Abstract
Multi-colored, water soluble fluorescent carbon nanodots (C-Dots) with quantum yield changing from 4.6 to 18.3% were synthesized in multi-gram using dated cola beverage through a simple thermal synthesis method and implemented as conductive and ion donating supercapacitor component. Various properties of C-Dots, including size, crystal structure, morphology and surface properties along with their Raman and electron paramagnetic resonance spectra were analyzed and compared by means of their fluorescence and electronic properties. α-Manganese Oxide-Polypyrrole (PPy) nanorods decorated with C-Dots were further conducted as anode materials in a supercapacitor. Reduced graphene oxide was used as cathode along with the dicationic bis-imidazolium based ionic liquid in order to enhance the charge transfer and wetting capacity of electrode surfaces. For this purpose, we used octyl-bis(3-methylimidazolium)diiodide (C8H16BImI) synthesized by N-alkylation reaction as liquid ionic membrane electrolyte. Paramagnetic resonance and impedance spectroscopy have been undertaken in order to understand the origin of the performance of hybrid capacitor in more depth. In particular, we obtained high capacitance value (C = 17.3 μF/cm2) which is exceptionally related not only the quality of synthesis but also the choice of electrode and electrolyte materials. Moreover, each component used in the construction of the hybrid supercapacitor is also played a key role to achieve high capacitance value.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Along with the depletion of fossil fuel reserves environmental problems due to evaluated carbon dioxide emission, increase in the population worldwide resulted in an increased energy demand. Development of new technologies providing efficient conversion of sustainable energy resources into usable energy or advanced electric transportation/storage technologies to be used in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and stationary electrical grids has become gradually more important1,2,3. Recent research tendencies are mainly focused on energy conversion and storage devices including lithium batteries, lead-acid batteries, fuel cells and supercapacitors, in which the supercapacitors are featured by their high performance in energy and power density aspects together with the simple operating conditions and long cycling life4,5,6,7. In a supercapacitor (SC), the surface of electrode usually made from a conductive layer of porous carbon. The specific capacitance of the SC is the order of surface area along with other parameters such as pore size distribution, pore shape and structure, accessibility of the electrolyte, and electrical conductivity8, 9. Due to poor electrolyte accessibility to the solid electrode surface and the liquid electrolyte, only a small portion of the theoretical specific capacitance could be achieved. In this regard, recent developments in nanotechnology has opened up new frontiers by using various carbon nanomaterials, mixed-metal oxides, conducting polymers and recently metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) to overcome many of these drawbacks9,10,11,12,13,14. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) for example offer both high surface area and conductivity12, 15. However, the application of CNTs to commercial SC has been limited both by high contact resistance at the electrode–current collector and the high cost and laborsome synthesis routes which constrain the scale-up process for larger scale manufacturing16, 17. Graphene nanosheets, on the other hand, gain particular interest due to structured, accessible pores and interlayer spaces possessing higher accessibility of ions18. In a study conducted by Zhang et al., showed that with a clever functionalization of graphene surface with ZnO, high capacitance values can be achieved together with reversible charging/discharging ability19. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has electrical conductivity close to that of graphene with the superiority that they could be produced in upscale and a large surface area that can efficiently host the electrolyte ions20, 21. Heterostructured electrodes consist of carbon and other nanomaterials with transition metal oxides (e.g., RuO2, IrO2, MnO2, NiO, V2O5, Co3O4 and NiCo2O4) were found to be effective to increase the specific capacitance by appending a high pseudo-capacitance attributed to their multiple valence state changes9, 12, 22, 23. Among these investigated metal oxides, manganese dioxide (MnO2), a basic transition metal oxide, was widely confirmed as an ideal and alternative capacitive electrode material with lower cost and high environmentally friendly nature6, 23. MnO2 nanomaterials of various polymorphs can be synthesized and the resulting phases and morphologies are determinative on many properties of the resulting material24, 25. Among them, electrodes prepared from one-dimensional (1D) MnO2 nanostructures (α-, β-, γ-, and R-MnO2) show excellent electrochemical capacitive behavior due to the redox reactions occur on their surface providing a superior electron transport26. It was found that electrochemical performance of MnO2 depended on the crystal structure and α -MnO2 is more suitable to store cations than β-, γ- or R-MnO2 due to its larger tunnel size27.
Despite their benefits, the limitations in cell capacitance, cycling life and rate performance of α-MnO2 electrodes associated with the poor conductivity is still waiting to be improved to meet the requirements of their practical application in SC28. Employing carbonaceous materials, conductive polymers and metal oxides to MnO2 electrodes were demonstrated to be a reliable strategy to enhance conductivity and specific capacitance10, 11, 22, 29,30,31,32. Nanocomposites formed by decorating MnO2/rGO with silver nanoparticles were reported as they improved the capacitive performance with a specific capacitance reaching to 467.5 F g−1 at the scan rate of 5 mV s−1 with no significant degeneration after 1000 cycles at the scan rate of 80 mV s−1 29. In another study, a high power density electrode constructed by MnO2 deposition on the carbon nanotube was reported15. Authors claimed a faster electron/ion transfer kinetics and an altered areal capacitance of 1.0 F cm−2 at 0.2 A g−1 (1.28 mA cm−2) that induced by the porous structure of composite formed by a three-dimensional (3D) carbon nanotube cage15. Electrodes prepared by conductive wrapping of MnO2/graphene nanostructures with carbon nanotubes or conducting polymer have been shown as they greatly improved the conductivity and increased the supercapacitive performances by ∼20% and ∼45%, respectively32.
Carbon Dot (C-Dots) are a new class of carbon allotropes formed of densely packed carbon atoms arranged as zero-dimensional (0D) spherical particles with intriguing fluorescent properties33,34,35. The most prominent feature of carbon nanodots as oppose to other carbon nanomaterials is that C-Dots can be synthesized in multi-gram scale simply by heating foods, food wastes, plant extracts, and beverages to high temperatures in water or organic solvents by carbonization of the carbon-rich matrix36,37,38,39. However, for the synthesis of fluorescent C-Dots with improved fluorescence efficiency, homogeneity in size and in physicochemical properties, it is essential to use a carbon source which is cheap, accessible, easy to handle and non-toxic40. Use of passivating agents, mostly polymers, has been extansively used to alter the C-Dot fluorescence41. However, this clearly incures an additional cost to the synthesis. C-Dots generally emits fluorescence in the blue range, however, there are examples of C-Dots emitting fluorescence of different colors that can be synthesized by tuning their size and surface properties42,43,44. C-Dots recently have been used in many electronic applications due to their highly tailorable surface chemistry, uniform shape, ultra-small size leading large specific surface area per volume along with their electronic and optical properties. These areas include, but are not limited to the sensors45, light emitting diodes46 and solar cells47, 48. Recently, C-Dots were also considered as new environmentally friendly electrode material that improves the electron transport, ionic motion and enlarges the contact area between electrode and electrolyte in SC14, 47, 49,50,51,52.
In this work, combination of state-of-art spectroscopic techniques EPR, Raman and impedance spectroscopies were used in order to characterize and detect the paramagnetically active defect centers, vibrational properties of such defects and finally electrical transport properties of defects and capacitance properties of hybrid supercapacitor. Structural defects in the electrode materal playing vital role in the capacitance value of a supercapacitor. Because capacitance is highly dependent not only on the configuration of the oxidation, as it modifies the electrode surface accessibility of the ions but also the art and the concentration of defect centers13, 53,54,55,56. It has been reported that effects of many parameters, such as carbon hybridization (sp 2 or sp 3), pore shape, structural intrinsic defects are extremely important to understand the charge storage mechanism in sub-nanometre pores and to propose strategies to design the next generation of high-capacitance materials and material-electrolyte systems57. For this purpose, a novel hybrid supercapacitor constructed using α-MnO2 nanorods decorated with C-Dots synthesized from degassed Cola-drink and rGO as electrode material along with a special type of ionic liquid membrane (C8H16BImI) as electrolyte were introduced as a model and its electrical properties were characterized.
Results and Discussion
Synthesis and Fluorescent Properties of Carbon Dots
Cola drinks are popular gaseous beverages which are rich in sugar, fructose/glucose syrup, carbon dioxide, caramel, phosphoric acid, caramel, caffeine and some other natural aroma58. Thermal synthesis methods used for C-Dot preparation are simple and cost efficient however, they mostly show low synthesis efficiency below 50% with a carbonated bulky waste59, 60. More importantly, the fluorescence efficiency of carbon dots are upregulated by use of passivating agents such as polymers, polypeptides and polysaccharides61.
Here, we reported the synthesis of water-soluble multi-color fluorescent C-Dots using dated Cola drink as starting material following thermal synthesis method (see the Experimental Section for details) devoiding the use of any additional passivating agent. Instead, here we used the rich ingredient of Cola drink as not only carbon source but also passivating and fluorescence enhancing agent62. As explained in Fig. 1a, C-Dots emitting yellowish green fluorescence (C-Dotgreen) were prepared directly by thermal treatment of degassed Cola at 300 °C for 30 min. Particles are collected quite efficiently (67.4%) by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min40. Note that we also have some attempts at different temperatures to produce C-Dots. However, such attempts made at lower temperatures than 300 °C decreased the efficiency of the C-Dots synthesis and at higher temperatures a full carbonization resulted in bulky carbonaceous material rather than C-Dots. To avoid additional parameter to be controlled we kept the heating time constant.
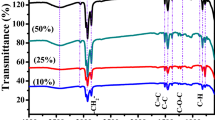
Schematic illustration of the synthesis procedures of (a) green, (b) red and (c) blue emitting fluorescent C-Dots using degassed Cola drink as starting carbon source and representative digital images of as-synthesized C-Dots under bright and UV light (λEx:365 nm, distance = 10 cm). (d) Fluorescence emission spectrum of the C-Dots.
Bright blue fluorescent (Fig. 1b) (λ Ex:365 nm) but yet water soluble C-Dots were obtained pre-mixing degassed Cola with a hydrophobic and purple colored fluorescent dye (Nile Red). This showed that Nile Red was also contributed to the nanoparticle structure, and both Nile-Red and C-Dot surface energy states were transformed. There are couple of studies on the use of fluorescent dyes (e.g., Fluorescein and Rhodamine B) for tailoring the fluorescence properties of C-Dots by a post-modification of particle surfaces using chemical conjugation steps63, 64. Here, we showed that fluorescence character of C-Dots can also be manipulated by direct incorporation of the fluorescence dye during the synthesis avoiding any further surface doping. Red emitting C-Dots were achieved on the other hand by coincidence as a side product of a parallel study on the synthesis of C-Dot embedding GOx composites via hydrothermal treatment (Fig. 1c) of C-Dotgreen with graphene nanosheets. The washing water collected from the reaction was purified from larger particulates by centrifugation. Resulting carbon dot suspension in pure water showed only a weak red emission under ultra violet (UV) light.
The emission spectra and measured emission maxima (λ max) of each sample (λ Ex:365 nm) were plotted in Fig. 1d and values were listed in Table 1. At same C-Dot concentrations (2 mg/mL), C-Dotgreen possessed the highest photoluminescence (PL) intensity with emission maxima at 495 nm followed by C-Dotblue with a red-shifted emission maximum centered at 435 nm. A poor PL response at shorter wavelengths (475–700 nm) was observed for C-dotred with a red shifted λ max in the near-infrared (IR) region (600 nm). This red-shifted fluorescence presumably aroused due to sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate residuals left from graphene oxide33, 65.
Excitation dependency of the nanodot fluorescence was measured by collecting emission spectra of each C-Dot at changing excitation wavelengths. As shown in Fig. S1 both C-Dotgreen and C-Dotblue showed excitation dependent fluorescence emission while PL of C-Dotred was found to be independent of the excitation. PL emission of C-Dotgreen and C-Dotblue can be extended into the near-IR wavelength range by the recombination of localized electron–hole pairs in sp 2 clusters66. Fluorescence quantum yields were then measured by taking quinine sulfate (QS) as a reference and estimated as 18.3%, 16.2% and 4.6% for C-Dotgreen, C-Dotblue, and C-Dotred, respectively.
Size and Morphological Characteristics of C-Dots
Table 1 summarizes the several physical characteristics of the resulting C-Dots. Hydrodynamic size and size distribution of C-Dots were evaluated by pursuing dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements. C-dotgreen and C-dotred were sized below 15 nm while C-Dotblue has the hydrodynamic size around 45 nm with a polydispersity index (PDI) below 0.5. High-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) images of resulting C-Dots along with the size distribution graph of each sample were represented in Fig. 2. C-Dotblue were observed as agglomerates with ca. 50 nm diameter, consisting of tiny C-Dots with diameter of ≃1–2 nm (Fig. 1a). C-Dotgreen and C-Dotred were noted as uniformly distributed individual nanodots with an average size below 5 and 7 nm, respectively. The smaller core size than the size estimated by DLS is due to charge electrical double layer formed by the liquid surrounding the particle.
Surface Zeta Potential and Electrical Conductivity of C-Dot Suspensions
Surface net charge and electrical conductivity are other important parameters that are essential to predict the colloidal stability, surface and electrical properties of nanomaterials. In the case of carbonaceous materials, these properties may vary between metallic or insulating states depending on the surface defect types and functional groups67. As presented in Table 1, all three of the C-Dots exhibited a negative surface charge at pH 4 and C-Dotred has the highest ζ-Pot (−48.4 ± 2.1 mV) due to increased number of acidic functional groups as compared to C-Dotblue (−30.1 ± 2.0 mV) and C-Dotgreen (−20.8 ± 2.2 mV). Particle conductivity differed in each sample, where C-Dotgreen showed the highest value (153 S/cm) and the C-Dotred (90 S/cm) have the least. Thus, Dotgreen is the most suitable candidate material to use as anode material for the hybrid SC compare to red and blue dots while its higher conductivity can be attributed to the high number of intrinsic defects most likely located on the surface which help the electronic transport. Such effect have been recently observed for ZnO nanoparticles68 and rGO69 as well as ZnO-rGO hybrid70. This also explains the higher fluorescence quantum yield of this sample. Although it is difficult to proof, there are some reports indicating that the optical properties have strong influence on the electrical or electrochemical properties of the C-Dots71, 72.
Crystal Structure of C-Dots
The lattice spacing values differ in each C-Dots as shown in Fig. 2b,e and h. C-Dotgreen contain two different species: 2.45 Å which is the in-plane lattice spacing of graphene ({100} facet)35 and 1.41 Å (the C-C bond length in elemental carbon (diamond) that connect the C atoms and are common for the pentagon–hexagon pair73. C-Dotred showed a lattice space as short as 1.36 Å which is assigned to the sp 2 C-C bond length connecting C atoms of two adjacent hexagons. C-Dotblue showed a lattice spacing (1.62 Å) corresponds to a single sp 3 C-C bond length74, 75.
Figure 3a,b, and c represents the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of each CDots. C-Dotgreen showed a strong peak centered at 19.4° along with a shoulder centered at 41.7°. These peaks are attributed to {100}, {101} planes presenting a higher number of oxygen-containing groups49, 76, 77. C-Dotred had three peaks centered at 23.8° with accompanying fairly sharp peak centered at 43.8° of {002} and {101} plane of reduced graphene oxide, respectively. XRD diffractogram show that both C-Dotgreen and C-Dotred were formed of polyaromatic C domains surrounded with amorphous carbon network78. C-Dotblue, on the other hand, showed several distinctive peaks correspond to a polycrystalline structure (Fig. 3a)79. The peaks centered at 28.2°, 40.2°, 50.3°, 58.7°, and 73.8° were identified as the {002}, {101}, {004}, {103}, and {110} reflections of C-Dots while peak at 66.4° could not be identified. C-Dots are often amorphous and this type of C-Dots with polycrystalline organization is rare in the literature80.
Surface functional groups dominated on C-Dots
Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analysis was performed to determine the acting surface functional groups present on the C-Dots’ surfaces, and corresponding IR spectra were depicted in Fig. 3 and full interpretation was given in the supporting information file. C-Dotgreen and C-Dotblue displayed a broad peak centered at around 3300 cm−1 associated with the hydrogen bonding. The larger hydrodynamic size of the C-Dotblue (Fig. 1c) can be explained by the presence of higher number of water appealing -OH groups on their surface as compared to C-Dotred and C-Dotgreen. FT-IR studies reported here show no contradiction with the literature that shifts in emission maximum often correlated with the increased number of oxidized species on the particle surface which results in a red-shifted PL emission81. A comparison of the FT-IR spectra of the three samples reveals that low quantum yield and emission intensity on the other hand correlated with the presence of higher ratio of methyl groups, and domination of C=C bonds as respect to oxygen rich-species82, 83. A surface favoring the interfacial hydrogen bonding between C-Dots, decreases the intensity of the fluorescence emitted from those samples due to decreased inter-particle distance between C-Dot pairs (Fig. 1a).
The elemental composition of multi-colored carbon dots, EDX analysis was also performed (Tables S1, 2 and 3). They all show mainly three peaks for ‘C’, ‘O’, ‘P’ and ‘P’ of varying ranges together with some small contamination of other ions.
Vibrational properties of C-Dots (Raman Analysis)
Vibrational properties of C-Dots were analysed by Raman spectroscopy. It is expected that the Raman active carbonaceous materials show two characteristic main peaks, the so-called D and G-band, at around 1350 cm−1 and 1600 cm−1. The intensity of the D-band is thereby proportional to the amount of disordered sp3 carbon; and the intensity of the G-band proportional to the amount of ordered graphitic (sp 2) carbon contained in the analysed sample. These two correlations represent a possibility to determine the graphitization degree of the synthesized samples by calculating relative intensity ratio of these two bands \((\frac{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{D}}}}{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{G}}}})\). Low values for this ratio would mean that the graphitization degree is elevated, which would theoretically lead to a better electrical conductivity. A third very intense peak at around 3200 cm−1 can be observed as well. This dominant, so-called 2D-band is also related to the amount of disordered sp3 carbon, but in contrast to the D-band, the intensity of this peak is generally correlated to the performance or intensity of the used laser. Therefore, this 2D-band peak is in general not used for analysing the hybridization behavior or conductivity of the samples. Individual Raman spectra of the samples are shown in Fig. 4a–c. According to this knowledge the blue sample given in Fig. 4a revealed the highest conductivity due to its lowest \((\frac{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{D}}}}{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{G}}}})\) ratio which is 1.08 compare to >1.18 ratio of C-Dotred sample (Fig. 4c). The D- and G-band of C-Dotgreen sample (Fig. 4b) strongly overlap thus it is not possible to determine the ratio even by deconvolution. This is indication of high disorder or defects. On the other hand, it is also reported that \((\frac{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{D}}}}{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{G}}}})\) ratio is another way of measuring the extent of the disorder and crystallinity. The shift in D and G band of C-Dotblue shows an increased order as compared to C-Dotred 66, 84. Moreover, C-Dots with \((\frac{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{D}}}}{{{\bf{I}}}_{{\bf{G}}}})\) ratios larger than 1 are contributed to the structure defects appeared in the C-Dots66. In summary, the Raman spectra presented in Fig. 4 show the existence of defects and also show that how these defect structures affect the vibrational modes of C-Dots. Therefore, we have deeply investigated the defect structures via EPR spectroscopy which is highly sensitive to the detection of paramagnetic defect centers.
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) analysis
It is well known that carbonaceous materials such as graphite, graphene, graphene oxide and as well as C-Dots have intrinsically plenty of EPR active paramagnetic defect centers69, 70. These defects mainly arise due to so-called dangling bonds or other defects that possibly generate sub-bandgap defect states. Based on the extraordinary sensitivity and power of EPR spectroscopy on defects, lots of useful microscopic information can be obtained85.
The observed EPR signals in Fig. 5a can be assigned to either paramagnetic carbon related dangling bond (DB) centers or to other structural intrinsic defects. For the designation of the observed dangling bond centers the g-values as determined from EPR data can be used. Carbon radical centers typically occur in an interval of g-values ranging from 2.0020–2.003086,87,88. In addition, by considering the EPR spectral linewidth (ΔB) it may be possible to distinguish between sp 2- and sp 3 hybridization. Values for sp 3-hybridized carbon centers, as found in diamond, for example, have been determined to ΔB(sp 3) < 1 mT. For graphitic carbon centers with sp 2-hybridization, generally broader EPR line widths, ΔB(sp 2) ≥ 1 mT, were reported86, 89,90,91. In the present work, the corresponding variation in g-factors and ΔB is given in Table 2, and according to the abovementioned knowledge we clearly distinguish, experimentally, the difficult issue of defect assignment and carbon hybridization state. The results strongly suggest the existence of the enormous amount of dangling bonds and predominantly occurrence of sp 3-hybridization. The finding of sp 3 hybridization is corroborated based on a theory by first principle studies. Nevertheless, it is worth to mention here that the C-Dotred sample nearly approaches to sp 3 hybridization which also has a strong deviation with respect to g-factor as compared to the blue and green C-Dot.
Moreover, in order to understand the dependency of carbon related dangling bond defect centers to the microwave power (MW), we have investigated the saturation behavior of EPR signal of all three samples via X-band EPR (Fig. 5b). The peak-to-peak intensities of EPR spectra for all samples rise with increasing microwave power P. However, the C-Dotred signal has highly different saturation behavior than other two and deviates strongly at 7.2 mW showing a hard saturation behavior whereas blue and green sample can easily saturate at 0.12 mW (Table 2). Low saturation microwave power is indication of high number of surface defects85. This observation represents that we should safely make EPR measurements below saturation values without saturating the signal intensity. Accurate determination of this saturation limit enables us to get off course reliable results about the EPR intensity. Here most importantly to be mentioned is the broader linewidth gives harder saturation points which may be also related to approaching of sp 2 hybridization in EPR spectral point of view. That shows the unpaired electrons of the defect centers has a totally different electronic environment in C-Dotred as compared to C-Dotblue and C-Dotgreen ones. This also strongly point out that the reaction to microwave power can be attributed to the localization of defect centers in the C-Dotred samples which are more delocalized electrons (bound states at the defect site) and defect centers in the C-Dotblue and C-Dotgreen samples are rather localized and located on the surface85, 92. Finally, due to its higher conductivity determined during zeta potential measurements, higher disorderness as a result of overlapping of D- and G-band from Raman measurements and its higher defect concentration on the surface from EPR measurements, we conclude that the C-Dotgreen is the most suitable candidate as a constituent of the anode material to be used in hybrid SC.
Preparation of C-Dots/MnO2 hybrid nanorods and structural characterizations
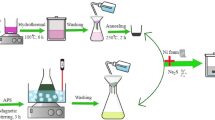
Single-crystal α-MnO2 nanorods were prepared by hydrothermal treatment of KMnO4 under acidic conditions as described in the experimental part. Figure 6a shows a typical high-magnification SEM image of the MnO2 nanorods. They exhibit a uniform size distribution with a width of about 50–150 nm and a length in the range of several micrometers24, 93. The XRD analysis indicated that α-MnO2 nanorods are highly pure (Fig. S2) and they show a body-centered tetragonal α-MnO2 phase (space group I4/m(87)) with lattice constants a) 9.7847 Å and c) 2.8630 Å (JCPDS 44–0141). C-Dotgreen was further complexed with hydrothermally synthesized α-MnO2 nanorods (1:1 w/w) by post-treatment of them hydrothermally in the presence and absence of polypyrrole. Although there is room for the investigation of different mass ratio for maximum supercapacitance performance, in present work we present our lucky-choice ratio which has so far the best results. Presence of polypyyrole could add additional help to enhancement of surface conductivity94. S3). Figures 6a and S3c, shows the representative SEM images of α-MnO2 samples and their composite with carbon nanodots at different magnifications. α-MnO2 nanorods were further decorated with While α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen hybrid nanostructures show similar properties to as-synthesized α-MnO2 (Fig. 6a) nanorods, the spherical formations observed on the nanorods in the presence of PPy hybrid structures are noteworthy (Fig. S3). The polymerization of pyrrole on the surface of α-MnO2 nanorods enhanced the surface coverage of C-Dots and as a result particle thickness of the rods increased, as clearly be seen in the SEM images shown in Fig. S3d,e 31, 95.
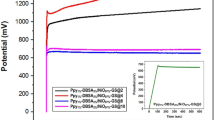
(a) Schematic illustrations of the synthesis method of α-MnO2/PPy/C-Dotgreen hybrids from pre-synthesized α-MnO2 nanorods and representing scanning electron microscope images. (b) Graphical illustration of hybrid supercapacitor model. (c) Equivalent modified Randles circuit obtained via fitting of Nyquist plot. (d) EIS in Nyquist plot of hybrid supercapacitor. (e) The variation of characteristic impedance (absolute value | Z |) with frequency (Bode-plot) for hybrid supercapacitor.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) analysis
Advanced characterization techniques such as Raman, EPR, and impedance spectroscopy can reveal detailed information on the electronic, vibrational, and electrical transport properties. According to Raman (overlapping of D- and G-band) and EPR spectroscopy (higher linewidth compare to blue) results given above C-Dotgreen includes plenty of functional defects causes the most disorderness. Such defects are crucially important for the charge transport phenomena and the electrical properties such as resistivity (or conductivity). We recently reported for semiconductor ZnO nanocrystals that the defect-charge density has the key role for non-ohmic behavior of due to the defect distribution and interactions in the surface structure68. In order to demonstrate such effect, we measured the electrical conductivity of α-MnO2/PPy nanorods before/after doped with C-Dots. The electrical conductivity of nanorods (10.75 × 10−6 S/cm) increased several orders of magnitude up to 4.75 × 10−4 S/cm after deposition of C-Dots. These results are in accordance to what previously reported, in particular by H. Bi et al., about the potential of carbon dots on the enhancement of surface conductivity and many other properties96,97,98. Similar effects were also reported by us for the lead-free manganese ion modified ferroelectric ceramics K0.5Nb0.5NaO3 92.
The illustration in Fig. 6b presents the model for the hybrid supercapacitor containing C-Dotgreen decorated α-MnO2-PPy nanorods and rGO as a negative and positive electrode, respectively, separated with cellulose. C8H16BImI ionic liquid electrolyte was synthesized and characterizations were performed by 1H and 13C NMR (See supporting file and Figs S5, S6 and S7). The C-Dotgreen decorated-MnO2-PPy nanorods and C8H16BImI ionic liquid electrolyte (Fig. S4) material have a crucial role in the capacitor device by enabling surface reactions and faster charge transfer99, 100. Alternative electrolyte would be LiPF6 but it cannot handle high voltage and material should not react with moisture. The hybrid supercapacitors presented here use the advantages of both capacitive behavior and the faradaic reaction to enhance energy density and power density instantaneously. Large surface area, high porosity, high electronic transport efficiency and structural stability are the benefits of C-related components101, 102. Here to describe the hybrid supercapacitor the Nyquist plot (Fig. 6d) were fitted to a modified Randles electrical circuit (Fig. 6c) by using the following elements: active Ohmic electrolyte resistance (R 1), impedance of a faradaic reaction consists of an active charge transfer resistance (R 2) and the double layer capacity (C). A constant phase element (CPE) has been used during the fitting procedure to correct the ideal capacitor behavior to a real one. Note that one can present the CPE of 45° as the Warburg diffusion element. The impedance spectra in Fig. 6d revealed a semicircle in the high-frequency region and a near-linear line in the low-frequency region. The semicircle can be related to the charge-transfer resistance R 2 while the linear region is caused by Warburg diffusion element which is in this work described as CPE. At high frequencies, the intercept with the real axis (Z′) can treated as the electrolyte resistance R 1. The Bode-plot in Fig. 6e shows the variation of the impedance as a function of the frequency (0.1 Hz–100 kHz) for hybrid supercapacitor. It confirms the validation of capacitance measurements while the curve follows the expected Kramers-Kronig relation which is an obvious increasing of the impedance at low frequency. Bode-plot of Randles circuit has three specific regions in Fig. 6e: (i). Above 1.5 kHz, magnitude approaches 5.4 Ω. The R 1 dominates the region103, 104. (ii) Between 1.5 kHz and 20 Hz, capacitance (C) controls the impedance. Moreover, the maximum point of Z-phase between hybrid capacitor mechanisms is shown in Fig. 6e for 45 ° at 0.14 kHz which corresponds to the almost linear behavior (on the Bode plot of frequency versus impedance) with a slope of ~1. Finally, (iii) below 20 Hz the impedance begins a transition back towards resistive behavior as R 2 becomes dominant. This transition is not complete even at down to 0.1 Hz.
As depicted in Table 3, the high area capacitance value can be read as 17.3 μF cm−2 at a working voltage of 3 V. Such a high value is completely related due to hybrid capacitance from the surface interaction between carbon related defects and C-Dots and/or rGO and of course related to the enhanced ion mobility of C8H16BImI electrolyte. Such intrinsic defects can act as reactive sites providing an effective charge transfer and good electrode-electrolyte interfaces that minimize the internal resistance of supercapacitor devices105. Here, we present geometric area due to the simplicity and accuracy reasons. Capacitance values reported in the literature for surface decorated MnO2 and carbon based materials including graphene and C-Dots vary between 0.08 and 50 µF/cm2, which is within the range that was obtained in this study97, 106,107,108. Note that, gravimetric specific capacitance of the MnO2/PPy/C-Dots will be investigated in future works as well. Thus, we omit such measurements while multiple additional effects influenced the capacity of supercapacitors such as redox, adsorption and intercalation which are not comparable via relative surface measurements.
Experimental Section
Materials
Nile Red, Manganese sulfate monohydrate (MnSO4.H2O), potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and pyrrole were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Ethanol (96% pure. grad.) and other solvents were obtained from Fluka. All the reagents were analytical grade and used without further purification. Cola was purchased from a local supermarket. Octyl-bis(3-methylimidazolium) diiodide (C8H16BImI) was prepared according to previously reported procedures109, 110, and its molecular structure and NMR spectra were shown in Figs S5 and S6. Water used during the synthesis was purified using a Millipore Milli-Q system (18.2 MQ-cm).
C-Dot Synthesis
Fluorescent Carbon Dots (C-Dots) synthesis was accomplished according to the method described previously62. 1 g. of C source mixture as described below was diluted in 1:10 ratio with MilliQ-water (Millipore Inc., Ω = 18 MΩ·cm) and dispersed in 2 mL of 1:1 water/ethanol in a Teflon oven vessel (approximately 20 mL inner volume). A homogeneous suspension was obtained without aggregation by vigorous mixing. The mixture was maintained at 300 °C for 30 minutes until a dark, caramelized, semi-solid texture was obtained. The resulting material was dissolved in 2 mL of MilliQ-water. The suspension was centrifuged at 6.000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was passed through a 0.45 µm Millipore HV hydrophilic membrane filter for eliminating any impurities. The final product was vacuum-dried at 90 °C for overnight. Sample codes were shown in Table 1. Green emitting C-Dots (C-Dotgreen) were prepared directly using degassed Cola drink as carbon source without the utilization of any passivating agent. The synthesis of Blue emitting C-Dots (C-Dotblue) was achieved by mixing an equal volume of Nile Red (5 mg/mL) with Cola drink at the beginning. Red emitting C-Dots (C-Dotred) were synthesized following a hydrothermal synthesis route for preparation of reduced graphene oxide/C-dotgreen hydrogels65. As prepared C-Dotsgreen (0.1 g) were dissolved in pre-synthesized graphene oxide (GOx) (2 mg/mL). The mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave, and heated at 180 °C for 12 h. Resulting material was immersed in hydrazine monohydrate (50%) in a a glass tube and were left for 8 h at 95 °C. Then, the resulting graphene oxide/C-dotgreen hydrogels were washed via ultrapure water-cycles to remove the residuals. C-Dots were further collected from the washing water by centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 10 min and dried as mentioned above.
Characterization of Carbon Dots
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectra of C-Dots were recorded using a UV-VIS spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800). Fluorescence properties were measured using a Varian Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer. Quantum yields (QY) of each sample was calculated by taking quinine sulfate (QS) in 0.1 M H2SO4 as reference fluorophore. Quinine sulfate (QS) has the quantum yield of 0.54 (Ex. 360 nm). QY of each C-Dot is calculated following the procedure reported previously111. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses were performed with X-ray diffractometer (XRD) (Rigaku Smartlab Intelligent Americas, Texas USA). The XRD was recorded at the voltage of 40 kV with 2θ values between 8° and 80° at a scan rate of 2°/min. The dried powders of Carbon Dots were diluted with Mili-Q water to perform Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (Perkin Elmer Frontier Waltham, A 02451 USA) and spectrum GX spectrometry within the wavenumber range of 400–4.000 cm−1. High-Resolution Transmission Electron microscopy imaging was performed using High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope (HRTEM) 200 kV with Field Emission (TECNAI G2 20 S-TWIN, FEI) to determine the size and morphology of the dispersed C-Dots and size analysis of the sample were carried out using Image J. Fluorescence spectra of particle solutions were measured using a Fluorescence Spectrophotometer (Varian Cary Eclipse.) Solid-state Raman spectra were recorded at room temperature (WITec GmbH Alpha300 R Raman Module). 785 nm wavelength laser was used under 50x magnification and 2.03 s integration times. X-band (9.86 GHz) EPR measurements were performed by BRUKER EMX spectrometer with the aid of a rectangular TE102 resonator from Bruker. The offset in the magnetic field and the exact g-factors in X-band measurements were determined with a polycrystalline DPPH (2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) reference sample of well-known g-factor (g = 2.0036). The EPR spectral analysis has been performed using the WINEPR program from Bruker. For cooling (to liquid helium temperatures) an Oxford CF-935 cryostat was used. The temperature was regulated by a temperature controller (Oxford ITC-503). The following EPR experimental parameters were used: microwave power: 1 mW; modulation amplitude: 0.5 G; time constant: 163.84 ms; receiver gain: 2 × 104.
Hydrothermal synthesis of α-MnO2 Nanorods
α-MnO2 was synthesized by a hydrothermal method using MnSO4.H2O (0.3 g) and KMnO4 (0.6 g) mixture in 20 ml of ultrapure water. The homogeneous mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated at 140 °C for 12 h. The autoclave was allowed to cool to room temperature, and then the precipitate was collected and washed four times with distilled water to remove any possible residual reactant. Finally, the α-MnO2 powder was dried in air at 40 °C24, 112.
α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen hybrid Nanorod Synthesis
Synthesis procedure starts with the preparation of α-MnO2 hybrid nanorods as explained in the previous section. Once nanorods synthesized, 60 mg of α-MnO2 and 60 mg of C-Dotgreen were dispersed in 20 mL of ultrapure water; then the mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave, and heated at 140 °C for 12 h. The autoclave was allowed to cool to room temperature. The obtained product in hydrogel form was washed with distilled water to remove any possible residual reactant and then dried in a freeze dryer.
α-MnO2/PPy Nanorod Synthesis
60 mg of α-MnO2 was dispersed in 20 mL of ultrapure water and sonicated. During sonication process, 200 µl of pyrrole added dropwise to this mixture. Then, the mixture was transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave, and heated at 140 °C for 12 h. The autoclave was allowed to cool to room temperature. The obtained product in hydrogel form was washed with distilled water to remove any possible residual reactant and then dried in a freeze dryer.
In situ preparation of α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen hybrid Nanorods
α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen hybrid nanorods were synthesized by mixing reactants (0.3 g of MnSO4.H2O, 0.6 g of KMnO4) with 0.1 g of C-Dotgreen in 20 mL ultrapure water. This mixture was sonicated and transferred into a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave, and heated at 140 °C for 12 h. After hydrothermal reaction, the product was collected, washed, and dried in a manner similar to that of α-MnO2.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements
EIS measurements were carried out using a Versastat IV potentiostat (Princeton Applied Research) in atmospheric pressure at room temperature in the frequency range between 0.1 Hz and 100 kHz. For analyzing the spectra we used the Versa Studio V2.4 software. The amplitude of voltage modulation was set to 500 mV. In present case a four-point electrode-setup was used, so that the potentials for any electrochemical reactions that are occurring at the working electrode(s) are not being measured. The setup consisted of a copper foil for anode (thickness = 2 mm) and an aluminium foil for cathode (thickness = 0.5 mm) current collector on which the electrode material was coated. Both electrodes were separated by a cellulosic paper membrane. The setup was hold between two glass object plates, for a better adhesiveness
Conclusions
In this study, multicolored (red, blue and green) fluorescent C-Dots were prepared through thermal synthesis using degassed Cola beverage as a C source; and optical and physicochemical properties were analyzed using various analysis methods. The synthesized α-MnO2/PPy hybrid nanorod was decorated with C-Dots as used for anode material for high performance hybrid SC. In addition to present work, other C rich materials can be used as C source such as waste water or exhaust filters of combustion vehicles or factory chimney filters. Liquid ionic membrane electrolyte octyl-bis(3-methylimidazolium)diiodide (C8H16BImI) were synthesized by N-alkylation reaction in order to enhance the electron transfer exceptionally in hybrid SC. C8H16BImI electrolyte is highly promising material for larger voltage window in the use of next-generation SC. Accordingly, conductivity and the ion-donating ability of C-Dots together with the capacitative property of α-MnO2 nanorods and C8H16BImI demonstrated markedly superior capacitive and rate performance compared with those standard electrode-electrolyte combinations. EPR and Raman spectroscopy results revealed the importance function of the defect centers in the performance of the SC device. Nowadays, SC are suffering plenty of limitation factors: High leakage current, thermal aging, high equivalent series resistance (ESR), low voltage window etc. To overcome such drawback one should consider the variety of materials in a smart way. Of course there are materials giving higher capacity values such as graphite however the performance of them in SC is limited and saturated. We believe new intelligent materials with alternative sources may have high impact in engineering to produce next generation SC while there is plenty of space on the materials selection compared to Li-ion batteries. Thus, such hybrid SC can be used as a standard high power source in electrical vehicles in the near future.
References
Viswanathan, S., Radecka, H. & Radecki, J. Electrochemical biosensor for pesticides based on acetylcholinesterase immobilized on polyaniline deposited on vertically assembled carbon nanotubes wrapped with ssDNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 2772–7 (2009).
Shi, J. et al. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 67, 595–600 (2015).
Dresselhaus, M. S., Dresselhaus, G. & Eklund, P. C. Science of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes: Their Properties and Applications. (Academic Press, 1996).
Li, J., Chen, Y. & Liu, Y. Research on a Stand-alone Photovoltaic System with a Supercapacitor as the Energy Storage Device. Energy Procedia 16, 1693–1700 (2012).
Yan, K. et al. Selective deposition and stable encapsulation of lithium through heterogeneous seeded growth. Nat. Energy 1, 16010 (2016).
Huang, M., Li, F., Dong, F., Zhang, Y. X. & Zhang, L. L. MnO 2 -based nanostructures for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 21380–21423 (2015).
Aricò, A. S., Bruce, P., Scrosati, B., Tarascon, J.-M. & van Schalkwijk, W. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Mater. 4, 366–377 (2005).
Candelaria, S. L. et al. Nanostructured carbon for energy storage and conversion. Nano Energy 1, 195–220 (2012).
Li, X. & Wei, B. Supercapacitors based on nanostructured carbon. Nano Energy 2, 159–173 (2013).
Pan, L. et al. Conducting Polymer Nanostructures: Template Synthesis and Applications in Energy Storage. 2636–2657, doi:10.3390/ijms11072636 (2010).
Han, J. W. & Kim, J. Reduced graphene oxide – silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: a potential anticancer nanotherapy. Int. J. Nanomedecine 10, 6257–6276 (2015).
Lu, W. & Dai, L. In Carbon Nanotubes, doi:10.5772/39444 (InTech, 2010).
Yu, Z., Tetard, L., Zhai, L. & Thomas, J. Supercapacitor electrode materials: nanostructures from 0 to 3 dimensions. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 702–730 (2015).
Zhang, S. et al. Graphene quantum dots as the electrolyte for solid state supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 6, 19292 (2016).
Wang, K. et al. MnO2-Carbon nanotube composite for high-areal-density supercapacitors with high rate performance. J. Power Sources 305, 30–36 (2016).
Yuki Matsuda, Wei-Qiao Deng, † & William A. Goddard, I. Contact Resistance Properties between Nanotubes and Various Metals from Quantum Mechanics, doi:10.1021/JP072794A (2007).
Prasek, J. et al. Methods for carbon nanotubes synthesis—review. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 15872 (2011).
Lei, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, L. L., Kumar, N. A. & Zhao, X. S. Functionalization of chemically derived graphene for improving its electrocapacitive energy storage properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 9, 1891–1930 (2016).
Zhang, Y., Li, H., Pan, L., Lu, T. & Sun, Z. Capacitive behavior of graphene–ZnO composite film for supercapacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 634, 68–71 (2009).
Seo, H. et al. Multi-resistive Reduced Graphene Oxide Diode with Reversible Surface Electrochemical Reaction induced Carrier Control. Sci. Rep. 4, 574–578 (2014).
Chen, Y. et al. Reduced Graphene Oxide Films with Ultrahigh Conductivity as Li-Ion Battery Current Collectors. Nano Lett. 16, 3616–3623 (2016).
Singh, A. K., Sarkar, D., Karmakar, K., Mandal, K. & Khan, G. G. High-Performance Supercapacitor Electrode Based on Cobalt Oxide–Manganese Dioxide–Nickel Oxide Ternary 1D Hybrid Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 20786–20792 (2016).
Wang, Y. et al. Mesoporous Transition Metal Oxides for Supercapacitors. Nanomaterials 5, 1667–1689 (2015).
Cheng, F. et al. Facile Controlled Synthesis of MnO 2 Nanostructures of Novel Shapes and Their Application in Batteries. Inorg. Chem. 45, 2038–2044 (2006).
Liu, X., Chen, C., Zhao, Y. & Jia, B. A Review on the Synthesis of Manganese Oxide Nanomaterials and Their Applications on Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Nanomater. 2013, 1–7 (2013).
Wu, M.-S. Electrochemical capacitance from manganese oxide nanowire structure synthesized by cyclic voltammetric electrodeposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 153102 (2005).
Devaraj, S. & Munichandraiah, N. Effect of Crystallographic Structure of MnO2 on Its Electrochemical Capacitance Properties, doi:10.1021/JP7108785 (2008).
Lang, X., Hirata, A., Fujita, T. & Chen, M. Nanoporous metal/oxide hybrid electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6, 232–236 (2011).
Ma, L., Shen, X., Ji, Z., Zhu, G. & Zhou, H. Ag nanoparticles decorated MnO2/reduced graphene oxide as advanced electrode materials for supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 252, 95–103 (2014).
Shi, P. et al. Design of Amorphous Manganese Oxide@Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Fiber for Robust Solid-State Supercapacitor. ACS Nano 11, 444–452 (2017).
Zhang, J., Shi, Y., Ding, Y., Zhang, W. & Yu, G. In Situ Reactive Synthesis of Polypyrrole-MnO2 Coaxial Nanotubes as Sulfur Hosts for High-Performance Lithium–Sulfur Battery. Nano Lett. 16, 7276–7281 (2016).
Yu, G. et al. Enhancing the Supercapacitor Performance of Graphene/MnO 2 Nanostructured Electrodes by Conductive Wrapping. Nano Lett. 11, 4438–4442 (2011).
Bhunia, S. K., Saha, A., Maity, A. R., Ray, S. C. & Jana, N. R. Carbon nanoparticle-based fluorescent bioimaging probes. Sci. Rep. 3, 1473 (2013).
Baker, S. N. & Baker, G. A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 49, 6726–6744 (2010).
Mao, L. H. et al. Facile access to white fluorescent carbon dots toward light-emitting devices. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 6417–6425 (2014).
Park, S. Y. et al. Photoluminescent green carbon nanodots from food-waste-derived sources: large-scale synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 3365–70 (2014).
Wang, Q. et al. Microwave–hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from graphite oxide. Carbon N. Y. 49, 3134–3140 (2011).
Liu, H., Ye, T. & Mao, C. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 46, 6473–6475 (2007).
Bhaisare, M. L., Talib, A., Khan, M. S., Pandey, S. & Wu, H. F. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via microwave carbonization of citric acid in presence of tetraoctylammonium ion, and their application to cellular bioimaging. Microchim. Acta 182, 2173–2181 (2015).
Meiling, T. T., Cywiński, P. J., Bald, I., Ponti, A. & Kang, Z. White carbon: Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles with tunable quantum yield in a reproducible green synthesis. Sci. Rep. 6, 28557 (2016).
Wu, L. et al. Surface passivation of carbon nanoparticles with branched macromolecules influences near infrared bioimaging. Theranostics 3, 677–86 (2013).
Jiang, K. et al. Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: Full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 54, 5360–5363 (2015).
Ray, S. C., Saha, A., Jana, N. R. & Sarkar, R. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and bioimaging application. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 18546–18551 (2009).
Wang, X., Qu, K., Xu, B., Ren, J. & Qu, X. Multicolor luminescent carbon nanoparticles: Synthesis, supramolecular assembly with porphyrin, intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity and applications. Nano Res. 4, 908–920 (2011).
Tang, J. et al. Carbon nanodots featuring efficient FRET for real-time monitoring of drug delivery and two-photon imaging. Adv. Mater. 25, 6569–74 (2013).
Zhang, X. et al. Color-switchable electroluminescence of carbon dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Nano 7, 11234–41 (2013).
Batmunkh, M., Shearer, C. J., Biggs, M. J. & Shapter, J. G. Nanocarbons for mesoscopic perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 9020–9031 (2015).
Wei, Z. et al. Cost-efficient clamping solar cells using candle soot for hole extraction from ambipolar perovskites. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 3326–3333 (2014).
Chen, G. et al. Assembling carbon quantum dots to a layered carbon for high-density supercapacitor electrodes. Sci. Rep. 6, 19028 (2016).
Xu, J. et al. The carbon quantum dots/nickel oxide (CQDs/NiO) nanorods with high capacitance for supercapacitor. RSC Adv. 6, 5541–5546 (2013).
Margraf, J. T., Strauss, V., Guldi, D. M. & Clark, T. The Electronic Structure of Amorphous Carbon Nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 7258–65 (2015).
Strauss, V. et al. Carbon Nanodots: Supramolecular Electron Donor-Acceptor Hybrids Featuring Perylenediimides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54, 8292–7 (2015).
Yun, Y. S., Yoon, G., Kang, K. & Jin, H.-J. High-performance supercapacitors based on defect-engineered carbon nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 80, 246–254 (2014).
Kaftelen, H. et al. Mn-substituted spinel Li4Ti5O12 materials studied by multifrequency EPR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 9973 (2013).
Bello, A. et al. High-performance symmetric electrochemical capacitor based on graphene foam and nanostructured manganese oxide. AIP Adv. 3, 82118 (2013).
Lee, J. H., Shin, W. H., Lim, S. Y., Kim, B. G. & Choi, J. W. Modified graphite and graphene electrodes for high-performance lithium ion hybrid capacitors. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 3, 22 (2014).
Simon, P. & Gogotsi, Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nat. Mater. 7, 845–854 (2008).
Varnam, A. H. & Sutherland, J. P. Beverages: technology, chemistry and microbiology. (Aspen, 1999).
Han, S. et al. Fabrication, gradient extraction and surface polarity-dependent photoluminescence of cow milk-derived carbon dots. RSC Adv. 4, 58084–58089 (2014).
Zhu, S. et al. Highly Photoluminescent Carbon Dots for Multicolor Patterning, Sensors, and Bioimaging. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 52, 3953–3957 (2013).
Li, H., Kang, Z., Liu, Y. & Lee, S.-T. Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 24230 (2012).
Mukherjee, P. et al. Tunable Luminescent Carbon Nanospheres with Well-Defined Nanoscale Chemistry for Synchronized Imaging and Therapy. Small 11, 4691–4703 (2015).
Loukanov, A. et al. Photosensitizer-Conjugated Ultrasmall Carbon Nanodots as Multifunctional Fluorescent Probes for Bioimaging. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 15867–15874 (2016).
Kim, Y., Jang, G. & Lee, T. S. New Fluorescent Metal-Ion Detection Using a Paper-Based Sensor Strip Containing Tethered Rhodamine Carbon Nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 15649–15657 (2015).
Zhang, L. & Shi, G. Preparation of Highly Conductive Graphene Hydrogels for Fabricating Supercapacitors with High Rate Capability. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 17206–17212 (2011).
Ming, H. et al. Large scale electrochemical synthesis of high quality carbon nanodots and their photocatalytic property. Dalt. Trans. 41, 9526 (2012).
Vicarelli, L., Heerema, S. J., Dekker, C. & Zandbergen, H. W. Controlling defects in graphene for optimizing the electrical properties of graphene nanodevices. ACS Nano 9, 3428–35 (2015).
Parashar, S. K. S., Murty, B. S., Repp, S., Weber, S. & Erdem, E. Investigation of intrinsic defects in core-shell structured ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 113712 (2012).
Pham, C. V., Krueger, M., Eck, M., Weber, S. & Erdem, E. Comparative electron paramagnetic resonance investigation of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes with different chemical functionalities for quantum dot attachment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 132102 (2014).
Pham, C. V. et al. Charge transfer and surface defect healing within ZnO nanoparticle decorated graphene hybrid materials. Nanoscale 8, 9682–9687 (2016).
Barman, M. K., Jana, B., Bhattacharyya, S. & Patra, A. Photophysical Properties of Doped Carbon Dots (N, P, and B) and Their Influence on Electron/Hole Transfer in Carbon Dots–Nickel (II) Phthalocyanine Conjugates. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 20034–20041 (2014).
Essner, J. B. et al. The emerging roles of carbon dots in solar photovoltaics: a critical review. Environ. Sci. Nano 4, 1216–1263 (2017).
Zong, J. et al. Photoluminescence enhancement of carbon dots by gold nanoparticles conjugated via PAMAM dendrimers. Nanoscale 5, 11200 (2013).
Georgakilas, V., Perman, J. A., Tucek, J. & Zboril, R. Broad Family of Carbon Nanoallotropes: Classification, Chemistry, and Applications of Fullerenes, Carbon Dots, Nanotubes, Graphene, Nanodiamonds, and Combined Superstructures. Chem. Rev. 115, 4744–4822 (2015).
Li, L., Reich, S. & Robertson, J. Defect energies of graphite: Density-functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 72, 184109 (2005).
Skowroński, J. M. & Osińska, M. The influence of thermal treatment on the electrochemical properties of carbon–Ni–Pd composites. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 71, 109–117 (2014).
Dong, Y. et al. Natural carbon-based dots from humic substances. Sci. Rep. 5, 10037 (2015).
Kwon, W., Do, S., Kim, J.-H., Seok Jeong, M. & Rhee, S.-W. Control of Photoluminescence of Carbon Nanodots via Surface Functionalization using Para-substituted Anilines. Sci. Rep. 5, 12604 (2015).
Chandra, S., Das, P., Bag, S., Laha, D. & Pramanik, P. Synthesis, functionalization and bioimaging applications of highly fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. Nanoscale 3, 1533 (2011).
Zhao, M., Song, H., Chen, X. & Lian, W. Large-scale synthesis of onion-like carbon nanoparticles by carbonization of phenolic resin. Acta Mater. 55, 6144–6150 (2007).
Xiao, J., Liu, P., Li, L. & Yang, G. Fluorescence origin of nanodiamonds. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 2239–2248 (2015).
Roy, P., Chen, P.-C., Periasamy, A. P., Chen, Y.-N. & Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent carbon nanodots: synthesis, physicochemical properties and analytical applications. Mater. Today 18, 447–458 (2015).
Brito, J. B. et al. Blue–green luminescent carbon nanodots produced in a silica matrix. Carbon N. Y. 91, 234–240 (2015).
Yun, J., Chen, L., Zhang, X., Feng, J. & Liu, L. The Effect of Introducing B and N on Pyrolysis Process of High Ortho Novolac Resin. Polymers (Basel). 8, 35 (2016).
Erdem, E. Microwave power, temperature, atmospheric and light dependence of intrinsic defects in ZnO nanoparticles: A study of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy. J. Alloys Compd. 605, 34–44 (2014).
Bateni, A. et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance and Raman spectroscopy studies on carbon-doped MgB2 superconductor nanomaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 153905 (2015).
Walters, G. K. & Estle, T. L. Paramagnetic Resonance of Defects Introduced Near the Surface of Solids by Mechanical Damage. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 1854–1859 (1961).
Berger, F., Müller, A., Aldinger, F. & Müller, K. Solid-state NMR Investigations on Si-B-C-N Ceramics derived from Boron-Modified Poly(allylmethylsilazane). Zeitschrift für Anorg. und Allg. Chemie 631, 355–363 (2005).
Erdem, E. et al. Defect structure in lithium-doped polymer-derived SiCN ceramics characterized by Raman and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 5628 (2009).
Chauvet, O., Zuppiroli, L. & Solomon, I. Electronic properties of disordered SiC materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 11, 303–306 (1992).
Prasad, B. L. V. et al. Heat-treatment effect on the nanosized graphite π-electron system during diamond to graphite conversion. Phys. Rev. B 62, 11209–11218 (2000).
Kaftelen, H. et al. EPR and photoluminescence spectroscopy studies on the defect structure of ZnO nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 86, 14113 (2012).
Wang, X. & Li, Y. Selected-control hydrothermal synthesis of α- and β-MnO2 single crystal nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 2880–2881 (2002).
Li, C. M., Sun, C. Q., Chen, W. & Pan, L. Electrochemical thin film deposition of polypyrrole on different substrates. Surf. Coatings Technol. 198, 474–477 (2005).
de Oliveira, A. H. P. et al. Carbon Nanotube@MnO2@Polypyrrole Composites: Chemical Synthesis, Characterization and Application in Supercapacitors. Mater. Res. 19, 1080–1087 (2016).
Liu, J. et al. Room-temperature Magnetism in Carbon Dots and Enhanced Ferromagnetism in Carbon Dots-Polyaniline Nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 7, 2165 (2017).
Zhang, X. et al. Design and preparation of a ternary composite of graphene oxide/carbon dots/polypyrrole for supercapacitor application: Importance and unique role of carbon dots. Carbon N. Y. 115, 134–146 (2017).
Paulo, S., Palomares, E. & Martinez-Ferrero, E. Graphene and Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Materials in Photovoltaic Devices: From Synthesis to Applications. Nanomaterials 6, 157 (2016).
Unnikrishnan, B. et al. Carbon Dot-Mediated Synthesis of Manganese Oxide Decorated Graphene Nanosheets for Supercapacitor Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 3008–3016 (2016).
Armand, M., Endres, F., MacFarlane, D. R., Ohno, H. & Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 8, 621–629 (2009).
Xiao, N. et al. High-Performance Supercapacitor Electrodes Based on Graphene Achieved by Thermal Treatment with the Aid of Nitric Acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 9656–9662 (2013).
Roldán, S., Granda, M., Menéndez, R., Santamaría, R. & Blanco, C. Mechanisms of Energy Storage in Carbon-Based Supercapacitors Modified with a Quinoid Redox-Active Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 17606–17611 (2011).
Kalvøy, H., Tronstad, C., Nordbotten, B., Grimnes, S. & Martinsen, Ø. G. Electrical Impedance of Stainless Steel Needle Electrodes. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38, 2371–2382 (2010).
Esteban, J. M. & Orazem, M. E. On the Application of the Kramers-Kronig Relations to Evaluate the Consistency of Electrochemical Impedance Data. J. Electrochem. Soc. 138, 67 (1991).
Jung, H. Y., Karimi, M. B., Hahm, M. G., Ajayan, P. M. & Jung, Y. J. Transparent, flexible supercapacitors from nano-engineered carbon films. Sci. Rep. 2, 507–514 (2012).
Borysiewicz, M. A., Wzorek, M., Ekielski, M., Kaczmarski, J. & Wojciechowski, T. Controlling the nanoscale morphology and structure of the ZnO/MnO2 system for efficient transparent supercapacitors. MRS Commun. 7, 173–178 (2017).
Wu, Z.-S., Parvez, K., Feng, X. & Müllen, K. Graphene-based in-plane micro-supercapacitors with high power and energy densities. Nat. Commun. 4, 2487 (2013).
Kumar, V. B. et al. Activated Carbon Modified with Carbon Nanodots as Novel Electrode Material for Supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 13406–13413 (2016).
Zafer, C., Ocakoglu, K., Ozsoy, C. & Icli, S. Dicationic bis-imidazolium molten salts for efficient dye sensitized solar cells: Synthesis and photovoltaic properties. Electrochim. Acta 54, 5709–5714 (2009).
Erten-Ela, S. & Ocakoglu, K. Iridium dimer complex for dye sensitized solar cells using electrolyte combinations with different ionic liquids. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 27, 532–540 (2014).
Sk, M. P. & Chattopadhyay, A. Induction coil heater prepared highly fluorescent carbon dots as invisible ink and explosive sensor. RSC Adv. 4, 31994 (2014).
Wang, X. & Li, Y. Selected-Control Hydrothermal Synthesis of α- and β-MnO 2 Single Crystal Nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 2880–2881 (2002).
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Oya San Keskin for Raman measurements. E.E. thanks to financial support from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (Grant No: Er 662/1-1 and-2). The article processing charge was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the University of Freiburg in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of R.G., K.O. and E.E. R.G. planned and designed C-Dot studies, M.O.A. performed the experiments on C-Dots. R.G. and M.O.A. collected and analyzed the data. K.O. planned and designed the studies on in situ preparation of α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen hybrid nanorods and C8H16BImI. E.H. synthesized and characterized α-MnO2/C-Dotgreen nanorods and analyzed the data with K.O. S.G.C. synthesized the C8H16BImI. E.E. and S.R. planned and design EPR and EIS studies along with the modeling of supercapacitor device. E.E., S.R., N.K. and M.C. performed the EPR and EIS experiments, produced the hybrid supercapacitor, collected and analyzed the data. All authors take full responsibility for the content of the paper and have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Genc, R., Alas, M.O., Harputlu, E. et al. High-Capacitance Hybrid Supercapacitor Based on Multi-Colored Fluorescent Carbon-Dots. Sci Rep 7, 11222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11347-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11347-1
This article is cited by
-
Green perspective of N-CDs towards energy crisis and photodegradation of toxic dyes
Discover Materials (2024)
-
High energy density storage, antifungal activity and enhanced bioimaging by green self-doped heteroatom carbon dots
Discover Nano (2023)
-
Quinone-rich N-carbon spheres loaded carbon cloth as high-performance electrode for double-layer capacitor
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2023)
-
Influence of composite mixtures between nematic liquid crystal and porous carbon nanoparticles towards photoluminescence and UV absorbance
Applied Physics A (2023)
-
Rational design of α-MnO2/HT-GCN nanocomposite for effective photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin and pernicious activity
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.