Abstract
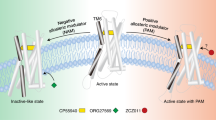
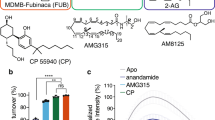
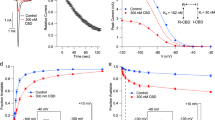
The CB1 receptor mediates the central nervous system response to cannabinoids, and is a drug target for pain, anxiety and seizures. CB1 also responds to allosteric modulators, which influence cannabinoid binding and efficacy. To understand the mechanism of these compounds, we solved the crystal structure of CB1 with the negative allosteric modulator (NAM) ORG27569 and the agonist CP55940. The structure reveals that the NAM binds to an extrahelical site within the inner leaflet of the membrane, which overlaps with a conserved site of cholesterol interaction in many G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The ternary structure with ORG27569 and CP55940 captures an intermediate state of the receptor, in which aromatic residues at the base of the agonist-binding pocket adopt an inactive conformation despite the large contraction of the orthosteric pocket. The structure illustrates a potential strategy for drug modulation of CB1 and other class A GPCRs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Structural data have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) with coordinate accession number 6KQI. All other data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files) or are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Mechoulam, R. & Parker, L. A. The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 64, 21–47 (2013).
Whiting, P. F. et al. Cannabinoids for medical use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 313, 2456–2473 (2015).
Devinsky, O. et al. Trial of cannabidiol for drug-resistant seizures in the Dravet syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 2011–2020 (2017).
Kunos, G., Osei-Hyiaman, D., Bátkai, S., Sharkey, K. A. & Makriyannis, A. Should peripheral CB1 cannabinoid receptors be selectively targeted for therapeutic gain? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30, 1–7 (2009).
Thal, D. M., Glukhova, A., Sexton, P. M. & Christopoulos, A. Structural insights into G-protein-coupled receptor allostery. Nature 559, 45–53 (2018).
Price, M. R. et al. Allosteric modulation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 68, 1484–1495 (2005).
Baillie, G. L. et al. CB1 receptor allosteric modulators display both agonist and signaling pathway specificity. Mol. Pharmacol. 83, 322–338 (2013).
Fay, J. F. & Farrens, D. L. A key agonist-induced conformational change in the cannabinoid receptor CB1 is blocked by the allosteric ligand Org 27569. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 33873–33882 (2012).
Fay, J. F. & Farrens, D. L. Structural dynamics and energetics underlying allosteric inactivation of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 8469–8474 (2015).
Khurana, L., Mackie, K., Piomelli, D. & Kendall, D. A. Modulation of CB1 cannabinoid receptor by allosteric ligands: pharmacology and therapeutic opportunities. Neuropharmacology 124, 3–12 (2017).
Shao, Z. et al. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 540, 602–608 (2016).
Suno, R. et al. Structural insights into the subtype-selective antagonist binding to the M2 muscarinic receptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14, 1150–1158 (2018).
Hua, T. et al. Crystal structures of agonist-bound human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Nature 547, 468–471 (2017).
Krishna Kumar, K. et al. Structure of a signaling cannabinoid receptor 1–G protein complex. Cell 176, 448–458.e12 (2019).
Johnson, M. R. et al. Selective and potent analgetics derived from cannabinoids. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 21, 271S–282S (1981).
Herkenham, M. et al. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 1932–1936 (1990).
Shim, J.-Y., Bertalovitz, A. C. & Kendall, D. A. Identification of essential cannabinoid-binding domains: structural insights into early dynamic events in receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 33422–33435 (2011).
Murphy, J. W. & Kendall, D. A. Integrity of extracellular loop 1 of the human cannabinoid receptor 1 is critical for high-affinity binding of the ligand CP 55,940 but not SR 141716A. Biochem. Pharmacol. 65, 1623–1631 (2003).
Ahn, K. H., Bertalovitz, A. C., Mierke, D. F. & Kendall, D. A. Dual role of the second extracellular loop of the cannabinoid receptor 1: ligand binding and receptor localization. Mol. Pharmacol. 76, 833–842 (2009).
Singh, R. et al. Activation of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor may involve a W6 48/F3 36 rotamer toggle switch. J. Pept. Res. 60, 357–370 (2002).
Rosenbaum, D. M. et al. GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into β2-adrenergic receptor function. Science 318, 1266–1273 (2007).
Stornaiuolo, M. et al. Endogenous vs exogenous allosteric modulators in GPCRs: a dispute for shuttling CB1 among different membrane microenvironments. Sci. Rep. 5, 15453 (2015).
Shore, D. M. et al. Allosteric modulation of a cannabinoid G protein-coupled receptor: binding site elucidation and relationship to G protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 5828–5845 (2014).
Bari, M., Battista, N., Fezza, F., Finazzi-Agrò, A. & Maccarrone, M. Lipid rafts control signaling of type-1 cannabinoid receptors in neuronal cells. Implications for anandamide-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 12212–12220 (2005).
Vallée, M. et al. Pregnenolone can protect the brain from cannabis intoxication. Science 343, 94–98 (2014).
Lu, J. et al. Structural basis for the cooperative allosteric activation of the free fatty acid receptor GPR40. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 24, 570–577 (2017).
Liu, H. et al. Orthosteric and allosteric action of the C5a receptor antagonists. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 25, 472–481 (2018).
Liu, X. et al. Mechanism of intracellular allosteric β2AR antagonist revealed by X-ray crystal structure. Nature 548, 480–484 (2017).
Zheng, Y. et al. Structure of CC chemokine receptor 2 with orthosteric and allosteric antagonists. Nature 540, 458–461 (2016).
Kruse, A. C. et al. Activation and allosteric modulation of a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature 504, 101–106 (2013).
De Lean, A., Stadel, J. M. & Lefkowitz, R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled β-adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 7108–7117 (1980).
Hanson, M. A. et al. Crystal structure of a lipid G protein-coupled receptor. Science 335, 851–855 (2012).
Ahn, K. H., Mahmoud, M. M., Shim, J.-Y. & Kendall, D. A. Distinct roles of β-arrestin 1 and β-arrestin 2 in ORG27569-induced biased signaling and internalization of the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1). J. Biol. Chem. 288, 9790–9800 (2013).
Kang, Y. et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 523, 561–567 (2015).
Gamage, T. F., Anderson, J. C. & Abood, M. E. CB1 allosteric modulator Org27569 is an antagonist/inverse agonist of ERK1/2 signaling. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 1, 272–280 (2016).
D’Ambra, T. E. et al. Conformationally restrained analogues of pravadoline: nanomolar potent, enantioselective, (aminoalkyl)indole agonists of the cannabinoid receptor. J. Med. Chem. 35, 124–135 (1992).
Kulkarni, P. M. et al. Novel electrophilic and photoaffinity covalent probes for mapping the cannabinoid 1 receptor allosteric site(s). J. Med. Chem. 59, 44–60 (2016).
Horswill, J. G. et al. PSNCBAM-1, a novel allosteric antagonist at cannabinoid CB1 receptors with hypophagic effects in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 152, 805–814 (2007).
Di Marzo, V. New approaches and challenges to targeting the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17, 623–639 (2018).
Osei-Hyiaman, D. et al. Hepatic CB1 receptor is required for development of diet-induced steatosis, dyslipidemia, and insulin and leptin resistance in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 3160–3169 (2008).
Fernández-Ruiz, J. et al. Cannabidiol for neurodegenerative disorders: important new clinical applications for this phytocannabinoid? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 75, 323–333 (2013).
Thomas, A. et al. Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 150, 613–623 (2007).
Hua, T. et al. Crystal structure of the human cannabinoid receptor CB1. Cell 167, 750–762.e14 (2016).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
McCoy, A. J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Horcajada, C., Guinovart, J. J., Fita, I. & Ferrer, J. C. Crystal structure of an archaeal glycogen synthase: insights into oligomerization and substrate binding of eukaryotic glycogen synthases. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 2923–2931 (2006).
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 486–501 (2010).
Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 213–221 (2010).
Schüttelkopf, A. W. & van Aalten, D. M. F. PRODRG: a tool for high-throughput crystallography of protein-ligand complexes. Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 1355–1363 (2004).
Chen, V. B. et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 12–21 (2010).
Morales-Perez, C. L., Noviello, C. M. & Hibbs, R. E. Manipulation of subunit stoichiometry in heteromeric membrane proteins. Structure 24, 797–805 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of the GM/CA-CAT beamline 23ID at the Advanced Photon Source for support during data collection. This project was supported by the Edward Mallinckrodt, Jr. Foundation (Scholar Award to D.M.R.), the Welch Foundation (grant no. I-1770 to D.M.R.) and the National Young Thousand Talents Program of China (to Z.S.). APS is a US Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility operated for the Department of Energy Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory (no. DE-AC02-06CH11357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.S. developed the CB1 construct and purification; expressed, purified and crystallized the receptor; collected diffraction data and solved and refined the structures. W.Y. and X.W. assisted in receptor expression, purification and structure refinement. K.C., K.R. and A.J.F. performed ligand-binding assays on CB1 constructs. J.Y. and Q.X. assisted in diffraction data collection and analysis. D.M.R. supervised the overall project, assisted with collection of diffraction data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–11 and Table 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Z., Yan, W., Chapman, K. et al. Structure of an allosteric modulator bound to the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nat Chem Biol 15, 1199–1205 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0387-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0387-2
This article is cited by
-
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): advances in structures, mechanisms, and drug discovery
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2024)
-
Structural insights into the activation and inhibition of CXC chemokine receptor 3
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2024)
-
Insight into the mechanism of action of ORG27569 at the cannabinoid type one receptor utilising a unified mathematical model
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2024)
-
Structure, function and drug discovery of GPCR signaling
Molecular Biomedicine (2023)
-
Structural basis for activation of CB1 by an endocannabinoid analog
Nature Communications (2023)