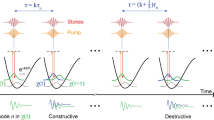
Abstract
All molecules consist of chemical bonds, and much can be learned from mapping the spatiotemporal dynamics of these bonds. Since its invention a decade ago, stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy has become a powerful modality for imaging chemical bonds with high sensitivity, resolution, speed and specificity. We introduce the fundamentals of SRS microscopy and review innovations in SRS microscopes and imaging probes. We highlight examples of exciting biological applications, and share our vision for potential future breakthroughs for this technology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ploetz, E., Laimgruber, S., Berner, S., Zinth, W. & Gilch, P. Femtosecond stimulated Raman microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 87, 389–393 (2007).
Freudiger, C. W. et al. Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Science 322, 1857–1861 (2008).
Nandakumar, P., Kovalev, A. & Volkmer, A. Vibrational imaging based on stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. New J. Phys. 11, 033026 (2009).
Ozeki, Y., Dake, F., Kajiyama, S., Fukui, K. & Itoh, K. Analysis and experimental assessment of the sensitivity of stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Opt. Express 17, 3651–3658 (2009).
Bloembergen, N. The stimulated Raman effect. Am. J. Phys. 35, 989 (1967).
Owyoung, A. Sensitivity limitations for CW stimulated Raman-spectroscopy. Opt. Commun. 22, 323–328 (1977).
Levine, B. F., Shank, C. V. & Heritage, J. P. Surface vibrational spectroscopy using stimulated Raman-scattering. IEEE J. Quantum Elect. 15, 1418–1432 (1979).
Levenson, M. D. & Kano, S. S. Introduction to Nonlinear Laser Spectroscopy (Acad. Press, 1988).
Kukura, P., McCamant, D. W. & Mathies, R. A. Femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 58, 461–488 (2007).
Min, W., Freudiger, C. W., Lu, S. J. & Xie, X. S. Coherent nonlinear optical imaging: beyond fluorescence microscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 62, 507–530 (2011).
Cheng, J. X. & Xie, X. S. Vibrational spectroscopic imaging of living systems: an emerging platform for biology and medicine. Science 350, aaa8870 (2015).
Camp, C. H. & Cicerone, M. T. Chemically sensitive bioimaging with coherent Raman scattering. Nat. Photon. 9, 295–305 (2015).
Prince, R. C., Frontiera, R. R. & Potma, E. O. Stimulated Raman scattering: from bulk to nano. Chem. Rev. 117, 5070–5094 (2017).
Saar, B. G. et al. Video-rate molecular imaging in vivo with stimulated Raman scattering. Science 330, 1368–1370 (2010).
Ozeki, Y. et al. High-speed molecular spectral imaging of tissue with stimulated Raman scattering. Nat. Photon. 6, 844–850 (2012).
Wakisaka, Y. et al. Probing the metabolic heterogeneity of live Euglena gracilis with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Nat. Microbiol. 1, 16124 (2016).
Freudiger, C. W. et al. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a robust fibre laser source. Nat. Photon. 8, 153–159 (2014).
Kong, L. et al. Multicolor stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a rapidly tunable optical parametric oscillator. Opt. Lett. 38, 145–147 (2013).
Suhalim, J. L. et al. Characterization of cholesterol crystals in atherosclerotic plaques using stimulated Raman scattering and second-harmonic generation microscopy. Biophys. J. 102, 1988–1995 (2012).
Freudiger, C. W. et al. Highly specific label-free molecular imaging with spectrally tailored excitation stimulated Raman scattering (STE-SRS) microscopy. Nat. Photon. 5, 103–109 (2011).
Zhang, D. et al. Quantitative vibrational imaging by hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy and multivariate curve resolution analysis. Anal. Chem. 85, 98–106 (2013).
Andresen, E. R., Berto, P. & Rigneault, H. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy by spectral focusing and fiber-generated soliton as Stokes pulse. Opt. Lett. 36, 2387–2389 (2011).
Fu, D., Holtom, G., Freudiger, C., Zhang, X. & Xie, X. S. Hyperspectral imaging with stimulated Raman scattering by chirped femtosecond lasers. J. Phys. Chem. B 117, 4634–4640 (2013).
He, R. Y. et al. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy and spectroscopy with a rapid scanning optical delay line. Opt. Lett. 42, 659–662 (2017).
Alshaykh, M. S. et al. High-speed stimulated hyperspectral Raman imaging using rapid acousto-optic delay lines. Opt. Lett. 42, 1548–1551 (2017).
Liao, C. S. et al. Stimulated Raman spectroscopic imaging by microsecond delay-line tuning. Optica 3, 1377–1380 (2016).
Figueroa, B. et al. Broadband hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a parabolic fiber amplifier source. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 9, 6116–6131 (2018).
He, R. Y. et al. Dual-phase stimulated Raman scattering microscopy for real-time two-color imaging. Optica 4, 44–47 (2017).
Lu, F. K. et al. Multicolor stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy. Mol. Phys. 110, 1927–1932 (2012).
Seto, K., Okuda, Y., Tokunaga, E. & Kobayashi, T. Development of a multiplex stimulated Raman microscope for spectral imaging through multi-channel lock-in detection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 84, 083705 (2013).
Rock, W., Bonn, M. & Parekh, S. H. Near shot-noise limited hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy using low energy lasers and a fast CMOS array. Opt. Express 21, 15113–15120 (2013).
Liao, C. S. et al. Microsecond scale vibrational spectroscopic imaging by multiplex stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e265 (2015).
Zhang, C. et al. Stimulated Raman scattering flow cytometry for label-free single-particle analysis. Optica 4, 103–109 (2017).
Fu, D. et al. Quantitative chemical imaging with multiplex stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 3623–3626 (2012).
Liao, C. S. et al. Spectrometer-free vibrational imaging by retrieving stimulated Raman signal from highly scattered photons. Sci. Adv. 1, e1500738 (2015).
Saltarelli, F. et al. Broadband stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy by a photonic time stretcher. Opt. Exp. 24, 21264–21275 (2016).
Wei, L. et al. Live-cell imaging of alkyne-tagged small biomolecules by stimulated Raman scattering. Nat. Meth. 11, 410–412 (2014).
Hu, F. et al. Supermultiplexed optical imaging and barcoding with engineered polyynes. Nat. Meth. 15, 194–200 (2018).
Wei, L. et al. Super-multiplex vibrational imaging. Nature 544, 465–470 (2017).
Xiong, H. et al. Stimulated Raman excited fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging. Nat. Photon. 13, 412–417 (2019).
Frontiera, R. R., Henry, A. I., Gruenke, N. L. & Van Duyne, R. P. Surface-enhanced femtosecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 1199–1203 (2011).
Yampolsky, S. et al. Seeing a single molecule vibrate through time-resolved coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Nat. Photon. 8, 650–656 (2014).
Zong, C. et al. Plasmon-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with single-molecule detection sensitivity. Preprint at arXiv https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.05167 (2019).
Bi, Y. et al. Near-resonance enhanced label-free stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with spatial resolution near 130 nm. Light Sci. Appl. 7, 81 (2018).
Gong, L. & Wang, H. Breaking the diffraction limit by saturation in stimulated-Raman-scattering microscopy: a theoretical study. Phys. Rev. A 90, 013818 (2014).
Gong, L. & Wang, H. F. Suppression of stimulated Raman scattering by an electromagnetically-induced-transparency-like scheme and its application for super-resolution microscopy. Phys. Rev. A 92, 023828 (2015).
Kim, D. et al. Selective suppression of stimulated Raman scattering with another competing stimulated Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 6118–6123 (2017).
Hell, S. W. & Wichmann, J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 19, 780–782 (1994).
Silva, W. R., Graefe, C. T. & Frontiera, R. R. Toward label-free super-resolution microscopy. ACS Photon. 3, 79–86 (2016).
Gong, L., Zheng, W., Ma, Y. & Huang, Z. W. Saturated stimulated-Raman-scattering microscopy for far-field superresolution vibrational imaging. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 034041 (2019).
Wei, M. et al. Volumetric chemical imaging by clearing-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 6608–6617 (2019).
Chen, X. L. et al. Volumetric chemical imaging by stimulated Raman projection microscopy and tomography. Nat. Commun. 8, 15117 (2017).
Liao, C. S. et al. In vivo and in situ spectroscopic imaging by a handheld stimulated Raman scattering microscope. ACS Photon. 5, 947–954 (2018).
Ji, M. et al. Rapid, label-free detection of brain tumors with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Sci. Transl. Med. 5, 201ra119 (2013).
Freudiger, C. W. et al. Multicolored stain-free histopathology with coherent Raman imaging. Lab. Investig. 92, 1492–1502 (2012).
Wang, M. C., Min, W., Freudiger, C. W., Ruvkun, G. & Xie, X. S. RNAi screening for fat regulatory genes with SRS microscopy. Nat. Meth. 8, 135–138 (2011).
Fu, D. et al. In vivo metabolic fingerprinting of neutral lipids with hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 8820–8828 (2014).
Lu, F. K. et al. Label-free DNA imaging in vivo with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 11624–11629 (2015).
Wang, P. et al. Label-free quantitative imaging of cholesterol in intact tissues by hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 13042–13046 (2013).
Yue, S. et al. Cholesteryl ester accumulation induced by PTEN loss and PI3K/AKT activation underlies human prostate cancer aggressiveness. Cell Metab. 19, 393–406 (2014).
Saar, B. G. et al. Label-free, real-time monitoring of biomass processing with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49, 5476–5479 (2010).
Ding, S. Y. et al. How does plant cell wall nanoscale architecture correlate with enzymatic digestibility? Science 338, 1055–1060 (2012).
Wei, L. et al. Live-cell bioorthogonal chemical imaging: stimulated Raman scattering microscopy of vibrational probes. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 1494–1502 (2016).
Shen, Y., Hu, F. & Min, W. Raman imaging of small biomolecules. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 48, 347–369 (2019).
Saar, B. G., Contreras-Rojas, L. R., Xie, X. S. & Guy, R. H. Imaging drug delivery to skin with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Mol. Pharma. 8, 969–975 (2011).
Zhang, D., Slipchenko, M. N. & Cheng, J. X. Highly sensitive vibrational imaging by femtosecond pulse stimulated Raman loss. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 1248–1253 (2011).
Wei, L., Yu, Y., Shen, Y., Wang, M. C. & Min, W. Vibrational imaging of newly synthesized proteins in live cells by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 11226–11231 (2013).
Hu, F., Wei, L., Zheng, C., Shen, Y. & Min, W. Live-cell vibrational imaging of choline metabolites by stimulated Raman scattering coupled with isotope-based metabolic labeling. Analyst 139, 2312–2317 (2014).
Alfonso-Garcia, A., Pfisterer, S. G., Riezman, H., Ikonen, E. & Potma, E. O. D38-cholesterol as a Raman active probe for imaging intracellular cholesterol storage. J. Biomed. Opt. 21, 061003 (2016).
Li, J. & Cheng, J. X. Direct visualization of de novo lipogenesis in single living cells. Sci. Rep. 4, 6807 (2014).
Wei, L. et al. Imaging complex protein metabolism in live organisms by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with isotope labeling. ACS Chem. Biol. 10, 901–908 (2015).
Shi, L. Y., Shen, Y. H. & Min, W. Visualizing protein synthesis in mice with in vivo labeling of deuterated amino acids using vibrational imaging. Appl. Photon. 3, 092401 (2018).
Shi, L. et al. Optical imaging of metabolic dynamics in animals. Nat. Commun. 9, 2995 (2018).
Zhang, L. et al. Spectral tracing of isotope deuterium (STRIDE) for imaging glucose metabolism. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 3, 402–413 (2019).
Shen, Y., Xu, F., Wei, L., Hu, F. & Min, W. Live-cell quantitative imaging of proteome degradation by stimulated Raman scattering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53, 5596–5599 (2014).
Yamakoshi, H. et al. Imaging of EdU, an alkyne-tagged cell proliferation probe, by Raman microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 6102–6105 (2011).
Yamakoshi, H. et al. Alkyne-tag Raman imaging for visualization of mobile small molecules in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20681–20689 (2012).
Prescher, J. A. & Bertozzi, C. R. Chemistry in living systems. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 13–21 (2005).
Grammel, M. & Hang, H. C. Chemical reporters for biological discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 9, 475–484 (2013).
Hu, F., Lamprecht, M. R., Wei, L., Morrison, B. & Min, W. Bioorthogonal chemical imaging of metabolic activities in live mammalian hippocampal tissues with stimulated Raman scattering. Sci. Rep. 6, 39660 (2016).
Hong, S. et al. Live-cell stimulated Raman scattering imaging of alkyne-tagged biomolecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53, 5827–5831 (2014).
Hu, F. et al. Vibrational imaging of glucose uptake activity in live cells and tissues by stimulated Raman scattering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54, 9821–9825 (2015).
Lee, H. J. et al. Assessing cholesterol storage in live cells and C. elegans by stimulated Raman scattering imaging of phenyl-Diyne cholesterol. Sci. Rep. 5, 7930 (2015).
Gaschler, M. M. et al. Determination of the subcellular localization and mechanism of action of ferrostatins in suppressing ferroptosis. ACS Chem. Biol. 13, 1013–1020 (2018).
Chen, Z. et al. Multicolor live-cell chemical imaging by isotopically edited alkyne vibrational palette. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 8027–8033 (2014).
Mansfield, J. C. et al. Label-free chemically specific imaging in planta with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Anal. Chem. 85, 5055–5063 (2013).
Crawford, J. M., Portmann, C., Zhang, X., Roeffaers, M. B. & Clardy, J. Small molecule perimeter defense in entomopathogenic bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 10821–10826 (2012).
Valm, A. M. et al. Applying systems-level spectral imaging and analysis to reveal the organelle interactome. Nature 546, 162–167 (2017).
Hu, F., Brucks, S. D., Lambert, T. H., Campos, L. M. & Min, W. Stimulated Raman scattering of polymer nanoparticles for multiplexed live-cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 53, 6187–6190 (2017).
Jin, Q. et al. Multicolor Raman beads for multiplexed tumor cell and tissue imaging and in vivo tumor spectral detection. Anal. Chem. 91, 3784–3789 (2019).
Long, R. et al. Two-color vibrational imaging of glucose metabolism using stimulated Raman scattering. Chem. Commun. 54, 152–155 (2018).
Shen, Y. et al. Metabolic activity induces membrane phase separation in endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 13394–13399 (2017).
Li, J. J. et al. Lipid desaturation is a metabolic marker and therapeutic target of ovarian cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 20, 303–314 (2017).
Yu, Y., Mutlu, A. S., Liu, H. & Wang, M. C. High-throughput screens using photo-highlighting discover BMP signaling in mitochondrial lipid oxidation. Nat. Commun. 8, 865 (2017).
Villareal, V. A., Fu, D., Costello, D. A., Xie, X. S. & Yang, P. L. Hepatitis C virus selectively alters the intracellular localization of desmosterol. ACS Chem. Biol. 11, 1827–1833 (2016).
Garcia-Bermudez, J. et al. Squalene accumulation in cholesterol auxotrophic lymphomas prevents oxidative cell death. Nature 567, 118–122 (2019).
Bae, K., Zheng, W., Ma, Y. & Huang, Z. Real-time monitoring of pharmacokinetics of antibiotics in biofilms with Raman-tagged hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Theranostics 9, 1348–1357 (2019).
Schiessl, K. T. et al. Phenazine production promotes antibiotic tolerance and metabolic heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nat. Commun. 10, 762 (2019).
Ji, M. et al. Detection of human brain tumor infiltration with quantitative stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Sci. Transl. Med. 7, 309ra163 (2015).
Orringer, D. A. et al. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 1, 0027 (2017).
Zhang, L. Y. & Min, W. Bioorthogonal chemical imaging of metabolic changes during epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 22, 106010 (2017).
Fu, D., Yang, W. & Xie, X. S. Label-free imaging of neurotransmitter acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions with stimulated Raman scattering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 583–586 (2017).
Lee, H. J. et al. Label-free vibrational spectroscopic imaging of neuronal membrane potential. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 1932–1936 (2017).
Tian, F. et al. Monitoring peripheral nerve degeneration in ALS by label-free stimulated Raman scattering imaging. Nat. Commun. 7, 13283 (2016).
Ji, M. et al. Label-free imaging of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Sci. Adv. 4, eaat7715 (2018).
Chen, A. J. et al. Fingerprint stimulated Raman scattering imaging reveals retinoid coupling lipid metabolism and survival. Chem. Phys. Chem. 19, 2500–2506 (2018).
Tipping, W. J., Lee, M., Serrels, A., Brunton, V. G. & Hulme, A. N. Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy: an emerging tool for drug discovery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 2075–2089 (2016).
Slipchenko, M. N. et al. Vibrational imaging of tablets by epi-detected stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Analyst 135, 2613–2619 (2010).
Francis, A. T. et al. In situ stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy study of the dissolution of sustained-release implant formulation. Mol. Pharma. 15, 5793–5801 (2018).
Wang, C. C. et al. In situ chemically specific mapping of agrochemical seed coatings using stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. J. Biophoton. 11, e201800108 (2018).
Fu, D. et al. Imaging the intracellular distribution of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in living cells with quantitative hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering. Nat. Chem. 6, 614–622 (2014).
Chiu, W. S. et al. Molecular diffusion in the human nail measured by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 7725–7730 (2015).
Tipping, W. J., Lee, M., Serrels, A., Brunton, V. G. & Hulme, A. N. Imaging drug uptake by bioorthogonal stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Chem. Sci. 8, 5606–5615 (2017).
Seidel, J. et al. Structure-activity-distribution relationship study of anti-cancer antimycin-type depsipeptides. Chem. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc03051d (2019).
Gaiduk, A., Yorulmaz, M., Ruijgrok, P. V. & Orrit, M. Room-temperature detection of a single molecule’s absorption by photothermal contrast. Science 330, 353–356 (2010).
Zhang, D. et al. Depth-resolved mid-infrared photothermal imaging of living cells and organisms with submicrometer spatial resolution. Sci. Adv. 2, e1600521 (2016).
Robles, F. E., Zhou, K. C., Fischer, M. C. & Warren, W. S. Stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopic optical coherence tomography. Optica 4, 243–246 (2017).
Tamma, V. A., Beecher, L. M., Shumaker-Parry, J. S. & Wickramasinghe, H. K. Detecting stimulated Raman responses of molecules in plasmonic gap using photon induced forces. Opt. Exp. 26, 31439–31453 (2018).
Knoll, B. & Keilmann, F. Near-field probing of vibrational absorption for chemical microscopy. Nature 399, 134–137 (1999).
Zeng, C., Hu, F., Long, R. & Min, W. A ratiometric Raman probe for live-cell imaging of hydrogen sulfide in mitochondria by stimulated Raman scattering. Analyst 143, 4844–4848 (2018).
Zhang, J. et al. Small unnatural amino acid carried Raman tag for molecular imaging of genetically targeted proteins. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 4679–4685 (2018).
Hiramatsu, K. et al. High-throughput label-free molecular fingerprinting flow cytometry. Sci. Adv. 5, eaau0241 (2019).
Suzuki, Y. et al. Label-free chemical imaging flow cytometry by high-speed multicolor stimulated Raman scattering. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902322116 (2019).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Wei, L. Shi, H. Xiong and X. Liu for reading the manuscript. W.M. acknowledges support from National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s New Innovator Award, NIH R01 (EB020892 to W. M.), NIH R01 (GM128214 to W. M.), NIH R01 (GM132860 to W. M.), the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation, and a Pilot and Feasibility grant from the New York Obesity Nutrition Research Center. F.H. acknowledges support from a Raymond and Beverly Sackler Center Postdoctoral Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F. H., L. S., and W. M. conceived and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information: Rita Strack was the primary editor on this article and managed its editorial process and peer review in collaboration with the rest of the editorial team.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, F., Shi, L. & Min, W. Biological imaging of chemical bonds by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Nat Methods 16, 830–842 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0538-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0538-0
This article is cited by
-
Low-input lipidomics reveals lipid metabolism remodelling during early mammalian embryo development
Nature Cell Biology (2024)
-
Hyper spectral resolution stimulated Raman spectroscopy with amplified fs pulse bursts
Light: Science & Applications (2024)
-
Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Transient stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy and imaging
Light: Science & Applications (2024)
-
Fast Real-Time Brain Tumor Detection Based on Stimulated Raman Histology and Self-Supervised Deep Learning Model
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine (2024)