Abstract
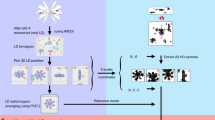
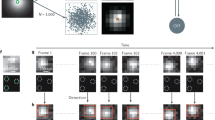
Single-particle reconstruction (SPR) from electron microscopy (EM) images is widely used in structural biology, but it lacks direct information on protein identity. To address this limitation, we developed a computational and analytical framework that reconstructs and coaligns multiple proteins from 2D super-resolution fluorescence images. To demonstrate our method, we generated multicolor 3D reconstructions of several proteins within the human centriole, which revealed their relative locations, dimensions and orientations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Sample datasets are available on Zenodo (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1288783).
References
Campbell, M. G., Veesler, D., Cheng, A., Potter, C. S. & Carragher, B. eLife 4, e06380 (2015).
Jiang, J., Pentelute, B. L., Collier, R. J. & Zhou, Z. H. Nature 521, 545–549 (2015).
Byeon, I.-J. L. et al. Cell 139, 780–790 (2009).
Beck, M., Lucić, V., Förster, F., Baumeister, W. & Medalia, O. Nature 449, 611–615 (2007).
Strauss, M., Schotte, L., Karunatilaka, K. S., Filman, D. J. & Hogle, J. M. J. Virol. 91, e01443-16 (2017).
Chang, Y.-W. et al. Science 351, aad2001 (2016).
Chang, Y.-W. et al. Nat. Microbiol. 2, 16269 (2017).
Szymborska, A. et al. Science 341, 655–658 (2013).
Salas, D. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 9273–9278 (2017).
Douglass, K. M., Sieben, C., Archetti, A., Lambert, A. & Manley, S. Nat. Photonics 10, 705–708 (2016).
Bornens, M. Science 335, 422–426 (2012).
Bauer, M., Cubizolles, F., Schmidt, A. & Nigg, E. A. EMBO J. 35, 2152–2166 (2016).
Graser, S. et al. J. Cell. Biol. 179, 321–330 (2007).
Kitagawa, D. et al. Cell 144, 364–375 (2011).
Gönczy, P. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 425–435 (2012).
Ester, M., Kriegel, H.-P., Sander, J. & Xu, X. in Proc. 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (eds Simoudis, E., Han, J. & Fayyad, U.) 226–231 (AAAI Press, Palo Alto, CA, 1996).
Sorzano, C. O. S. et al. J. Struct. Biol. 171, 197–206 (2010).
Scheres, S. H. W. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 348, 139–149 (2005).
Lukinavičius, G. et al. Curr. Biol. 23, 265–270 (2013).
Momotani, K., Khromov, A. S., Miyake, T., Stukenberg, P. T. & Somlyo, A. V. Biochem. J. 412, 265–273 (2008).
Sonnen, K. F., Schermelleh, L., Leonhardt, H. & Nigg, E. A. Biol. Open 1, 965–976 (2012).
Banterle, N. & Gönczy, P. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 33, 23–49 (2017).
Loncarek, J., Hergert, P., Magidson, V. & Khodjakov, A. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 322–328 (2008).
Paoletti, A., Moudjou, M., Paintrand, M., Salisbury, J. L. & Bornens, M. J. Cell. Sci. 109, 3089–3102 (1996).
Gogendeau, D., Guichard, P. & Tassin, A.-M. Methods Cell Biol. 129, 171–189 (2015).
Bornens, M., Paintrand, M., Berges, J., Marty, M.-C. & Karsenti, E. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 8, 238–249 (1987).
Bourdin, G. et al. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 1469–1476 (2014).
Edelstein, A., Amodaj, N., Hoover, K., Vale, R. & Stuurman, N. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 92, 14.20.1–14.20.17 (2010).
Olivier, N., Keller, D., Gönczy, P. & Manley, S. PLoS One 8, e69004 (2013).
Huang, F. et al. Nat. Methods 10, 653–658 (2013).
Churchman, L. S. & Spudich, J. A. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2012, 141–149 (2012).
Nieuwenhuizen, R. P. J. et al. Nat. Methods 10, 557–562 (2013).
Banterle, N., Bui, K. H., Lemke, E. A. & Beck, M. J. Struct. Biol. 183, 363–367 (2013).
de la Rosa-Trevín, J. M. et al. J. Struct. Biol. 195, 93–99 (2016).
Sorzano, C. O. S. et al. J. Struct. Biol. 148, 194–204 (2004).
Ludtke, S. J., Baldwin, P. R. & Chiu, W. J. Struct. Biol. 128, 82–97 (1999).
Scheres, S. H. W. J. Struct. Biol. 180, 519–530 (2012).
Pettersen, E. F. et al. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).
Gartenmann, L. et al. Curr. Biol. 27, R1054–R1055 (2017).
Guizar-Sicairos, M., Thurman, S. T. & Fienup, J. R. Opt. Lett. 33, 156–158 (2008).
Shi, X. et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 19, 1178–1188 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Lehmann for growth, purification and AFM characterization of T4 bacteriophages; J.M. de la Rosa-Trevín for support regarding the optimal use of Scipion; and C.G. Morrison (Centre for Chromosome Biology, School of Natural Sciences and National University of Ireland Galway, Galway, Ireland) for providing the Cep164 antibody (1F3G10). We thank B. Huang and X. Shi for providing their 2D particle-alignment code. We also thank R. Laine and C. Kaminski for providing an HSV SMLM dataset. This work was supported by the European Research Council (ERC; grant AdG 340227 to P.G.), the EPFL Fellows postdoctoral fellowship program funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Programme for Research and Innovation (grant agreement 665667 to N.B., MSCA-COFUND), and the National Centre for Competence in Research (NCCR) Chemical Biology (S.M.). We thank M. Daszykowski for providing a public DBSCAN implementation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.S., N.B., P.G. and S.M. conceived and designed the project. C.S., P.G. and S.M. supervised the project. C.S. and N.B. performed all experiments and data analysis. C.S. and K.M.D. wrote analysis code. All authors wrote, revised and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–20, Supplementary Notes 1–5 and Supplementary Tables 1–3
Supplementary Video 1
Four-color 3D reconstruction of centriolar proteins with a shared symmetry axis. Animated 360° rotation of the four-color 3D model showing Cep152 (magenta), Cep164 (green), Cep57 (cyan) and Cep63 (white mesh).
Supplementary Video 2
3D reconstruction of centriolar proteins without a shared symmetry axis. Animated 360° rotation of 3D reconstructed model of Cep152 (magenta) and Hs-SAS6 (cyan). The 3D reconstructed sum of Cep152 and Hs-SAS-6 is shown as a yellow mesh.
Supplementary Software 1
GUI application and source code.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sieben, C., Banterle, N., Douglass, K.M. et al. Multicolor single-particle reconstruction of protein complexes. Nat Methods 15, 777–780 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0140-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0140-x
This article is cited by
-
Simcryocluster: a semantic similarity clustering method of cryo-EM images by adopting contrastive learning
BMC Bioinformatics (2024)
-
Detecting continuous structural heterogeneity in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Architectural basis for cylindrical self-assembly governing Plk4-mediated centriole duplication in human cells
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Maximum-likelihood model fitting for quantitative analysis of SMLM data
Nature Methods (2023)
-
Fluorophores’ talk turns them dark
Nature Methods (2022)