighed on a Shimadzu AUW220D fine balance. Liquid components included Aedes Physiological Saline (APS) 10X, which was used as the primary solvent for all diets (1L - NaCl - 17.53 g, KCl - 0.5964 g, NaHCO3 - 0.0168 g, MgCl2 - 0.1143 g, CaCl2 - 0.3783 g, HEPES - 11.92 g, pH - 7.0), this was autoclaved and diluted to generate a 1X working solution26. APS was allowed to warm to room temperature prior to feeding. Human or Cow blood fractions (Plasma and Red Blood Cells) were obtained by centrifuging whole blood at 1500 rpm for 5 mins. ATP (Sigma Aldrich A2383-5 g, ConcFinal = 2 mM) was added to all diets as a phagostimulant30. Stocks of APS were stored at 4 °C, while stocks of ATP were stored at −30 °C at a concentration of 100 mM. Diets were prepared on the day of feeding, according to the specifications presented in Table 2. More detail on experiments describing the development stages of the ADM diet is provided in Supplementary File 1.
Maternal transmission and Wolbachia density
MelR mosquitoes were fed either blood or the ADM diet, and then moved into individual cups, as described above. After 4 days, the mothers were removed and stored at −80 °C. Egg numbers were calculated, and then papers dried and hatched independently using the method described above. The mothers were screened for the presence of Wolbachia using wMel-specific wd0513 primers and probe, described previously7. Adult mosquito samples were washed in 70% ethanol, and then DNA was extracted in a mixture of 8 parts squash buffer (200 mL stock: 0.242 g TRIS Base, 0.075 g EDTA, 0.292 g NaCl, pH 8.3) to 1 part proteinase K (QIAGEN 19133, 15 mg/mL), with a final reaction volume of 56.25 μL. Samples were heated on a thermocycler at 56 °C for 5 mins, followed by 98 °C for 15 mins, and were stored at 12 °C.
Levels of the wMel-specific gene wd0513 (NC_002978.6) were then quantified relative to the Ae. aegypti rps17 gene (XM_001648533) using TaqMan-based qPCR and a Lightcycler 96 (Roche). The mastermix contained the following components per reaction: (DNA - 1 μL, FastStart Essential DNA Probes Master Mix (Roche) - 5 μL, rps17 primers (10 μM) - 0.3 μL, wd0513 primers (10 μM) - 0.25 μL, rps17 probe (10 μM) - 0.06 μL, wd0513 probe (10 μM) - 0.15 μL, H2O - 3.34 μL). Each sample was run in duplicate. The run profile was as follows (Pre-incubation: 95 °C for 10 mins, 45 cycles of 2-step amplification: 95 °C for 15 sec, 60 °C for 30 sec). Primers and probes are described in Supplementary File 1.
Mean normalized expression values for each sample were calculated using qGene31. The progeny of mothers that were positive for Wolbachia were reared as above, and then sexed and collected at 3–6 days post-eclosion. Up to 15 F1 females each from 20 WB-fed mothers, and 20 ADM-fed mothers were screened for Wolbachia, as above in order to compare the effect of the ADM diet on the maternal transmission of Wolbachia, and adult Wolbachia density. In a separate assay, we reared F1 Mel_WB and Mel_ADM to adulthood, fed a human blood meal, recorded fecundity, and then conducted a similar experiment comparing the Wolbachia density of F2 Mel_WB and Mel_ADM adults, examining 15 5 day-old adult female mosquitoes from 15 mothers from each treatment.
Cytoplasmic incompatibility
Cytoplasmic incompatibility levels were compared between Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes, using WT mosquitoes as a Wolbachia-uninfected control line. Mosquitoes were reared to pupation as described above. Pupae were then sexed under a stereomicroscope, and then divided into large cages to make up all 9 reciprocal crosses. At 5 days post-eclosion the cages were offered a human blood meal using a hemotek. Unfed females and males were removed from the cages immediately post-feeding. 48 hours later, females were then separated into individual cups (N = 27–41 per cross), and fecundity and fertility data were obtained for each cross, as described above. This experiment was repeated twice.
Longevity
WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM eggs were hatched and reared to pupation, as above. Female pupae were sexed using a stereomicroscope, and then moved to small cages, while male pupae were discarded. Pupae were allowed 2 days to eclose, and then cups were removed so that the experiment involved a cohort of similar age. Mortality was recorded daily until day 60, with dead mosquitoes removed from cages daily. Mosquitoes were provided 10% sucrose, which was changed 3 times per week. The assay was run twice, and each experiment involved 3 cages per treatment (N = 109–141 mosquitoes per treatment).
ZIKV infection
WT, Mel_WB and Mel_ADM mosquitoes were reared to adulthood, as described above. At 4 days of age, females were separated into small cages and then starved overnight. Mosquitoes were orally infected with ZIKV using the waterbath feeding system described above. Stocks of ZIKV BRPE (ZIKV/H. sapiens/Brazil/BRPE243/2015)7 (titer: 3.5 × 108 pfu/mL) were maintained at −80 °C, and defrosted immediately prior to feeding. These were mixed 2:1 with freshly drawn human blood. Mosquitoes were allowed 1 hour to feed, and were then screened for the presence of a blood meal on ice, and all mosquitoes that were not fully engorged were discarded. Mosquitoes were provided with 10% sucrose, which was changed daily. Whole mosquitoes were collected at 7 and 14 dpi, and then stored at −80 °C. Total RNA was extracted using the High Pure Viral Nucleic Acid Kit (Roche), and then total ZIKV (AY632535.2) copies were quantified via RT-qPCR using the Lightcycler Multiplex RNA Virus Master kit (Roche) and a Lightcycler 96 (Roche), as previously described7. Two independent infections were performed.
Statistical analysis
Data for diet development experiments were compiled across experimental replicates and examined jointly. All data were examined for normality using the D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test. Data sets that failed the assumption of normality were examined using non-parametric tests. Fecundity and hatch rate data, including those from the CI experiments, were compared by Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA, and by Dunn’s multiple comparison tests. Wolbachia density data were organized by family and diet, and then compared by 2-way ANOVA. ZIKV infection prevalence of infection data were compared via Fisher’s exact test, while ZIKV load data were compared by Mann Whitney U test. Longevity data were compared via Mantel-Cox test. All statistical analyses were performed using Prism V 6.0 g (Graphpad), except for the analysis of the longevity data, which was performed using SPSS V17 (IBM). Statistical output from characterization assays is presented in Supplementary File 1.
Ethics statement
The human blood used in these experiments was drawn from one willing, adult volunteer by trained medical personnel, after obtaining informed, written consent. This process was conducted according to established guidelines, and approved by The Committee for Ethics in Research (CEP)/FIOCRUZ (License - CEP 732.621). Our use of human blood was in accordance with Brazilian laws 196/1996 and 01/1988, which govern human ethics issues in scientific research in compliance with the National Council of Ethics in Research (CONEP). The bovine blood used in these experiments was produced by Dimeza Alimentos Ltd as a by-product of their operations, and was donated to our group for research purposes, according to the terms of an agreement with Centro de Pesquisas René Rachou.
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hoffmann, A. A. et al. Successful establishment of Wolbachia in Aedes populations to suppress dengue transmission. Nature 476, 454–U107, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10356 (2011).
Dutra, H. L. et al. From lab to field: the influence of urban landscapes on the invasive potential of Wolbachia in Brazilian Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9, e0003689, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003689 (2015).
Walker, T. et al. A non-virulent Wolbachia infection blocks dengue transmission and rapidly invades Aedes aegypti populations. Nature 476, 450–455 (2011).
Joubert, D. A. et al. Establishment of a Wolbachia Superinfection in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes as a Potential Approach for Future Resistance Management. PLoS Pathog 12, e1005434, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005434 (2016).
Aliota, M. T., Peinado, S. A., Velez, I. D. & Osorio, J. E. The wMel strain of Wolbachia reduces transmission of Zika virus by Aedes aegypti. Sci Rep 6, 28792, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28792 (2016).
Aliota, M. T. et al. The wMel Strain of Wolbachia reduces transmission of chikungunya virus in Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10, e0004677, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004677 (2016).
Dutra, H. L. et al. Wolbachia blocks currently circulating Zika virus isolates in Brazilian Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Cell Host Microbe 19, 771–774, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.021 (2016).
Ferguson, N. M. et al. Modeling the impact on virus transmission of Wolbachia-mediated blocking of dengue virus infection of Aedes aegypti. Sci Transl Med 7, 279ra237, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3010370 (2015).
de Oliveira, C. D. et al. Broader prevalence of Wolbachia in insects including potential human disease vectors. Bull Entomol Res 105, 305–315, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007485315000085 (2015).
Zug, R. & Hammerstein, P. Still a host of hosts for Wolbachia: analysis of recent data suggests that 40% of terrestrial arthropod species are infected. PLoS One 7, e38544, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038544 (2012).
Dobson, S. L., Bordenstein, S. R. & Rose, R. I. Wolbachia mosquito control: Regulated. Science 352, 526–527, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.352.6285.526-b (2016).
O’Neill, S. L. Wolbachia mosquito control: Tested. Science 352, 526, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.352.6285.526-a (2016).
Gonzales, K. K. & Hansen, I. A. Artificial Diets for Mosquitoes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121267 (2016).
Kogan, P. H. Substitute blood meal for investigating and maintaining Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 27, 709–712 (1990).
Pitts, R. J. A blood-free protein meal supporting oogenesis in the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus (Skuse). J Insect Physiol 64, 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2014.02.012 (2014).
Talyuli, O. A. et al. The use of a chemically defined artificial diet as a tool to study Aedes aegypti physiology. J Insect Physiol 83, 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2015.11.007 (2015).
Wu, M. et al. Phylogenomics of the reproductive parasite Wolbachia pipientis wMel: A streamlined genome overrun by mobile genetic elements. Plos Biol 2, 327–341, https://doi.org/10.1371/Journal.Pbio.0020069 (2004).
Rancès, E., Ye, Y. H., Woolfit, M., McGraw, E. A. & O’Neill, S. L. The relative importance of innate immune priming in Wolbachia-mediated Dengue interference. Plos Pathogens 8, e1002548, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002548 (2012).
Brownlie, J. C. et al. Evidence for metabolic provisioning by a common invertebrate endosymbiont, Wolbachia pipientis, during periods of nutritional stress. PLoS Pathog 5, e1000368, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000368 (2009).
Caragata, E. P. et al. Dietary cholesterol modulates pathogen blocking by Wolbachia. Plos Pathogens 9, e1003459, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003459 (2013).
Caragata, E. P., Rancès, E., O’Neill, S. L. & McGraw, E. A. Competition for amino acids between Wolbachia and the mosquito host, Aedes aegypti. Microb Ecol 67, 205–218, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0339-4 (2014).
Caragata, E. P., Rezende, F. O., Simoes, T. C. & Moreira, L. A. Diet-Induced Nutritional Stress and Pathogen Interference in Wolbachia-Infected Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10, e0005158, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005158 (2016).
McMeniman, C. J., Hughes, G. L. & O’Neill, S. L. A Wolbachia symbiont in Aedes aegypti disrupts mosquito egg development to a greater extent when mosquitoes feed on nonhuman versus human blood. Journal of Medical Entomology 48, 76–84, https://doi.org/10.1603/Me09188 (2011).
Ponton, F. et al. Macronutrients mediate the functional relationship between Drosophila and Wolbachia. Proc Biol Sci 282, 20142029, https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.2029 (2015).
Serbus, L. R. et al. The impact of host diet on Wolbachia titer in Drosophila. PLoS Pathog 11, e1004777, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004777 (2015).
Gonzales, K. K., Tsujimoto, H. & Hansen, I. A. Blood serum and BSA, but neither red blood cells nor hemoglobin can support vitellogenesis and egg production in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti. PeerJ 3, e938, https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.938 (2015).
Kosmidis, S. et al. Behavioral decline and premature lethality upon pan-neuronal ferritin overexpression in Drosophila infected with a virulent form of Wolbachia. Front Pharmacol 5, 66, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00066 (2014).
Kremer, N. et al. Wolbachia interferes with ferritin expression and iron metabolism in insects. PLoS Pathog 5, e1000630, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000630 (2009).
Pan, X. et al. Wolbachia induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of the Toll pathway to control dengue virus in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109, E23–E31, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1116932108 (2012).
Moskalyk, L. A. & Friend, W. G. Feeding behaviour of female Aedes aegypti: effects of diet temperature, bicarbonate and feeding technique on the response to ATP. Physiological Entomology 19, 223–229 (1994).
Simon, P. Q-Gene: processing quantitative real-time RT-PCR data. Bioinformatics 19, 1439–1440 (2003).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Prof Scott L O’Neill for the donation of the original wMel-infected line, Probiotica (Sr. Lucio Fernandes) and Growth Supplements for the donation of the proteins used in these experiments, Gustavo Mena Brandenberger Valente of Dimeza Alimentos Ltda for donation of cow blood, Dr Marcele N. Rocha for preparation and titration of ZIKV stocks, Dr Pedro Oliveira and Dr Marcos Sorgine for helpful discussion of results, and Eliane Moreira and Mariana Magalhães for assistance with grant management. This work was supported by a development grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to H.L.C.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.L.C.D., S.L.R., S.B.M., S.P.O., and E.P.C. performed experiments. H.L.C.D., E.P.C. and L.A.M. designed experiments. E.P.C. analysed data, performed statistical analyses, prepared figures, and drafted the manuscript. H.L.C.D., E.P.C. and L.A.M. wrote the final manuscript. All authors reviewed the final manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Dutra, H.L.C., Rodrigues, S.L., Mansur, S.B. et al. Development and physiological effects of an artificial diet for Wolbachia-infected Aedes aegypti . Sci Rep 7, 15687 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16045-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16045-6
This article is cited by
-
Ad libitum consumption of protein- or peptide-sucrose solutions stimulates egg formation by prolonging the vitellogenic phase of oogenesis in anautogenous mosquitoes
Parasites & Vectors (2022)
-
The Effect of SkitoSnack, an Artificial Blood Meal Replacement, on Aedes aegypti Life History Traits and Gut Microbiota
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.